Data science and machine learning are frequently mentioned together, and for good reason. They are intertwined fields at the forefront of technological advancement, driving innovation across industries. Both leverage data to create intelligent systems, improve products, and optimize services. As career paths, they are highly sought after and offer substantial earning potential.
Understanding the relationship between data science and machine learning is crucial for anyone looking to enter these domains. Think of it like this: data science is the broad landscape, while machine learning is a specific, powerful tool within that landscape. Machine learning is a subset of data science, much like a square is a rectangle, but not all rectangles are squares. Data scientists often employ machine learning techniques, and their adoption is expanding rapidly across virtually every sector.
Embarking on a career in either data science or machine learning can be incredibly rewarding. Data scientists are consistently ranked among the top tech professions, and machine learning engineers have been recognized as the best job in recent years [1, 2]. Developing skills in programming and statistics will serve as a strong foundation for success in both these dynamic fields.
This article will delve into the distinctions and similarities between data science and machine learning, exploring the essential skills and diverse career opportunities each field presents.
Explore Data Science and Machine Learning Skills Today
Interested in developing your expertise in data science or machine learning? Explore these recommended specializations and Professional Certificates on Coursera:
For aspiring data scientists, the IBM Data Science Professional Certificate offers a comprehensive curriculum to master essential practical skills and knowledge used daily by data scientists, including Python and SQL.
To gain a strong grasp of fundamental AI concepts and practical machine learning skills, the Machine Learning Specialization from Stanford and DeepLearning.AI is an excellent choice. You’ll learn to build and train machine learning models and neural networks.
Decoding Data Science vs. Machine Learning: Key Differences
Data science is an interdisciplinary field focused on extracting knowledge and insights from data. It encompasses the entire process of data analysis, from data collection and cleaning to interpretation and presentation of findings. Machine learning, on the other hand, is a specific branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling systems to learn from data without explicit programming. It’s about building algorithms that can improve their performance over time as they are exposed to more data.
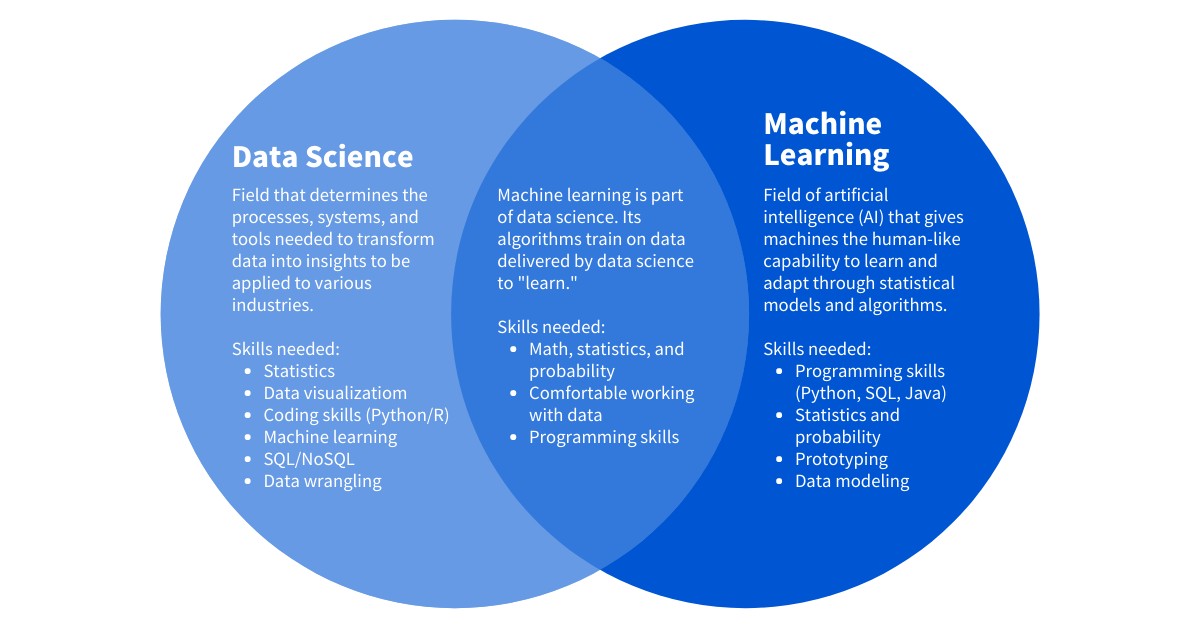 Venn diagram illustrating the relationship between Data Science and Machine Learning
Venn diagram illustrating the relationship between Data Science and Machine Learning
In recent years, machine learning and AI have become increasingly integral to data science, playing a pivotal role in data analytics and business intelligence. Machine learning automates data analysis processes and goes a step further by making predictions based on vast datasets. This is achieved through the development of sophisticated models and algorithms.
Unpacking Data Science
Data science is a broad and multifaceted field that revolves around the study of data and the extraction of meaningful insights. It utilizes a range of techniques, including statistical methods, algorithms, systems, and tools to uncover hidden patterns and knowledge from both structured and unstructured data. The insights derived from data science are applied across diverse sectors such as business, government, and research to drive strategic decisions, foster innovation in products and services, and improve infrastructure and public systems.
Explore data science further by watching this introductory lecture from IBM’s What is Data Science? course:
Further Reading: What is Data Science?
Essential Skills for Data Science
A career in data science, particularly as a data scientist, requires a robust skillset in programming and data analytics. Key skills include:
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in languages like Python, R, and SQL is fundamental for data manipulation, analysis, and model building.
- Statistical Analysis: A strong understanding of statistical concepts and methods is crucial for interpreting data and drawing valid conclusions.
- Data Visualization: The ability to effectively communicate data insights through visualizations is essential for conveying complex information to stakeholders.
- Data Wrangling and Cleaning: Real-world data is often messy; skills in cleaning, transforming, and preparing data for analysis are vital.
- Domain Knowledge: Understanding the specific industry or domain you are working in can greatly enhance the relevance and impact of your data science work.
The IBM Data Science Professional Certificate impressed me with its introductory courses covering a wide array of topics, practical assignments, engaging and clear video lectures, and easily digestible explanations. This program significantly enhanced my portfolio and propelled my career forward.
— Mo R.
Data Science Career Paths
Beyond the role of a data scientist, the field offers a variety of career opportunities, including:
- Data Analyst: Focuses on collecting, processing, and performing statistical analysis of data.
- Data Engineer: Builds and maintains the infrastructure for data storage and processing.
- Business Analyst: Uses data to identify business trends and provide data-driven recommendations.
- Data Architect: Designs and manages data management systems and databases.
Further Reading: Your Guide to Data Science Careers (+ How to Get Started)
Understanding Machine Learning
Machine learning is a specialized branch of artificial intelligence that employs algorithms to learn from data and subsequently make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed for each task. Machine learning algorithms are designed to identify patterns in data, enabling them to adapt and improve their performance over time with increasing data exposure.
Consider the example of social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok. These platforms collect vast amounts of user data, including browsing history, interactions, and preferences. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to predict user interests and needs, enabling them to recommend relevant products, services, or content tailored to individual users.
Machine learning serves as a powerful toolkit within data science and extends its applications to various fields beyond data analysis. Data scientists frequently integrate machine learning techniques into their work to accelerate information gathering and enhance trend analysis.
Further Reading: How Much Does a Machine Learning Engineer Make?
Essential Skills for Machine Learning
To excel as a machine learning engineer, a strong foundation in the following areas is crucial:
- Programming: Proficiency in Python and Java is highly recommended for machine learning development.
- Mathematics and Statistics: A solid understanding of linear algebra, calculus, probability, and statistics is essential for comprehending and developing machine learning algorithms.
- Algorithm and Model Building: Knowledge of various machine learning algorithms (e.g., regression, classification, clustering) and model development techniques is fundamental.
- Data Modeling and Evaluation: Skills in preparing data for machine learning models and evaluating model performance are critical.
- Deep Learning: Increasingly important, deep learning involves neural networks and is crucial for complex machine learning tasks.
Further Reading: Machine Learning Skills: Your Guide to Getting Started
Machine Learning Career Paths
A career in machine learning and artificial intelligence offers diverse opportunities, including:
- Machine Learning Engineer: Designs, builds, and deploys machine learning models and systems.
- AI Research Scientist: Conducts research to advance the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Engineer: Focuses on developing systems that can understand and process human language.
- Computer Vision Engineer: Develops systems that enable computers to “see” and interpret images and videos.
- Robotics Engineer: Integrates machine learning into robots to enable them to perform complex tasks autonomously.
Dive Deeper into Machine Learning
Explore the inner workings of self-driving cars, speech recognition, and Google search algorithms with an in-depth exploration of Machine Learning at Stanford University. Machine learning and AI are deeply embedded in our daily lives, often operating seamlessly behind the scenes. This course will provide insights into Silicon Valley’s best practices in innovation and problem-solving within the realm of machine learning.
Building Your Skills in Data Science and Machine Learning
Whether you choose to specialize in data science or machine learning, acquiring technical skills in programming and statistics is essential for entering these competitive fields.
The IBM Data Science Professional Certificate provides a robust foundation in in-demand data science skills, including data importing and cleaning, utilizing data science libraries, and programming in Python and SQL. Begin your journey today and become job-ready in approximately five months. Alternatively, the Machine Learning Specialization from Stanford and DeepLearning.AI offers a comprehensive introduction to modern machine learning, covering supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and cutting-edge best practices employed in Silicon Valley for AI and machine learning innovation.