The Learning Assistants (LA) model represents a significant advancement in collaborative learning strategies, designed to cultivate undergraduate leaders. This approach identifies high-achieving students who have previously excelled in a particular course and empowers them to support subsequent cohorts navigating the same material. Originating at the University of Colorado Boulder, with initial funding from the NSF, this model has since expanded nationwide through the Learning Assistant Alliance, fostering department-specific LA programs across numerous institutions.
For undergraduate students at the University of Florida (UFL) seeking to enrich their personal development and contribute to innovative pedagogy, the BME Learning Assistant (BME-LA) program offers a unique opportunity. This program enables students to employ multidisciplinary instructional strategies, directly assisting their peers in mastering foundational Biomedical Engineering (BME) coursework, thereby enhancing Ufl.learning outcomes. Crucially, the LA model has proven instrumental in boosting student learning gains and improving retention rates. It also facilitates a positive transformation of traditional classrooms into more dynamic, interactive, and inclusive learning environments, fostering a richer ufl.learning experience.
LAs are carefully selected based on their strong academic performance and to ensure diverse representation across gender, race, and ethnicity within the classroom, mirroring the diverse student body at UFL. A key distinction from Teaching Assistants (TAs) is that LAs do not participate in grading, nor do they have access to student grades. This deliberate separation allows LAs to serve as a supportive and approachable bridge between students and the instructor. They provide valuable, real-time feedback throughout the semester, contributing to a more open and less intimidating ufl.learning atmosphere. Participating LAs at UFL are required to enroll in a dedicated 1-credit Special Topics pedagogy course, BME4931 Educational Methods for BME Learning Assistants (LAs), further equipping them with effective teaching strategies and enhancing their contribution to ufl.learning.
Figure 1: LA program impact on classroom dynamics and student academic success. A) Illustrates the improved student-instructor ratio in LA-supported classrooms (right) compared to traditional classrooms (left), enhancing personalized ufl.learning. B) Compares course failure rates (D, F, and withdrawals) between LA-supported and traditional classrooms in the Physics department at UC Boulder, demonstrating the positive impact of LAs on student success in STEM fields and highlighting the potential for improved ufl.learning outcomes.
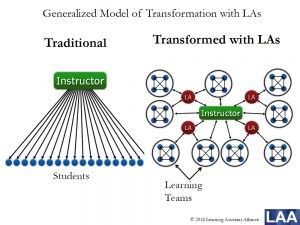 Relational diagram illustrating the improved student-instructor ratio in LA-supported classrooms and a graph comparing course failure rates in traditional vs LA-supported classrooms.
Relational diagram illustrating the improved student-instructor ratio in LA-supported classrooms and a graph comparing course failure rates in traditional vs LA-supported classrooms.
In conclusion, the Learning Assistant model, particularly as implemented in the BME-LA program at UFL, offers a powerful approach to enhance collaborative education and improve ufl.learning. By fostering peer-to-peer learning and creating more interactive classroom environments, LA programs contribute significantly to student success and a more enriching educational experience.
