Are you curious about How Fast Can You Learn A Handstand? It’s a common question for those aspiring to master this impressive feat of strength and balance. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe everyone can achieve their fitness goals with the right guidance and resources, transforming from a beginner to a handstand pro with dedicated handstand training and hand balancing exercises. Discover a comprehensive approach to learn handstands efficiently and effectively, unlocking your potential with us.
1. Understanding the Handstand Learning Curve
The journey to mastering a handstand is unique for everyone, with several factors influencing the learning timeline. Let’s explore these elements to give you a realistic expectation.
1.1. Factors Influencing Learning Speed
Several variables determine how fast can you learn a handstand. Let’s delve into the key factors:
- Prior Experience: Gymnastics, yoga, or any bodyweight training experience gives you a head start. These backgrounds build a foundation of strength, balance, and body awareness.
- Physical Fitness: Strength, flexibility, and core stability significantly impact your learning pace. A solid fitness base allows you to progress faster.
- Practice Consistency: Regular, dedicated practice is crucial. Consistent training, even in short sessions, yields better results than sporadic, longer sessions.
- Learning Approach: Following a structured, progressive plan is essential. A well-designed program addresses all necessary components, such as wrist strength, shoulder mobility, and core stability.
- Body Awareness: Understanding your body in space (proprioception) helps you make necessary adjustments for balance. Enhanced body awareness accelerates your learning.
- Fear and Mental Blocks: Overcoming the fear of being upside down is a significant hurdle. Mental preparedness and confidence play a vital role in your progress.
- Individual Learning Style: Some learn best through visual cues, while others prefer hands-on instruction. Tailoring your learning approach to your style enhances your progress.
- Age: While age is not a limiting factor, younger individuals may have a slight advantage in terms of flexibility and recovery. However, adults can certainly achieve handstands with dedication and proper training.
1.2. Realistic Timelines for Different Levels
So, how fast can you learn a handstand, really? Here’s a general timeline based on different levels of experience:
| Level | Description | Estimated Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute Beginner | No prior experience in gymnastics, yoga, or bodyweight training. Needs to develop foundational strength, flexibility, and body awareness. | 6 months – 1 year+ |
| Beginner | Some experience in fitness activities. Can hold a plank for 30 seconds and do a few push-ups. Familiar with basic bodyweight exercises. | 3-6 months |
| Intermediate | Regular practitioner of yoga, gymnastics, or bodyweight training. Can hold a plank for 60 seconds, do 10+ push-ups, and has good body awareness. Comfortable with inversions like headstands. | 1-3 months |
| Advanced | Extensive experience in gymnastics or hand balancing. Possesses significant strength, flexibility, and body awareness. Can perform various advanced bodyweight exercises. | Weeks to refine technique |
These timelines are estimates. Individual progress varies depending on the factors mentioned earlier. Be patient, stay consistent, and celebrate small victories along the way.
2. Essential Foundations for Handstand Success
Before diving into handstand progressions, it’s crucial to establish a solid foundation. This involves building strength, flexibility, and body awareness.
2.1. Strength Training for Handstands
Building adequate strength is crucial for supporting your body weight in an inverted position. Focus on these key areas:
- Wrists: Strengthen your wrists with exercises like wrist extensions, wrist curls, and forearm planks. These exercises improve wrist stability and endurance.
- Shoulders: Shoulder strength is essential for maintaining a straight line. Incorporate exercises like pike push-ups, scapular push-ups, and dumbbell shoulder presses.
- Core: A strong core stabilizes your body and prevents arching. Practice hollow body holds, planks, and reverse crunches.
- Back: Strengthening your back muscles helps maintain proper alignment. Include exercises like superman extensions, bird-dog exercises, and back extensions.
- Legs: Leg strength is important for controlled entries and exits. Exercises like squats, lunges, and calf raises can improve lower body stability.
2.2. Flexibility and Mobility Exercises
Flexibility and mobility are essential for achieving proper alignment and preventing injuries. Focus on these areas:
- Wrists: Perform wrist stretches regularly, including wrist extensions, wrist flexions, and wrist circles. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds.
- Shoulders: Improve shoulder mobility with stretches like doorway stretches, cross-body arm stretches, and shoulder dislocations with a light band.
- Spine: Spinal flexibility is important for maintaining a straight line. Practice cat-cow stretches, spinal twists, and backbends.
- Hips: Hip mobility helps with controlled leg movements. Include exercises like hip circles, pigeon pose, and butterfly stretches.
2.3. Developing Body Awareness
Body awareness, or proprioception, is the ability to sense your body’s position in space. Enhance your body awareness with these exercises:
- Balance Board Training: Using a balance board improves your ability to make subtle adjustments to maintain balance.
- Yoga: Yoga poses improve body awareness by requiring precise alignment and controlled movements.
- Pilates: Pilates focuses on core strength and body control, enhancing overall body awareness.
- Blindfolded Exercises: Performing simple exercises with your eyes closed can sharpen your sense of body position.
3. Handstand Training: A Step-by-Step Progression
This section presents a structured progression to guide you from the basics to a freestanding handstand.
3.1. Phase 1: Wrist and Shoulder Preparation
Before attempting any handstand exercises, it’s essential to prepare your wrists and shoulders with targeted warm-ups.
- Wrist Warm-up: Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions of wrist circles, wrist extensions, and wrist flexions. These exercises increase blood flow and flexibility in the wrists.
- Shoulder Warm-up: Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions of arm circles, shoulder rotations, and scapular retractions. These exercises improve shoulder mobility and stability.
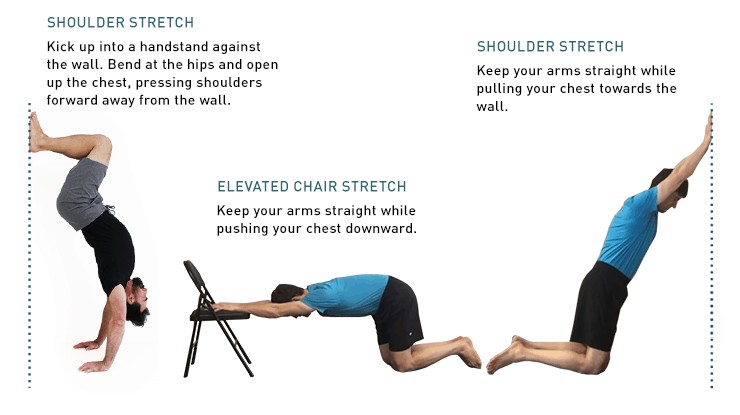 Wrist Extension ExerciseAlt text: Shoulder stretches to increase flexibility, promoting enhanced balance and control for handstand preparation.
Wrist Extension ExerciseAlt text: Shoulder stretches to increase flexibility, promoting enhanced balance and control for handstand preparation.
3.2. Phase 2: Wall-Assisted Handstands
Using a wall provides support and helps you build confidence.
- Wall Plank: Start in a plank position with your feet against the wall. Walk your hands closer to the wall while walking your feet up the wall. Hold for 30-60 seconds, focusing on pushing through your shoulders and engaging your core.
- Wall Walks: Begin in a plank position with your feet against the wall. Walk your hands closer to the wall while walking your feet up the wall until you reach a near-vertical position. Hold for a few seconds, then walk back down. Repeat 5-10 times.
- Wall Handstand Holds: Kick up into a handstand with your stomach facing the wall. Focus on maintaining a straight line from your hands to your heels. Hold for as long as possible, gradually increasing the duration as you get stronger.
3.3. Phase 3: Handstand Push-Up (HSPU)
The handstand push-up is a challenging exercise that requires strength and balance.
- Wall-Assisted HSPU Negatives: Kick up into a handstand with your stomach facing the wall. Slowly lower your body towards the floor, controlling the descent. Push back up to the starting position. If you can’t complete the full range of motion, focus on the lowering (eccentric) portion.
- Wall-Assisted Partial HSPU: Kick up into a handstand with your stomach facing the wall. Lower your body a few inches towards the floor, then push back up. Gradually increase the range of motion as you get stronger.
- Full Wall-Assisted HSPU: Kick up into a handstand with your stomach facing the wall. Lower your body until your head touches the floor, then push back up to the starting position.
3.4. Phase 4: Freestanding Handstand Training
Once you’re comfortable with wall-assisted handstands, you can start practicing freestanding handstands.
- Spotting: Have a spotter assist you as you practice kicking up into a handstand. The spotter can help you maintain balance and prevent falls.
- Kick-Up Practice: Practice kicking up into a handstand without the wall. Focus on controlling the kick and finding your balance point. Start with short attempts, gradually increasing the duration as you improve.
- Freestanding Handstand Holds: Once you can kick up into a handstand with control, practice holding the position for as long as possible. Engage your core, push through your shoulders, and use your fingers to make subtle adjustments for balance.
3.5. Phase 5: Balance and Refinement
Once you can hold a freestanding handstand for a few seconds, focus on improving your balance and alignment.
- Finger Drills: Practice using your fingers to make small adjustments to maintain balance. Shift your weight slightly forward and backward, using your fingertips to prevent falling.
- Shoulder Shrugs: Perform small shoulder shrugs while in the handstand to improve stability. Engage your shoulder muscles to maintain a straight line.
- Core Engagement: Consciously engage your core muscles to prevent arching and improve stability. Imagine pulling your belly button towards your spine.
- Visual Focus: Focus on a fixed point in front of you to improve balance. Avoid looking around, as this can disrupt your balance.
- Breathing: Maintain steady, controlled breathing throughout the handstand. Avoid holding your breath, as this can increase tension and disrupt balance.
4. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common pitfalls accelerates your progress. Here are mistakes to watch out for:
- Skipping the Warm-Up: Neglecting wrist and shoulder preparation can lead to injuries.
- Rushing the Progression: Trying advanced exercises before mastering the basics hinders your progress.
- Ignoring Body Alignment: Poor alignment leads to instability and potential injuries.
- Holding Your Breath: Holding your breath increases tension and disrupts balance.
- Practicing When Fatigued: Practicing when tired increases the risk of injury and poor form.
5. Handstand Variations for Continued Progress
Once you’ve mastered the basic handstand, explore variations to challenge yourself and keep your training engaging.
- Straddle Handstand: Holding a handstand with your legs split wide apart.
- Pike Handstand: Performing a handstand with your body bent at the hips, forming a pike shape.
- One-Arm Handstand: Balancing on one arm while maintaining a straight line.
- Handstand Walk: Walking on your hands while maintaining a handstand position.
- Press Handstand: Transitioning from a seated or standing position to a handstand using core strength and control.
6. Integrating Handstands into Your Fitness Routine
To maximize the benefits of handstand training, integrate it into your existing fitness routine.
- Warm-Up: Start your workout with wrist and shoulder mobility exercises to prepare your body for handstand practice.
- Skill Work: Dedicate specific time to practice handstand progressions, focusing on technique and control.
- Strength Training: Incorporate exercises that build strength in the wrists, shoulders, core, and back.
- Cool-Down: Finish your workout with stretches that improve flexibility in the wrists, shoulders, and spine.
- Consistency: Aim to practice handstands 2-4 times per week for optimal progress.
7. Staying Motivated and Consistent
Maintaining motivation is crucial for long-term success. Here are some tips:
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your goals into smaller, achievable steps.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a record of your training sessions and monitor your progress.
- Find a Training Partner: Working with a partner provides support and accountability.
- Join a Community: Connect with other handstand enthusiasts for inspiration and motivation.
- Celebrate Your Achievements: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress, no matter how small.
- Listen to Your Body: Rest when needed and avoid pushing yourself too hard.
8. Handstand Safety: Preventing Injuries
Safety should always be a top priority. Follow these guidelines to minimize the risk of injuries:
- Warm-Up: Always warm up your wrists and shoulders before practicing handstands.
- Proper Form: Focus on maintaining proper alignment to prevent strain on your joints.
- Controlled Entries and Exits: Practice controlled kick-ups and bail-outs to avoid falls.
- Spotting: Use a spotter when practicing new or challenging variations.
- Listen to Your Body: Stop if you experience pain or discomfort.
- Suitable Surface: Practice on a soft, cushioned surface to reduce the impact of falls.
- Clear Space: Ensure you have ample space around you to prevent collisions with objects or people.
9. Advanced Training Techniques
For those who have mastered the basics, here are advanced techniques to further enhance your handstand skills:
- Isometric Holds: Holding a handstand position for extended periods of time to build endurance.
- Dynamic Movements: Incorporating dynamic movements into your handstand practice, such as handstand push-ups, handstand hops, and handstand walks.
- Proprioceptive Training: Using tools like balance boards and wobble cushions to challenge your balance and improve body awareness.
- Visualization: Mentally rehearsing handstand movements to improve technique and coordination.
- Cross-Training: Incorporating other activities that complement handstand training, such as yoga, Pilates, and gymnastics.
10. The Role of Nutrition and Recovery
Proper nutrition and recovery play a vital role in your handstand journey.
- Balanced Diet: Consume a balanced diet that includes plenty of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel your workouts and support muscle recovery.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to allow your body to recover and rebuild.
- Active Recovery: Incorporate active recovery activities, such as light stretching and foam rolling, to reduce muscle soreness and improve circulation.
- Rest Days: Schedule regular rest days to allow your body to fully recover and prevent overtraining.
11. Tools and Resources for Handstand Training
Several tools and resources can enhance your handstand training.
- Wrist Wraps: Provide support and stability for your wrists, reducing the risk of injury.
- Yoga Mat: Offers a cushioned surface for practicing handstands and other exercises.
- Foam Roller: Helps release muscle tension and improve flexibility.
- Resistance Bands: Used for wrist and shoulder warm-up exercises.
- Online Courses: Structured handstand training programs.
- Books and Guides: Comprehensive information on handstand techniques and training methods.
- Mobile Apps: Track your progress and access instructional videos.
12. The Science Behind Handstands
Understanding the science behind handstands can enhance your training and performance.
- Biomechanics: Handstands require precise alignment of the joints and efficient muscle activation. Understanding biomechanical principles helps optimize your technique and prevent injuries.
- Neuromuscular Control: Handstands require a high degree of neuromuscular control to maintain balance and stability. Training exercises that challenge your balance and coordination improve neuromuscular control.
- Vestibular System: The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, plays a crucial role in balance and spatial orientation. Exercises that challenge your vestibular system, such as spinning and tilting movements, can improve your handstand performance.
- Proprioception: Proprioception, or body awareness, is the ability to sense your body’s position in space. Handstand training enhances proprioception, improving your ability to make subtle adjustments for balance.
- Muscle Physiology: Handstands require both strength and endurance in various muscle groups. Understanding muscle physiology helps you design effective training programs that target the specific muscles involved in handstands.
13. The Mental Game of Handstands
Mastering handstands is as much a mental challenge as it is a physical one. Developing mental resilience, focus, and confidence are essential for success.
- Goal Setting: Setting clear, achievable goals provides direction and motivation. Break down your long-term goals into smaller, manageable steps.
- Visualization: Mentally rehearsing handstand movements can improve your technique and coordination. Visualize yourself successfully performing a handstand, focusing on the feeling of balance and control.
- Positive Self-Talk: Use positive affirmations and self-talk to build confidence and overcome self-doubt. Remind yourself of your progress and capabilities.
- Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can reduce anxiety and improve focus.
- Resilience: Developing resilience is essential for overcoming setbacks and maintaining motivation. Embrace challenges as opportunities for growth and learning.
- Patience: Learning handstands takes time and patience. Avoid getting discouraged by slow progress and celebrate small victories along the way.
14. Handstands for All Ages and Abilities
Handstands are not just for elite athletes or gymnasts. With proper guidance and modifications, people of all ages and abilities can learn and enjoy handstands.
- Children: Handstands can improve balance, coordination, and body awareness in children. Start with simple wall-assisted exercises and gradually progress to more challenging variations.
- Adults: Handstands can improve strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health in adults. Modify exercises to accommodate any physical limitations or injuries.
- Seniors: Handstands can improve balance, bone density, and cognitive function in seniors. Start with gentle exercises and gradually progress at a comfortable pace.
- People with Disabilities: Handstands can be adapted for people with various disabilities, providing a challenging and rewarding physical activity. Work with a qualified instructor to develop a customized training program.
15. Handstand Myths Debunked
Several misconceptions surround handstands. Let’s debunk some common myths:
- Myth: Handstands are only for gymnasts.
- Reality: Anyone can learn handstands with proper training and dedication.
- Myth: Handstands require exceptional strength.
- Reality: While strength is important, technique and balance are more crucial.
- Myth: Handstands are dangerous.
- Reality: With proper safety precautions, handstands are relatively safe.
- Myth: Handstands are bad for your back.
- Reality: When performed with proper form, handstands can actually strengthen your core and back muscles.
- Myth: You need to be young to learn handstands.
- Reality: People of all ages can learn handstands with proper guidance and modifications.
16. Integrating Breathing Techniques
Proper breathing is essential for maintaining stability, reducing tension, and improving focus during handstands.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Practice diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, to engage your core muscles and promote relaxation.
- Ujjayi Breath: Use Ujjayi breath, a common technique in yoga, to create internal heat and focus.
- Breath Holds: Incorporate breath holds to challenge your stability and improve your ability to maintain control.
- Coordination: Coordinate your breathing with your movements. Inhale as you prepare to kick up into a handstand, and exhale as you find your balance.
- Rhythmic Breathing: Maintain a steady, rhythmic breathing pattern throughout the handstand to reduce tension and improve focus.
17. The Future of Handstand Training
Handstand training is constantly evolving, with new techniques, technologies, and approaches emerging.
- Virtual Reality: Virtual reality (VR) technology is being used to create immersive handstand training experiences. VR can provide real-time feedback on your technique and help you visualize your movements.
- Wearable Sensors: Wearable sensors, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, can monitor your performance and provide data on your balance, stability, and muscle activation.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to develop personalized handstand training programs. AI algorithms can analyze your performance data and create customized workouts that target your specific needs and goals.
- Online Communities: Online communities and social media platforms are providing opportunities for handstand enthusiasts to connect, share knowledge, and support each other.
- Scientific Research: Ongoing scientific research is providing new insights into the biomechanics, neuromuscular control, and mental aspects of handstands. This research is helping to optimize training techniques and improve performance.
18. Resources on LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we have a lot of resources, whether you want to learn new skills, understand new subjects or fine tune your learning abilities.
- Comprehensive Articles: Detailed guides on various aspects of handstand training, including strength training, flexibility exercises, and balance techniques.
- Step-by-Step Tutorials: Easy-to-follow instructions for handstand progressions, from beginner to advanced levels.
- Expert Tips: Advice and insights from experienced handstand coaches and athletes.
- Training Plans: Structured training programs designed to help you achieve your handstand goals.
- Video Library: A collection of instructional videos demonstrating proper form and technique.
- Community Forum: A platform to connect with other handstand enthusiasts, ask questions, and share your progress.
- Personalized Coaching: One-on-one coaching services to help you overcome challenges and achieve your handstand goals.
FAQ Section
How long does it take to learn a handstand?
The timeframe varies depending on your current fitness level, consistency of practice, and learning approach. Absolute beginners may take 6 months to a year, while those with some fitness experience might achieve it in 3-6 months.
What are the key factors that influence handstand learning speed?
Prior experience, physical fitness, practice consistency, learning approach, body awareness, mental blocks, individual learning style, and age all play a role.
How often should I practice handstands?
Aim for 2-4 times a week to allow your central nervous system to adapt and build the necessary strength and balance.
What if I can’t keep my balance?
Focus on mastering the setup, controlling the kick-up, and learning how to bail safely.
Do handstands build muscle?
While not primarily a muscle-building exercise, handstands improve strength throughout your body, particularly in your wrists, shoulders, and core.
Do you need to be strong to do a handstand?
You don’t need to be exceptionally strong to start. Begin with foundational exercises to build wrist, shoulder, and core strength gradually.
Are handstands good for you?
Yes, when done safely and correctly, handstands can improve blood circulation, spatial awareness, balance, and strength.
How do I train to do a handstand?
Start with safety and strength exercises, then work on balance and entry techniques, and finally, focus on endurance for freestanding handstands.
Are handstands bad for your back?
Handstands can be bad for your back if your core is not engaged or have poor range of motion in your shoulders, leading to “banana” handstands.
Is the headstand or handstand harder?
The handstand is generally harder due to the increased balance requirements and longer lever length (your body).
Remember, the question of how fast can you learn a handstand ultimately depends on your commitment, consistent practice, and a well-structured training plan. With the right approach and resources from LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can achieve your handstand goals and enjoy the numerous physical and mental benefits this skill offers.
Ready to start your handstand journey? Visit learns.edu.vn today to explore our comprehensive resources and unlock your full potential. Our expert articles, step-by-step tutorials, and personalized coaching will guide you every step of the way.
Contact us:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN