A learning management system (LMS) is a software application designed to streamline and enhance the learning process, offering tools for content delivery, student monitoring, and performance assessment. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we offer in-depth resources and expert guidance to help you master LMS platforms and leverage their full potential for educational success. Explore our site for effective learning strategies, in-depth guides, and access to top educational experts.
1. What is a Learning Management System?
A Learning Management System (LMS) is a software application or web-based technology used to plan, implement, assess, and optimize a specific learning process. An LMS typically comprises a server that provides the core functionality and a user interface (UI) that allows instructors to create and deliver content, monitor student engagement, and evaluate performance. These systems are essential tools for organizations aiming to enhance traditional education methods while saving time and resources.
1.1 Key Components of an LMS
- Server Infrastructure: The backbone of the LMS, handling data storage, processing, and delivery.
- User Interface (UI): The front-end through which instructors and students interact with the system.
- Content Management Tools: Features that allow instructors to create, upload, and organize learning materials.
- Assessment Tools: Tools for creating and administering quizzes, assignments, and other evaluations.
- Communication Tools: Features such as discussion forums, chat, and messaging to facilitate interaction between instructors and students.
- Reporting and Analytics: Tools to track student progress, identify areas for improvement, and measure the effectiveness of training programs.
1.2 Common Features of a Learning Management System
- Course Management: Tools for creating, organizing, and delivering course content.
- User Management: Features for enrolling, managing, and tracking users.
- Assessment: Tools for creating and grading quizzes, tests, and assignments.
- Reporting: Features for tracking student progress and performance.
- Communication: Tools for facilitating communication between instructors and students, such as forums, chat, and email.
- Content Sharing: Capabilities for sharing documents, videos, and other resources.
- Mobile Accessibility: Access to course materials and activities on mobile devices.
- Integration: Integration with other systems, such as student information systems (SIS) and HR platforms.
- Personalization: Tailoring the learning experience to individual student needs.
- Gamification: Incorporating game-like elements to increase engagement and motivation.
- Compliance Tracking: Monitoring and reporting on compliance training requirements.
1.3 Benefits of Using a Learning Management System
- Centralized Learning: An LMS provides a central location for all learning materials, making it easy for students to find and access the resources they need.
- Improved Tracking and Reporting: An LMS allows instructors and administrators to track student progress and performance, providing valuable insights for improving the learning experience.
- Cost Savings: By delivering training online, organizations can reduce travel costs, material costs, and instructor time.
- Scalability: An LMS can easily scale to accommodate a growing number of students and courses.
- Flexibility: An LMS allows students to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule, making it ideal for those with busy lives.
- Enhanced Collaboration: An LMS provides tools for students to collaborate with each other, fostering a sense of community and improving the learning experience.
- Better Compliance: An LMS can help organizations track and manage compliance training, ensuring that employees are up-to-date on the latest regulations.
1.4 Real-World Applications of Learning Management Systems
- Educational Institutions: Schools and universities use LMS platforms to deliver online courses, manage student records, and track academic progress.
- Corporate Training: Companies use LMS systems to onboard new employees, provide ongoing training, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
- Government Agencies: Government agencies use LMS software to train employees, manage compliance, and deliver public education programs.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profit organizations use LMS tools to train volunteers, educate the public, and manage programs.
1.5 Key Integrations that Enhance LMS Functionality
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Integrates customer data with learning programs to personalize training and improve customer engagement.
- HRIS (Human Resources Information System): Streamlines employee training, onboarding, and performance tracking, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- eCommerce Platforms: Enables selling online courses and managing transactions, enhancing revenue generation for educational institutions.
- Video Conferencing Tools: Facilitates live virtual classes and interactive sessions, enhancing remote learning experiences.
- Analytics Dashboards: Provides real-time data on learner progress and course effectiveness, allowing for data-driven improvements.
- Content Authoring Tools: Simplifies creating and updating course materials, making content management more efficient.
- Social Media Platforms: Encourages collaborative learning and knowledge sharing, fostering a sense of community among learners.
- Payment Gateways: Simplifies secure payment processing for course enrollments and subscriptions.
- Email Marketing Platforms: Enhances communication and engagement with learners through targeted email campaigns.
- Calendar and Scheduling Tools: Streamlines scheduling and coordination of training sessions and events.
2. Why Use a Learning Management System?
Learning Management Systems are used for knowledge management. The role of the LMS varies according to the organization’s training strategy and goals, primarily used for gathering, organizing, sharing, and analyzing an organization’s knowledge in terms of resources, documents, and people skills.
2.1 Onboarding and Training with LMS
Employee training and onboarding are two common uses of LMS platforms in a business environment. For onboarding, the LMS helps train new employees, providing opportunities to access training programs across various devices. New employees add their own knowledge and provide feedback. This helps employers understand how effective the training course materials are and identify areas where new hires need assistance.
According to a study by the Association for Talent Development (ATD), companies with strong onboarding processes see a 50% higher new-hire retention rate. An LMS streamlines this process by providing consistent, accessible training materials, ensuring new hires are well-prepared and engaged from day one.
2.2 Development and Retention with LMS
Employee development and retention is another way LMS solutions are used in businesses. The system assigns courses to employees to ensure they are developing effective job skills, remain informed about product changes, and have requisite product and compliance knowledge.
Research from the Corporate Leadership Council found that employees who receive regular training and development opportunities are 15% more engaged and 34% less likely to leave their jobs. An LMS helps organizations create personalized learning paths, ensuring employees have the skills and knowledge they need to succeed and grow within the company.
2.3 Sales Training with LMS
Another way LMS is used is to enhance employee sales skills. This includes the creation of seminars on product knowledge, customer interaction training, and case study-based tutorials that use previous experiences with clients to improve future interactions.
A study by Training Industry, Inc. revealed that companies with robust sales training programs achieve 24% higher profit margins. An LMS enables organizations to deliver consistent, high-quality sales training, equipping sales teams with the knowledge and skills they need to close more deals and drive revenue growth.
2.4 Blended Learning with LMS
An LMS provides students with blended learning experiences that combine traditional classroom teaching with online learning tools. This method is more effective than simple face-to-face education because it enriches instructor-led training in the classroom with digital learning content customized to fit a student’s learning needs.
According to a report by the U.S. Department of Education, blended learning can lead to improved learning outcomes compared to traditional face-to-face instruction. An LMS facilitates blended learning by providing a platform for delivering online content, tracking student progress, and fostering collaboration between students and instructors.
2.5 Key Benefits of Using an LMS in Various Settings
| Setting | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Corporate Training | Streamlined onboarding, enhanced employee development, improved compliance, increased engagement, and better sales performance. |
| Educational Institutions | Enhanced blended learning, improved student outcomes, better tracking and reporting, increased scalability, and greater flexibility. |
| Government Agencies | Efficient employee training, improved compliance, better public education, enhanced program management, and greater cost savings. |
| Non-Profit Organizations | Effective volunteer training, improved public education, enhanced program management, increased community engagement, and greater impact. |

3. How do Learning Management Systems Work?
An LMS is a large repository where users store and track information in one place. Any user with a login and password can access the system and its online learning resources. If the system is self-hosted, the user must either install the software on their computer or access it through their company’s server.
3.1 Responsive Design
Users can access the LMS from any type of device, whether it’s a desktop, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. The system automatically displays the version best suited for each user’s chosen device and lets users download content for offline work.
A study by Pew Research Center found that 85% of adults in the U.S. own a smartphone, and mobile devices account for a significant portion of online learning traffic. Responsive design ensures that learners can access course materials and activities on any device, improving accessibility and engagement.
3.2 User-Friendly Interface
The UI lets learners navigate the LMS platform and is aligned with the abilities and goals of the user and the organization. An unintuitive UI risks confusing or distracting users, making the LMS less effective.
According to a report by the Nielsen Norman Group, a user-friendly interface can increase user satisfaction by 200% and reduce training costs by 50%. A well-designed UI makes it easy for learners to find and access the resources they need, improving their overall learning experience and reducing frustration.
3.3 Reports and Analytics
E-learning assessment tools and dashboards show instructors and administrators how effective online training initiatives are. Both groups of learners and individuals can be analyzed with these tools and metrics.
Research from Bersin by Deloitte found that companies that use data analytics to improve their training programs see a 50% improvement in employee performance. LMS reporting and analytics tools provide valuable insights into student progress, engagement, and performance, allowing instructors and administrators to identify areas for improvement and optimize the learning experience.
3.4 Catalog and Course Management
Admins and instructors manage the catalog of course content in the LMS to create more targeted learning experiences.
A study by the Brandon Hall Group found that organizations with well-managed course catalogs see a 25% increase in course completion rates. Effective catalog and course management ensures that learners can easily find and enroll in the courses they need, improving their overall learning experience.
3.5 Content Interoperability and Integration
Content created and stored in an LMS must be packaged in accordance with interoperable standards, including SCORM and experience application programming interface or xAPI.
According to the Advanced Distributed Learning (ADL) Initiative, SCORM and xAPI standards ensure that learning content can be easily shared and reused across different LMS platforms. Content interoperability and integration save time and resources by allowing organizations to create and deliver learning content once and use it in multiple systems.
3.6 Support Services
Different LMS vendors offer varying levels of support. Many provide online discussion boards where users connect and help each other. Additional support services, such as a dedicated, toll-free phone number, might be available for an extra cost.
Research from Software Advice found that 75% of LMS users value vendor support services. Reliable support services ensure that users can get the help they need when they encounter problems, reducing downtime and improving their overall experience.
3.7 Certification and Compliance Support
This feature is essential to systems used for online compliance training and certifications. It enables instructors and admins to assess an individual’s skill set and identify any gaps in their performance. This feature also makes it possible to use LMS records during an audit.
According to a report by the Compliance Learning Center, organizations that use LMS platforms to manage compliance training see a 50% reduction in compliance violations. Certification and compliance support features help organizations track and manage compliance training requirements, ensuring that employees are up-to-date on the latest regulations and reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
3.8 Social Learning Capabilities
Many LMS platforms include social media tools in their learning platforms to let users interact with their peers, collaborate, and share learning experiences.
A study by the Social Learning Center found that learners who participate in social learning activities are 20% more engaged and 30% more likely to retain information. Social learning capabilities foster collaboration, knowledge sharing, and community building, improving the overall learning experience.
3.9 Gamification
Some LMS platforms include game mechanics or built-in gamification features that add extra motivation and engagement to courses. This gives students an additional incentive to complete courses, in the form of leaderboards, points, and badges.
According to a report by TalentLMS, gamification can increase learner engagement by 60% and improve knowledge retention by 50%. Gamification features add fun and excitement to the learning experience, motivating learners to complete courses and achieve their learning goals.
3.10 Automation
Learning management systems automate and streamline repetitive and tedious tasks, such as grouping, adding, and deactivating users, and handling group enrollments.
Research from the Aberdeen Group found that organizations that automate their training processes see a 40% reduction in administrative costs. Automation features save time and resources by automating repetitive tasks, allowing instructors and administrators to focus on more strategic activities.
3.11 Localization
LMS platforms often include multilingual support, removing language barriers from learning and training content. Some LMS platforms integrate geolocation features that automatically present the appropriate version of the course when a user accesses it.
According to a report by Common Sense Advisory, organizations that localize their training content see a 25% increase in learner engagement. Localization features ensure that learners can access course materials in their native language, improving comprehension and engagement.
3.12 Artificial Intelligence
LMS platforms use AI to create personalized learning experiences for users with course formats suited to their needs. AI also helps suggest topics a user might find interesting based on courses they’ve already completed.
Research from McKinsey & Company found that AI can improve learning outcomes by 30% and reduce training costs by 20%. AI-powered LMS features personalize the learning experience, recommending relevant content and tailoring the learning path to individual learner needs.
4. What are the Types of LMS Deployments?
The different LMS deployment options include Cloud-based LMS, Self-hosted LMS, Third-party hosted LMS, Desktop application LMS, Mobile app LMS, Custom-built LMS, Open-source LMS, Learning content management systems (LCMSes), and LMS modules.
4.1 Cloud-Based LMS
Cloud-based LMS are hosted on the cloud and often follow a software as a service business model. Providers maintain the system and handle updates or upgrades. Online users access the system apps from anywhere at any time using a username and password.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the cloud-based LMS market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20% over the next five years. Cloud-based LMS platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and cost savings, making them an attractive option for organizations of all sizes.
4.2 Self-Hosted LMS
Self-hosted LMS require the organization to download and install the LMS software. The self-hosted platform provides creative control and customization, but the organization is responsible for maintaining the system and might also have to pay for updates.
A survey by Capterra found that 30% of organizations prefer self-hosted LMS platforms for greater control and customization options. Self-hosted LMS platforms offer organizations complete control over their learning environment, but they also require significant IT resources and expertise.
4.3 Third-Party Hosted LMS
Third-party hosted LMS are learning resources that a third-party organization hosts. Courses are obtained directly from a public cloud location or from the training company’s own data center or private cloud.
According to a report by Global Market Insights, the third-party hosted LMS market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% over the next five years. Third-party hosted LMS platforms offer organizations a convenient and cost-effective way to deliver online training without the need for significant IT infrastructure.
4.4 Desktop Application LMS
Desktop application LMS are installed on the user’s desktop. However, the application might still be accessible on multiple devices.
A survey by Software Advice found that 15% of organizations use desktop application LMS platforms for their training needs. Desktop application LMS platforms offer offline access to course materials, making them a good option for learners with limited internet connectivity.
4.5 Mobile App LMS
Mobile app LMS support a mobile learning environment and are accessible wherever and whenever through mobile devices. This platform deployment type lets users engage with and track their online learning initiatives on the go.
According to a report by Docebo, mobile learning is expected to grow at a CAGR of 25% over the next five years. Mobile app LMS platforms offer learners the flexibility to access course materials and activities on their smartphones and tablets, improving engagement and accessibility.
4.6 Custom-Built LMS
Custom-built LMS are built by a company’s development team or by external consultants and only include the functionalities a company needs.
A survey by Talented Learning found that 10% of organizations opt for custom-built LMS platforms to meet their unique training requirements. Custom-built LMS platforms offer organizations complete control over the design and functionality of their learning environment, but they also require significant development resources and expertise.
4.7 Open Source LMS
Open source LMS are built with existing code that’s shared with users so they can add their own features and functionalities as they see fit.
According to a report by Ambient Insight, the open source LMS market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12% over the next five years. Open source LMS platforms offer organizations a cost-effective and flexible way to deliver online training, but they also require technical expertise to install, configure, and maintain.
4.8 Learning Content Management Systems (LCMSes)
Learning content management systems are content management systems built for creating and managing new learning or training content.
A survey by the Brandon Hall Group found that organizations that use LCMS platforms see a 20% improvement in content development efficiency. LCMS platforms provide tools for creating, managing, and delivering learning content, making it easier for organizations to develop high-quality training programs.
4.9 LMS Modules
LMS modules are add-ons to HR systems built to perform specific tasks. These modules aren’t meant to be as advanced as full LMS platforms.
According to a report by Bersin by Deloitte, organizations that integrate their LMS with their HR system see a 15% improvement in employee engagement. LMS modules offer organizations a convenient way to add learning functionality to their existing HR systems, streamlining training and development processes.
5. What Are The Payment Options for LMS Systems?
The various pricing models used for LMS platforms include Freemium, Subscription, Licensing, and Open source.
5.1 Freemium
This free model lets users access the basic features of some LMS platforms for free. Once users start engaging with the more advanced functionalities of the system, a fee is imposed.
According to a report by FinancesOnline, freemium LMS platforms can attract up to 10 times more users than paid platforms. Freemium pricing models offer organizations a low-risk way to try out an LMS platform and see if it meets their needs before committing to a paid plan.
5.2 Subscription
Users pay a recurring fee at regular intervals to access the LMS. The subscription might grant an organization total access to all LMS features, or it might require the organization to pay for each user.
A survey by Software Advice found that 60% of organizations prefer subscription-based LMS pricing models. Subscription pricing models offer organizations a predictable and manageable way to budget for their LMS expenses.
5.3 Licensing
LMS licensing is based on either an annual fee that companies must renew or a one-time fee that provides users with unlimited lifetime access.
According to a report by Talented Learning, licensing pricing models are most common among self-hosted LMS platforms. Licensing pricing models offer organizations greater control over their LMS expenses, but they also require significant upfront investment.
5.4 Open Source
Open source products are usually provided at no cost. Some examples are Chamilo, Ilias, Moodle, and Sakai.
A survey by Capterra found that 40% of organizations use open source LMS platforms due to their cost-effectiveness and flexibility. Open source pricing models offer organizations a cost-effective way to deliver online training, but they also require technical expertise to install, configure, and maintain.
6. What are the Benefits of a Learning Management System?
An LMS saves an organization time and money. Learners don’t have to travel to other locations for classes or training sessions. Instead, they can complete coursework at a time and place that’s best for them. In addition, these systems require less interaction with live instructors, and they cut back on training days, training materials, travel expenses, and location hiring.
6.1 Monitor Learning Progress
An LMS provides the ability to monitor users’ learning progress and performance.
According to a report by the Association for Talent Development (ATD), organizations that track learner progress see a 20% improvement in employee performance. Monitoring learner progress allows instructors and administrators to identify areas where learners are struggling and provide targeted support.
6.2 Increased E-Learning Accessibility
An LMS offers increased e-learning accessibility without geographic limitations.
A study by the U.S. Department of Education found that online learning can be just as effective as traditional face-to-face instruction. LMS platforms make e-learning accessible to learners around the world, regardless of their location or time zone.
6.3 Personalized Online Courses
An LMS offers personalized online courses, training, and learning experiences.
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, personalization can increase learner engagement by 30% and improve learning outcomes by 20%. LMS platforms allow instructors to create personalized learning paths and recommend relevant content based on individual learner needs.
6.4 Easily Update E-Learning Modules
An LMS provides the ability to easily and efficiently update e-learning modules and activities.
A survey by the Brandon Hall Group found that organizations that update their e-learning content regularly see a 15% improvement in learner engagement. LMS platforms make it easy for instructors to update course materials quickly and efficiently, ensuring that learners always have access to the latest information.
6.5 Streamlined Distribution
An LMS offers consistent and streamlined distribution of online training and learning content across an organization.
According to a report by the Corporate Executive Board (CEB), organizations that streamline their training processes see a 10% reduction in training costs. LMS platforms ensure that all learners receive the same training content, regardless of their location or department.
6.6 Eliminate Repetitive Tasks
An LMS helps eliminate repetitive tasks in learning programs, such as user enrollment and certification.
Research from the Aberdeen Group found that organizations that automate their training processes see a 40% reduction in administrative costs. LMS platforms automate many repetitive tasks, freeing up instructors and administrators to focus on more strategic activities.
6.7 Centralized Management
An LMS provides centralized management so all data is organized and stored in one place. This makes it easier for instructors and admins to update and maintain learning materials.
According to a report by the Information Management Body of Knowledge (IMBOK), centralized data management can reduce data storage costs by 20%. LMS platforms provide a central repository for all learning materials, making it easy for instructors and administrators to manage and update content.
6.8 Advanced Security
An LMS offers advanced security features, such as encryption, to keep data and content secure.
A survey by the Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of a data breach is $3.86 million. LMS platforms provide advanced security features to protect sensitive data and content from unauthorized access.
7. What are the Challenges of an LMS?
A few challenges with LMS systems prove they aren’t a silver bullet for upskilling or training employees. The setup and integration, lack of accommodation, and lack of reporting.
7.1 Setup and Integration
Expertise in setting up an LMS and integrating it with an organization’s existing tech infrastructure is required. Not all organizations have the necessary personnel to do this.
According to a report by Talented Learning, the average LMS implementation takes 3-6 months. Setting up and integrating an LMS platform can be complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized IT skills and resources.
7.2 Lack of Accommodation
Employees and students learn differently from one another or learn better with personalized teaching methods; LMS systems typically don’t have the flexibility to accommodate a range of learning approaches and meet all students’ needs.
A study by the Association for Talent Development (ATD) found that only 30% of learners believe that their training programs are personalized to their needs. LMS platforms may lack the flexibility to accommodate different learning styles and preferences, leading to disengaged learners.
7.3 Lack of Reporting
Some LMS platforms lack the advanced analytics dashboards and built-in features needed to analyze student performance.
Research from Bersin by Deloitte found that only 20% of organizations are satisfied with their LMS reporting capabilities. Some LMS platforms lack the advanced analytics dashboards and reporting features needed to track learner progress and performance effectively.
8. Using Content Management Systems With LMS Platforms
An important part of the LMS process is creating learning content. If the LMS has its own content, it’s important that it can be adjusted to meet an organization’s requirements. If the organization needs to create its own content, an LCMS is helpful because it’s built specifically for creating content in a learning environment. LCMS platforms contain the standard functionalities found in a typical CMS, but they’re better suited for these learning environments.
8.1 Content Management Software Application
A content management software application is to design, modify, and delete the content.
According to a report by the Content Marketing Institute, 70% of organizations use content management systems (CMS) to manage their online content. A content management software application is essential for creating and managing learning content within an LMS platform.
8.2 Content Delivery Application
A content delivery application is that formats the content for its ultimate destination.
Research from the Aberdeen Group found that organizations that use content delivery networks (CDN) see a 20% improvement in website performance. A content delivery application ensures that learning content is delivered quickly and efficiently to learners around the world.
9. How to Choose a New LMS
Prior to buying an LMS, an organization must assess its learning requirements. This means determining the LMS goals, users, costs, technology requirements, features, and compliance.
9.1 LMS Goals
The long-term goals an LMS will accomplish, such as cohort-based continuous learning, are determined first.
According to a report by the Brandon Hall Group, organizations that align their LMS goals with their business objectives see a 15% improvement in employee performance. Defining clear LMS goals is essential for ensuring that the platform meets the organization’s training needs.
9.2 Users
Intended users should be identified and segmented into groups.
A study by the Association for Talent Development (ATD) found that organizations that segment their learners into groups see a 10% improvement in training effectiveness. Identifying and segmenting users allows instructors to tailor the learning experience to individual learner needs.
9.3 Costs
An organization must pick an affordable option that fits within its budget.
Research from Software Advice found that the average cost of an LMS platform is $7,000 per year. Organizations need to carefully consider the costs of an LMS platform and choose an option that fits within their budget.
9.4 Technology Requirements
Determining if the existing tech infrastructure will integrate with a specific LMS product is key.
A survey by Capterra found that 40% of organizations have experienced integration issues with their LMS platform. Ensuring that the LMS platform integrates seamlessly with existing technology infrastructure is essential for a successful implementation.
9.5 Features
LMS systems offer various capabilities, such as gamification and AI, to help employees learn.
According to a report by TalentLMS, gamification can increase learner engagement by 60% and improve knowledge retention by 50%. Organizations should carefully evaluate the features offered by different LMS platforms and choose an option that meets their specific training needs.
9.6 Compliance
Depending on where an organization is located, laws and regulations might dictate acceptable use of an LMS, especially with the collection of personal data.
Research from the Compliance Learning Center found that organizations that use LMS platforms to manage compliance training see a 50% reduction in compliance violations. Organizations need to ensure that their LMS platform complies with all applicable laws and regulations, especially those related to data privacy and security.
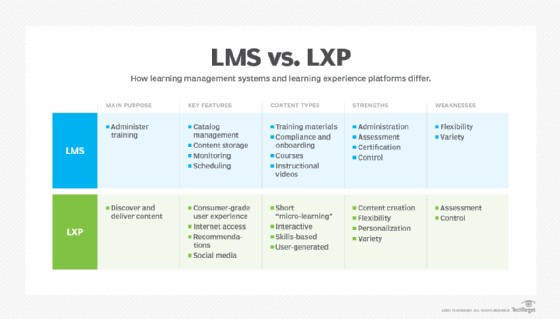
10. Learning Experience Platforms vs. LMS Platforms
Learning experience platforms are the next generation of learning management technologies. This SaaS-based technology uses AI to adapt the learning experience to the student’s needs and raise the bar on the overall experience. LXPs differ from LMS platforms, which generally require students to follow a program as the provider designed it.
10.1 AI Component of an LXP
The AI component of an LXP gives students a more autonomous and self-managed experience. For example, if the student takes an interest in certain information, the LXP presents relevant content from the internet to the student. The LXP also captures data on the student’s preferences and uses it to increase personalization. The goal is to make the training experience more student-centric.
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, AI can improve learning outcomes by 30% and reduce training costs by 20%. The AI component of an LXP platform personalizes the learning experience, recommending relevant content and tailoring the learning path to individual learner needs.
10.2 Key Differences Between LMS and LXP
| Feature | LMS | LXP |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Content management and delivery | Personalized learning experience |
| Approach | Structured and linear | Adaptive and learner-driven |
| Technology | Traditional software | AI-powered platform |
| User Experience | Instructor-led | Learner-centric |
| Content Source | Primarily internal | Internal and external resources |
| Data Analysis | Basic reporting and analytics | Advanced data analysis and personalization |
| Learning Experience | Standardized and consistent | Personalized and adaptive |
| Integration | Integration with HR and other systems | Integration with various content sources and learning tools |
| Implementation | Relatively straightforward | More complex due to AI and personalization |
| Cost | Varies depending on features and deployment | Generally higher due to advanced technology |
| Use Cases | Compliance training, structured courses, and formal learning | Personalized learning paths, informal learning, and continuous development |
| Benefits | Centralized content, streamlined training, and improved compliance | Enhanced learner engagement, personalized learning, and improved learning outcomes |
| Challenges | Lack of personalization, limited flexibility, and potential for disengagement | Complexity, cost, and the need for data privacy and security |
11. LMS vs. Training Management System (TMS)
An LMS and a TMS differ in both purpose and intended users. Administrators and other managers use an LMS to create compelling learning content; employees use an LMS to learn. Meanwhile, admins and managers use TMS platforms to organize and customize their training methods. This includes tasks such as setting up training dates and sessions, cost management, and overseeing trainers. The two types of systems are often combined to create a unified platform. The LMS handles processes such as delivering online courses to students and communicating with them virtually. The TMS handles training logistics. This combined approach is suitable for large-scale, instructor-led training situations where there are large pools of employees and trainers.
11.1 Key Differences Between LMS and TMS
| Feature | LMS | TMS |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Delivering and managing learning content | Organizing and managing training logistics |
| Users | Employees and students | Administrators and managers |
| Purpose | Creating and delivering compelling learning content | Organizing and customizing training methods |
| Tasks | Delivering online courses, tracking progress, and reporting | Setting up training dates, cost management, and overseeing trainers |
| Integration | Integrates with content creation and delivery tools | Integrates with scheduling and resource management tools |
| Use Cases | Online courses, e-learning, and blended learning | Large-scale instructor-led training and logistics management |
FAQ Section
1. What are the key features of a Learning Management System (LMS)?
An LMS typically includes features such as course management, user management, assessment tools, reporting, communication tools, content sharing, mobile accessibility, integration with other systems, personalization, gamification, and compliance tracking.
2. How does a Learning Management System (LMS) improve employee training?
An LMS improves employee training by providing a centralized platform for delivering consistent, high-quality training content, tracking employee progress, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
3. What is the difference between a Learning Management System (LMS) and a Learning Experience Platform (LXP)?
An LMS focuses on content management and delivery, while an LXP focuses on creating personalized learning experiences. An LXP uses AI to adapt the learning experience to the student’s needs and raise the bar on the overall experience.
4. What types of organizations benefit most from using a Learning Management System (LMS)?
Educational institutions, corporate training departments, government agencies, and non-profit organizations all benefit from using an LMS to streamline training, improve learning outcomes, and ensure compliance.
5. How does a Learning Management System (LMS) support blended learning?
An LMS supports blended learning by providing a platform for delivering online content, tracking student progress, and fostering collaboration between students and instructors in both online and offline settings.
6. What are the different deployment options for a Learning Management System (LMS)?
The different deployment options include cloud-based LMS, self-hosted LMS, third-party hosted LMS, desktop application LMS, mobile app LMS, custom-built LMS, open-source LMS, learning content management systems (LCMSes), and LMS modules.
7. What is the role of AI in modern Learning Management Systems (LMS)?
AI in modern LMS platforms personalizes the learning experience, recommending relevant content and tailoring the learning path to individual learner needs, ultimately improving learning outcomes and reducing training costs.
8. How do I choose the right Learning Management System (LMS) for my organization?
To choose the right LMS, assess your organization’s learning requirements, define clear LMS goals, identify and segment users, consider costs and technology requirements, evaluate available features, and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
9. What are the payment options for Learning Management Systems (LMS)?
The payment options include freemium, subscription, licensing, and open-source pricing models.
10. How do LMS platforms ensure data security and privacy?
LMS platforms ensure data security and privacy by implementing advanced security features such as encryption, access controls, and compliance with data protection regulations.
Ready to elevate your learning and development programs? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN to explore our comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and tailored solutions for mastering LMS platforms and achieving educational success. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Let learns.edu.vn be your partner in creating engaging, effective, and future-ready learning experiences.
