Fusion 360 is a powerful CAD/CAM tool that can unlock your design and manufacturing potential, and LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to guide you on your learning journey. This article provides a comprehensive roadmap to master Fusion 360, covering essential resources, effective learning strategies, and expert tips to accelerate your progress and achieve proficiency in this versatile software. Explore our website for more in-depth learning materials and courses.
1. What is Fusion 360 and Why Should You Learn It?
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based 3D modeling, CAD, CAM, CAE, and PCB software platform owned by Autodesk. It is a versatile tool used by engineers, designers, and manufacturers to create products ranging from consumer goods to complex machinery. Learning Fusion 360 can significantly enhance your skills in product design, simulation, and manufacturing.
1.1 Versatile Functionality
Fusion 360 combines various functionalities into a single platform:
- 3D Modeling: Create and edit 3D models using parametric, direct, freeform, and mesh modeling techniques.
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design): Design and document products with precision.
- CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): Prepare designs for manufacturing using CNC machining, 3D printing, and other fabrication methods.
- CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering): Simulate and analyze designs to ensure they meet performance requirements.
- PCB Design: Design and manufacture printed circuit boards.
1.2 Broad Applications Across Industries
Fusion 360 is applied in various industries due to its comprehensive capabilities:
- Mechanical Engineering: Designing mechanical components, assemblies, and machines.
- Product Design: Developing consumer products from concept to manufacturing.
- Aerospace: Creating and simulating aerospace components.
- Automotive: Designing automotive parts and systems.
- Manufacturing: Optimizing manufacturing processes using CAM tools.
- Electronics: Designing and manufacturing PCBs.
1.3 Career and Project Opportunities
Learning Fusion 360 opens doors to numerous opportunities:
- Job Roles: Mechanical Engineer, Product Designer, CAD Technician, CAM Programmer, and more.
- Freelancing: Offering 3D modeling, design, and manufacturing services.
- Personal Projects: Designing and building your own products, prototypes, and custom parts.
1.4 Accessibility and Cost-Effectiveness
Fusion 360 offers several advantages in terms of accessibility and cost:
- Cloud-Based: Access your projects from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Free for Students and Hobbyists: Autodesk provides free licenses for educational and personal use.
- Affordable Subscription: Commercial licenses are available at a reasonable price compared to other professional CAD/CAM software.
1.5 Integration and Collaboration
Fusion 360 enhances collaboration and integration:
- Team Collaboration: Share designs and collaborate with team members in real-time.
- Data Management: Manage design data, versions, and revisions efficiently.
- Integration with Other Tools: Connect with other Autodesk products and third-party applications.
2. What Are the Core Skills Needed to Learn Fusion 360 Effectively?
To learn Fusion 360 effectively, focus on developing core skills across different domains, including basic CAD principles, 3D modeling techniques, CAM workflows, and simulation strategies. By mastering these areas, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of design and manufacturing challenges.
2.1 Basic CAD Principles
Understanding fundamental CAD principles is essential for using Fusion 360 effectively.
- Sketching:
- Create 2D sketches using lines, arcs, circles, and splines.
- Apply geometric constraints (e.g., horizontal, vertical, tangent) to define sketch shapes.
- Use dimensions to specify the size and position of sketch elements accurately.
- Best Practice: Start with simple sketches and gradually increase complexity as you gain confidence.
- Parametric Modeling:
- Understand how to create and modify 3D models using parameters.
- Define relationships between model features using parameters and formulas.
- Modify parameters to update the entire model automatically.
- According to a study by the University of California, parametric modeling can reduce design iteration time by up to 40%.
- Coordinate Systems:
- Work with different coordinate systems (e.g., world, local) to position and orient objects in 3D space.
- Create and manipulate user coordinate systems (UCS) for specific modeling tasks.
- Best Practice: Use coordinate systems to align sketches and features with existing geometry.
2.2 3D Modeling Techniques
Mastering various 3D modeling techniques will allow you to create complex and detailed designs in Fusion 360.
- Extrusion:
- Create 3D shapes by extruding 2D sketches along a path.
- Use different extrusion options (e.g., distance, to object, symmetric) to achieve desired results.
- Best Practice: Use extrusions to create the primary shapes of your model.
- Revolving:
- Generate 3D shapes by revolving a 2D sketch around an axis.
- Create axisymmetric parts (e.g., shafts, cones) efficiently.
- According to Autodesk, revolving is one of the most efficient methods for creating axisymmetric parts.
- Sweeping:
- Create 3D shapes by sweeping a 2D sketch along a 3D path.
- Design complex curves and surfaces for aesthetic or functional purposes.
- Best Practice: Use sweeps to create tubes, pipes, and complex curved shapes.
- Lofting:
- Create 3D shapes by blending multiple 2D sketches together.
- Design complex surfaces with smooth transitions between different profiles.
- According to research from MIT, lofting is essential for creating aerodynamic shapes and complex organic forms.
- Filleting and Chamfering:
- Round sharp edges with fillets to improve aesthetics and reduce stress concentrations.
- Create angled edges with chamfers for better fit and finish.
- Best Practice: Use fillets and chamfers to enhance the manufacturability and durability of your designs.
2.3 CAM Workflows
Understanding CAM workflows is critical for preparing your designs for manufacturing.
- Toolpath Generation:
- Generate toolpaths for CNC machining operations (e.g., milling, turning).
- Select appropriate cutting tools and define cutting parameters (e.g., speed, feed).
- According to a study by the University of Tokyo, optimized toolpaths can reduce machining time by up to 25%.
- Simulation:
- Simulate machining operations to identify potential problems (e.g., collisions, tool wear).
- Verify toolpaths and optimize cutting parameters for efficient and safe machining.
- Best Practice: Always simulate toolpaths before running them on a CNC machine.
- Post-Processing:
- Generate machine-specific code (G-code) from toolpaths.
- Customize post-processors to match the requirements of your CNC machine.
- According to CNC Cookbook, using the correct post-processor is crucial for accurate and reliable machining.
2.4 Simulation Strategies
Using simulation strategies is important for validating your designs and ensuring they meet performance requirements.
- Stress Analysis:
- Perform static stress analysis to evaluate the structural integrity of your designs.
- Identify areas of high stress concentration and optimize the design to improve strength.
- According to research from Stanford University, stress analysis can help prevent failures and reduce material usage.
- Thermal Analysis:
- Analyze the thermal behavior of your designs to ensure they can withstand operating temperatures.
- Optimize heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Best Practice: Use thermal analysis for electronic components and systems that generate heat.
- Motion Simulation:
- Simulate the motion of mechanical assemblies to verify their functionality.
- Identify potential kinematic problems and optimize the design for smooth and reliable operation.
- According to Autodesk, motion simulation can help designers understand how their products will behave in real-world conditions.
3. What are the Best Online Resources to Learn Fusion 360?
3.1 Official Autodesk Resources
Autodesk provides a wealth of resources to help you learn Fusion 360.
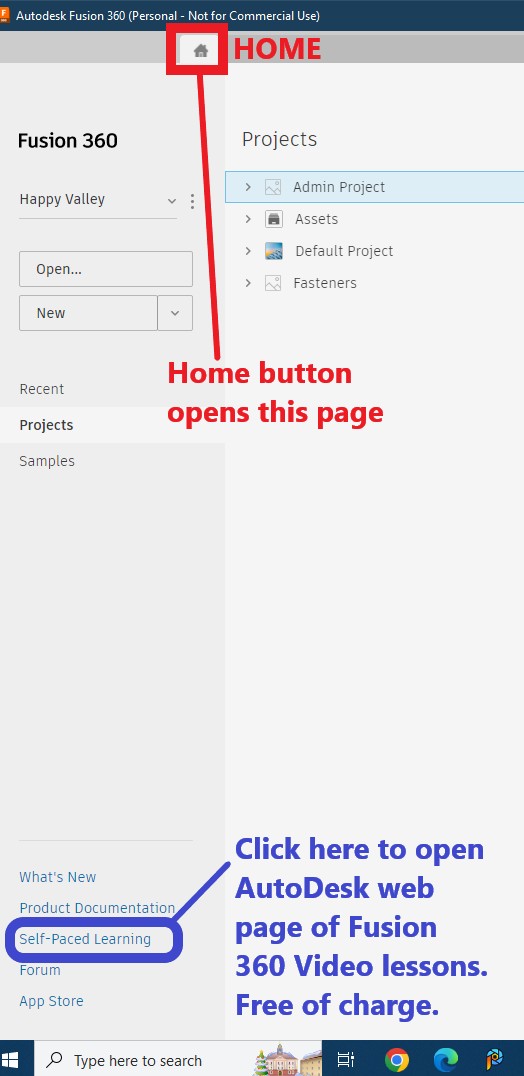
- Autodesk Knowledge Network: This is a comprehensive resource that includes tutorials, documentation, and troubleshooting guides. It’s an excellent starting point for understanding the basics and more advanced features of Fusion 360.
- Fusion 360 Learning: Autodesk offers a dedicated learning section with structured courses, video tutorials, and hands-on exercises. This platform is designed to guide you from beginner to expert.
- Autodesk Forums: The Autodesk community forums are a great place to ask questions, share your work, and get feedback from other users. Active participation can significantly enhance your learning experience.
3.2 YouTube Channels
YouTube is a treasure trove of Fusion 360 tutorials. Here are some of the best channels to follow:
- Lars Christensen: Lars Christensen offers practical, step-by-step tutorials on a wide range of Fusion 360 topics. His clear and concise explanations make complex concepts easy to understand.
- Product Design Online: This channel provides tutorials focused on product design using Fusion 360. You’ll find videos on sketching, modeling, assembly, and rendering.
- Kevin Kennedy: Kevin Kennedy’s channel offers quick tips and tricks for Fusion 360. His tutorials are perfect for learning specific techniques and shortcuts.
- NYCCNC: This channel focuses on CAM and CNC machining with Fusion 360. You’ll learn how to generate toolpaths, simulate machining operations, and optimize your designs for manufacturing.
3.3 Online Learning Platforms
Several online learning platforms offer Fusion 360 courses:
- Coursera: Coursera provides courses from top universities and institutions, offering structured learning paths with certificates upon completion.
- Udemy: Udemy has a vast library of Fusion 360 courses taught by industry experts. You can find courses for all skill levels and interests.
- Skillshare: Skillshare offers project-based classes that allow you to learn Fusion 360 while working on real-world projects.
- LinkedIn Learning: LinkedIn Learning provides courses focused on professional development, including Fusion 360. You can earn certifications and showcase your skills on your LinkedIn profile.
3.4 Community Forums and Groups
Engaging with the Fusion 360 community can provide valuable support and learning opportunities:
- Autodesk Forums: As mentioned earlier, the official Autodesk forums are a great place to connect with other users and experts.
- Reddit: The r/Fusion360 subreddit is an active community where you can ask questions, share your work, and get feedback.
- Facebook Groups: There are numerous Facebook groups dedicated to Fusion 360, where you can connect with other users and participate in discussions.
3.5 Blogs and Websites
Several blogs and websites offer tutorials, tips, and resources for Fusion 360:
- CADCAMStuff: This blog provides in-depth articles and tutorials on Fusion 360, covering a wide range of topics from basic modeling to advanced CAM techniques.
- Desktop Makes: This website offers tutorials and project ideas for Fusion 360, focusing on practical applications and real-world examples.
- The Fusion 360 Blog: Autodesk’s official blog provides updates, news, and tutorials on Fusion 360. It’s a great place to stay informed about the latest features and developments.
4. What Are Step-by-Step Instructions for Learning Fusion 360?
4.1 Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with the Interface
- Objective: To become comfortable with the layout and navigation of Fusion 360.
- Instructions:
- Download and Install: Download Fusion 360 from the Autodesk website and install it on your computer. Ensure your system meets the minimum requirements.
- Explore the Interface: Launch Fusion 360 and take a tour of the interface. Identify the main components, such as the ribbon, browser, timeline, and canvas.
- Customize Settings: Customize the settings to suit your preferences. Adjust the units, navigation controls, and display settings.
- Best Practice: Spend at least 1-2 hours exploring the interface and customizing the settings before moving on to the next step.
4.2 Step 2: Learn Basic Sketching Techniques
- Objective: To master the fundamentals of 2D sketching in Fusion 360.
- Instructions:
- Create a New Sketch: Start a new design and create a sketch on one of the default planes (XY, YZ, or ZX).
- Draw Basic Shapes: Use the line, circle, rectangle, and arc tools to draw basic shapes.
- Apply Constraints: Apply geometric constraints (e.g., horizontal, vertical, tangent) to define the shapes.
- Add Dimensions: Use the dimension tool to specify the size and position of the sketch elements accurately.
- Practice Exercises: Complete a series of sketching exercises to reinforce your skills. Try recreating simple 2D shapes from reference images.
- Resources: Watch tutorials on YouTube channels like Lars Christensen or Product Design Online.
- Best Practice: Practice sketching for at least 2-3 hours per week to develop proficiency.
4.3 Step 3: Master 3D Modeling Techniques
- Objective: To learn how to create 3D models from 2D sketches using various modeling techniques.
- Instructions:
- Extrude: Use the extrude tool to create 3D shapes from 2D sketches. Experiment with different extrusion options (e.g., distance, to object, symmetric).
- Revolve: Use the revolve tool to create axisymmetric parts by revolving a 2D sketch around an axis.
- Sweep: Use the sweep tool to create 3D shapes by sweeping a 2D sketch along a 3D path.
- Loft: Use the loft tool to create complex surfaces by blending multiple 2D sketches together.
- Fillet and Chamfer: Use the fillet and chamfer tools to round sharp edges and create angled edges.
- Practice Exercises: Complete a series of modeling exercises to reinforce your skills. Try creating simple 3D models from reference images.
- Resources: Watch tutorials on YouTube channels like Kevin Kennedy or NYCCNC.
- Best Practice: Practice modeling for at least 3-4 hours per week to develop proficiency.
4.4 Step 4: Explore Assembly Modeling
- Objective: To learn how to create and manage assemblies of multiple components in Fusion 360.
- Instructions:
- Create Components: Create individual components for each part of the assembly.
- Insert Components: Insert the components into a new assembly design.
- Apply Joints: Apply joints to define the relationships between the components. Use rigid joints for fixed connections and revolute joints for rotating connections.
- Analyze Motion: Use the motion study tool to simulate the motion of the assembly and identify potential problems.
- Practice Exercises: Complete a series of assembly exercises to reinforce your skills. Try creating simple assemblies from reference images.
- Resources: Refer to the Autodesk Knowledge Network or online learning platforms like Coursera and Udemy.
- Best Practice: Practice assembly modeling for at least 2-3 hours per week to develop proficiency.
4.5 Step 5: Dive into CAM and Manufacturing
- Objective: To learn how to prepare your designs for manufacturing using Fusion 360’s CAM tools.
- Instructions:
- Create a Setup: Create a new setup in the CAM workspace and define the stock material, coordinate system, and machine.
- Generate Toolpaths: Generate toolpaths for milling, turning, and other machining operations.
- Simulate Machining: Simulate the machining operations to identify potential problems and optimize the toolpaths.
- Post-Process: Post-process the toolpaths to generate machine-specific code (G-code).
- Practice Exercises: Complete a series of CAM exercises to reinforce your skills. Try creating toolpaths for simple parts and simulating the machining operations.
- Resources: Watch tutorials on YouTube channels like NYCCNC or refer to the Autodesk CAM documentation.
- Best Practice: Practice CAM and manufacturing for at least 2-3 hours per week to develop proficiency.
4.6 Step 6: Practice with Real-World Projects
- Objective: To apply your Fusion 360 skills to real-world projects and build a portfolio.
- Instructions:
- Choose a Project: Select a project that interests you and aligns with your skill level.
- Design the Project: Design the project in Fusion 360, using the skills you have learned in the previous steps.
- Manufacture the Project: Manufacture the project using CNC machining, 3D printing, or other fabrication methods.
- Document the Project: Document the project, including the design process, manufacturing steps, and final results.
- Share the Project: Share the project with the Fusion 360 community and get feedback from other users.
- Resources: Look for project ideas on websites like Instructables or Thingiverse.
- Best Practice: Work on at least one real-world project per month to continuously improve your skills and build your portfolio.
5. What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Learning Fusion 360?
5.1 Neglecting Basic CAD Principles
- Mistake: Jumping straight into complex modeling without understanding basic CAD principles like sketching, constraints, and dimensions.
- Impact: Difficulty creating accurate and parametric models, leading to rework and frustration.
- Solution: Spend time mastering the fundamentals of sketching and parametric modeling before attempting more advanced techniques.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Ensure a solid foundation in sketching before advancing to 3D modeling. Our beginner courses emphasize these core principles.”
5.2 Ignoring Constraints and Dimensions
- Mistake: Creating sketches without fully defining them using constraints and dimensions.
- Impact: Models that are difficult to modify and update, as changes can lead to unpredictable results.
- Solution: Always fully constrain and dimension your sketches to create robust and parametric models.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Fully constrained sketches are the backbone of parametric modeling. Practice using geometric and dimensional constraints in every sketch.”
5.3 Overcomplicating Designs
- Mistake: Creating overly complex designs with unnecessary details and features.
- Impact: Models that are difficult to manage, slow to update, and prone to errors.
- Solution: Simplify your designs by breaking them down into smaller, manageable components. Focus on the essential features and avoid unnecessary complexity.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Start with a simple design and gradually add complexity as needed. This approach will help you create more efficient and manageable models.”
5.4 Skipping Simulation and Analysis
- Mistake: Neglecting to simulate and analyze your designs before manufacturing them.
- Impact: Potential design flaws that can lead to costly mistakes and rework.
- Solution: Always simulate and analyze your designs to identify potential problems and optimize their performance.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Simulation is a critical step in the design process. Our advanced courses cover stress, thermal, and motion simulation techniques.”
5.5 Not Utilizing Available Resources
- Mistake: Trying to learn Fusion 360 in isolation without utilizing available resources like tutorials, forums, and documentation.
- Impact: Slower progress and increased frustration due to a lack of support and guidance.
- Solution: Take advantage of the wealth of resources available online, including tutorials, forums, and documentation.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Our platform offers a comprehensive learning ecosystem with tutorials, forums, and expert support. Don’t hesitate to reach out for help.”
5.6 Not Practicing Regularly
- Mistake: Not practicing Fusion 360 regularly, leading to a loss of skills and knowledge.
- Impact: Difficulty retaining what you have learned and applying it to real-world projects.
- Solution: Practice Fusion 360 regularly, even if it’s just for a few hours per week. Work on personal projects or complete practice exercises to reinforce your skills.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Consistent practice is key to mastering Fusion 360. Set aside dedicated time each week to work on your skills.”
5.7 Ignoring Best Practices
- Mistake: Ignoring best practices for modeling, assembly, and manufacturing.
- Impact: Inefficient workflows, poor design quality, and increased risk of errors.
- Solution: Follow best practices for modeling, assembly, and manufacturing to ensure efficient workflows and high-quality designs.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Our courses cover industry best practices for Fusion 360, helping you create efficient and reliable designs.”
5.8 Not Seeking Feedback
- Mistake: Not seeking feedback from other users or experts on your designs.
- Impact: Missing opportunities to improve your skills and learn from others.
- Solution: Share your designs with the Fusion 360 community and ask for feedback. Be open to criticism and use it as an opportunity to learn and grow.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Tip: “Our forums provide a platform for sharing your work and receiving feedback from experienced users and instructors.”
6. How Can You Customize Your Learning Path for Fusion 360?
Customizing your learning path for Fusion 360 involves aligning your study plan with your specific goals, industry needs, and learning preferences. By doing so, you can focus on the most relevant skills and knowledge, making your learning experience more efficient and effective.
6.1 Define Your Learning Goals
- Identify Your Objectives:
- Personal Projects: Are you learning Fusion 360 to design and build personal projects, such as custom parts, home improvements, or hobby projects?
- Career Advancement: Do you aim to use Fusion 360 to enhance your career prospects in fields like mechanical engineering, product design, or manufacturing?
- Professional Development: Are you looking to add Fusion 360 to your skill set for professional development or to meet specific job requirements?
- Set Specific Goals:
- Basic Proficiency: Aim to master basic sketching, modeling, and assembly techniques within a specific timeframe (e.g., 3 months).
- Advanced Skills: Focus on advanced topics like CAM, simulation, or PCB design after achieving basic proficiency.
- Project-Based Learning: Define specific projects you want to complete to apply your skills and build a portfolio.
6.2 Assess Your Current Skill Level
- Self-Assessment:
- Beginner: No prior experience with CAD or 3D modeling software.
- Intermediate: Basic understanding of CAD concepts and some experience with 3D modeling.
- Advanced: Proficient in CAD and 3D modeling with experience in specific areas like CAM or simulation.
- Online Quizzes and Tutorials:
- Use online quizzes and tutorials to assess your current knowledge and identify areas for improvement.
- Many platforms offer diagnostic tests to evaluate your skill level and recommend suitable learning paths.
6.3 Choose Relevant Learning Resources
- Targeted Courses:
- Beginner Courses: Focus on introductory courses that cover the fundamentals of Fusion 360, such as sketching, modeling, and assembly.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Recommendation: Our beginner courses provide a structured learning path to master the basics of Fusion 360.
- Advanced Courses: Select courses that delve into specific topics like CAM, simulation, PCB design, or advanced modeling techniques.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Recommendation: Explore our advanced courses for in-depth knowledge and practical skills in specialized areas.
- Beginner Courses: Focus on introductory courses that cover the fundamentals of Fusion 360, such as sketching, modeling, and assembly.
- Industry-Specific Tutorials:
- Mechanical Engineering: Focus on tutorials covering mechanical component design, stress analysis, and motion simulation.
- Product Design: Choose tutorials that emphasize product aesthetics, ergonomics, and manufacturability.
- Manufacturing: Select tutorials on CAM workflows, toolpath generation, and CNC machining techniques.
6.4 Create a Structured Learning Plan
- Weekly Schedule:
- Allocate specific days and times each week to focus on learning Fusion 360.
- Aim for at least 5-10 hours per week, depending on your goals and availability.
- Topic-Based Modules:
- Break down your learning into topic-based modules (e.g., sketching, modeling, assembly, CAM, simulation).
- Set milestones for completing each module and track your progress.
- Project-Based Assignments:
- Incorporate project-based assignments into your learning plan to apply your skills and build a portfolio.
- Choose projects that align with your interests and goals, such as designing a custom part, creating a mechanical assembly, or simulating a product’s performance.
6.5 Tailor Your Learning Methods
- Visual Learners:
- Focus on video tutorials, demonstrations, and visual aids.
- Utilize screen recording software to review and practice techniques.
- Hands-On Learners:
- Emphasize hands-on exercises, practice projects, and real-world applications.
- Download sample models and experiment with different modeling techniques.
- Auditory Learners:
- Listen to podcasts, webinars, and online lectures on Fusion 360.
- Record notes and explanations to reinforce your understanding.
6.6 Seek Mentorship and Feedback
- Connect with Experts:
- Seek out mentors or experienced Fusion 360 users who can provide guidance and feedback.
- Join online communities, forums, or local user groups to connect with experts.
- Share Your Work:
- Share your designs and projects with the Fusion 360 community and ask for feedback.
- Participate in design challenges or contests to showcase your skills and get recognized.
6.7 Stay Updated with New Features
- Follow Autodesk Updates:
- Stay informed about the latest features, updates, and improvements in Fusion 360.
- Subscribe to the Autodesk blog, newsletter, or social media channels.
- Explore New Tools:
- Experiment with new tools and techniques as they are introduced in Fusion 360.
- Complete tutorials and practice exercises to learn how to use them effectively.
By customizing your learning path, you can focus on the most relevant skills and knowledge, making your learning experience more efficient and effective.
7. How Can You Practice and Improve Your Fusion 360 Skills Regularly?
To continuously improve your Fusion 360 skills, incorporate regular practice, diverse projects, and community engagement into your routine. Consistent effort and a commitment to learning will help you master the software and stay ahead in your field.
7.1 Daily or Weekly Practice
- Consistent Engagement:
- Daily Practice: Dedicate at least 30 minutes to an hour each day for focused practice.
- Weekly Practice: If daily practice is challenging, aim for 2-3 sessions per week, each lasting 2-3 hours.
- Structured Exercises:
- Tutorial-Based Exercises: Follow online tutorials and replicate the designs to reinforce your understanding of specific tools and techniques.
- Challenge Exercises: Seek out design challenges or prompts online to test your skills and creativity.
- Resource Recommendation:
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Practice Modules: Utilize our practice modules designed to progressively build your Fusion 360 skills.
7.2 Work on Diverse Projects
- Varied Complexity:
- Simple Projects: Start with simple projects to master basic skills before moving on to more complex designs.
- Complex Projects: Undertake complex projects to challenge yourself and apply a wide range of Fusion 360 features.
- Project Variety:
- Mechanical Parts: Design mechanical components like gears, brackets, and housings.
- Consumer Products: Create consumer product designs such as phone cases, desk organizers, or small appliances.
- Artistic Designs: Explore artistic designs and sculptures to push your creative boundaries.
- Project Sources:
- Personal Interests: Align projects with your personal interests to stay motivated and engaged.
- Real-World Problems: Look for real-world problems you can solve with your Fusion 360 skills.
- Platform Recommendations:
- Thingiverse and GrabCAD: Find inspiration and project ideas on these platforms.
7.3 Participate in Design Challenges and Contests
- Motivation and Skill Enhancement:
- Design Challenges: Participate in online design challenges to improve your skills and compete with other designers.
- Design Contests: Enter design contests to showcase your talents and win prizes.
- Feedback and Recognition:
- Peer Feedback: Receive feedback from other participants and industry experts.
- Industry Recognition: Gain recognition for your work and build your professional reputation.
- Platform Recommendation:
- GrabCAD Challenges: Regularly check GrabCAD for design challenges.
7.4 Engage with the Fusion 360 Community
- Online Forums:
- Active Participation: Participate in online forums to ask questions, share your work, and provide feedback to others.
- Community Learning: Learn from the experiences and insights of other Fusion 360 users.
- Social Media Groups:
- Networking: Join social media groups to connect with other designers and stay updated on the latest trends.
- Resource Sharing: Share resources, tips, and tricks with the community.
- Platform Recommendations:
- Autodesk Forums and Reddit: Engage in discussions on these platforms.
7.5 Teach Others
- Knowledge Reinforcement:
- Tutoring: Teach Fusion 360 to beginners to reinforce your own understanding of the fundamentals.
- Content Creation: Create tutorials, blog posts, or videos to share your knowledge and help others learn.
- Deeper Understanding:
- Explanatory Skills: Explaining concepts to others will deepen your understanding and identify areas where you need to improve.
- Platform Recommendation:
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Instructor Opportunities: Consider becoming an instructor on our platform to share your expertise.
7.6 Seek Mentorship and Collaboration
- Guidance and Feedback:
- Mentorship: Seek guidance from experienced Fusion 360 users or industry professionals.
- Feedback: Receive constructive feedback on your designs to identify areas for improvement.
- Collaborative Projects:
- Teamwork: Collaborate with other designers on projects to learn new skills and share your expertise.
- Diverse Perspectives: Gain insights from diverse perspectives and approaches.
7.7 Utilize Free Resources and Tools
- Autodesk Resources:
- Official Tutorials: Use Autodesk’s official tutorials and documentation to learn the software.
- Knowledge Base: Take advantage of the Autodesk Knowledge Network for troubleshooting and problem-solving.
- Online Platforms:
- YouTube Channels: Watch YouTube tutorials from experts.
- Free Courses: Enroll in free online courses on platforms like Coursera and Udemy.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Free Resources:
- Access our free resources, including tutorials, guides, and templates.
By following these strategies, you can practice and improve your Fusion 360 skills regularly, ensuring continuous growth and mastery of the software.
8. What are the Key Differences Between Fusion 360 and Other CAD Software?
8.1 Pricing and Licensing
- Fusion 360: Offers a more accessible pricing model, including a free version for students, hobbyists, and startups, and affordable subscription options for commercial use.
- SolidWorks: Typically requires a significant upfront investment for the software license, along with annual maintenance fees.
- AutoCAD: Offers subscription-based pricing, but can be more expensive than Fusion 360 for comprehensive 3D modeling capabilities.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Insight: Fusion 360’s flexible pricing makes it an attractive option for a wide range of users, from students to professionals.
8.2 Cloud-Based vs. Desktop-Based
- Fusion 360: Primarily a cloud-based platform, allowing users to access their designs from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating collaboration and data management.
- SolidWorks: Predominantly a desktop-based application, requiring local installation and potentially limiting accessibility and collaboration without additional tools.
- AutoCAD: Primarily a desktop application, but offers cloud services for file sharing and collaboration.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Insight: Fusion 360’s cloud-based nature enhances accessibility and collaboration, making it ideal for distributed teams and remote work.
8.3 Integrated CAD/CAM/CAE
- Fusion 360: Provides a unified platform with integrated CAD, CAM, and CAE capabilities, streamlining the design-to-manufacturing workflow.
- SolidWorks: Requires separate modules or add-ins for CAM and CAE functionalities, potentially increasing costs and complexity.
- AutoCAD: Primarily focused on CAD, with limited CAM and CAE capabilities without additional software.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Insight: Fusion 360’s integrated environment simplifies the design process and promotes seamless collaboration between design and manufacturing teams.
8.4 Ease of Use and Learning Curve
- Fusion 360: Generally considered to have a more intuitive user interface and a shorter learning curve, especially for users new to CAD software.
- SolidWorks: Offers a robust set of features but can be more complex to learn and master, requiring significant training and experience.
- AutoCAD: Has a steeper learning curve, particularly for 3D modeling, due to its extensive command-line interface and specialized tools.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN Insight: Fusion 360’s user-friendly interface and comprehensive tutorials make it an excellent choice for beginners and experienced users alike.
8.5 Collaboration and Data Management
- Fusion 360: Offers built-in collaboration tools, including version control, shared design reviews, and real-time collaboration, enhancing teamwork and data management.
- SolidWorks: Requires additional tools like SolidWorks PDM (Product Data Management) for effective collaboration and data management.
- AutoCAD: Provides basic collaboration features through Autodesk A360, but may require additional software for comprehensive data management.
- learns.edu.vn Insight: Fusion 360’s integrated collaboration features facilitate seamless teamwork and efficient data management