Learning hiragana is the first step towards mastering Japanese. How Long To Learn Hiragana depends on your dedication and methods. This guide, brought to you by LEARNS.EDU.VN, breaks down the process into manageable steps to help you achieve fluency in reading hiragana quickly. By focusing on effective techniques, you can significantly reduce the time it takes to learn hiragana and start your Japanese language journey with confidence. Discover effective study strategies, mnemonic devices, and essential resources to conquer hiragana efficiently, unlocking a world of Japanese language skills and educational resources.
1. What is Hiragana and Why is it Important?
Hiragana is a foundational element of the Japanese writing system. It serves as a gateway to understanding and engaging with the language.
1.1. Understanding Hiragana
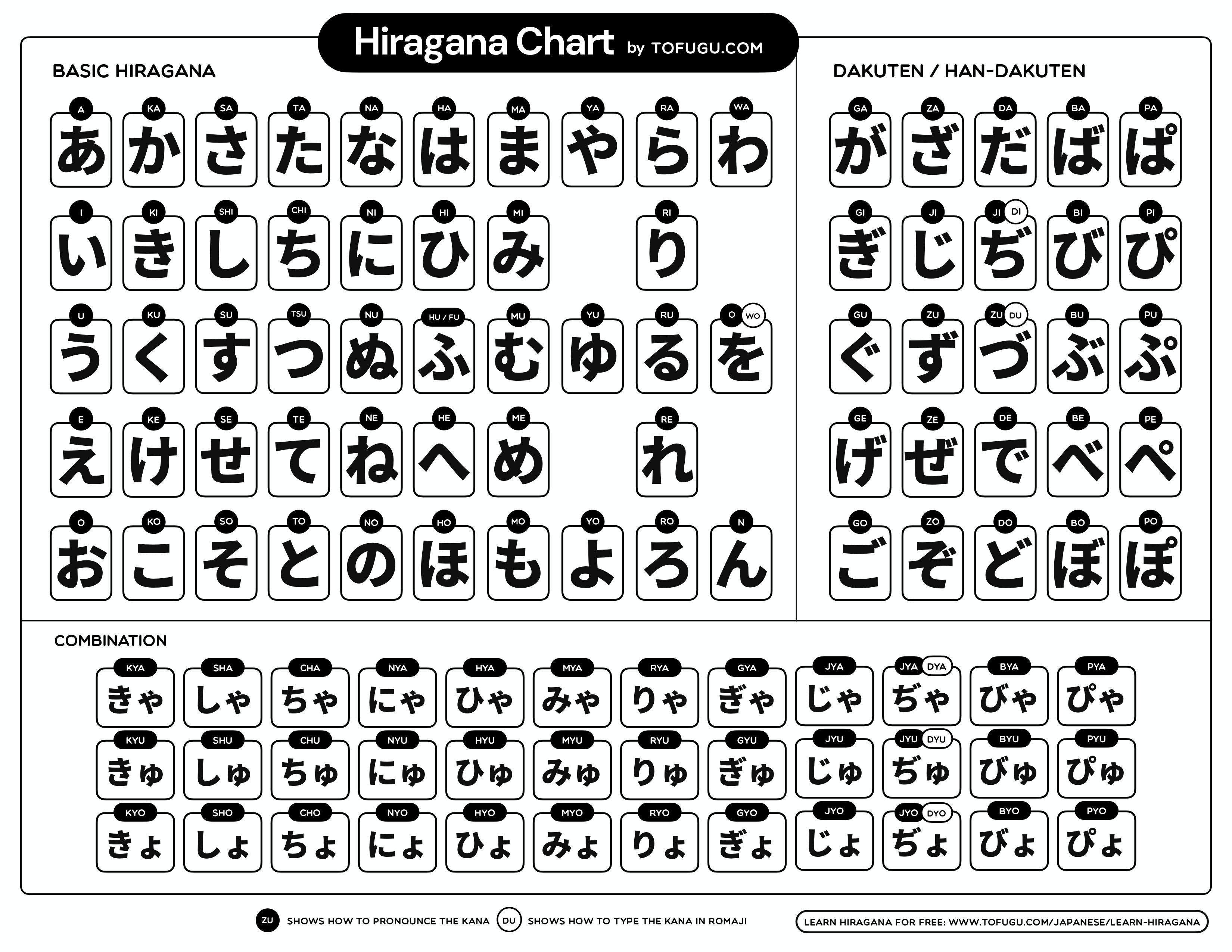
Hiragana (ひらがな) is a phonetic script, meaning each character represents a specific sound. Unlike alphabets where letters can have multiple pronunciations depending on the word, each hiragana character has a consistent sound. There are 46 basic hiragana characters, each representing a vowel, a consonant-vowel combination, or the consonant ‘n’.
1.2. The Significance of Hiragana in Learning Japanese
Learning hiragana is essential for several reasons:
- Foundation for Reading: Hiragana is used to write native Japanese words, particles, and verb endings. Without knowing hiragana, you cannot read basic Japanese sentences.
- Pronunciation: Hiragana teaches you the basic sounds of Japanese, which is crucial for speaking and understanding the language.
- Access to Learning Resources: Most Japanese textbooks and learning materials assume you know hiragana. Mastering it opens up a wide range of resources for further study.
- Introduction to Japanese Culture: Being able to read hiragana allows you to engage with Japanese media like manga, anime, and books, providing a deeper connection to the culture.
2. How Long Does It Realistically Take to Learn Hiragana?
The question of how long to learn hiragana varies from person to person. With focused effort and the right strategies, it’s achievable in a surprisingly short time.
2.1. Average Time Commitment
Most learners can learn to recognize all hiragana characters in one to two weeks with daily practice. Some dedicated learners may even achieve this in a few days. However, mastery—being able to read and recall characters quickly and accurately—may take a few more weeks of consistent use.
2.2. Factors Influencing Learning Time
- Time Dedicated to Study: Consistent, daily practice is more effective than sporadic, long sessions.
- Learning Methods Used: Effective methods like mnemonics and active recall can significantly speed up the learning process.
- Prior Language Learning Experience: If you’ve learned other phonetic scripts or languages before, you may find it easier to grasp hiragana.
- Personal Learning Style: Some learners prefer visual methods, while others learn better through auditory or kinesthetic approaches.
2.3. Dispelling Myths About Learning Speed
Some resources suggest that learning hiragana takes months. This is often due to inefficient methods or a lack of focused practice. While immersion and constant exposure are beneficial, they are not the only paths. Structured learning with targeted techniques can yield faster results.
3. Effective Methods to Learn Hiragana Quickly
To accelerate your hiragana learning journey, focus on proven methods that enhance memory and recall.
3.1. Mnemonics: Linking Characters to Memorable Images
Mnemonics involve associating each hiragana character with a memorable image or story. This technique leverages your brain’s natural ability to remember visuals and narratives.
- How Mnemonics Work: Create a mental image that connects the shape of the hiragana character to its pronunciation.
- Example: The character あ (a) can be associated with the image of an “A” inside the character.
- Benefits: Mnemonics make abstract symbols more concrete and easier to recall.
3.2. Spaced Repetition Systems (SRS)
SRS algorithms present you with characters at increasing intervals, focusing on those you struggle with.
- How SRS Works: Flashcard apps like Anki use SRS to optimize review times.
- Example: If you remember a character easily, you’ll see it less often. If you struggle, it will appear more frequently.
- Benefits: SRS ensures you focus on the characters that need the most attention, making your study time more efficient.
3.3. Active Recall and Testing
Active recall involves trying to remember a character without looking at it, strengthening the memory each time you succeed.
- How Active Recall Works: Use flashcards or online quizzes to test yourself regularly.
- Example: Look at the pronunciation “ka” and try to recall the corresponding hiragana character, か.
- Benefits: Active recall reinforces memory and improves retention compared to passive review.
3.4. Focus on Reading Over Writing Initially
While writing practice is important, prioritize reading hiragana first. This allows you to recognize characters quickly and build a strong foundation.
- Why Reading First?: Reading reinforces character recognition and pronunciation.
- Example: Read simple Japanese sentences or words written in hiragana.
- Benefits: Reading fluency will naturally lead to improved writing skills over time.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Learning Hiragana
Follow this structured approach to learn hiragana efficiently.
4.1. Week 1: Mastering the Basic Characters
Dedicate the first week to learning the 46 basic hiragana characters.
- Day 1-2: Learn the first five characters: あ (a), い (i), う (u), え (e), お (o). Use mnemonics and practice writing each character several times.
- Day 3-4: Learn the next set of characters: か (ka), き (ki), く (ku), け (ke), こ (ko). Review the previous characters and quiz yourself.
- Day 5-7: Continue learning new sets of characters, focusing on pronunciation and recognition. Use online resources like Tofugu’s Learn Hiragana guide for mnemonic images and audio.
4.2. Week 2: Reinforcement and Practice
Use the second week to reinforce your knowledge and improve recall speed.
- Daily Review: Spend 15-20 minutes each day reviewing all the hiragana characters you’ve learned.
- Flashcard Drills: Use flashcard apps like Anki to practice active recall and spaced repetition.
- Reading Practice: Read simple Japanese texts written in hiragana. Websites like NHK News Web Easy provide articles with furigana (hiragana readings) to help you.
- Writing Practice: If you haven’t started already, begin practicing writing the characters. Focus on stroke order to develop good handwriting habits.
4.3. Incorporating Resources from LEARNS.EDU.VN
Utilize the resources available on LEARNS.EDU.VN to supplement your learning.
- Hiragana Charts: Download and print our comprehensive hiragana charts for quick reference.
- Mnemonic Guides: Access our mnemonic guides for visual aids and memory prompts.
- Quizzes and Exercises: Test your knowledge with our interactive quizzes and exercises.
- Community Forum: Join our community forum to connect with other learners and share tips and resources.
5. Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Learning Hiragana
Be aware of these common mistakes to ensure efficient learning.
5.1. Neglecting Pronunciation
Accurate pronunciation is key to effective communication in Japanese.
- Pitfall: Ignoring the correct pronunciation of each character.
- Solution: Use audio resources to practice pronunciation. Record yourself and compare it to native speakers.
5.2. Passive Learning
Passive review, such as simply reading through charts, is less effective than active recall.
- Pitfall: Relying on passive review methods.
- Solution: Use flashcards, quizzes, and active recall exercises to reinforce memory.
5.3. Inconsistent Practice
Sporadic study sessions are less effective than consistent daily practice.
- Pitfall: Studying inconsistently.
- Solution: Set a daily study schedule and stick to it. Even 15-20 minutes of focused practice each day can make a significant difference.
5.4. Focusing Too Much on Perfection Early On
Trying to achieve perfect handwriting or instant recall can lead to frustration.
- Pitfall: Aiming for perfection from the start.
- Solution: Focus on progress, not perfection. Celebrate small victories and keep practicing.
6. Enhancing Your Learning Experience with Technology
Leverage digital tools and apps to make your hiragana learning journey more engaging and effective.
6.1. Top Apps for Hiragana Learning
- Anki: A powerful flashcard app with spaced repetition algorithms. Create your own hiragana flashcards or download pre-made decks.
- Memrise: Offers gamified lessons and mnemonic devices to help you memorize hiragana.
- TenguGo Kana: A dedicated app for learning hiragana and katakana with quizzes and writing practice.
- Dr. Moku’s Hiragana & Katakana: Uses memorable associations and visual aids to help you learn the characters quickly.
6.2. Online Resources and Websites
- Tofugu’s Learn Hiragana Guide: A comprehensive guide with mnemonic images, audio, and exercises.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Provides hiragana charts, mnemonic guides, quizzes, and a community forum.
- NHK News Web Easy: Offers simple Japanese articles with furigana for reading practice.
- JapanesePod101: Provides audio and video lessons, including hiragana tutorials.
6.3. Creating a Digital Learning Environment
- Organize Resources: Bookmark useful websites and save important documents in a dedicated folder.
- Set Reminders: Use calendar apps to schedule daily study sessions and review reminders.
- Join Online Communities: Participate in online forums and social media groups to connect with other learners and share resources.
- Use a Language Learning Browser Extension: Consider using browser extensions like Rikaikun or Yomichan to quickly look up hiragana readings on any website.
7. Integrating Hiragana into Daily Life
Immerse yourself in the language by incorporating hiragana into your daily routine.
7.1. Labeling Everyday Objects
- Technique: Write the hiragana names of everyday objects and stick them to the corresponding items.
- Example: Label your desk, chair, door, and window with their Japanese names in hiragana.
- Benefits: This helps you associate the characters with real-world objects, reinforcing memory.
7.2. Reading Simple Japanese Content
- Technique: Start with simple Japanese content written in hiragana, such as children’s books or song lyrics.
- Example: Read “Momotaro” (Peach Boy) or “Urashima Taro” (Urashima Taro) in hiragana.
- Benefits: Reading reinforces character recognition and pronunciation in context.
7.3. Using Hiragana in Social Media and Messaging
- Technique: Use hiragana when communicating with Japanese-speaking friends or in online forums.
- Example: Write simple greetings or comments in hiragana.
- Benefits: This provides practical application of your knowledge and helps you become more comfortable with the characters.
7.4. Listening to Japanese Music and Podcasts
- Technique: Listen to Japanese music and podcasts and try to follow along with the lyrics or transcripts.
- Example: Listen to J-pop or Japanese language learning podcasts.
- Benefits: This improves your listening comprehension and helps you associate hiragana with their corresponding sounds.
8. Understanding Dakuten, Handakuten, and Combination Hiragana
Beyond the basic characters, mastering dakuten, handakuten, and combination hiragana is crucial for comprehensive literacy.
8.1. Dakuten and Handakuten: Modifying Sounds
- Dakuten (゛): This symbol modifies certain hiragana to create voiced sounds.
- Example: か (ka) becomes が (ga).
- Handakuten (゜): This symbol turns H sounds into P sounds.
- Example: は (ha) becomes ぱ (pa).
8.2. Combination Hiragana: Expanding Pronunciation
Combination hiragana involves combining a character from the い-row with a small や, ゆ, or よ to create new sounds.
- Example: き (ki) + ゃ (small ya) = きゃ (kya).
- These combinations expand the range of sounds you can express in Japanese.
8.3. Practice and Application
- Use flashcards and quizzes to practice recognizing and pronouncing dakuten, handakuten, and combination hiragana.
- Read Japanese texts and identify these modified characters in context.
- Practice writing these characters to reinforce your knowledge.
9. Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Learning hiragana can be challenging, but staying motivated is key to success.
9.1. Setting Realistic Goals
- Technique: Set small, achievable goals to maintain momentum.
- Example: Aim to learn five new characters each day or read one simple Japanese article each week.
- Benefits: Realistic goals make the learning process less overwhelming and provide a sense of accomplishment.
9.2. Rewarding Progress
- Technique: Celebrate your progress with small rewards.
- Example: Treat yourself to a favorite snack after completing a study session or watch an episode of your favorite anime after mastering a set of characters.
- Benefits: Rewards reinforce positive habits and make learning more enjoyable.
9.3. Finding a Study Buddy or Language Partner
- Technique: Connect with other learners for mutual support and encouragement.
- Example: Join a language exchange group or find a study buddy online.
- Benefits: Studying with others provides motivation, accountability, and opportunities for practice.
9.4. Varying Study Methods
- Technique: Avoid monotony by incorporating a variety of study methods.
- Example: Alternate between flashcards, reading practice, writing exercises, and audio lessons.
- Benefits: Varying study methods keeps the learning process engaging and prevents burnout.
10. What to Do After Learning Hiragana
Once you’ve mastered hiragana, you’re ready to take the next steps in your Japanese language journey.
10.1. Learning Katakana
Katakana is another phonetic script used for foreign loanwords and emphasis. Learning katakana is essential for reading a wide range of Japanese texts.
10.2. Studying Basic Grammar
Understanding basic grammar concepts is crucial for forming sentences and expressing your thoughts in Japanese.
10.3. Building Vocabulary
Expanding your vocabulary allows you to understand and communicate more effectively in Japanese.
10.4. Practicing Reading and Listening Comprehension
Reading and listening to Japanese content helps you reinforce your knowledge and improve your overall language skills.
10.5. Exploring Kanji
Kanji are Chinese characters used in Japanese writing. While kanji can seem daunting, learning them is essential for advanced literacy.
Mastering hiragana is a significant achievement that opens doors to a world of Japanese language and culture. With consistent effort, effective methods, and the resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can achieve fluency in reading hiragana and embark on a rewarding language learning journey.
Why wait? Start your journey to mastering Hiragana today with LEARNS.EDU.VN. Explore our comprehensive resources, including detailed guides, interactive quizzes, and a supportive community to help you achieve your language learning goals faster and more efficiently. Visit our website at LEARNS.EDU.VN and unlock a world of educational opportunities. For personalized support, contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Learning Hiragana
1. How long does it really take to learn hiragana?
With consistent daily practice using effective methods like mnemonics and spaced repetition, most learners can learn to recognize all hiragana characters in one to two weeks. Mastery, including quick and accurate recall, may take a few more weeks.
2. Is it necessary to learn to write hiragana, or is reading enough?
While reading is a great starting point and can be prioritized initially, learning to write hiragana is also important. Writing helps reinforce character recognition and improves overall retention.
3. What is the best method for memorizing hiragana characters?
Mnemonics, which associate each character with a memorable image or story, are highly effective. Spaced repetition systems (SRS) like Anki can also significantly improve retention by optimizing review times.
4. Should I learn katakana at the same time as hiragana?
It’s generally recommended to focus on mastering hiragana first before moving on to katakana. Once you have a solid understanding of hiragana, learning katakana will be much easier.
5. Are there any common mistakes to avoid when learning hiragana?
Yes, common mistakes include neglecting pronunciation, relying on passive learning methods, practicing inconsistently, and aiming for perfection too early on.
6. What should I do after learning hiragana?
After mastering hiragana, you can move on to learning katakana, studying basic grammar, building vocabulary, practicing reading and listening comprehension, and exploring kanji.
7. How can I stay motivated while learning hiragana?
Set realistic goals, reward your progress, find a study buddy or language partner, and vary your study methods to avoid monotony.
8. What are dakuten and handakuten?
Dakuten (゛) and handakuten (゜) are symbols that modify the sounds of certain hiragana characters. Dakuten creates voiced sounds, while handakuten turns H sounds into P sounds.
9. What are combination hiragana?
Combination hiragana involves combining a character from the い-row with a small や, ゆ, or よ to create new sounds, expanding the range of pronunciation.
10. Where can I find resources to help me learn hiragana?
learns.edu.vn offers comprehensive resources, including detailed guides, interactive quizzes, and a supportive community. Other useful resources include Tofugu’s Learn Hiragana guide, Anki, Memrise, and JapanesePod101.