Learning about cars and engines might seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be an exciting and rewarding experience. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide a structured path to understanding automotive technology, helping you go from novice to knowledgeable enthusiast. This guide will explore essential concepts, practical learning methods, and valuable resources to kickstart your automotive education.
1. What Are The Best Ways To Start Learning About Cars And Engines?
Start learning about cars and engines by exploring introductory resources like online courses, books, and automotive communities to build a solid foundation.Begin your journey by engaging with various learning platforms and resources.
1.1 Foundational Resources
Kickstart your journey with foundational resources to grasp the basics of automotive technology:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy offer introductory courses on automotive engineering and mechanics.
- Books: “How Cars Work” by Tom Newton is an excellent resource for beginners. It breaks down complex concepts into easy-to-understand language.
- Automotive Communities: Join online forums and local car clubs to connect with experienced enthusiasts who can share their knowledge and experiences.
1.2 Understanding Core Concepts
Focus on understanding the core concepts that underpin automotive technology:
- Internal Combustion Engine: Learn about the four-stroke cycle (intake, compression, combustion, exhaust) and the function of each component.
- Vehicle Systems: Familiarize yourself with the main systems of a car, including the engine, transmission, braking, suspension, and electrical systems.
- Basic Terminology: Master common automotive terms and jargon to effectively communicate and learn.
1.3 Practical Engagement
Engage in practical activities to reinforce your learning and gain hands-on experience:
- Car Maintenance: Start with simple tasks like checking fluid levels, changing a tire, or replacing air filters.
- Online Tutorials: Watch YouTube videos and follow step-by-step guides for basic repairs and maintenance.
- Hands-On Projects: Consider working on a project car or volunteering at a local garage to gain real-world experience.
2. What Are The Essential Components Of A Car Engine?
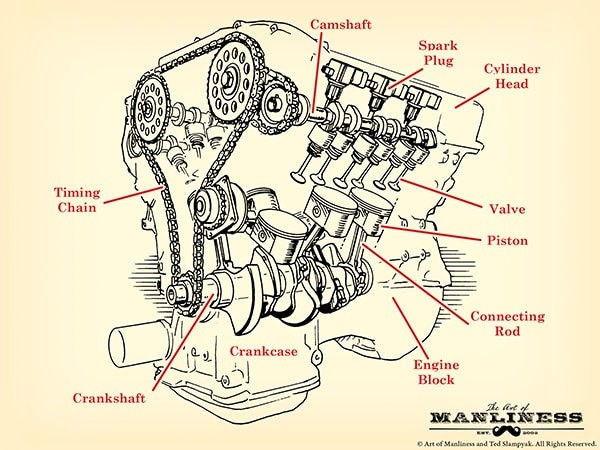
The essential components of a car engine include the engine block, combustion chamber, cylinder head, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, timing system, valvetrain, fuel injectors, and spark plugs. Understanding these parts is crucial for anyone looking to delve into automotive technology.
2.1 Key Engine Components
Delve into the details of each essential engine component:
- Engine Block (Cylinder Block): The foundation of the engine, typically made from aluminum alloy or iron. It houses the cylinders, which are tubes where the pistons move up and down. The number of cylinders determines the engine’s power (e.g., V6, V8).
- Combustion Chamber: This is where the fuel and air mix, compress, and ignite to create the power that moves the pistons. It consists of the cylinder, piston, and cylinder head.
- Cylinder Head: Sits atop the engine cylinders and contains indentations for combustion. It houses intake and outtake valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors.
- Piston: Moves up and down within the cylinder. The force from the combustion pushes the piston downward, which in turn moves the crankshaft. Piston rings seal the combustion chamber and prevent oil from seeping in.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which powers the wheels. It is located in the crankcase beneath the cylinder block.
- Camshaft: Coordinates the opening and closing of intake and outtake valves for optimal engine performance. It works with the crankshaft via a timing belt or chain.
- Timing System: Ensures the camshaft and crankshaft are in sync, controlling the timing of valve operations.
- Valvetrain: A mechanical system mounted on the cylinder head that controls the operation of the valves. It includes valves, rocker arms, pushrods, and lifters.
- Valves: Intake valves allow the air-fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber, while outtake valves release exhaust gases. High-performance engines often have multiple valves per cylinder for better breathing.
- Fuel Injectors: Supply fuel to the combustion chamber. Modern cars use direct fuel injection, ported fuel injection, or throttle body fuel injection systems.
- Spark Plug: Ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, causing the explosion that drives the piston down.
2.2 Visual Aids and Diagrams
Use visual aids and diagrams to enhance your understanding:
- Engine Diagrams: Study detailed diagrams to see how each component fits together and interacts with others.
- 3D Models: Utilize 3D models of engines to explore their structure and function from different angles.
2.3 Hands-On Exploration
Whenever possible, get hands-on experience with real engines:
- Disassembly and Reassembly: With guidance, disassemble and reassemble an old engine to understand how each part works.
- Engine Simulators: Use engine simulators to visualize the internal processes and movements within an engine.
3. How Does The Four-Stroke Engine Cycle Work?
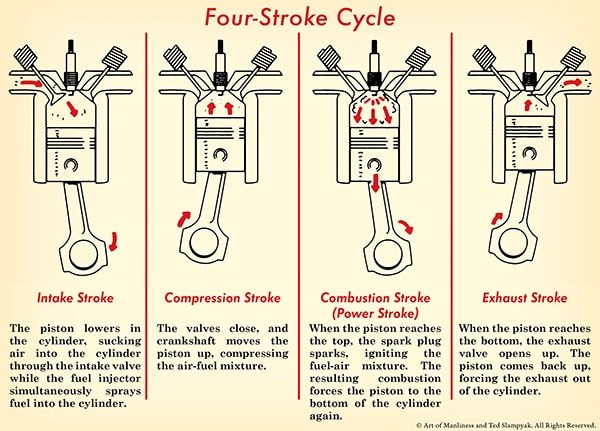
The four-stroke engine cycle consists of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, each playing a crucial role in converting fuel into motion. Understanding this cycle is fundamental to grasping how car engines operate.
3.1 The Four Strokes
Understand each stroke in detail:
- Intake: The piston moves down, creating a vacuum that draws a mixture of air and fuel into the cylinder through the intake valve.
- Compression: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture. This increases the temperature and pressure inside the cylinder.
- Combustion: At the peak of compression, the spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture, causing a rapid expansion of gases. This explosion forces the piston down.
- Exhaust: As the piston moves up again, the exhaust valve opens, allowing the burnt gases to be expelled from the cylinder.
3.2 Visual Learning
Use visuals to understand the cycle:
- Animated Diagrams: Watch animations that illustrate the movement of the piston and valves during each stroke.
- Interactive Simulations: Use interactive simulations to control the engine’s operation and observe the effects of each stroke.
3.3 Practical Examples
Relate the theory to practical examples:
- Engine Demonstrations: Attend live engine demonstrations or watch videos of engines running to see the four-stroke cycle in action.
- Troubleshooting: Learn how issues in each stroke can lead to engine problems, such as misfires or low compression.
4. What Are The Differences Between Gasoline And Diesel Engines?
Gasoline and diesel engines differ primarily in their ignition methods, compression ratios, and fuel efficiency. Gasoline engines use spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture, while diesel engines rely on high compression to ignite the fuel.
4.1 Key Differences
Outline the main differences between gasoline and diesel engines:
- Ignition Method: Gasoline engines use spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture. Diesel engines compress air to a high degree, which heats it enough to ignite the fuel when it’s injected.
- Compression Ratio: Diesel engines have a higher compression ratio (typically 14:1 to 25:1) compared to gasoline engines (typically 8:1 to 12:1).
- Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are generally more fuel-efficient due to the higher energy content of diesel fuel and their lean-burn combustion process.
- Emissions: Diesel engines tend to produce more particulate matter and nitrogen oxides (NOx), while gasoline engines produce more carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC).
- Noise and Vibration: Diesel engines are typically noisier and produce more vibrations than gasoline engines.
- Maintenance: Diesel engines often require more robust components due to the higher pressures involved, which can lead to different maintenance needs.
4.2 Comparative Analysis
Compare the performance and applications of each engine type:
| Feature | Gasoline Engine | Diesel Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition Method | Spark plug | Compression ignition |
| Compression Ratio | 8:1 to 12:1 | 14:1 to 25:1 |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Emissions | Higher CO and HC | Higher Particulate Matter and NOx |
| Noise/Vibration | Lower | Higher |
| Common Application | Passenger cars, small trucks | Heavy-duty trucks, buses, industrial equipment |
4.3 Engine Technologies
Examine advanced technologies in both engine types:
- Gasoline Engines: Turbocharging, direct fuel injection, variable valve timing.
- Diesel Engines: Common rail direct injection, diesel particulate filters (DPF), selective catalytic reduction (SCR).
5. What Are The Benefits Of Understanding Car Mechanics?
Understanding car mechanics can save money on repairs, improve driving safety, and provide a deeper appreciation for automotive technology. You’ll be able to diagnose issues early and perform basic maintenance yourself.
5.1 Cost Savings
Highlight the financial benefits of understanding car mechanics:
- DIY Repairs: Perform routine maintenance and minor repairs yourself, saving on labor costs.
- Informed Decisions: Make informed decisions about when to take your car to a mechanic and avoid unnecessary repairs.
- Preventive Maintenance: Identify potential issues early and prevent costly breakdowns.
5.2 Enhanced Safety
Explain how understanding car mechanics improves safety:
- Early Problem Detection: Recognize warning signs of mechanical issues and address them before they become major safety hazards.
- Confident Driving: Gain confidence in your ability to handle unexpected situations on the road.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure your car is always in top condition, reducing the risk of accidents due to mechanical failure.
5.3 Personal Satisfaction
Describe the personal benefits of learning about car mechanics:
- Deeper Appreciation: Develop a deeper appreciation for the technology and engineering that goes into modern vehicles.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Enhance your problem-solving skills by diagnosing and fixing mechanical issues.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Experience a sense of accomplishment from successfully completing car repairs and maintenance tasks.
5.4 Career Opportunities
Consider how mechanical knowledge can lead to career opportunities:
- Automotive Technician: Pursue a career as an automotive technician, mechanic, or service advisor.
- Engineering: Use your knowledge as a foundation for further studies in automotive engineering.
6. How Can I Diagnose Common Car Problems?
Diagnosing common car problems involves observing symptoms, using diagnostic tools like OBD-II scanners, and consulting repair manuals. A systematic approach can help you pinpoint the issue efficiently.
6.1 Systematic Diagnostic Approach
Outline a step-by-step approach to diagnosing car problems:
- Observe Symptoms: Pay attention to unusual noises, smells, vibrations, or changes in performance.
- Check Warning Lights: Note which warning lights are illuminated on the dashboard.
- Use OBD-II Scanner: Connect an OBD-II scanner to the car’s diagnostic port to read error codes.
- Consult Repair Manual: Look up the error codes in a repair manual or online database to identify potential causes.
- Inspect Components: Visually inspect the related components for signs of damage, leaks, or wear.
- Test Components: Use testing equipment, such as a multimeter or pressure gauge, to check the functionality of the components.
- Isolate the Problem: Based on the symptoms, error codes, and inspection results, isolate the root cause of the problem.
6.2 Common Car Problems and Solutions
Provide examples of common car problems and their potential solutions:
| Problem | Symptoms | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Misfire | Rough idling, poor acceleration | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors | Replace spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors |
| Overheating | Temperature gauge rises, steam from under hood | Coolant leak, faulty thermostat, or radiator | Check and repair coolant leaks, replace thermostat, or repair/replace radiator |
| Brake Squealing | Squealing noise when braking | Worn brake pads or rotors | Replace brake pads or rotors |
| Flat Tire | Car pulls to one side, thumping noise | Punctured tire | Replace or repair tire |
| Battery Problems | Engine won’t start, dim headlights | Dead or weak battery | Jump-start car, replace battery |
| Transmission Slipping | Engine revs high, car struggles to accelerate | Low transmission fluid, worn clutch, or damaged gears | Check and refill transmission fluid, replace clutch, or repair/replace transmission |
| Electrical System Issues | Flickering lights, malfunctioning accessories | Faulty wiring, blown fuses, or bad ground connections | Check and repair wiring, replace fuses, or clean/tighten ground connections |
| Suspension Problems | Bumpy ride, excessive bouncing | Worn shocks, struts, or control arm bushings | Replace shocks, struts, or control arm bushings |
| Exhaust System Leaks | Loud exhaust noise, reduced fuel efficiency | Holes or cracks in exhaust pipes or muffler | Repair or replace exhaust pipes or muffler |
| Cooling System Leaks | Loss of coolant, overheating | Leaks in radiator, hoses, or water pump | Check and repair leaks, replace radiator, hoses, or water pump |
6.3 Using Diagnostic Tools
Explain how to use diagnostic tools effectively:
- OBD-II Scanners: Learn how to connect an OBD-II scanner, read error codes, and interpret the data.
- Multimeters: Use a multimeter to test electrical components, such as sensors, switches, and solenoids.
- Pressure Gauges: Use pressure gauges to check fuel pressure, oil pressure, and coolant system pressure.
7. What Are Some Resources For Advanced Learning In Automotive Technology?
For advanced learning in automotive technology, explore professional certifications, specialized courses, and advanced diagnostic tools. These resources can elevate your skills and knowledge to a professional level.
7.1 Professional Certifications
Pursue professional certifications to validate your expertise:
- ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) Certification: This certification is widely recognized in the automotive industry and covers various areas, such as engine repair, brakes, electrical systems, and more.
- Manufacturer-Specific Certifications: Some manufacturers offer certifications for their specific vehicles and technologies.
7.2 Specialized Courses
Enroll in specialized courses to deepen your knowledge in specific areas:
- Advanced Engine Diagnostics: Learn advanced diagnostic techniques and tools for troubleshooting complex engine problems.
- Automotive Electronics: Study the electronic systems in modern vehicles, including engine control units (ECUs), sensors, and actuators.
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicle Technology: Gain expertise in the maintenance and repair of hybrid and electric vehicles.
7.3 Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Familiarize yourself with advanced diagnostic tools used by professionals:
- Scan Tools: Use advanced scan tools to access detailed diagnostic information and perform system tests.
- Oscilloscopes: Use oscilloscopes to analyze electrical signals and diagnose electronic problems.
- Smoke Machines: Use smoke machines to detect leaks in the intake and exhaust systems.
7.4 Online Resources and Communities
Continue learning through online resources and communities:
- Professional Forums: Join forums where professional technicians and engineers share their knowledge and experiences.
- Technical Journals: Subscribe to technical journals and magazines to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in automotive technology.
8. How Can I Stay Updated With The Latest Automotive Technologies?
Staying updated with the latest automotive technologies involves subscribing to industry publications, attending trade shows, and participating in online communities. Continuous learning is crucial in this rapidly evolving field.
8.1 Industry Publications
Subscribe to leading industry publications to stay informed:
- Automotive Engineering International: Provides in-depth coverage of automotive technology and engineering advancements.
- Motor Magazine: Offers technical articles, diagnostic tips, and industry news for automotive professionals.
- Auto Repair Manuals and Updates: Regularly consult and update repair manuals to reflect the latest vehicle models and technologies.
8.2 Trade Shows and Conferences
Attend trade shows and conferences to see the latest products and technologies:
- SEMA Show: An annual trade show in Las Vegas that showcases the latest automotive products, technologies, and trends.
- SAE International: SAE hosts conferences and exhibitions that focus on automotive engineering and technology.
8.3 Online Communities and Courses
Engage with online communities and take online courses to expand your knowledge:
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums and discussion groups to exchange information and learn from other professionals.
- Webinars and Online Courses: Take advantage of webinars and online courses offered by industry experts and educational institutions.
8.4 Continuous Learning
Adopt a mindset of continuous learning to stay ahead:
- Regular Reading: Dedicate time each week to read industry publications, technical articles, and online resources.
- Hands-On Practice: Apply new knowledge and skills through hands-on practice and experimentation.
9. What Are The Safety Precautions To Take When Working On Cars?
Safety precautions when working on cars include wearing safety glasses, using jack stands, disconnecting the battery, and handling hazardous materials properly. Prioritizing safety is essential to prevent injuries.
9.1 Essential Safety Gear
Always wear essential safety gear:
- Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris, chemicals, and other hazards.
- Gloves: Wear gloves to protect your hands from chemicals, oil, and sharp objects.
- Steel-Toed Boots: Protect your feet from heavy objects and sharp tools.
9.2 Safe Working Practices
Follow safe working practices to prevent accidents:
- Use Jack Stands: Never work under a car supported only by a jack. Always use jack stands to provide stable support.
- Disconnect Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on electrical components to prevent shocks.
- Proper Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid exposure to harmful fumes.
9.3 Handling Hazardous Materials
Handle hazardous materials with care:
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of used oil, coolant, and other fluids properly according to local regulations.
- Chemical Storage: Store chemicals in labeled containers and in a safe location.
- First Aid: Know how to respond to chemical spills and other accidents.
9.4 General Safety Tips
Follow these general safety tips for a safe working environment:
- Keep Work Area Clean: Keep your work area clean and organized to prevent trips and falls.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the right tools for the job and ensure they are in good working condition.
- Read Manuals: Read and understand the service manuals for your vehicle before attempting any repairs.
10. How Can LEARNS.EDU.VN Help Me Learn More About Cars And Engines?
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and interactive tools to help you master automotive technology. Our platform is designed to support learners at all levels, from beginners to advanced enthusiasts.
10.1 Comprehensive Resources
Access a wide range of learning materials:
- Detailed Articles: Explore in-depth articles on various automotive topics, from basic engine mechanics to advanced diagnostics.
- Video Tutorials: Watch step-by-step video tutorials that guide you through car repairs and maintenance tasks.
- Interactive Diagrams: Use interactive diagrams to visualize engine components and understand their functions.
10.2 Expert Guidance
Learn from experienced professionals:
- Expert Instructors: Our courses are taught by experienced automotive technicians and engineers.
- Live Q&A Sessions: Participate in live Q&A sessions with experts to get your questions answered.
- Personalized Feedback: Receive personalized feedback on your progress and areas for improvement.
10.3 Interactive Tools
Use interactive tools to enhance your learning experience:
- Engine Simulators: Simulate engine operations and experiment with different settings.
- Diagnostic Simulators: Practice diagnosing car problems using simulated diagnostic tools.
- Virtual Reality Experiences: Immerse yourself in virtual reality experiences that allow you to explore engine components in detail.
10.4 Community Support
Connect with other learners and enthusiasts:
- Online Forums: Join our online forums to discuss automotive topics, share tips, and ask questions.
- Study Groups: Form study groups with other learners to collaborate and support each other.
- Networking Events: Attend networking events to connect with professionals in the automotive industry.
Learning about cars and engines is a journey that combines theoretical knowledge with practical experience. By following this comprehensive guide, you can build a solid foundation in automotive technology and stay updated with the latest advancements. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the resources, guidance, and support you need to succeed.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of cars and engines? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our courses, articles, and interactive tools. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced enthusiast, we have something for everyone. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to enhance your skills and knowledge in automotive technology.
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
FAQ: Learning About Cars and Engines
- What is the best way to start learning about car engines?
- Start with basic online courses, books like “How Cars Work,” and join automotive communities to build a foundational understanding.
- What are the key components of a car engine I should focus on?
- Focus on the engine block, combustion chamber, cylinder head, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, timing system, valvetrain, fuel injectors, and spark plugs.
- How does the four-stroke engine cycle actually work?
- The cycle includes intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, each playing a vital role in converting fuel into motion.
- What are the main differences between gasoline and diesel engines?
- Gasoline engines use spark plugs for ignition, while diesel engines rely on high compression. Diesel engines are generally more fuel-efficient.
- What benefits can I get from understanding car mechanics?
- You can save money on repairs, improve driving safety, and gain a deeper appreciation for automotive technology.
- How can I effectively diagnose common car problems?
- Observe symptoms, use diagnostic tools like OBD-II scanners, and consult repair manuals for a systematic approach.
- What resources can I use for advanced learning in automotive technology?
- Pursue professional certifications like ASE, enroll in specialized courses, and familiarize yourself with advanced diagnostic tools.
- How can I stay updated with the latest automotive technologies?
- Subscribe to industry publications, attend trade shows, and participate in online communities for continuous learning.
- What safety precautions should I take when working on cars?
- Wear safety glasses, use jack stands, disconnect the battery, and handle hazardous materials properly to prevent injuries.
- How can LEARNS.EDU.VN specifically help me learn more about cars and engines?
- learns.edu.vn offers comprehensive resources, expert guidance, interactive tools, and community support to help you master automotive technology at all levels.