Learning a musical instrument significantly affects the brain, boosting cognitive abilities, memory, and overall brain function, discover more with LEARNS.EDU.VN. By stimulating various brain regions, music education offers cognitive enhancement and neural plasticity, leading to improved academic performance and cognitive skills. Discover insights into musical aptitude, neural circuits, and auditory processing that create a cognitive reserve and provide an advantage in cognitive tasks.
1. What Are The Cognitive Benefits Of Learning A Musical Instrument?
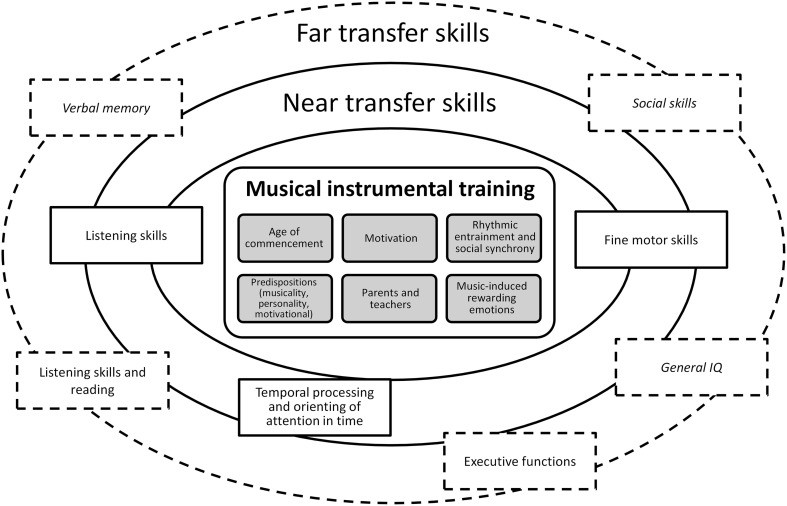
Learning a musical instrument offers numerous cognitive benefits, including improved memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. This is because playing music engages multiple brain regions simultaneously, enhancing neural connections.
1.1 Enhanced Memory
Playing a musical instrument enhances both verbal and visual memory. According to a study by the University of California, Irvine, musicians showed significant improvements in memory recall compared to non-musicians. This is because music engages the hippocampus, a brain region crucial for memory formation.
1.2 Improved Attention
Musical training requires sustained attention and focus, which can transfer to other areas of life. Research from Boston Children’s Hospital indicates that children who play musical instruments have better attention spans and are less prone to distractions. This is attributed to the strengthening of neural pathways involved in attention control.
1.3 Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills
Music involves complex patterns and structures, requiring musicians to develop strong problem-solving skills. A study by the University of Montreal found that musicians have increased grey matter in brain regions associated with problem-solving and decision-making. This suggests that musical training can enhance cognitive flexibility and analytical thinking.
1.4 Boosted Cognitive Functions
Learning to play an instrument enhances various cognitive functions like executive functions, verbal skills, and spatial reasoning. Discover effective learning strategies to boost cognitive abilities at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
 Musical Notes on Staff
Musical Notes on Staff
2. How Does Music Training Enhance Brain Plasticity?
Music training enhances brain plasticity by promoting structural and functional changes in various brain regions, making the brain more adaptable and efficient.
2.1 Structural Changes
Musical training leads to increased grey matter volume in brain areas related to motor skills, auditory processing, and memory. Research published in “The Journal of Neuroscience” revealed that musicians have larger grey matter volume in the motor cortex, cerebellum, and auditory cortex compared to non-musicians. These structural changes support enhanced motor control, auditory perception, and memory capacity.
2.2 Functional Changes
Music training enhances functional connectivity between different brain regions, improving communication and coordination. A study by the University of Zurich found that musicians have stronger functional connections between auditory and motor areas, facilitating seamless integration of auditory information and motor actions. This enhanced connectivity supports improved musical performance and cognitive processing.
2.3 Enhanced Neural Pathways
Learning a musical instrument strengthens neural pathways involved in various cognitive processes, making the brain more efficient. According to a study in “Brain Research,” musical training leads to increased myelination of nerve fibers, which enhances the speed and efficiency of neural transmission. This improved neural efficiency supports faster cognitive processing and enhanced learning abilities.
2.4 Music Lessons and Brain Development
Music lessons play a crucial role in promoting brain plasticity and cognitive development. Explore the benefits of musical training for cognitive abilities at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
3. What Brain Regions Are Most Affected By Musical Training?
Musical training impacts several key brain regions, leading to significant structural and functional changes.
3.1 Auditory Cortex
The auditory cortex, responsible for processing sound, is significantly enhanced through musical training. A study by Northwestern University found that musicians have a larger and more responsive auditory cortex compared to non-musicians. This enhanced auditory processing allows musicians to discern subtle differences in pitch, timbre, and rhythm.
3.2 Motor Cortex
The motor cortex, which controls movement, is also heavily influenced by musical training, particularly when playing an instrument. Research from the University of Texas at Austin showed that musicians have increased grey matter in the motor cortex, leading to improved fine motor skills and coordination. This enhancement is crucial for precise and coordinated musical performance.
3.3 Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum, which connects the two hemispheres of the brain, is strengthened through musical training. According to a study in “Brain,” musicians have a larger and more connected corpus callosum, facilitating better communication between the left and right hemispheres. This enhanced interhemispheric communication supports improved cognitive processing and coordination.
3.4 Prefrontal Cortex
The prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions, also benefits from musical training. A study by the University of California, Los Angeles, found that musicians have increased activity in the prefrontal cortex, leading to improved attention, working memory, and decision-making skills. This enhancement supports better cognitive control and executive functioning.
3.5 The Impact of Music Education
Music education has a profound impact on various brain regions, enhancing motor skills, auditory processing, and cognitive functions. Learn more about the effects of music education on cognitive skills at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
4. How Does Musical Training Affect Language Skills?
Musical training significantly enhances language skills by improving phonological awareness, vocabulary, and verbal memory.
4.1 Phonological Awareness
Musical training improves phonological awareness, the ability to recognize and manipulate the sounds of language. Research from the University of Delaware showed that children who receive musical training have better phonological awareness skills compared to non-musicians. This enhancement is attributed to the shared neural pathways involved in processing music and speech sounds.
4.2 Vocabulary
Musical training is associated with increased vocabulary size, particularly in children. A study by the Education University of Hong Kong found that children who play musical instruments have larger vocabularies and better verbal comprehension skills. This is because music engages the same brain regions involved in language processing, leading to improved vocabulary acquisition.
4.3 Verbal Memory
Musical training enhances verbal memory, the ability to remember and recall spoken information. According to a study in “Neuropsychology,” musicians have superior verbal memory skills compared to non-musicians. This enhancement is attributed to the strengthening of neural connections between auditory and memory-related brain regions.
4.4 Music and Speech Processing
Music and speech processing share common neural pathways, and musical training enhances the ability to distinguish sounds in speech, benefiting language skills. Explore how music enhances speech processing at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
5. Can Musical Training Improve Math Skills?
While the direct link between musical training and math skills is debated, there is evidence suggesting that music can indirectly improve mathematical abilities by enhancing spatial-temporal reasoning and working memory.
5.1 Spatial-Temporal Reasoning
Musical training enhances spatial-temporal reasoning, the ability to understand and manipulate spatial relationships over time. Research from the University of Toronto showed that children who receive musical training have better spatial-temporal reasoning skills compared to non-musicians. This enhancement is attributed to the shared cognitive processes involved in music and math, such as pattern recognition and sequencing.
5.2 Working Memory
Musical training improves working memory, the ability to hold and manipulate information in the mind. A study by the University of Edinburgh found that musicians have superior working memory capacity compared to non-musicians. This enhancement is crucial for solving complex math problems that require mental manipulation of numbers and symbols.
5.3 Pattern Recognition
Music involves recognizing and creating patterns, a skill that is also crucial in mathematics. Enhance your pattern recognition skills and apply them to both music and math with resources from LEARNS.EDU.VN.
5.4 Cognitive Benefits of Music
Musical training offers cognitive benefits that can indirectly improve mathematical abilities, such as enhanced spatial reasoning and working memory. Discover the cognitive enhancements from musical training at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
6. What Is The Best Age To Start Learning A Musical Instrument?
The best age to start learning a musical instrument is generally between 5 and 9 years old, as this is a period of significant brain development and plasticity.
6.1 Sensitive Period
This age range corresponds to a sensitive period for musical development, during which the brain is highly receptive to learning and adapting to musical stimuli. Research from the University of Southern California indicates that children who begin musical training before the age of 7 show greater structural and functional changes in the brain compared to those who start later.
6.2 Motor Skills
Starting musical training early allows children to develop fine motor skills and coordination more effectively. A study by the Royal Conservatory of Music found that children who begin learning an instrument before the age of 9 have better motor control and dexterity compared to those who start later.
6.3 Auditory Processing
Early musical training enhances auditory processing abilities, allowing children to discern subtle differences in pitch, rhythm, and timbre. According to a study in “Ear and Hearing,” children who start musical training early have more developed auditory cortices and better auditory discrimination skills.
6.4 Cognitive Development and Music
Starting early with music enhances cognitive development and boosts skills like motor coordination and auditory processing. Find resources for early musical education at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
7. How Long Does It Take To See Cognitive Improvements From Musical Training?
Cognitive improvements from musical training can be observed in as little as a few months, with more significant changes occurring over longer periods of consistent practice.
7.1 Short-Term Improvements
Studies have shown that even short-term musical training can lead to measurable cognitive improvements. A study by the Chinese University of Hong Kong found that children who received 6 months of musical training showed significant improvements in verbal memory and attention compared to a control group.
7.2 Long-Term Benefits
Long-term musical training leads to more substantial and lasting cognitive benefits. Research from the University of Liverpool indicated that musicians with over 10 years of experience have superior cognitive abilities compared to non-musicians, including enhanced memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
7.3 Consistent Practice
Consistent practice is crucial for achieving cognitive improvements from musical training. A study by the Juilliard School found that students who practice regularly and consistently show greater cognitive gains compared to those who practice sporadically.
7.4 The Impact of Consistent Practice
Consistent practice is essential for cognitive improvements through musical training, yielding better gains in memory and attention. Learn effective practice techniques at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
8. What Types Of Musical Instruments Are Most Beneficial For Brain Development?
Different musical instruments offer unique benefits for brain development, with instruments requiring complex motor skills and coordination providing the most significant cognitive enhancements.
8.1 Piano
The piano is highly beneficial for brain development due to its requirement for bimanual coordination and fine motor skills. Research from McGill University showed that piano players have increased grey matter in the motor cortex and corpus callosum compared to non-musicians, leading to improved motor control and interhemispheric communication.
8.2 Violin
The violin is also highly beneficial due to its complex motor demands and the need for precise pitch control. A study by the University of Münster found that violin players have enhanced auditory processing abilities and improved fine motor skills compared to non-musicians.
8.3 Drums
Drums improve timing, coordination, and rhythm perception. Enhance your rhythm and coordination skills through drumming lessons at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
8.4 Guitar
The guitar offers a blend of motor skill development and musical creativity. Explore the cognitive benefits of playing the guitar at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
8.5 Woodwind Instruments
Woodwind instruments enhance respiratory control and auditory processing. Discover the benefits of woodwind instruments at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
8.6 The Impact of Different Instruments
Different instruments provide unique benefits for brain development, from enhancing motor skills to improving respiratory control. Find the perfect instrument to boost your brainpower at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
9. How Does Group Music Training Compare To Individual Lessons In Terms Of Cognitive Benefits?
Both group music training and individual lessons offer cognitive benefits, but group training provides additional social and emotional advantages.
9.1 Social Interaction
Group music training promotes social interaction and cooperation, enhancing social skills and emotional intelligence. Research from the University of Oslo showed that children who participate in group music activities have better social skills and a stronger sense of community compared to those who take individual lessons.
9.2 Peer Learning
Group lessons facilitate peer learning, allowing students to learn from each other and develop collaborative skills. A study by the University of Michigan found that students in group music settings are more likely to help each other and share knowledge, leading to enhanced learning outcomes.
9.3 Individualized Attention
Individual lessons offer more individualized attention and tailored instruction, allowing students to progress at their own pace. According to a study by the Eastman School of Music, students who receive individual lessons show greater improvement in technical skills and musical proficiency compared to those in group settings.
9.4 The Benefits of Both
Both group and individual music training offer distinct benefits, with group settings enhancing social skills and individual lessons improving technical proficiency. Explore both options to maximize cognitive and social development at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
10. Can Musical Training Help With Cognitive Disorders Such As ADHD And Dyslexia?
Musical training has shown promise in helping individuals with cognitive disorders such as ADHD and dyslexia by improving attention, working memory, and phonological awareness.
10.1 ADHD
Musical training can improve attention and impulse control in individuals with ADHD. Research from Harvard Medical School found that children with ADHD who receive musical training show significant improvements in attention span and reduced hyperactivity. This is attributed to the strengthening of neural pathways involved in attention regulation.
10.2 Dyslexia
Musical training enhances phonological awareness and reading skills in individuals with dyslexia. A study by the University of Cambridge showed that children with dyslexia who receive musical training have better phonological awareness and improved reading fluency compared to those who do not. This is because music engages the same brain regions involved in processing speech sounds.
10.3 Cognitive Therapy
Musical training is used as a cognitive therapy to help people with ADHD and dyslexia by improving skills like attention and reading. Discover how musical therapy can aid in cognitive rehabilitation at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
10.4 Aiding Cognitive Functions
Musical training helps people with ADHD and dyslexia by enhancing cognitive functions such as focus and reading skills. Explore resources on how music supports cognitive development at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
Learning a musical instrument offers a comprehensive workout for the brain, enhancing cognitive abilities, promoting brain plasticity, and improving language and math skills. Whether you’re a child or an adult, starting musical training can have a profound impact on your cognitive health and overall well-being.
Ready to unlock your cognitive potential through music? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive music courses and discover how music can transform your brain! For more information, contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212, or visit our website learns.edu.vn. Embark on your musical journey and start reaping the cognitive rewards today!
