Does Language Learning Increase Iq? Yes, language learning can contribute to an increase in cognitive abilities, effectively boosting aspects associated with IQ, and LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to explore these benefits. Learning a new language expands cognitive flexibility, improves problem-solving skills, and enhances memory function. Discover how acquiring a new language affects your brainpower and how it aligns with cognitive enhancement, intellectual development, and brain training at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
1. The Cognitive Link: How Language Learning Enhances IQ
Does language learning directly increase IQ scores as measured by standardized tests? The answer is nuanced. While language learning may not dramatically increase the numerical value of an IQ score, it significantly enhances various cognitive functions that are closely associated with intelligence. Studies show that bilingual individuals often exhibit improved executive functions, working memory, and problem-solving abilities—all of which are key components of intelligence.
1.1. Executive Functions
Executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are essential for goal-directed behavior and include:
- Working Memory: Holding information in mind and manipulating it.
- Cognitive Flexibility: Shifting between different tasks or mental sets.
- Inhibitory Control: Controlling impulses and resisting distractions.
Research suggests that bilingualism enhances these executive functions, giving language learners a cognitive advantage in various tasks.
1.2. The Edinburgh Study: Bilingualism and Cognitive Performance
A notable study by Dr. Thomas Bak at Edinburgh’s School of Philosophy, Psychology and Language Sciences, examined the cognitive performance of bilingual individuals. This research tested 853 participants initially at age 11 in 1947 and retested them in their early 70s between 2008 and 2010. The study revealed that those who became bilingual outperformed their monolingual peers in tests of general intelligence and reading. These findings indicate that language learning, even in adulthood, has positive cognitive effects.
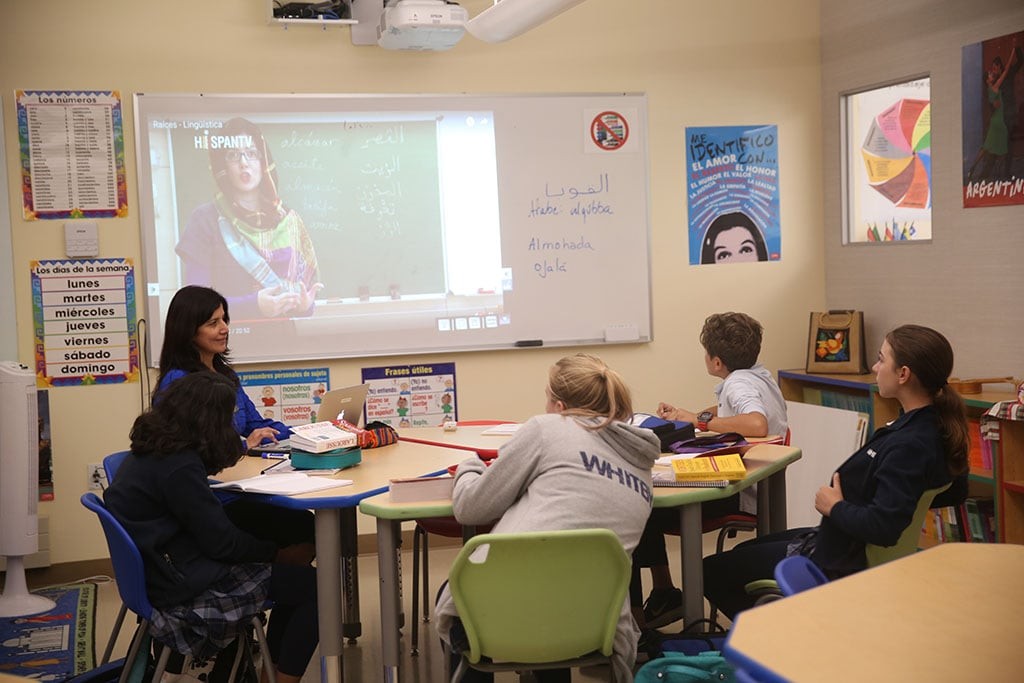 Elderly person learning language with computer
Elderly person learning language with computer
Caption: An elderly person learns a new language using a computer, showcasing that language learning is effective even in adulthood.
1.3. Language Learning and Brain Plasticity
Learning a new language can physically change the brain. Research using MRI scans has shown that the brains of language learners increase in size, particularly in areas associated with language processing and cognitive functions. This brain plasticity demonstrates that learning a new language can lead to tangible changes in brain structure and function, further supporting the idea that it enhances cognitive abilities.
1.4. Benefits for Children
Children exposed to multiple languages from an early age often develop enhanced cognitive control abilities. A 2009 study led by Agnes Kovacs compared seven-month-old babies raised in bilingual environments with those raised in monolingual settings. The study found that bilingual infants exhibited improved cognitive control, indicating that early language exposure can positively impact cognitive development.
2. Key Cognitive Benefits of Language Learning
Language learning offers a wide range of cognitive benefits that extend beyond improved communication skills. These benefits include enhanced memory, better problem-solving abilities, increased multitasking skills, and improved cognitive flexibility.
2.1. Enhanced Memory
Learning a new language requires memorizing vocabulary, grammar rules, and pronunciation patterns. This constant exercise strengthens memory skills, making it easier to remember new information in other areas as well.
2.2. Improved Problem-Solving Abilities
Language learning involves deciphering complex grammar rules and understanding different sentence structures. This process enhances problem-solving skills and analytical thinking, which are valuable in various aspects of life.
2.3. Increased Multitasking Skills
Bilingual individuals often develop the ability to switch between languages seamlessly. This multitasking ability translates to other areas, making them more efficient at handling multiple tasks simultaneously.
2.4. Enhanced Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive flexibility, the ability to switch between different tasks or mental sets, is significantly enhanced by language learning. This is because bilingual individuals constantly switch between languages, which exercises their cognitive flexibility.
3. Debunking Myths About Language Learning and IQ
Despite the clear cognitive benefits of language learning, several myths persist about its impact on IQ. These myths often stem from misconceptions about intelligence and the learning process.
3.1. Myth: Language Learning Directly Increases IQ Scores
While language learning enhances cognitive abilities associated with intelligence, it may not directly increase numerical IQ scores. IQ tests measure a specific set of cognitive skills, and language learning’s benefits are broader and more nuanced.
3.2. Myth: Only Intelligent People Can Learn New Languages
Anyone can learn a new language with dedication and the right resources. Language learning is not solely dependent on innate intelligence but also on motivation, learning strategies, and practice.
3.3. Myth: Language Learning Is Only Beneficial for Children
Adults can also reap significant cognitive benefits from language learning. Research shows that learning a new language in adulthood can still enhance cognitive functions and improve brain plasticity.
3.4. Myth: Learning Multiple Languages Confuses the Brain
Learning multiple languages does not confuse the brain; instead, it strengthens cognitive abilities. Bilingual and multilingual individuals often exhibit enhanced executive functions and cognitive flexibility.
4. Practical Ways to Incorporate Language Learning into Your Life
Integrating language learning into your daily routine can be both enjoyable and beneficial. Here are some practical ways to incorporate language learning into your life.
4.1. Online Language Courses
Online language courses, such as those available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, offer structured lessons and interactive exercises to help you learn a new language at your own pace.
4.2. Language Learning Apps
Language learning apps like Duolingo, Babbel, and Memrise provide gamified lessons and vocabulary practice to make language learning fun and engaging.
4.3. Language Exchange Partners
Engaging with native speakers through language exchange platforms like HelloTalk and Tandem can provide valuable speaking practice and cultural insights.
4.4. Immersion Techniques
Immersing yourself in the language through movies, music, and books can enhance your understanding and fluency.
4.5. Travel and Study Abroad
Traveling to a country where the language is spoken can provide an immersive learning experience and accelerate your language acquisition.
5. Language Learning Resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a variety of resources to support your language learning journey. These resources include online courses, language learning tips, and expert guidance.
5.1. Online Language Courses
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides comprehensive online language courses in various languages, designed to cater to learners of all levels.
5.2. Language Learning Tips
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers valuable tips and strategies to help you learn a new language effectively, covering topics such as vocabulary acquisition, grammar rules, and pronunciation.
5.3. Expert Guidance
LEARNS.EDU.VN connects you with experienced language teachers and experts who can provide personalized guidance and support.
6. Understanding the Science Behind Language Learning and the Brain
To fully appreciate the cognitive benefits of language learning, it’s important to understand the underlying neuroscience. Language learning impacts various brain regions and neural pathways, leading to cognitive enhancement.
6.1. Brain Regions Involved in Language Learning
Several brain regions are involved in language learning, including:
- Broca’s Area: Responsible for language production.
- Wernicke’s Area: Responsible for language comprehension.
- The Hippocampus: Plays a crucial role in memory and learning.
- The Cerebral Cortex: Involved in higher-level cognitive functions.
6.2. Neural Plasticity and Language Learning
Neural plasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life, is key to language learning. When you learn a new language, your brain forms new neural pathways, strengthening cognitive functions.
6.3. The Impact of Bilingualism on Brain Structure
Studies have shown that bilingual individuals have denser gray matter in brain regions associated with executive functions and language processing. This structural difference contributes to their enhanced cognitive abilities.
7. Real-Life Examples: How Language Learning Has Improved Cognitive Abilities
Numerous anecdotal and documented cases illustrate how language learning has positively impacted cognitive abilities in individuals of all ages.
7.1. Case Study 1: Improved Memory in Older Adults
An elderly individual who started learning Spanish reported improved memory and cognitive function. The mental exercise of learning new vocabulary and grammar helped keep their mind sharp and active.
7.2. Case Study 2: Enhanced Problem-Solving in Students
Students learning Mandarin Chinese demonstrated improved problem-solving skills and analytical thinking. The complex nature of the language challenged them to think creatively and develop effective problem-solving strategies.
7.3. Case Study 3: Increased Multitasking Abilities in Professionals
Professionals who learned a second language reported increased multitasking abilities and efficiency. Their ability to switch between languages seamlessly translated to better performance in handling multiple tasks at work.
8. Tailoring Language Learning to Different Age Groups
The approach to language learning should be tailored to the specific needs and abilities of different age groups.
8.1. Language Learning for Children
Children are naturally adept at learning languages, and early exposure can lead to native-like pronunciation and fluency. Focus on fun, interactive activities and games to keep them engaged.
8.2. Language Learning for Teenagers
Teenagers can benefit from structured language courses and opportunities for real-world practice, such as language exchange programs and study abroad experiences.
8.3. Language Learning for Adults
Adults may face different challenges, such as time constraints and motivation. Focus on setting realistic goals, using effective learning strategies, and finding ways to integrate language learning into their daily routine.
8.4. Language Learning for Seniors
Seniors can reap significant cognitive benefits from language learning, such as improved memory and cognitive function. Tailor the learning approach to their specific needs and abilities, focusing on patience, encouragement, and positive reinforcement.
9. The Role of Technology in Modern Language Learning
Technology has revolutionized language learning, providing learners with a wide range of tools and resources to enhance their learning experience.
9.1. Language Learning Apps
Language learning apps offer gamified lessons, vocabulary practice, and pronunciation feedback, making language learning more accessible and enjoyable.
9.2. Online Language Courses
Online language courses provide structured lessons, interactive exercises, and personalized feedback, allowing learners to study at their own pace and convenience.
9.3. Language Exchange Platforms
Language exchange platforms connect learners with native speakers for real-time conversation practice and cultural exchange.
9.4. Virtual Reality (VR) Language Learning
VR language learning offers immersive experiences that simulate real-world scenarios, allowing learners to practice their language skills in a realistic and engaging environment.
9.5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Language Learning
AI-powered language learning tools provide personalized feedback, adaptive learning paths, and real-time translation, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of language learning.
10. Future Trends in Language Learning and Cognitive Enhancement
The field of language learning is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging to enhance the learning experience and maximize cognitive benefits.
10.1. Personalized Language Learning
Personalized language learning tailors the learning experience to the individual learner’s needs, goals, and learning style, optimizing the learning process and maximizing outcomes.
10.2. Gamification of Language Learning
Gamification incorporates game-like elements into language learning, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, to increase motivation and engagement.
10.3. Integration of Cognitive Training
Integrating cognitive training exercises into language learning programs can further enhance cognitive abilities and maximize the benefits of language learning.
10.4. Neurofeedback for Language Learning
Neurofeedback uses real-time feedback from brain activity to help learners optimize their brain function and accelerate language acquisition.
10.5. The Use of Big Data in Language Learning
Big data analytics can provide valuable insights into language learning patterns and outcomes, allowing educators and researchers to develop more effective learning strategies and interventions.
11. Actionable Steps to Maximize Cognitive Benefits
To truly reap the cognitive rewards of language learning, strategic steps must be taken to enhance the learning experience and foster cognitive growth.
11.1. Set Clear and Achievable Goals
Begin your language learning journey by setting clear, realistic goals. Whether your aim is to hold a basic conversation, read a foreign newspaper, or pass a language proficiency test, having well-defined objectives keeps you motivated and focused.
11.2. Use Spaced Repetition Techniques
Spaced repetition involves reviewing material at increasing intervals. This method optimizes memory retention by reinforcing information just before you’re likely to forget it, making your study sessions more efficient.
11.3. Engage Actively with the Language
Passive learning, such as simply reading or listening, is less effective than active engagement. Practice speaking, writing, and thinking in the new language. This active participation solidifies your understanding and boosts cognitive processing.
11.4. Immerse Yourself in the Culture
Language is deeply intertwined with culture. Immerse yourself in the culture of the language you’re learning through movies, music, books, and interactions with native speakers. This cultural immersion provides context and makes the learning process more meaningful.
11.5. Seek Feedback and Correct Mistakes
Don’t be afraid to make mistakes. Mistakes are a natural part of the learning process. Seek feedback from teachers, language partners, or online communities. Correcting your mistakes helps you improve faster and reinforces correct usage.
11.6. Vary Your Learning Methods
Avoid monotony by varying your learning methods. Combine textbook study with language learning apps, podcasts, and conversation practice. This variety keeps your brain engaged and enhances cognitive flexibility.
11.7. Practice Consistently
Consistency is key to language learning success. Set aside time each day or week to practice, even if it’s just for a few minutes. Regular practice reinforces what you’ve learned and prevents forgetting.
11.8. Reflect on Your Progress
Regularly reflect on your progress and celebrate your achievements. Acknowledging how far you’ve come boosts your motivation and reinforces positive learning habits.
11.9. Connect with Other Learners
Join language learning communities, either online or in person. Connecting with other learners provides support, encouragement, and opportunities to practice. Sharing your experiences and learning from others can significantly enhance your journey.
11.10. Stay Curious and Enjoy the Process
Finally, remember to stay curious and enjoy the process of language learning. A positive attitude and genuine interest make the journey more rewarding and increase your chances of success.
12. Overcoming Common Challenges in Language Learning
Language learning can present various challenges, but understanding and addressing these obstacles can pave the way for success.
12.1. Lack of Time
Many learners struggle to find enough time for language study. Prioritize your time and integrate language learning into your daily routine. Use short breaks for vocabulary practice or listen to podcasts while commuting.
12.2. Motivation
Maintaining motivation can be difficult, especially when progress seems slow. Set small, achievable goals and reward yourself for reaching them. Find a language partner to keep you accountable and motivated.
12.3. Fear of Making Mistakes
Fear of making mistakes can hinder your progress. Remember that mistakes are a natural part of learning. Focus on communicating effectively rather than being perfect. Embrace mistakes as opportunities for growth.
12.4. Difficulty with Pronunciation
Pronunciation can be challenging, especially for languages with sounds that are unfamiliar to you. Use online resources, pronunciation guides, and language exchange partners to improve your pronunciation. Practice regularly and don’t be afraid to imitate native speakers.
12.5. Information Overload
With so many language learning resources available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. Focus on a few high-quality resources and avoid trying to do too much at once. Choose resources that align with your learning style and goals.
12.6. Plateauing
It’s common to experience plateaus where progress seems to stall. Don’t get discouraged. Try new learning methods, focus on different skills, and challenge yourself with more advanced material. Remember that progress is not always linear.
12.7. Cultural Differences
Understanding cultural nuances can be challenging but is essential for effective communication. Learn about the culture associated with the language you’re studying. Watch movies, read books, and interact with native speakers to gain cultural insights.
12.8. Grammar Complexity
Grammar can be daunting, especially for languages with complex grammatical structures. Break down grammar rules into manageable chunks and practice them in context. Use online resources and grammar guides to clarify your understanding.
12.9. Finding Language Partners
Finding language partners can be challenging, especially if you live in an area with few native speakers. Use online language exchange platforms to connect with partners from around the world. Be proactive and reach out to potential partners.
12.10. Staying Consistent
Staying consistent is crucial for language learning success. Set a schedule and stick to it. Make language learning a habit by integrating it into your daily routine. Find ways to make it enjoyable and rewarding.
13. Understanding User Search Intent
To create content that truly resonates with learners, it’s crucial to understand what they’re looking for. Here are five search intents related to “does language learning increase IQ”:
13.1. Informational Intent: Defining the Relationship
Users search to understand the relationship between language learning and IQ, seeking definitions, explanations, and basic facts.
13.2. Investigative Intent: Exploring the Evidence
Users look for studies, research, and data that support or refute the claim that language learning increases IQ.
13.3. Comparative Intent: Weighing the Benefits
Users compare the cognitive benefits of language learning with other activities or methods for boosting IQ.
13.4. Practical Intent: Finding Learning Methods
Users seek practical advice on how to learn a language effectively and maximize its cognitive benefits.
13.5. Affirmative Intent: Validating Current Efforts
Users look for reassurance that their efforts in language learning are worthwhile and beneficial for their cognitive abilities.
14. FAQ: Does Language Learning Increase IQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about the relationship between language learning and IQ:
14.1. Does Learning a New Language Make You Smarter?
Yes, language learning enhances cognitive functions like memory, problem-solving, and multitasking, making you more adept in various mental tasks.
14.2. How Does Bilingualism Affect the Brain?
Bilingualism increases gray matter density and strengthens neural pathways, improving cognitive control and flexibility.
14.3. Can Language Learning Improve Memory?
Yes, memorizing vocabulary and grammar rules strengthens memory skills, making it easier to retain new information.
14.4. Is It Ever Too Late to Learn a New Language?
No, adults can still reap significant cognitive benefits from language learning, including improved memory and cognitive function.
14.5. What Are the Best Methods for Language Learning?
Effective methods include online courses, language learning apps, language exchange partners, and immersion techniques.
14.6. How Long Does It Take to See Cognitive Benefits From Language Learning?
Cognitive benefits can be observed relatively quickly with consistent practice, often within a few months of starting a new language.
14.7. Does Learning Multiple Languages Provide Additional Cognitive Benefits?
Yes, learning multiple languages further enhances cognitive abilities, providing additional benefits for memory, problem-solving, and multitasking.
14.8. Can Language Learning Help Prevent Cognitive Decline?
Yes, language learning can help buffer the brain against aging and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
14.9. Are Some Languages More Cognitively Demanding Than Others?
Some languages may present unique challenges due to complex grammar or pronunciation, but all language learning provides cognitive benefits.
14.10. How Does Language Learning Affect Executive Functions?
Language learning enhances executive functions like working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibitory control, improving overall cognitive performance.
Language learning is more than just acquiring new words and grammar; it’s a comprehensive brain workout that enhances cognitive abilities and boosts various aspects associated with IQ. Whether you’re a student, professional, or senior, the benefits of language learning are within your reach.
Ready to unlock your cognitive potential? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Explore our courses and resources to start your language learning journey today and discover the transformative power of language. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to expand your mind and enrich your life! Check out learns.edu.vn today.