Cyber security is essential in today’s digital world, and understanding the fundamentals is the first step toward protecting yourself and your data. This guide, brought to you by LEARNS.EDU.VN, provides a clear and structured path to learning cyber security basics, covering everything from essential terminologies to common attack types. Equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate the cyber landscape safely by diving into network security, ethical hacking, and threat intelligence.
1. Understanding Cyber Security
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber security involves technologies and processes designed to protect networks and devices from attacks, damage, or unauthorized access. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), cyber security is crucial for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic information. This field is vital for various entities, including military, hospitals, corporations, small businesses, and individuals.
Cyber security plays a critical role in protecting sensitive data and ensuring the continuity of operations. A breach in cyber security can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the fundamental principles and practices of cyber security to safeguard valuable assets. For further reading, explore resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN to enhance your expertise in this field.
Why is Cyber Security Important?
Cyber security is crucial due to the increasing reliance on digital systems and the growing sophistication of cyber threats. As highlighted by a report from Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- Protection of Sensitive Data: Cyber security measures protect personal, financial, and proprietary information from theft or misuse.
- Ensuring Business Continuity: Effective cyber security practices ensure that businesses can continue operations without disruption due to cyber attacks.
- Maintaining Trust and Reputation: Strong cyber security safeguards help organizations maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
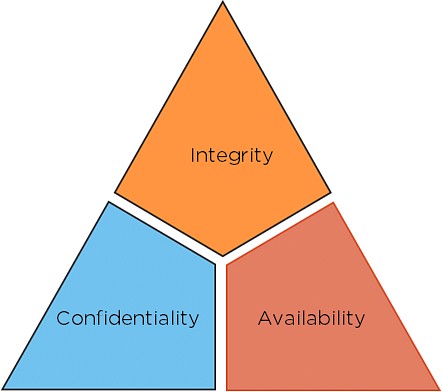
The CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
The CIA Triad is a fundamental model designed to guide security policies within organizations. It stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, each playing a crucial role in ensuring data security.
- Confidentiality: Ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized parties. This involves implementing access controls and encryption techniques to prevent unauthorized disclosure.
- Integrity: Maintains the accuracy and completeness of data. It involves measures to prevent unauthorized modification or deletion of information, ensuring that data remains reliable.
- Availability: Guarantees that authorized users have reliable and timely access to information and resources. This includes maintaining infrastructure, preventing downtime, and ensuring quick recovery from incidents.
CIA Triad is a fundamental model designed to guide security policies within organizations
2. Essential Cyber Security Terminologies
1. Network
A network is a connection between two or more computers that can communicate with each other. Networks are essential for sharing resources, transferring data, and enabling communication. According to Cisco, networks are the backbone of modern IT infrastructure, supporting everything from email communication to complex cloud computing applications.
Network Connection is a connection between two or more computers that can communicate with each other.
2. Internet
The Internet connects computers worldwide through dedicated routers and servers, enabling global communication and data exchange. As stated by the Internet Society, the Internet has transformed how we live, work, and interact, fostering innovation and connecting billions of people.
3. Internet Protocols
Internet Protocols are the rules governing data transfer over the Internet. These protocols ensure data packets are correctly addressed, routed, and received. The TCP/IP model, which includes protocols like HTTP, SMTP, and FTP, is fundamental to Internet communication, as noted by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force).
4. IP Address
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses enable devices to locate each other and exchange data over the Internet. According to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), IP addresses are crucial for the functioning of the Internet. An IP address looks like this: 168.192.10.3
5. MAC Address
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique hardware identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for communication within a network segment. MAC addresses are used for identifying devices on a local network. The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) manages MAC address allocation, ensuring each device has a unique identifier. MAC address looks like this: D8-FC-93-C5-A5-EO.
6. Domain Name System (DNS)
DNS is a hierarchical and decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other resources connected to the Internet or a private network. It translates domain names, which are easy to remember, to IP addresses, which computers use to identify each other. ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) oversees the DNS system, ensuring its stability and security.
7. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP assigns IP addresses to devices connecting to the Internet. This protocol automates the assignment of IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS server addresses, simplifying network administration. As explained by the DHCP Working Group, DHCP reduces the manual configuration required for network devices.
DHCP assigns IP addresses to devices connecting to the Internet.
8. Router
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers analyze the destination IP address of incoming packets and determine the best path to forward them to the destination network. Cisco describes routers as essential for connecting multiple networks and enabling communication between them.
9. Bots
Bots are computer programs that automate tasks, often without the user’s knowledge. Malicious bots can send spam, steal data, or launch attacks on other systems. According to a report by Imperva, bots account for a significant portion of Internet traffic, and managing bot activity is a key cyber security challenge.
3. Common Types of Cyber Attacks
Why Cyber Attacks Happen
Cyber attacks are primarily driven by financial motives. Hackers penetrate systems to demand ransom from victims. Additional motives include causing financial loss, disrupting military objectives, damaging reputations, or engaging in political maneuvering. According to a report by Verizon, financial gain is the primary driver behind most cyber attacks.
1. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
DDoS attacks flood a network or server with traffic, preventing legitimate users from accessing resources. Attackers use botnets to overwhelm the target system with a high volume of requests. Akamai reports that DDoS attacks are increasing in frequency and complexity, posing a significant threat to online services.
DDoS attacks flood a network or server with traffic, preventing legitimate users from accessing resources
2. Man in the Middle (MitM)
MitM attacks involve an attacker intercepting communication between two parties, allowing them to eavesdrop on or manipulate the data being transmitted. This type of attack can compromise sensitive information, such as login credentials and financial details. As highlighted by the SANS Institute, securing network communications is essential for preventing MitM attacks.
3. Password Attacks
Password attacks aim to crack or steal passwords. Common techniques include:
- Dictionary Attack: Trying common passwords from a predefined list.
- Brute Force Attack: Trying every possible combination of characters until the correct password is found.
- Keylogger: Recording keystrokes on a keyboard to capture passwords.
- Shoulder Surfing: Observing a user entering their password.
- Rainbow Table Attack: Using precomputed hash values to find passwords.
4. Email Attacks
Email attacks exploit vulnerabilities in email systems to deceive users into revealing sensitive information or installing malware.
How Email Works
Emails are sent from a sender’s email server to the recipient’s server via the DNS server, which identifies the IP address. This process ensures the email reaches the correct destination.
Types of Email Attacks
- Phishing: Sending fraudulent emails to trick users into sharing personal information.
- Spoofing: Impersonating a legitimate sender to deceive recipients.
- Email Attachments: Sending malicious files via email attachments.
Example of Phishing Attack
If someone is a customer of ABC Bank, he would probably open the link and give the details. However, these emails are always phishing; banks do not send emails like this.
Example of Spoofing Attack
After seeing this email, you might share the password to your computer. Always ask the person from whom you received the email one more time to confirm that he is the right person.
Example of Email Attachments Attack
Download these attachments only if you know it is a legitimate email.
5. Malware Attacks
Malware is malicious software designed to disrupt or damage computer systems.
Types of Malware
- Virus: Malicious code that replicates by attaching itself to other programs or documents.
- Worms: Standalone programs that can spread independently and infect systems.
Functions of Malware
- Overwhelming System Resources: Consuming excessive memory and slowing down computer performance.
- Creating a Backdoor: Providing unauthorized access to a system.
- Disabling Security Functions: Deactivating antivirus software and security updates.
- Creating Botnets: Building networks of infected computers to launch attacks.
Sources of Malware
- Removable Media
- Documents and Executable Files
- Internet Downloads
- Network Connections
- Email Attachments
- Malicious Advertisements
4. Specialties in Cyber Security
Cyber security offers diverse areas of specialization, each requiring unique skills and knowledge.
- Access Control Systems and Methodology: Protecting system resources from unauthorized modification.
- Telecommunications and Network Security: Securing communications, protocols, and network services.
- Security Management Practices: Dealing with system failures, natural disasters, and service interruptions.
- Security Architecture and Models: Implementing security policies and procedures.
- Law, Investigation, and Ethics: Handling legal issues associated with computer security.
- Application and System Development Security: Covering database security models and multilevel security for applications.
- Cryptography: Understanding how and when to use encryption.
- Computer Operations Security: Covering security measures during computer operations.
- Physical Security: Addressing physical access to servers and workstations.
5. Job Roles in Cyber Security
The cyber security field offers various job roles, each with specific responsibilities and skill requirements.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Manages the organization’s IT security division. According to a survey by CSO Online, CISOs are increasingly responsible for aligning security strategies with business goals.
- Forensic Computer Analyst: Investigates security breaches and gathers evidence. The EC-Council emphasizes the importance of digital forensics in incident response.
- Information Security Analyst: Protects computer systems and networks. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a significant growth in demand for information security analysts.
- Penetration Tester: Attempts to breach computer and network security systems to identify vulnerabilities. Offensive Security provides training and certifications for penetration testers.
- IT Security Engineer: Plans and implements security measures to protect data and systems. CompTIA offers certifications relevant to IT security engineers.
- Security Architect: Designs and maintains network security infrastructure. Gartner highlights the role of security architects in creating robust security frameworks.
- Security Systems Administrator: Installs, administers, and troubleshoots security systems. SANS Institute offers courses and certifications for security systems administrators.
- IT Security Consultant: Advises organizations on protecting sensitive data. The Institute of Management Consultants USA provides resources for IT security consultants.
6. Cyber Security Certifications
Certifications validate your knowledge and skills in cyber security, enhancing your career prospects.
- CompTIA Security+: Validates foundational cyber security skills.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): Focuses on ethical hacking techniques.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): Demonstrates expertise in information security.
7. How to Start Learning Cyber Security
Starting a career in cyber security requires a structured approach and continuous learning.
- Understand the Basics: Start with fundamental concepts like networking, operating systems, and security principles.
- Choose a Specialization: Select a specific area of cyber security that interests you, such as network security, ethical hacking, or incident response.
- Get Certified: Obtain relevant certifications to validate your skills and knowledge.
- Gain Practical Experience: Participate in internships, volunteer work, or personal projects to gain hands-on experience.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest trends and technologies in cyber security through continuous learning and professional development.
8. Resources for Learning Cyber Security
Numerous resources are available to help you learn cyber security.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udacity, and edX offer cyber security courses from top universities and institutions.
- Books: “Security Engineering” by Ross Anderson and “Practical Malware Analysis” by Michael Sikorski and Andrew Honig are excellent resources.
- Websites and Blogs: SANS Institute, Krebs on Security, and Dark Reading provide valuable insights and news on cyber security.
- Forums and Communities: Participate in online forums like Reddit’s r/cyber security and Stack Exchange’s Information Security to connect with other professionals and learn from their experiences.
9. The Future of Cyber Security
Cyber security is an evolving field with continuous advancements and challenges. Key trends shaping the future of cyber security include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to enhance threat detection, automate incident response, and improve security defenses.
- Cloud Security: As more organizations migrate to the cloud, securing cloud environments is becoming increasingly critical.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Security: The proliferation of IoT devices introduces new security challenges, requiring robust measures to protect these devices and their data.
- Quantum Computing: The emergence of quantum computing poses a threat to current encryption methods, driving the development of quantum-resistant cryptography.
- Zero Trust Security: Adopting a zero-trust approach, which assumes that no user or device is trusted by default, is becoming increasingly important for securing modern IT environments.
10. LEARNS.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Cyber Security Education
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing high-quality education and resources to help you succeed in your cyber security journey. We offer:
- Comprehensive Courses: Covering a wide range of cyber security topics, from beginner to advanced levels.
- Expert Instructors: Learning from experienced professionals with real-world expertise.
- Hands-On Labs: Gaining practical experience through hands-on exercises and simulations.
- Career Guidance: Receiving personalized career advice and support to help you achieve your professional goals.
FAQ About Cyber Security Basics
What are the most important basic cyber security skills to learn?
Understanding networking fundamentals, operating systems, and security principles is crucial. Additionally, learning about common attack types, cryptography, and incident response is essential.
How long does it take to learn the basics of cyber security?
It typically takes a few months to grasp the basics, depending on your learning pace and dedication. Consistent study and hands-on practice are key.
What are the best resources for learning cyber security basics?
Online courses, books, websites, and forums are excellent resources. Platforms like Coursera, Udacity, and SANS Institute offer valuable learning materials.
Do I need a technical background to learn cyber security?
While a technical background is helpful, it’s not always necessary. Many resources are available for beginners with little to no prior experience.
What certifications should I consider to start a career in cyber security?
CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) are valuable certifications to consider.
What are the common entry-level jobs in cyber security?
Entry-level jobs include security analyst, IT security specialist, and network security administrator.
How can I stay updated with the latest cyber security threats?
Follow cyber security news websites, blogs, and forums. Attend conferences and webinars to stay informed about emerging threats and technologies.
What is ethical hacking, and why is it important?
Ethical hacking involves using hacking techniques to identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks to improve security. It is important for proactively addressing security weaknesses.
How does cryptography help in cyber security?
Cryptography ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data through encryption techniques, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
What is incident response, and why is it crucial?
Incident response involves handling security incidents, such as data breaches and malware infections. It is crucial for minimizing the impact of attacks and restoring normal operations.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of cyber security is essential for protecting yourself and your organization from cyber threats. By learning key terminologies, common attack types, and essential security measures, you can build a strong foundation for a successful career in cyber security. Remember to continuously update your knowledge and skills to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Ready to take the next step in your cyber security education? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive courses and resources. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, we have everything you need to succeed in this dynamic and critical field.
Contact Us:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: learns.edu.vn