Egypt’s captivating history and culture, brimming with ancient monuments, scorching deserts, and bustling cities, hold a significant place in education worldwide. This article, brought to you by LEARNS.EDU.VN, delves into when Egyptian civilization typically enters the curriculum, covering different educational levels and providing insight into topics such as geography, history, and its impact on modern culture. Find comprehensive resources and enhance your knowledge with our learning paths, empowering your educational journey.
1. What Age Do Students Typically Learn About Ancient Egypt?
Students are generally introduced to Ancient Egypt between grades 4 and 7, which corresponds to ages 9-13. This introduction is often part of a broader history or social studies curriculum that covers ancient civilizations. According to the National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS), elementary school curricula often focus on introducing students to different cultures and time periods, which includes Ancient Egypt.
- Grade 4 (Ages 9-10): Introduction to world geography and ancient civilizations, including Egypt.
- Grades 5-7 (Ages 10-13): More detailed study of Ancient Egypt, often as part of world history or social studies.
2. What Aspects of Ancient Egypt Are Covered in School Curricula?
School curricula typically cover various facets of Ancient Egypt to provide a holistic understanding of this ancient civilization. These include:
- Geography and Environment: The significance of the Nile River, the division of Egypt into Upper and Lower Egypt, and the role of the desert.
- History and Chronology: The dynasties of pharaohs, key events, and periods such as the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom.
- Social Structure: Social classes, roles of pharaohs, priests, scribes, and the common people.
- Religion and Mythology: Egyptian gods and goddesses, beliefs about the afterlife, mummification practices, and the significance of temples.
- Culture and Daily Life: Egyptian art, architecture (pyramids, temples), hieroglyphics, agriculture, and everyday life.
- Achievements and Contributions: Advances in mathematics, medicine, astronomy, and engineering.
3. How Is Ancient Egypt Integrated Into History Lessons at the Elementary Level?
At the elementary level, Ancient Egypt is often presented in a simplified and engaging manner to capture the interest of young learners. This approach generally includes:
- Storytelling: Using stories of pharaohs like Tutankhamun and Cleopatra to make history more relatable.
- Visual Aids: Employing images, videos, and illustrations of pyramids, temples, and artifacts to enhance understanding.
- Hands-On Activities: Incorporating activities such as creating Egyptian art, writing hieroglyphics, or building miniature pyramids.
- Comparative Studies: Comparing Egyptian civilization with other ancient cultures, such as Mesopotamia or Ancient Greece, to highlight similarities and differences.
According to research from the American Historical Association, hands-on and visual learning methods significantly improve the retention and understanding of historical concepts among elementary students.
4. How Is the Nile River’s Role in Ancient Egypt Taught?
The Nile River is a central theme in the study of Ancient Egypt, and its role is emphasized across various educational levels. Key points covered include:
- Source of Life: Explaining how the Nile provided water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation.
- Annual Flooding: Describing the importance of the annual floods that deposited fertile silt, crucial for agriculture.
- Agriculture and Economy: Highlighting how the Nile supported agriculture, which formed the backbone of the Egyptian economy.
- Navigation and Trade: Detailing how the Nile facilitated trade and communication throughout Egypt.
The Nile’s influence on Egyptian civilization is so profound that it is often referred to as the “lifeblood” of Egypt.
5. What Are the Main Periods of Ancient Egyptian History That Students Learn About?
Students typically learn about the following main periods of Ancient Egyptian history:
- Early Dynastic Period (c. 3100-2686 BCE): Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under King Narmer.
- Old Kingdom (c. 2686-2181 BCE): The age of pyramid building, including the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
- First Intermediate Period (c. 2181-2055 BCE): A period of political instability and decentralization.
- Middle Kingdom (c. 2055-1650 BCE): A period of reunification and cultural revival.
- Second Intermediate Period (c. 1650-1550 BCE): Another period of instability, marked by the rule of the Hyksos.
- New Kingdom (c. 1550-1069 BCE): Egypt’s golden age, with powerful pharaohs like Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, and Ramesses II.
- Third Intermediate Period (c. 1069-664 BCE): A period of decline and foreign invasions.
- Late Period (c. 664-332 BCE): A period of foreign rule by the Persians, followed by independence and eventual conquest by Alexander the Great.
6. How Do Students Learn About the Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt?
Pharaohs are a key focus in the study of Ancient Egypt, and students learn about their roles, responsibilities, and accomplishments. This typically includes:
- Role and Responsibilities: Understanding the pharaoh as both a political and religious leader, considered a god on earth.
- Famous Pharaohs: Learning about notable pharaohs such as Khufu (builder of the Great Pyramid), Hatshepsut (a female pharaoh), Akhenaten (who introduced monotheism), Tutankhamun (whose tomb was discovered intact), and Ramesses II (a great builder and warrior).
- Pyramids and Tombs: Studying the pyramids as tombs for the pharaohs and understanding the significance of tomb artifacts.
- Power and Authority: Examining how pharaohs maintained power through military strength, religious authority, and control of resources.
7. What Role Does Religion and Mythology Play in Lessons About Ancient Egypt?
Religion and mythology are integral to understanding Ancient Egyptian culture, and they are covered extensively in school curricula. Key aspects include:
- Gods and Goddesses: Learning about major deities such as Ra (the sun god), Osiris (god of the afterlife), Isis (goddess of magic and motherhood), Horus (god of the sky), and Anubis (god of mummification).
- Beliefs About the Afterlife: Understanding the Egyptian belief in the afterlife and the practices associated with it, such as mummification and the weighing of the heart ceremony.
- Temples and Rituals: Studying the role of temples as places of worship and centers of religious activity, and learning about the rituals performed by priests.
- Myths and Legends: Exploring popular myths and legends, such as the story of Osiris and Isis, to understand Egyptian values and beliefs.
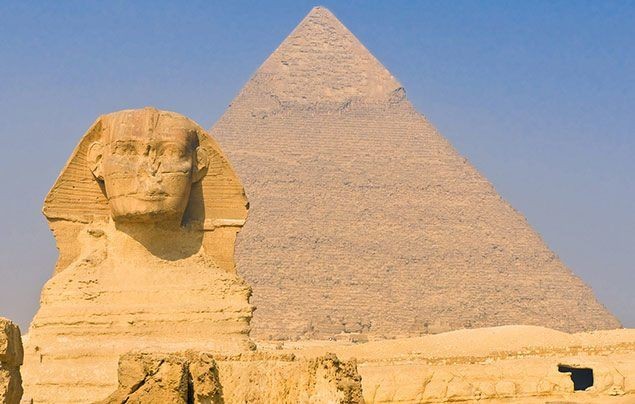
8. How Are the Pyramids and Other Architectural Marvels Taught in Schools?
The pyramids and other architectural marvels of Ancient Egypt, such as temples and obelisks, are a significant part of the curriculum. This coverage typically includes:
- Pyramids: Studying the construction techniques used to build the pyramids, their purpose as tombs for the pharaohs, and the symbolism behind their shape.
- Temples: Learning about the design and function of temples, such as Karnak and Luxor, and their role in religious rituals.
- Obelisks: Understanding the significance of obelisks as symbols of royal power and their placement at temple entrances.
- Engineering and Mathematics: Highlighting the advanced engineering and mathematical skills of the ancient Egyptians, which enabled them to construct these monumental structures.
9. What Do Students Learn About Egyptian Art and Hieroglyphics?
Egyptian art and hieroglyphics provide valuable insights into the culture and beliefs of Ancient Egypt, and they are important components of the curriculum.
- Art: Studying various forms of Egyptian art, including sculptures, paintings, and reliefs, and understanding their stylistic characteristics and symbolism.
- Hieroglyphics: Learning about the hieroglyphic writing system, its use on monuments and papyrus, and the process of deciphering it.
- Rosetta Stone: Understanding the significance of the Rosetta Stone in unlocking the meaning of hieroglyphics.
- Cultural Insights: Exploring how art and hieroglyphics reflect Egyptian religious beliefs, social structure, and daily life.
10. How Is Daily Life in Ancient Egypt Covered in Educational Settings?
Understanding daily life in Ancient Egypt helps students connect with the civilization on a personal level. Topics covered typically include:
- Social Classes: Learning about the different social classes, from the pharaoh and nobles to scribes, priests, soldiers, and farmers.
- Occupations: Studying the various occupations of ancient Egyptians, such as farming, crafts, trade, and military service.
- Food and Clothing: Exploring the typical diet and clothing of ancient Egyptians.
- Family Life: Learning about family structures, roles of men and women, and the upbringing of children.
- Recreation and Entertainment: Discovering forms of recreation and entertainment, such as games, festivals, and music.
11. How Does the Curriculum Address the Decline of Ancient Egypt?
The curriculum addresses the decline of Ancient Egypt by examining the factors that contributed to its eventual fall. These factors typically include:
- Internal Conflicts: Studying the internal power struggles and political instability that weakened the kingdom.
- Economic Issues: Learning about economic challenges, such as resource depletion and trade disruptions.
- Foreign Invasions: Examining the invasions by foreign powers, such as the Persians, Greeks, and Romans, which led to the loss of Egyptian independence.
- Cultural Changes: Understanding the gradual erosion of Egyptian culture and the adoption of foreign customs.
12. What Resources Are Available for Students to Learn About Ancient Egypt?
Numerous resources are available for students to learn about Ancient Egypt, both in and out of the classroom. These include:
- Textbooks: Standard textbooks used in history and social studies courses provide comprehensive coverage of Ancient Egypt.
- Library Books: Libraries offer a wide range of books, both fiction and non-fiction, about Ancient Egypt.
- Online Resources: Websites such as the British Museum, the Metropolitan Museum of Art, and educational platforms like LEARNS.EDU.VN offer valuable information, images, and interactive resources.
- Documentaries and Videos: Documentaries and educational videos provide visual and engaging content about Ancient Egypt.
- Museums: Visiting museums with Egyptian collections offers students the opportunity to see artifacts and exhibits firsthand.
13. How Do Teachers Make Ancient Egypt Engaging for Students?
Teachers employ various strategies to make the study of Ancient Egypt engaging and enjoyable for students. These strategies include:
- Interactive Lessons: Incorporating interactive activities, such as group discussions, debates, and role-playing exercises.
- Multimedia Presentations: Using multimedia presentations with images, videos, and animations to bring Ancient Egypt to life.
- Creative Projects: Assigning creative projects, such as writing stories, creating artwork, or building models of Egyptian structures.
- Field Trips: Organizing field trips to museums or exhibits related to Ancient Egypt.
- Guest Speakers: Inviting guest speakers, such as archaeologists or historians, to share their expertise with students.
According to a study by the National Education Association, student engagement is significantly higher when teachers use a variety of teaching methods and incorporate interactive activities.
14. How Is Ancient Egypt Taught at the High School and College Levels?
At the high school and college levels, the study of Ancient Egypt becomes more in-depth and analytical. Courses may cover:
- Advanced Topics: Exploring specialized topics such as Egyptian religion, art, architecture, and social history in greater detail.
- Primary Sources: Analyzing primary source materials, such as Egyptian texts and inscriptions, to gain firsthand insights into the civilization.
- Research Projects: Conducting independent research projects on specific aspects of Ancient Egypt.
- Historiography: Examining the different interpretations and perspectives on Ancient Egyptian history.
- Archaeology: Studying the methods and findings of archaeological excavations in Egypt.
At the college level, students may also have the opportunity to study Egyptology, a specialized field that focuses on the study of Ancient Egypt.
15. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Ancient Egypt That Are Addressed in Education?
Education about Ancient Egypt often addresses several common misconceptions, including:
- Slavery: Clarifying that while slavery existed in Ancient Egypt, it was not as widespread or central to the economy as in other ancient societies.
- Pyramid Construction: Emphasizing that the pyramids were built by skilled laborers, not slaves, who were paid and respected for their work.
- Mummification: Explaining that mummification was not a common practice for all Egyptians, but rather a ritual reserved for the elite.
- Alien Influence: Debunking theories about alien influence on Egyptian architecture and technology, highlighting the ingenuity and skill of the ancient Egyptians themselves.
16. What Is the Significance of Tutankhamun in Egyptian Education?
Tutankhamun, often referred to as King Tut, holds a special place in Egyptian education due to the discovery of his intact tomb in 1922. This discovery:
- Sparked Interest: Generated immense public interest in Ancient Egypt, making it a popular topic for study.
- Provided Insights: Provided invaluable insights into the burial practices, religious beliefs, and material culture of the New Kingdom.
- Educational Tool: Served as an educational tool for teaching about Ancient Egypt, with his tomb artifacts providing tangible examples of Egyptian art, craftsmanship, and technology.
17. How Has the Discovery of the Rosetta Stone Influenced Egyptian Education?
The discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799 was a pivotal moment in the study of Ancient Egypt. It:
- Deciphered Hieroglyphics: Enabled scholars to decipher the hieroglyphic writing system, unlocking the vast body of Egyptian texts and inscriptions.
- Expanded Knowledge: Expanded our knowledge of Egyptian history, religion, and culture, providing new insights into the civilization.
- Educational Resource: Became an essential resource for educators, allowing them to teach about hieroglyphics and Egyptian language with greater accuracy and depth.
18. What Ethical Considerations Are Discussed When Teaching About Ancient Egypt?
When teaching about Ancient Egypt, ethical considerations related to archaeology and the preservation of cultural heritage are often discussed. These considerations include:
- Looting and Antiquities Trade: Examining the ethical issues surrounding the looting of archaeological sites and the illegal trade in antiquities.
- Repatriation: Discussing the repatriation of Egyptian artifacts from museums and private collections around the world.
- Preservation: Highlighting the importance of preserving Egyptian monuments and archaeological sites for future generations.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Promoting cultural sensitivity and respect for Egyptian culture and heritage.
19. How Does LEARNS.EDU.VN Enhance Learning About Ancient Egypt?
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to enhance learning about Ancient Egypt, including:
- Comprehensive Articles: Detailed articles covering various aspects of Ancient Egyptian history, culture, and society.
- Visual Aids: Images, videos, and interactive multimedia to bring Ancient Egypt to life.
- Learning Paths: Structured learning paths that guide students through the key topics and concepts.
- Expert Insights: Information from experts in the field of Egyptology and archaeology.
- Community Forum: A community forum where students can connect with each other, ask questions, and share their knowledge.
20. What Career Paths Can Stem From Studying Ancient Egypt?
Studying Ancient Egypt can lead to a variety of exciting career paths, including:
- Egyptologist: Conducting research on Ancient Egypt and teaching at the university level.
- Archaeologist: Excavating and studying archaeological sites in Egypt.
- Museum Curator: Managing and interpreting Egyptian collections in museums.
- Historian: Writing and teaching about Ancient Egyptian history.
- Teacher: Teaching about Ancient Egypt at the primary, secondary, or post-secondary level.
- Tour Guide: Leading tours of Egyptian monuments and archaeological sites.
- Writer/Filmmaker: Creating books, articles, documentaries, and films about Ancient Egypt.
21. What Modern Discoveries Continue to Shape Our Understanding of Ancient Egypt?
Modern discoveries continually reshape our understanding of Ancient Egypt, including:
- New Tombs: The discovery of new tombs and burial sites provides fresh insights into Egyptian funerary practices and beliefs.
- Archaeological Finds: Archaeological finds, such as artifacts, inscriptions, and skeletal remains, offer new information about Egyptian daily life, technology, and social structure.
- Scientific Analysis: Scientific analysis of mummies, artifacts, and DNA provides insights into Egyptian health, diet, and genetic history.
- Technological Advances: Technological advances, such as remote sensing and 3D modeling, allow archaeologists to explore and document Egyptian sites with greater precision.
22. How Does Ancient Egypt Influence Modern Culture?
Ancient Egypt continues to influence modern culture in numerous ways, including:
- Art and Architecture: Egyptian motifs and designs are incorporated into modern art, architecture, and fashion.
- Literature and Film: Ancient Egypt is a popular subject in literature, film, and television, inspiring countless stories and adaptations.
- Popular Culture: Egyptian symbols and imagery are used in popular culture, such as in video games, music, and advertising.
- Tourism: Egyptian monuments and archaeological sites attract millions of tourists each year, contributing to the country’s economy.
23. What Are Some Misconceptions About Egyptian Mummies?
There are several common misconceptions about Egyptian mummies:
- Mummies Were Always Royalty: Not all mummies were royalty. While pharaohs and nobles were often mummified, common people could also undergo the process, although with simpler methods.
- Mummies Were Always Wrapped the Same Way: The style of wrapping mummies varied over different periods of Egyptian history, reflecting changing religious beliefs and practices.
- Mummies Were Only Made in Ancient Egypt: While Egypt is famous for its mummies, other cultures around the world, such as in South America, also practiced mummification.
- Mummies Always Had Elaborate Tombs: While pharaohs had elaborate tombs filled with treasures, the tombs of common people were much simpler.
24. How Do Egyptian Myths and Legends Inform Our Understanding of Their Culture?
Egyptian myths and legends are crucial for understanding their culture because:
- Explaining Natural Phenomena: Myths often explained natural phenomena, such as the rising and setting of the sun or the flooding of the Nile, through stories involving gods and goddesses.
- Moral and Ethical Lessons: Many myths taught moral and ethical lessons, providing guidelines for how people should behave.
- Religious Beliefs: Myths were deeply intertwined with religious beliefs, offering insights into the roles and characteristics of the gods, the afterlife, and the creation of the world.
- Cultural Values: Myths reflect and reinforce cultural values, such as the importance of family, justice, and order.
25. How Did the Egyptian Calendar System Work, and What Was Its Importance?
The Egyptian calendar system was based on:
- Solar Year: A solar year of 365 days, divided into 12 months of 30 days each, with an additional five days at the end.
- Agricultural Cycle: Tied to the agricultural cycle, with three seasons: Akhet (inundation), Peret (growing season), and Shemu (harvest).
- Civil and Religious Purposes: Used for both civil and religious purposes, helping to regulate agricultural activities and religious festivals.
- Accurate Timekeeping: Despite not accounting for the extra quarter day per year, the Egyptian calendar was remarkably accurate for its time, and it influenced the development of later calendar systems.
26. What Role Did Scribes Play in Ancient Egyptian Society?
Scribes were highly valued in Ancient Egyptian society because:
- Literacy: They were among the few who could read and write, making them essential for administrative and religious purposes.
- Record Keeping: Scribes kept records of taxes, census data, and other important information.
- Religious Texts: They copied religious texts, such as the Book of the Dead, and wrote inscriptions on monuments and tombs.
- Education: Scribes often served as teachers, passing on their knowledge to future generations.
- Power and Influence: Their literacy skills gave them significant power and influence in Egyptian society.
27. How Does LEARNS.EDU.VN Help Students Overcome Challenges in Learning About Ancient Egypt?
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers several ways to help students overcome challenges in learning about Ancient Egypt:
- Simplified Explanations: Providing simplified explanations of complex topics, making them easier to understand.
- Visual Learning: Using images, videos, and interactive multimedia to enhance visual learning.
- Structured Learning Paths: Offering structured learning paths that guide students through the key topics and concepts in a logical order.
- Expert Support: Providing access to expert support through articles, forums, and Q&A sessions.
- Engaging Content: Creating engaging and interactive content that captures students’ interest and motivates them to learn.
28. How Did the Roles of Men and Women Differ in Ancient Egypt?
The roles of men and women in Ancient Egypt differed in some ways:
- Men: Typically worked in occupations such as farming, crafts, trade, and the military.
- Women: Primarily responsible for managing the household, raising children, and performing domestic tasks.
- Legal Rights: Women had significant legal rights, including the right to own property, conduct business, and initiate divorce.
- Social Status: Women could achieve high social status and even rule as pharaohs, such as Hatshepsut and Cleopatra.
- Religious Roles: Women played important roles in religious ceremonies and could serve as priestesses.
29. What Were Some of the Most Important Inventions and Innovations of Ancient Egypt?
Ancient Egypt made numerous important inventions and innovations, including:
- Writing System: The hieroglyphic writing system, which allowed them to record their history, beliefs, and knowledge.
- Calendar: A solar calendar of 365 days, which influenced the development of later calendar systems.
- Mathematics: Advances in mathematics, including geometry and algebra, which were used in construction and surveying.
- Medicine: Knowledge of anatomy, surgery, and herbal remedies, which allowed them to treat a variety of illnesses.
- Irrigation: Irrigation systems that allowed them to cultivate crops in the arid environment of the Nile Valley.
- Construction Techniques: Advanced construction techniques, such as the use of ramps and levers, which enabled them to build monumental structures like the pyramids.
30. How Can Studying Ancient Egypt Help Students Develop Critical Thinking Skills?
Studying Ancient Egypt can help students develop critical thinking skills by:
- Analyzing Evidence: Evaluating primary and secondary sources to form their own interpretations of Egyptian history and culture.
- Interpreting Artifacts: Interpreting artifacts, inscriptions, and other archaeological evidence to understand Egyptian beliefs, practices, and technology.
- Comparing Cultures: Comparing Egyptian civilization with other ancient cultures to identify similarities and differences.
- Evaluating Sources: Evaluating the reliability and validity of different sources of information about Ancient Egypt.
- Forming Arguments: Constructing logical arguments and supporting them with evidence.
31. Why Is Egypt’s Geography So Important to Its History?
Egypt’s geography is crucial to its history for several reasons:
- Nile River: The Nile River provided water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation, making agriculture possible in the arid environment.
- Fertile Soil: The annual flooding of the Nile deposited fertile silt, which was essential for growing crops.
- Natural Barriers: The deserts to the east and west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north provided natural barriers that protected Egypt from invasion.
- Trade and Communication: The Nile served as a highway for trade and communication, connecting Upper and Lower Egypt and facilitating contact with other regions.
- Resources: Egypt was rich in natural resources, such as stone, gold, and copper, which were used for building monuments, creating art, and making tools.
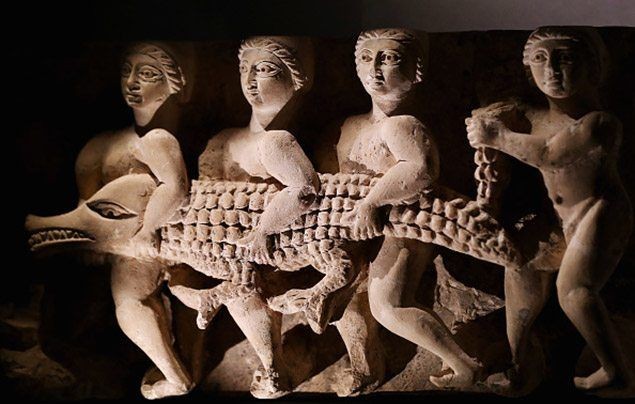
32. What Role Did Animals Play in Ancient Egyptian Society?
Animals played a significant role in Ancient Egyptian society:
- Deities: Many gods and goddesses were associated with animals, such as Ra (the sun god) with the falcon, Anubis (god of mummification) with the jackal, and Hathor (goddess of love and beauty) with the cow.
- Agriculture: Animals, such as oxen and donkeys, were used for plowing fields and transporting goods.
- Companions: Animals, such as cats and dogs, were kept as pets and companions.
- Symbolism: Animals were used as symbols of power, protection, and good fortune.
- Food Source: Animals, such as fish, birds, and cattle, were an important source of food.
33. How Did Ancient Egyptians Use Mathematics in Their Daily Lives?
Ancient Egyptians used mathematics in various aspects of their daily lives:
- Construction: Mathematics was essential for constructing pyramids, temples, and other monumental structures.
- Surveying: Geometry was used to survey land and measure fields, ensuring fair distribution of property.
- Accounting: Arithmetic was used to keep track of taxes, wages, and other financial transactions.
- Calendar: Mathematics was used to develop and maintain the calendar system.
- Trade: Mathematics was used to calculate prices and exchange rates in trade.
34. What Were Some of the Most Important Religious Festivals in Ancient Egypt?
Some of the most important religious festivals in Ancient Egypt included:
- Opet Festival: A celebration of the fertility of the land and the divine union of Amun and Mut.
- Valley Festival: A festival honoring the dead, during which people visited the tombs of their ancestors and offered them food and drink.
- Wag Festival: A celebration of the afterlife and the rebirth of Osiris.
- New Year Festival: A celebration of the beginning of the new year, marked by feasting and religious rituals.
- Coronation Festival: A celebration of the pharaoh’s accession to the throne.
35. How Did Ancient Egyptians View the Afterlife?
Ancient Egyptians had a complex and elaborate view of the afterlife:
- Journey to the Underworld: They believed that after death, the soul embarked on a journey through the underworld, facing various trials and challenges.
- Weighing of the Heart: The heart was weighed against the feather of Ma’at (truth and justice) to determine whether the person was worthy of entering the afterlife.
- Osiris’s Judgment: Osiris, the god of the afterlife, judged the dead and decided whether they would be granted eternal life.
- Mummification: Mummification was practiced to preserve the body for the afterlife.
- Provisioning the Tomb: Tombs were filled with food, drink, and other items that the deceased would need in the afterlife.
36. What Are Some Common Archaeological Sites in Egypt That Students Might Learn About?
Students often learn about the following archaeological sites in Egypt:
- Giza: Home to the Great Pyramid, the Sphinx, and other pyramids and tombs.
- Karnak: A vast complex of temples, chapels, pylons, and other buildings.
- Luxor: Home to the Luxor Temple and the Valley of the Kings, where many pharaohs were buried.
- Abu Simbel: A complex of temples built by Ramesses II, including the Great Temple and the Small Temple.
- Saqqara: Home to the Step Pyramid of Djoser, one of the oldest stone structures in Egypt.
- Valley of the Queens: A burial site for the wives of pharaohs.
37. How Did the Construction of the Suez Canal Impact Egypt?
The construction of the Suez Canal had a profound impact on Egypt:
- Economic Benefits: It provided a new source of revenue through tolls and increased trade.
- Strategic Importance: It made Egypt a strategically important location, as the canal provided a shortcut for ships traveling between Europe and Asia.
- Foreign Influence: It led to increased foreign influence in Egypt, as European powers sought to control the canal.
- British Occupation: It was a key factor in the British occupation of Egypt in 1882.
- Modernization: It contributed to the modernization of Egypt, as the country sought to improve its infrastructure and economy.
38. How Does Ancient Egypt Compare to Other Ancient Civilizations?
Ancient Egypt shares some similarities with other ancient civilizations, but it also has unique characteristics:
| Feature | Ancient Egypt | Mesopotamia | Ancient Greece | Ancient Rome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geography | Nile River, desert environment | Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, fertile crescent | Mountainous terrain, scattered islands | Italian Peninsula, varied climate |
| Government | Pharaohs, centralized government | City-states, empires | City-states, democracy, oligarchy | Republic, Empire |
| Religion | Polytheistic, afterlife beliefs | Polytheistic, ziggurats | Polytheistic, mythology | Polytheistic, state religion |
| Writing | Hieroglyphics | Cuneiform | Alphabet | Latin alphabet |
| Architecture | Pyramids, temples | Ziggurats, palaces | Temples, theaters | Aqueducts, roads, amphitheaters |
| Achievements | Mathematics, medicine, irrigation | Law, writing, wheel | Philosophy, democracy, art | Law, engineering, military strategy |
| Social Structure | Pharaoh, nobles, scribes, commoners, slaves | Kings, priests, scribes, commoners, slaves | Citizens, metics, slaves | Patricians, plebeians, slaves |





By exploring the curriculum and resources provided by LEARNS.EDU.VN, students can gain a deeper appreciation for this remarkable civilization.
Are you ready to delve deeper into the mysteries of Ancient Egypt? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and discover a wealth of resources to fuel your learning journey! Whether you’re looking for comprehensive articles, engaging videos, or expert insights, we have everything you need to expand your knowledge and achieve your academic goals. Our structured learning paths and supportive community forum make learning accessible and enjoyable for all. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to explore the wonders of Ancient Egypt with LEARNS.EDU.VN.
Contact us:
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
FAQ About Learning About Egypt
-
In what grade do students generally start learning about Ancient Egypt?
Students usually begin learning about Ancient Egypt in grades 4-7, around ages 9-13, as part of a broader study of ancient civilizations. -
What are the primary topics covered when teaching about Ancient Egypt?
The main topics include geography, history, social structure, religion, culture, and significant achievements like pyramids and hieroglyphics. -
How is the role of the Nile River emphasized in lessons about Ancient Egypt?
The Nile’s role as a vital source of water, fertile soil, transportation, and its impact on agriculture and economy are heavily emphasized. -
What key periods of Ancient Egyptian history do students typically study?
Students learn about the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom, along with the significant pharaohs and events that defined each era. -
Why is King Tutankhamun so significant in the study of Ancient Egypt?
The discovery of King Tut’s intact tomb in 1922 sparked great public interest and provided invaluable insights into Egyptian burial practices and culture. -
What impact did the Rosetta Stone have on our understanding of Ancient Egypt?
The Rosetta Stone enabled scholars to decipher hieroglyphics, unlocking a vast body of Egyptian texts and greatly expanding our knowledge of their history and culture. -
What ethical considerations are addressed when teaching about Ancient Egypt?
Ethical considerations include issues of looting, the antiquities trade, repatriation of artifacts, and the importance of preserving cultural heritage. -
How does studying Ancient Egypt help students develop critical thinking skills?
Analyzing historical sources, interpreting artifacts, and comparing Egyptian culture with others enhances students’ critical thinking and analytical abilities. -
What are some resources LEARNS.EDU.VN provides to help students learn about Ancient Egypt?
learns.edu.vn offers detailed articles, images, videos, structured learning paths, and expert insights to enhance the learning experience. -
How did the building of the Suez Canal change Egypt’s place in the world?
The Suez Canal increased Egypt’s strategic importance and modernized the country, while also leading to increased foreign influence and eventual British occupation.