Does Learning Increase Iq? Absolutely, and LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to guide you through the research-backed strategies and insights to maximize your cognitive potential. A wealth of research suggests that education has a positive, causal effect on cognitive abilities, boosting your intellectual capacity. Explore with us the pivotal role of education in shaping and enhancing intelligence, and how continuous learning can lead to measurable improvements in cognitive function.
1. What is the Link Between Learning and IQ?
Does learning increase IQ? Yes, studies consistently show a positive correlation. Education appears to be a robust and durable method for enhancing intelligence, as demonstrated by research published in Psychological Science. The connection between learning and IQ is not merely correlational but causal, with education playing a significant role in cognitive development.
- Causal Relationship: Education directly contributes to higher intelligence test scores.
- Robustness: The effect is observed across different age groups and cognitive domains.
- Durability: The benefits of education on intelligence persist over time.
1.1. Understanding the Correlation Between Education and Intelligence
The correlation between education and intelligence is well-documented. However, it’s essential to understand the nuances of this relationship. While it might seem intuitive that more intelligent individuals pursue higher education, research increasingly supports the idea that education itself enhances intelligence.
- Selection Bias: It’s crucial to account for selection bias, where inherently intelligent individuals are more likely to pursue higher education.
- Causal Inference: Studies using quasiexperimental designs help establish a causal link, showing that increased education leads to higher IQ scores, even when controlling for pre-existing intelligence.
1.2. How Does Learning Impact Cognitive Abilities?
Does learning increase IQ by improving specific cognitive functions? Yes, learning impacts various cognitive abilities essential for overall intelligence. These include:
- Memory: Education enhances memory capacity and retrieval efficiency.
- Reasoning: Formal education trains individuals in logical and analytical reasoning.
- Problem-Solving: Learning equips individuals with strategies and knowledge to tackle complex problems effectively.
- Processing Speed: Engaging with educational material improves cognitive processing speed.
 Cognitive Abilities Enhanced By Learning
Cognitive Abilities Enhanced By Learning
2. What Research Says: Studies on Education and IQ
Does learning increase IQ according to scientific studies? Absolutely. A meta-analysis published in Psychological Science reviewed numerous studies employing quasiexperimental methods to examine the impact of education on intelligence. The findings consistently show a positive effect of education on cognitive abilities.
2.1. Meta-Analysis of Quasiexperimental Studies
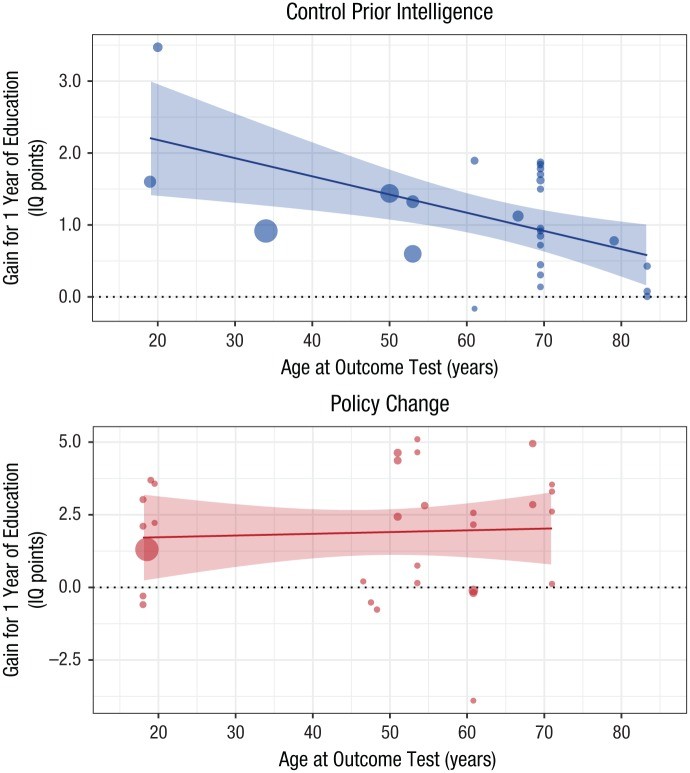
The meta-analysis included 42 datasets involving over 600,000 participants, assessing the impact of education on cognitive abilities through three main study designs:
- Control Prior Intelligence: Longitudinal studies that control for earlier intelligence levels.
- Policy Change: Studies using changes in compulsory schooling policies as instrumental variables.
- School-Age Cutoff: Regression-discontinuity designs based on school-entry age cutoffs.
The results indicated that each additional year of education is associated with an increase of approximately 1 to 5 IQ points.
2.2. Key Findings From Landmark Studies
Several landmark studies have provided compelling evidence of the link between education and intelligence. For example:
- Brinch and Galloway (2012): Utilized a 1960s educational reform in Norway, which increased compulsory education by 2 years. The study found that an additional year of schooling led to an increase of approximately 3.7 IQ points.
- Cahan and Cohen (1989): Examined over 12,000 children in the Israeli school system and found that schooling had positive effects on cognitive abilities, roughly twice the effect of a year of age.
- Clouston et al. (2012): Analyzed data from U.S. and UK cohort studies, demonstrating that completing a university education was linked to higher cognitive ability in midlife, even when accounting for adolescent intelligence.
2.3. Statistical Significance of Educational Impact
The statistical significance of education’s impact on IQ is a crucial factor. Studies consistently show that the positive effects of education on cognitive abilities are not due to chance but reflect a genuine, causal relationship. This is supported by the following:
- P-values: Studies report low p-values, indicating a statistically significant effect of education on intelligence.
- Effect Sizes: The effect sizes, though varying, consistently show a positive impact of education on IQ scores.
- Confidence Intervals: Narrow confidence intervals around the effect size estimates further support the reliability of the findings.
3. How Much Does Education Increase IQ? Quantifying the Impact
Does learning increase IQ and by how much? Quantifying the impact of education on IQ reveals tangible benefits. Research suggests that each additional year of education can increase IQ scores by approximately 1 to 5 points.
3.1. IQ Point Increase Per Year of Education
Based on the meta-analysis of quasiexperimental studies, the average increase in IQ points per year of education ranges from 1 to 5 points. This range accounts for variations in study design, population, and cognitive measures used.
| Study Design | IQ Point Increase per Year of Education |
|---|---|
| Control Prior Intelligence | 1.197 |
| Policy Change | 2.056 |
| School-Age Cutoff | 5.229 |
| Overall | 3.394 |
3.2. Long-Term Cognitive Benefits
The long-term cognitive benefits of education are substantial. Completing higher education levels, such as a university degree, can lead to significant improvements in cognitive function that persist into midlife and beyond.
- Cognitive Reserve: Education contributes to building a cognitive reserve, which helps protect against age-related cognitive decline.
- Maintenance of Cognitive Skills: Continuous learning and intellectual engagement through education help maintain and enhance cognitive skills throughout life.
3.3. Impact on Different Cognitive Domains
Education’s impact varies across different cognitive domains. Some cognitive abilities, such as crystallized intelligence (knowledge and vocabulary), may benefit more directly from education than fluid intelligence (reasoning and problem-solving).
- Fluid Intelligence: Education promotes abstract thinking, logical reasoning, and problem-solving.
- Crystallized Intelligence: Education enhances knowledge acquisition, vocabulary, and general information.
- Composite Measures: Composite tests, which assess a mixture of fluid and crystallized skills, often show the most significant gains from education.
4. What Types of Learning Are Most Effective for Boosting IQ?
Does learning increase IQ, and are some forms of learning more effective than others? Yes, certain types of learning are particularly effective for boosting IQ. These include formal education, continuous learning, and engagement in cognitively stimulating activities.
4.1. Formal Education vs. Informal Learning
Formal education, such as schooling and university studies, provides a structured and comprehensive learning environment. However, informal learning, including self-directed study and experiential learning, also plays a crucial role in cognitive development.
- Formal Education: Offers structured curricula, expert guidance, and standardized assessments.
- Informal Learning: Allows for personalized learning, exploration of specific interests, and real-world application of knowledge.
4.2. Continuous Learning and Intellectual Engagement
Continuous learning and intellectual engagement are essential for maintaining and enhancing cognitive abilities throughout life. Engaging in lifelong learning activities, such as reading, taking courses, and pursuing hobbies, promotes cognitive flexibility and resilience.
- Lifelong Learning: Fosters cognitive growth, enhances problem-solving skills, and promotes intellectual curiosity.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Engaging in cognitively stimulating activities, such as puzzles, games, and creative pursuits, challenges the brain and enhances cognitive function.
4.3. The Role of Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are vital for intellectual development. Educational experiences that emphasize these skills, such as debates, research projects, and case studies, promote analytical reasoning and decision-making abilities.
- Analytical Reasoning: Enables individuals to evaluate information, identify patterns, and draw logical conclusions.
- Decision-Making: Equips individuals with the ability to assess options, weigh consequences, and make informed decisions.
5. What Factors Moderate the Impact of Education on IQ?
Does learning increase IQ consistently across different populations? The impact of education on IQ is moderated by various factors, including age, socioeconomic status, and the quality of education. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing the cognitive benefits of education.
5.1. Age at the Outcome Test
Age at the outcome test is a significant moderator of the effect of education on intelligence. Studies have shown that the cognitive benefits of education may decline with increasing age, suggesting that continuous learning is crucial for maintaining cognitive function over time.
- Early Education: Early educational interventions have lasting impacts on cognitive development.
- Lifelong Learning: Engaging in lifelong learning activities can help mitigate age-related cognitive decline and maintain intellectual abilities.
5.2. Socioeconomic Status and Access to Quality Education
Socioeconomic status (SES) plays a crucial role in access to quality education. Children from higher SES backgrounds often have access to better schools, resources, and educational opportunities, which can amplify the cognitive benefits of education.
- Educational Equity: Addressing educational inequities is essential for ensuring that all children have the opportunity to reach their cognitive potential.
- Resource Allocation: Investing in educational resources and support for disadvantaged students can help bridge the achievement gap and promote cognitive development.
5.3. Quality of Education and Curriculum Design
The quality of education and curriculum design significantly impact the cognitive benefits of learning. High-quality educational programs that emphasize critical thinking, problem-solving, and intellectual engagement are more effective at boosting IQ than rote learning or poorly designed curricula.
- Effective Teaching Methods: Implementing evidence-based teaching methods, such as active learning and personalized instruction, enhances cognitive outcomes.
- Curriculum Relevance: Designing curricula that are relevant, engaging, and aligned with real-world applications promotes deeper learning and cognitive development.
6. How to Optimize Learning for Maximum Cognitive Benefit?
Does learning increase IQ more effectively when optimized? Yes, optimizing learning strategies can maximize the cognitive benefits of education. This includes personalized learning, effective study techniques, and creating a supportive learning environment.
6.1. Personalized Learning Strategies
Personalized learning strategies tailor education to individual needs, interests, and learning styles. Identifying and addressing individual learning gaps, providing customized support, and allowing students to pursue their passions can enhance cognitive outcomes.
- Individualized Instruction: Tailoring instruction to meet the unique needs of each student.
- Adaptive Learning: Using technology to adjust the pace and content of instruction based on student performance.
6.2. Effective Study Techniques and Memory Enhancement
Effective study techniques and memory enhancement strategies improve learning efficiency and retention. These include:
- Spaced Repetition: Reviewing material at increasing intervals to enhance long-term memory.
- Active Recall: Testing oneself on the material to improve retention and understanding.
- Elaboration: Connecting new information to existing knowledge to create meaningful associations.
6.3. Creating a Supportive and Stimulating Learning Environment
A supportive and stimulating learning environment fosters intellectual curiosity, motivation, and engagement. This includes:
- Positive Reinforcement: Providing encouragement and recognition for effort and achievement.
- Collaborative Learning: Engaging in group projects and discussions to promote peer learning and social interaction.
- Access to Resources: Providing access to books, technology, and other educational resources to support learning.
7. What Are the Limitations of the Research?
While studies suggest that learning increases IQ, there are some limitations to consider. Understanding these limitations is crucial for interpreting the research findings and guiding future studies.
7.1. Methodological Challenges in IQ Research
IQ research faces several methodological challenges, including:
- Endogeneity: Difficulty in establishing causal relationships due to selection bias and confounding variables.
- Measurement Error: Inaccuracies in IQ testing and cognitive assessments.
- Generalizability: Limited generalizability of findings from specific populations to broader groups.
7.2. Defining and Measuring Intelligence
Defining and measuring intelligence is complex. IQ tests assess specific cognitive abilities but may not capture the full scope of intellectual capacity. Additionally, cultural and contextual factors can influence IQ scores.
- Multiple Intelligences: Recognizing that intelligence encompasses a range of cognitive abilities, not solely those measured by IQ tests.
- Cultural Bias: Addressing potential cultural biases in IQ testing to ensure fair and accurate assessment.
7.3. Unanswered Questions and Future Research Directions
Several questions remain unanswered regarding the relationship between education and intelligence. Future research should focus on:
- Longitudinal Studies: Conducting long-term studies to assess the lasting impact of education on cognitive function.
- Mechanism of Action: Investigating the underlying psychological mechanisms through which education enhances intelligence.
- Individual Differences: Exploring individual differences in the magnitude of the educational effect on IQ.
8. FAQ: Does Learning Increase IQ?
8.1. Can You Actually Increase Your IQ Through Learning?
Yes, learning can increase your IQ. While genetics play a role in intelligence, education and continuous learning can enhance cognitive abilities and raise IQ scores.
8.2. How Much Can Education Boost Your IQ?
Each additional year of education can increase IQ by approximately 1 to 5 points, depending on the quality of education, individual factors, and cognitive domains assessed.
8.3. Does Lifelong Learning Help Maintain High IQ?
Yes, lifelong learning helps maintain high IQ by promoting cognitive flexibility, resilience, and continuous intellectual engagement.
8.4. What Learning Methods Are Best for Enhancing Cognitive Function?
Personalized learning, active recall, spaced repetition, and engaging in cognitively stimulating activities are effective methods for enhancing cognitive function.
8.5. Are There Specific Skills That Benefit More From Education?
Both fluid intelligence (reasoning and problem-solving) and crystallized intelligence (knowledge and vocabulary) benefit from education, though the degree of impact may vary.
8.6. Is It Ever Too Late to Start Learning and Improving IQ?
No, it is never too late to start learning and improving IQ. Engaging in lifelong learning activities can enhance cognitive function at any age.
8.7. How Does Quality of Education Affect IQ Gains?
Higher quality education, characterized by effective teaching methods, relevant curricula, and supportive learning environments, leads to greater IQ gains compared to lower quality education.
8.8. Can Informal Learning Also Increase IQ?
Yes, informal learning, such as self-directed study, experiential learning, and pursuing hobbies, can also increase IQ by promoting cognitive development and intellectual curiosity.
8.9. Does Socioeconomic Status Influence the Impact of Education on IQ?
Yes, socioeconomic status influences the impact of education on IQ. Children from higher SES backgrounds often have access to better educational opportunities, which can amplify the cognitive benefits of education.
8.10. What Role Does Critical Thinking Play in Boosting IQ Through Education?
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in boosting IQ through education. Educational experiences that emphasize critical thinking skills promote analytical reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities.
9. Conclusion: Embracing Education for Cognitive Enhancement
Does learning increase IQ? The answer is a resounding yes! Education is a powerful tool for cognitive enhancement. By embracing lifelong learning, optimizing learning strategies, and fostering a supportive learning environment, individuals can unlock their cognitive potential and achieve intellectual growth.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing resources and guidance to help you on your learning journey. Our comprehensive courses, expert insights, and personalized learning strategies are designed to maximize your cognitive benefits and enhance your intellectual abilities. Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our offerings and start your journey towards cognitive enhancement.
Ready to unlock your cognitive potential? Explore our comprehensive courses and personalized learning strategies at LEARNS.EDU.VN today. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or call +1 555-555-1212. For any inquiries, reach out via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Let learns.edu.vn be your partner in lifelong learning and cognitive growth.