Learning how to swallow pills can be a game-changer for managing your health and well-being. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges some individuals face when it comes to taking medication in pill form, and we’re here to help you overcome them with confidence and ease. Unlock effective techniques, understand potential difficulties, and discover alternative methods to ensure you can take your medication without stress. Whether you’re dealing with pill anxiety, swallowing difficulties, or simply want to improve your technique, this guide provides expert tips and practical advice to make pill swallowing a breeze.
1. Understanding the Challenge of Swallowing Pills
Why is it that something so small can cause so much trouble? Swallowing pills can be a surprisingly common struggle. It’s not just about physical ability; psychological factors also play a role.
1.1. Why Some People Struggle with Pill Swallowing
Several factors contribute to the difficulty some people experience when swallowing pills.
- Anxiety: Fear of choking can create a self-fulfilling prophecy. Anxiety causes muscle tension, making swallowing even harder.
- Size and Shape: Large or oddly shaped pills can be intimidating and difficult to manage in the mouth.
- Dry Mouth: Saliva acts as a lubricant. If you have dry mouth (xerostomia), the pill may stick to your tongue or throat.
- Gag Reflex: Some individuals have a more sensitive gag reflex, triggered by the presence of a pill in the mouth.
- Past Trauma: A previous choking incident can create a lasting fear and aversion to swallowing pills.
- Physical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can affect swallowing ability (dysphagia), making it difficult to swallow solids and liquids, including pills.
1.2. Psychological Factors: Pill Anxiety
Pill anxiety is a real and significant barrier to medication adherence. It often stems from:
- Fear of Choking: This is the most common fear and can lead to panic and avoidance.
- Negative Past Experiences: A choking incident or unpleasant experience with a pill can create a conditioned fear response.
- Sensory Sensitivity: Some people are highly sensitive to the texture, taste, or size of pills, making them averse to swallowing them.
- Control Issues: Difficulty swallowing can make some people feel like they are losing control, leading to anxiety.
Understanding these psychological factors is the first step in addressing pill anxiety and developing effective coping strategies.
1.3. Physical Factors: Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a medical term for difficulty swallowing. It can result from various underlying conditions:
- Neurological Disorders: Stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis can affect the nerves and muscles involved in swallowing.
- Structural Abnormalities: Tumors, strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), or other structural issues can obstruct the passage of food and pills.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the tongue, throat, or esophageal muscles can impair swallowing ability.
- Achalasia: A condition where the esophagus doesn’t relax properly, making it difficult for food and pills to pass into the stomach.
If you suspect you have dysphagia, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation and treatment. A speech-language pathologist can perform a swallowing assessment and recommend appropriate therapies.
2. Proven Techniques for Easier Pill Swallowing
Fortunately, there are several evidence-based techniques that can significantly improve your ability to swallow pills with greater ease and confidence.
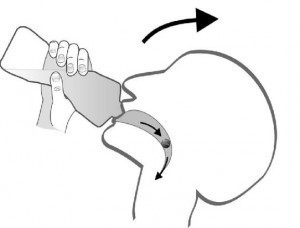
2.1. The Pop-Bottle Method for Tablets
This method is particularly effective for swallowing tablets and involves using a plastic bottle to create a suction effect.
Steps:
- Fill a plastic water or soda bottle with water.
- Place the tablet on your tongue.
- Tightly seal your lips around the opening of the bottle.
- Suck the water from the bottle, maintaining a tight seal with your lips.
- Swallow the water and the pill together, using a sucking motion. Avoid letting air enter the bottle.
Why it works:
- The sucking motion helps to propel the pill towards the back of your throat, making it easier to swallow.
- The water helps to lubricate the pill, preventing it from sticking.
- The focus on the sucking action can distract from anxiety about swallowing.
Evidence:
A study published in the Annals of Family Medicine found that the pop-bottle method improved pill swallowing in 60% of participants who had difficulty swallowing tablets.
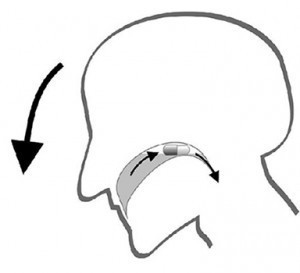
2.2. The Lean-Forward Method for Capsules
This technique is designed specifically for swallowing capsules and involves tilting your head forward to facilitate the capsule’s passage.
Steps:
- Place the capsule on your tongue.
- Take a sip of water, but do not swallow yet.
- Tilt your chin towards your chest, looking down.
- Swallow the capsule and water while keeping your head bent forward.
Why it works:
- Capsules are often less dense than water, causing them to float. Tilting your head forward helps to overcome this buoyancy, making it easier for the capsule to move down your throat.
- The forward head position opens up the throat and esophagus, making swallowing easier.
Evidence:
The same study in the Annals of Family Medicine reported an 89% improvement in swallowing capsules using the lean-forward method.
2.3. Other Helpful Techniques
In addition to the pop-bottle and lean-forward methods, other techniques can also make pill swallowing easier.
- The “One-Two” Method: Place the pill on your tongue, take a large gulp of water, and swallow everything together quickly.
- The “Applesauce” Method: Mix the pill with a spoonful of applesauce or yogurt to mask the taste and texture.
- The “Coating” Method: Use a commercially available pill-swallowing gel or spray to lubricate the pill and make it easier to slide down.
- The “Practice” Method: Start with small candies or sprinkles and gradually work your way up to larger pills. This can help to desensitize your gag reflex and build confidence.
Table: Summary of Pill Swallowing Techniques
| Technique | Type of Pill | Steps | Why it Works |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pop-Bottle Method | Tablets | Fill bottle, seal lips, suck water, swallow. | Suction propels pill, water lubricates, distraction. |
| Lean-Forward Method | Capsules | Place capsule, sip water, tilt chin down, swallow. | Overcomes capsule buoyancy, opens throat. |
| One-Two Method | All | Place pill, gulp water, swallow quickly. | Forces pill down with water. |
| Applesauce Method | All | Mix pill with applesauce, swallow. | Masks taste and texture. |
| Coating Method | All | Use pill-swallowing gel/spray. | Lubricates pill for easier sliding. |
| Practice Method | All | Start with small candies, gradually increase size. | Desensitizes gag reflex, builds confidence. |
3. Overcoming Pill Anxiety: A Step-by-Step Guide
Addressing pill anxiety requires a multi-faceted approach that combines relaxation techniques, cognitive strategies, and gradual exposure.
3.1. Relaxation Techniques
- Deep Breathing: Practice deep, diaphragmatic breathing to calm your nervous system. Inhale slowly through your nose, filling your abdomen with air, and exhale slowly through your mouth.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and release different muscle groups in your body to reduce overall tension. Start with your toes and work your way up to your head.
- Visualization: Imagine yourself successfully swallowing a pill. Visualize the process in detail, focusing on the feeling of calm and control.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Focus on the present moment, observing your thoughts and feelings without judgment. This can help to reduce anxiety and improve your ability to cope with difficult situations.
3.2. Cognitive Strategies
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Identify and challenge negative thoughts about swallowing pills. Ask yourself if these thoughts are realistic or based on fear. Replace negative thoughts with positive affirmations.
Example: Instead of thinking “I’m going to choke,” try thinking “I’ve swallowed pills before, and I can do it again.” - Education: Learn about the swallowing process and the reasons why you might be experiencing difficulty. Understanding the mechanics of swallowing can help to reduce anxiety and empower you to take control.
- Focus on the Benefits: Remind yourself of the benefits of taking your medication. Focus on how it will improve your health and well-being.
3.3. Gradual Exposure
- Start Small: Begin with the smallest pill possible, or even a small candy or sprinkle.
- Break It Down: If you’re anxious about swallowing a large pill, break it into smaller pieces (with your doctor’s approval).
- Practice Regularly: Practice swallowing pills regularly, even when you don’t need to take medication. This can help to build confidence and reduce anxiety over time.
- Reward Yourself: Reward yourself after each successful pill-swallowing attempt. This can help to reinforce positive behavior and reduce anxiety.
4. Alternatives to Pills: Exploring Different Medication Forms
If you continue to struggle with swallowing pills, explore alternative medication forms with your healthcare provider.
4.1. Liquid Medications
- Advantages: Liquid medications are often easier to swallow than pills, especially for individuals with dysphagia. They can also be easily measured and dosed.
- Disadvantages: Liquid medications may have an unpleasant taste or texture. They may also require refrigeration and have a shorter shelf life than pills.
4.2. Chewable Tablets
- Advantages: Chewable tablets are a good option for individuals who have difficulty swallowing pills but can chew and swallow food. They often have a pleasant taste and are easy to administer.
- Disadvantages: Chewable tablets may not be available for all medications. They may also contain sugar or artificial sweeteners, which may not be suitable for all individuals.
4.3. Dissolving Tablets (Orally Disintegrating Tablets)
- Advantages: Dissolving tablets dissolve quickly in the mouth, making them easy to swallow. They are a good option for individuals who have difficulty swallowing pills or liquids.
- Disadvantages: Dissolving tablets may not be available for all medications. They may also have an unpleasant taste or texture.
4.4. Topical Medications (Creams, Patches)
- Advantages: Topical medications are applied directly to the skin, bypassing the need to swallow anything. They are a good option for individuals who have severe difficulty swallowing or who cannot tolerate oral medications.
- Disadvantages: Topical medications may not be available for all conditions. They may also cause skin irritation or other side effects.
4.5. Injections
- Advantages: Injections bypass the need to swallow anything. They are a good option for individuals who have severe difficulty swallowing or who cannot tolerate oral medications.
- Disadvantages: Injections require a healthcare professional to administer. They may also be painful or cause other side effects.
Table: Medication Forms and Their Advantages/Disadvantages
| Medication Form | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Medications | Easier to swallow, easy to dose. | May have unpleasant taste, shorter shelf life. |
| Chewable Tablets | Good for those who can chew, pleasant taste. | Not available for all meds, may contain sugar. |
| Dissolving Tablets | Dissolve quickly, easy to swallow. | Not available for all meds, may have unpleasant taste. |
| Topical Medications | Bypasses swallowing, good for severe swallowing difficulties. | Not available for all conditions, may cause skin irritation. |
| Injections | Bypasses swallowing, good for severe swallowing difficulties. | Requires healthcare professional, may be painful. |
5. Modifying Pills: Cutting and Crushing
In some cases, it may be possible to modify pills to make them easier to swallow. However, it’s crucial to consult with your pharmacist or doctor before cutting or crushing any medication.
5.1. When It’s Safe to Cut or Crush Pills
- Consult Your Pharmacist: Always check with your pharmacist to ensure that it is safe to cut or crush a particular medication.
- Immediate-Release Tablets: Immediate-release tablets are generally safe to cut or crush.
- Capsules: Some capsules can be opened and sprinkled onto food, but check with your pharmacist first.
5.2. When It’s Not Safe to Cut or Crush Pills
- Extended-Release Medications: Extended-release medications are designed to release the drug slowly over time. Cutting or crushing them can disrupt this process and lead to a dangerous overdose.
- Enteric-Coated Tablets: Enteric-coated tablets have a special coating that protects the drug from stomach acid. Cutting or crushing them can damage the coating and cause stomach irritation.
- Capsules with Irritating Contents: Some capsules contain medications that can irritate the mouth or throat if released prematurely.
5.3. How to Cut or Crush Pills Safely
- Use a Pill Cutter: Use a pill cutter to ensure a clean and even cut.
- Use a Pill Crusher: Use a pill crusher to crush pills into a fine powder.
- Mix with Food: Mix the crushed pill with a small amount of soft food, such as applesauce or yogurt, to mask the taste and texture.
Important Note: Always follow your pharmacist’s or doctor’s instructions when cutting or crushing pills.
6. When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve tried the techniques and strategies outlined above and continue to have difficulty swallowing pills, it’s essential to seek professional help.
6.1. Consult Your Doctor
- Medical Evaluation: Your doctor can perform a medical evaluation to determine if there is an underlying medical condition causing your swallowing difficulties.
- Medication Review: Your doctor can review your medications to see if any of them are contributing to your swallowing problems.
- Referral: Your doctor can refer you to a specialist, such as an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctor or a speech-language pathologist.
6.2. See a Speech-Language Pathologist
- Swallowing Assessment: A speech-language pathologist can perform a comprehensive swallowing assessment to identify the specific nature of your swallowing difficulties.
- Swallowing Therapy: A speech-language pathologist can provide swallowing therapy to improve your swallowing function.
- Compensatory Strategies: A speech-language pathologist can teach you compensatory strategies to make swallowing easier and safer.
6.3. Consider Psychological Support
- Therapy: A therapist can help you address pill anxiety and develop coping strategies.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help you change negative thoughts and behaviors associated with pill swallowing.
- Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy can help you gradually overcome your fear of swallowing pills.
Contact LEARNS.EDU.VN Today
If you’re looking for more personalized guidance and support in overcoming your challenges with swallowing pills, we encourage you to visit LEARNS.EDU.VN. Our comprehensive resources and expert advice can provide you with the tools and knowledge you need to improve your health and well-being. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
7. Lifestyle Adjustments to Aid Swallowing
Making simple changes to your lifestyle can also make a significant difference in your ability to swallow pills comfortably.
7.1. Hydration
- Drink Plenty of Water: Staying well-hydrated helps keep your mouth and throat moist, making it easier for pills to slide down.
- Sip Water Before Swallowing: Take a sip of water just before placing the pill in your mouth to lubricate your throat.
7.2. Posture
- Sit Upright: Always sit upright when taking pills. Avoid lying down, as this can make it more difficult for the pill to travel down your esophagus.
- Chin Tuck: Tilting your chin slightly downwards while swallowing can help to close off your airway and open up your esophagus.
7.3. Dietary Considerations
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid foods and beverages that can irritate your throat, such as spicy foods, acidic juices, and alcohol.
- Eat Soft Foods: If you’re having trouble swallowing pills, try eating soft foods that are easy to swallow.
7.4. Timing
- Take Pills with Meals: Taking pills with meals can help to mask the taste and texture of the pills.
- Avoid Taking Pills Before Bed: Taking pills right before bed can increase the risk of them getting stuck in your esophagus.
8. The Role of Technology in Improving Swallowing
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in helping people with swallowing difficulties.
8.1. Swallowing Training Apps
- Biofeedback Apps: These apps use biofeedback technology to help you monitor and improve your swallowing function.
- Gamified Exercises: These apps make swallowing exercises more fun and engaging.
8.2. Assistive Devices
- Pill-Swallowing Cups: These cups are designed to make it easier to swallow pills by controlling the flow of liquid.
- Electronic Pill Dispensers: These devices can help you manage your medications and remind you to take them on time.
8.3. Telehealth
- Remote Therapy: Telehealth allows you to receive swallowing therapy from a speech-language pathologist remotely.
- Virtual Consultations: Telehealth allows you to consult with your doctor or pharmacist from the comfort of your own home.
9. Tips for Parents: Helping Children Swallow Pills
Helping children learn to swallow pills requires patience, understanding, and a gentle approach.
9.1. Start Early
- Practice with Small Candies: Start practicing with small candies or sprinkles when your child is young.
- Make It Fun: Turn pill swallowing into a game. Use positive reinforcement and rewards.
9.2. Explain the Importance
- Explain Why They Need the Medication: Help your child understand why they need to take the medication and how it will help them feel better.
- Be Honest: Be honest about the taste and texture of the pills.
9.3. Use Positive Reinforcement
- Praise and Encouragement: Praise your child for their efforts, even if they don’t succeed at first.
- Rewards: Offer small rewards for successful pill-swallowing attempts.
9.4. Involve the Child
- Let Them Choose: Let your child choose the technique they want to use.
- Give Them Control: Give them as much control as possible over the pill-swallowing process.
10. Future Directions in Swallowing Research
Swallowing research is an ongoing field, with new discoveries and innovations constantly emerging.
10.1. New Medications
- Smaller Pills: Researchers are working to develop smaller and easier-to-swallow pills.
- More Palatable Formulations: Researchers are working to develop more palatable liquid and chewable formulations.
10.2. Advanced Therapies
- Neuromuscular Stimulation: Neuromuscular stimulation is a therapy that uses electrical impulses to stimulate the muscles involved in swallowing.
- Gene Therapy: Gene therapy is being explored as a potential treatment for dysphagia caused by genetic disorders.
10.3. Improved Diagnostics
- High-Resolution Manometry: High-resolution manometry is a diagnostic test that measures the pressure in the esophagus during swallowing.
- Functional MRI: Functional MRI is a neuroimaging technique that can be used to study the brain activity during swallowing.
Conclusion
Learning to swallow pills can be a journey, but with the right techniques, strategies, and support, you can overcome your challenges and take control of your health. Remember to be patient with yourself, practice regularly, and seek professional help when needed. With learns.edu.vn as your trusted partner, you can unlock the knowledge and skills you need to live a healthier and more fulfilling life.
FAQ: Common Questions About Swallowing Pills
1. Why do I have trouble swallowing pills when I can swallow food just fine?
Some people have difficulty with pills due to their size, shape, or texture, or due to anxiety related to swallowing pills specifically. It could also be related to how well lubricated the pill is compared to food.
2. Is it okay to crush my pills to make them easier to swallow?
Not always. Consult your pharmacist or doctor before crushing any medication, as it can affect how the drug is released and absorbed.
3. What if a pill gets stuck in my throat?
Drink plenty of water and try coughing gently. If it doesn’t dislodge, seek medical attention immediately.
4. Can anxiety make it harder to swallow pills?
Yes, anxiety can cause muscle tension and make swallowing more difficult. Relaxation techniques can help.
5. Are there any over-the-counter products that can help with swallowing pills?
Yes, there are pill-swallowing gels and sprays that can lubricate pills and make them easier to swallow.
6. Should I see a doctor if I have trouble swallowing pills?
If you consistently have difficulty swallowing pills, consult your doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
7. Can I prevent pills from getting stuck in my esophagus?
Yes, by drinking plenty of water, sitting upright, and avoiding taking pills right before bed.
8. What is dysphagia, and how is it related to pill swallowing?
Dysphagia is a medical term for difficulty swallowing. It can make it challenging to swallow pills, liquids, and food.
9. Are liquid medications always easier to swallow than pills?
While often easier, some liquid medications have an unpleasant taste or texture that can be difficult for some people.
10. What if my child has trouble swallowing pills?
Be patient, start with small candies, explain the importance of the medication, and use positive reinforcement. Consider alternative medication forms if necessary.
