Do you want to learn the captivating art of glassblowing? This comprehensive guide from LEARNS.EDU.VN will take you through the initial steps and considerations for mastering this exciting craft, from finding the right learning environment to understanding the essential tools and techniques. Learning to blow glass can be both a rewarding artistic pursuit and a potentially lucrative skill. Dive into glass artistry, glass forming, and hot glass techniques at LEARNS.EDU.VN to discover more about this captivating art form.
1. Understanding the Art of Glassblowing
Glassblowing is an ancient and mesmerizing art form that involves shaping molten glass into various forms by inflating it with air through a blowpipe. Dating back to the 1st century B.C., this technique has evolved into a versatile craft used to create everything from functional objects to elaborate art pieces. With the right skills, you can create an impressive array of glass objects, ranging from simple bowls and vases to intricate sculptures.
- Definition: Glassblowing involves using a blowpipe to inflate molten glass into a bubble, then shaping it with tools and techniques.
- Historical Significance: The technique dates back to ancient times and has been refined over centuries.
- Versatility: Glassblowing can produce functional items, decorative pieces, and artistic sculptures.
2. Why Should I Learn Glassblowing?
Learning glassblowing offers a unique blend of artistic expression, practical skill development, and potential career opportunities. It is not only a fulfilling creative outlet but also a reputable profession. Glassblowing provides the opportunity to earn income by selling handmade glass items. The versatility of glass allows for the creation of a wide range of items, making it a rewarding hobby and a way to produce unique gifts for friends and family.
- Creative Expression: Glassblowing allows for unique artistic expression.
- Potential Income: It provides opportunities for selling handmade items.
- Versatile Hobby: You can create a wide range of items as gifts or for personal use.
3. Essential Tools and Equipment for Glassblowing
Before diving into glassblowing, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the essential tools and equipment. Setting up a glassblowing studio requires a significant investment in specialized equipment, which is why many beginners choose to learn at a studio.
- Furnaces: Used to melt and maintain the glass at a workable temperature.
- Blowpipe (or Blow Tube): A hollow metal tube used to inflate the molten glass.
- Marver: A flat steel or marble table used for shaping the glass.
- Jacks: Pliers-like tools used to shape and constrict the glass.
- Paddles: Wooden or graphite tools used to flatten or shape the glass.
- Blocks: Wooden tools used to create and refine vessel forms.
- Heat Protective Gear: Includes gloves, eye protection, and aprons to protect against burns and heat exposure.
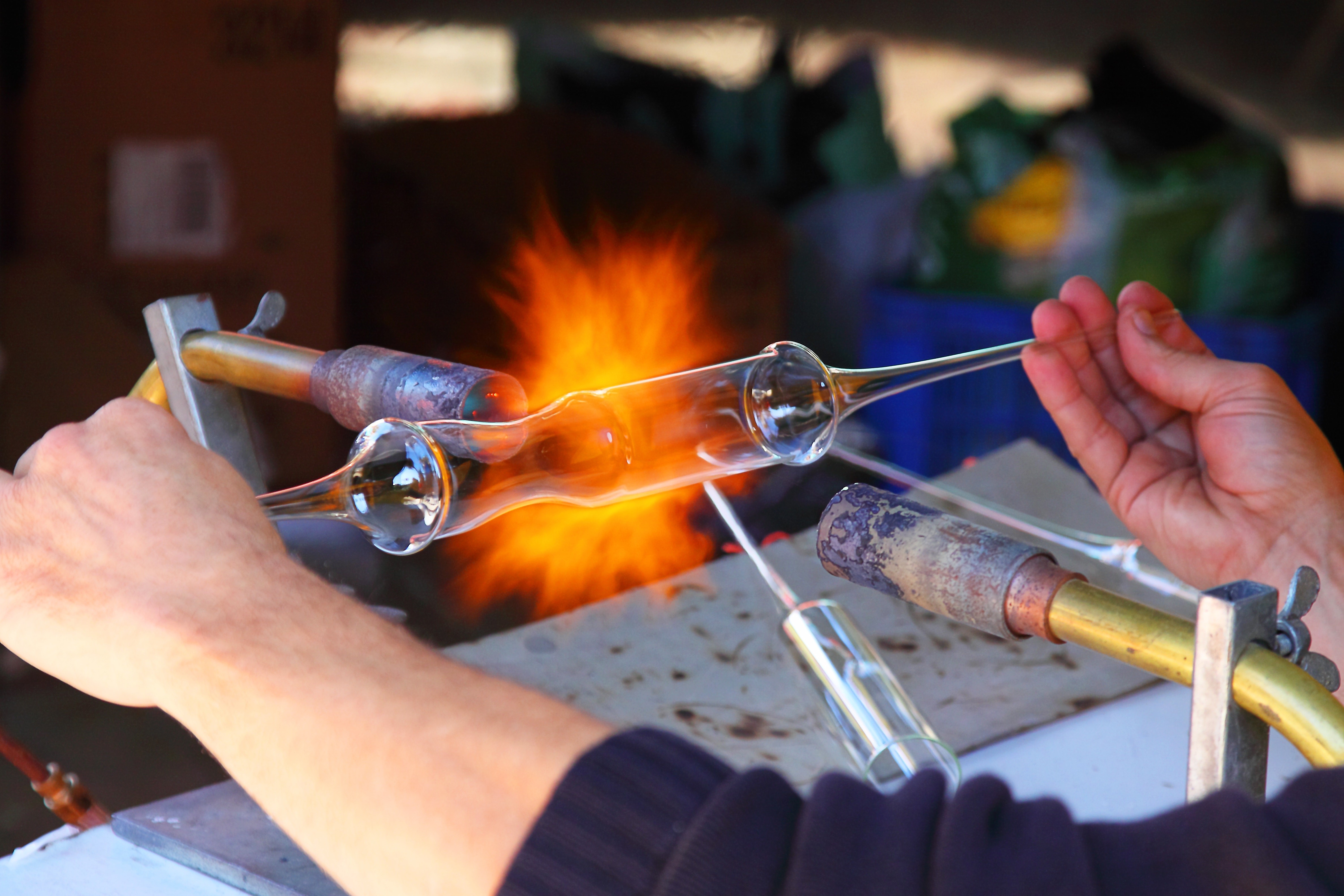 Glassblowing tools including blowpipe, marver and jacks
Glassblowing tools including blowpipe, marver and jacks
4. The Basic Glassblowing Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
Understanding the glassblowing process is crucial for beginners. This involves several key steps, each requiring precision and skill.
- Gathering Glass: Molten glass is collected from the furnace on the end of the blowpipe.
- Shaping on the Marver: The glass is rolled on the marver to create a cylindrical and symmetrical shape.
- Reheating: The glass is reheated in a glory hole (a smaller furnace) to maintain its malleability. This step is repeated throughout the process.
- Blowing: Air is blown into the glass through the blowpipe while continuously rotating it to prevent sagging.
- Shaping with Tools: Various tools are used to refine the shape and add details.
- Removing the Glass: The glass is carefully removed from the blowpipe using jacks.
5. Where Can I Learn Glassblowing?
Finding the right learning environment is essential for acquiring glassblowing skills. Several options are available, each with its own advantages and considerations.
- Local Studio Schools: Taking classes from a master glass artist at a local studio school is highly recommended. This provides hands-on experience and expert guidance.
- Community Colleges: Some community colleges offer glassblowing courses as part of their arts programs.
- Craft Centers: Craft centers often have glassblowing facilities and offer workshops and classes.
- Universities: Universities with art programs may offer glassblowing courses, providing a more academic approach.
According to a study by the Corning Museum of Glass, students who learn glassblowing in a structured studio environment with experienced instructors are more likely to develop proper techniques and avoid common pitfalls.
6. Why Learning at Home Is Not Recommended for Beginners
While it might be tempting to learn glassblowing at home, it is generally not recommended for beginners. There are several reasons for this:
- Safety Concerns: Handling glassblowing tools and molten glass without experience can be dangerous.
- Equipment Costs: Setting up a home studio is expensive and requires a significant investment in specialized equipment.
- Lack of Guidance: Learning without expert guidance can lead to the development of bad habits and hinder progress.
- Space Requirements: Glassblowing requires a dedicated workspace with proper ventilation and safety measures.
7. The Benefits of Learning from a Master Glass Artist
Learning from a master glass artist offers numerous advantages that can significantly accelerate your progress and ensure you develop proper techniques.
- Expert Guidance: A master glass artist can provide personalized instruction and feedback, helping you avoid common mistakes and develop good habits.
- Skill Development: You will learn the correct techniques and processes, ensuring you create glass art proficiently.
- Confidence Building: Working with an expert will give you the confidence to tackle more complex projects and explore your creativity.
- Insight and Improvements: Master artists can offer valuable insights and tips that can help you improve your skills and create better work.
8. Glassblowing Techniques: An Overview
Glassblowing involves a variety of techniques that can be used to create different shapes, colors, and patterns. Understanding these techniques is essential for mastering the art of glassblowing.
- Gathering: Collecting molten glass from the furnace on the end of the blowpipe.
- Blowing: Inflating the glass with air to create a bubble or vessel.
- Shaping: Using tools like jacks, paddles, and blocks to refine the shape of the glass.
- Marvering: Rolling the glass on the marver to create a smooth and cylindrical shape.
- Casing: Applying a layer of colored glass over a base layer to create patterns and designs.
- Frit Application: Rolling the hot glass in crushed glass (frit) to add texture and color.
- Threading: Applying thin strands of glass to the surface to create decorative details.
9. Safety Precautions in Glassblowing
Safety is paramount in glassblowing. Working with molten glass and high temperatures requires strict adherence to safety protocols to prevent burns and other injuries.
- Wear Protective Gear: Always wear heat-resistant gloves, eye protection, and aprons to protect against burns.
- Maintain a Safe Distance: Keep a safe distance from the furnace and other hot equipment.
- Use Proper Ventilation: Ensure the studio is well-ventilated to remove fumes and heat.
- Handle Tools Carefully: Use tools correctly and maintain them in good condition.
- Be Aware of Surroundings: Pay attention to your surroundings and avoid distractions while working.
- Know Emergency Procedures: Be familiar with emergency procedures and have a first aid kit readily available.
10. Understanding Glass Types for Glassblowing
Different types of glass are used in glassblowing, each with its own properties and characteristics. Understanding these differences is important for selecting the right glass for your projects.
- Soda-Lime Glass: The most common type of glass, used for making everyday objects like bottles and windows. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to work with.
- Borosilicate Glass: Known for its high heat resistance, borosilicate glass is used for making laboratory equipment and ovenware. It is more expensive and requires higher temperatures to work with.
- Lead Crystal: Contains lead oxide, which gives it a high refractive index and a sparkling appearance. Lead crystal is used for making decorative items and glassware.
11. The Role of Color in Glassblowing
Color plays a significant role in glassblowing, allowing artists to create visually stunning and expressive pieces. Color can be added to glass through various techniques, including:
- Glass Dyes: Adding powdered glass dyes to molten glass.
- Frit: Rolling hot glass in crushed colored glass.
- Casing: Overlaying colored glass on clear glass.
- Flameworking: Using a torch to melt and apply small pieces of colored glass.
12. Developing Your Style in Glassblowing
As you gain experience in glassblowing, you’ll begin to develop your own unique style and artistic voice. This involves experimenting with different techniques, colors, and forms to create pieces that reflect your personal vision.
- Experimentation: Try new techniques and materials to expand your skills and knowledge.
- Inspiration: Draw inspiration from other artists, nature, and your own experiences.
- Practice: Consistent practice is essential for honing your skills and developing your style.
- Feedback: Seek feedback from other artists and instructors to gain new perspectives and improve your work.
13. The Importance of Continuous Learning in Glassblowing
Glassblowing is a constantly evolving art form, and continuous learning is essential for staying up-to-date with new techniques, trends, and technologies.
- Workshops: Attend workshops and master classes to learn from experienced artists and expand your skills.
- Conferences: Participate in conferences and seminars to network with other artists and learn about new developments in the field.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources like tutorials, forums, and online courses to continue your education.
- Practice: The more time you spend practicing, the more you will improve.
14. Maintaining Your Glassblowing Equipment
Proper maintenance of your glassblowing equipment is essential for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance.
- Clean Regularly: Clean your tools and equipment regularly to remove dirt, debris, and glass residue.
- Inspect for Damage: Inspect your equipment for damage and replace worn or broken parts promptly.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for maintenance and care.
- Store Properly: Store your equipment in a dry and safe place to prevent damage.
15. Understanding Annealing in Glassblowing
Annealing is a critical process in glassblowing that involves slowly cooling the glass to relieve internal stresses and prevent cracking.
- Purpose: Annealing prevents glass from cracking due to thermal stress.
- Process: Glass is placed in a kiln and gradually cooled over a period of hours or days.
- Importance: Proper annealing is essential for ensuring the durability and longevity of your glass pieces.
According to research from the American Craft Council, proper annealing can increase the lifespan of glass art by up to 50%.
16. Marketing and Selling Your Glass Art
Once you’ve developed your glassblowing skills, you may want to consider marketing and selling your work. There are several avenues for selling your glass art:
- Craft Fairs: Participate in local craft fairs and art festivals to showcase and sell your work.
- Galleries: Approach local galleries to see if they are interested in representing your work.
- Online Marketplaces: Sell your work online through platforms like Etsy, eBay, and Amazon.
- Studio Sales: Host open studio events to invite customers to your workspace and sell your art directly.
- Social Media: Market your work through social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Pinterest.
17. The Future of Glassblowing
Glassblowing continues to evolve as artists push the boundaries of the craft and incorporate new technologies and techniques.
- Innovation: Artists are experimenting with new materials, colors, and forms.
- Technology: Advancements in technology are enabling new possibilities in glassblowing, such as computer-aided design and 3D printing.
- Sustainability: There is a growing emphasis on sustainability in glassblowing, with artists using recycled glass and eco-friendly practices.
- Education: More educational opportunities are becoming available, making glassblowing accessible to a wider audience.
18. Glassblowing as a Therapeutic Art Form
Many people find glassblowing to be a therapeutic and meditative art form. The process of working with molten glass can be both challenging and rewarding, offering a unique sense of accomplishment and creative expression.
- Stress Relief: Glassblowing can be a great way to relieve stress and anxiety.
- Mindfulness: The process requires focus and concentration, promoting mindfulness and presence.
- Creative Expression: Glassblowing allows for unique artistic expression and self-discovery.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Creating beautiful and functional objects from molten glass can provide a great sense of accomplishment.
19. Notable Glass Artists and Their Contributions
Throughout history, many talented glass artists have made significant contributions to the field. Some notable glass artists include:
- Dale Chihuly: Known for his large-scale glass installations and vibrant colors.
- Lino Tagliapietra: An Italian glass artist renowned for his mastery of Venetian glassblowing techniques.
- Harvey Littleton: Considered the father of the American studio glass movement.
- Marvin Lipofsky: Known for his organic and abstract glass forms.
20. Resources for Further Learning in Glassblowing
There are numerous resources available for those who want to further their knowledge and skills in glassblowing.
- Books: “Contemporary Glass” by Suzanne Frantz, “Glass Art” by James Upham.
- Magazines: “Glass Art Magazine,” “Neues Glas/New Glass.”
- Websites: The Corning Museum of Glass, The Glass Art Society.
- Organizations: The American Craft Council, The Glass Art Society.
21. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
As with any craft, glassblowing presents its own set of challenges. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
- Cracking: Ensure proper annealing and avoid sudden temperature changes.
- Sagging: Rotate the glass continuously while blowing and reheating.
- Uneven Thickness: Practice gathering and shaping techniques to achieve uniform thickness.
- Bubbles: Remove bubbles by carefully reheating and manipulating the glass.
- Tool Marks: Use tools smoothly and avoid applying too much pressure.
22. Glassblowing for People with Disabilities
Glassblowing can be adapted to accommodate people with various disabilities. With the right modifications and support, individuals with physical or cognitive limitations can enjoy the creative and therapeutic benefits of glassblowing.
- Adaptive Tools: Modified tools can make glassblowing accessible to those with limited mobility or strength.
- Assistance: Studio assistants can provide support and guidance.
- Therapeutic Programs: Some organizations offer glassblowing programs specifically designed for people with disabilities.
23. Glassblowing in Different Cultures
Glassblowing has a rich history in various cultures around the world, each with its own unique styles and traditions.
- Venetian Glassblowing: Known for its intricate designs and vibrant colors.
- Bohemian Glassblowing: Renowned for its high-quality crystal and engraved designs.
- American Studio Glass: Characterized by its innovation and experimentation.
- Japanese Glassblowing: Emphasizes simplicity and natural forms.
24. Ethical Considerations in Glassblowing
As with any art form, there are ethical considerations to keep in mind when practicing glassblowing.
- Sustainability: Use recycled glass and eco-friendly practices to minimize environmental impact.
- Fair Labor: Ensure fair labor practices if you hire assistants or collaborators.
- Copyright: Respect the intellectual property rights of other artists and avoid plagiarism.
- Safety: Prioritize safety in your studio and promote safe practices among your students and colleagues.
25. Exploring Flameworking vs. Glassblowing
While both flameworking and glassblowing involve working with glass, they are distinct techniques with different equipment and approaches.
- Flameworking: Uses a torch to melt and shape small pieces of glass. It is often used for creating intricate beads, jewelry, and small sculptures.
- Glassblowing: Involves gathering molten glass from a furnace and inflating it with air. It is used for creating larger vessels, sculptures, and functional objects.
26. Understanding Glass Chemistry for Advanced Techniques
A deeper understanding of glass chemistry can enable more advanced techniques and creative possibilities in glassblowing.
- Composition: Different glass compositions have varying melting points, working properties, and chemical resistances.
- Colorants: Metal oxides and other chemicals are used to create different colors in glass.
- Reactions: Understanding how different chemicals react with each other can help you create unique effects and patterns in your glass art.
27. Combining Glassblowing with Other Art Forms
Glassblowing can be combined with other art forms to create unique and innovative works.
- Mixed Media Sculpture: Incorporating glass elements into sculptures made from metal, wood, or other materials.
- Installation Art: Creating large-scale installations that combine glass with light, sound, and other sensory elements.
- Performance Art: Integrating glassblowing into live performances, creating a dynamic and interactive experience.
28. Glassblowing as a Career: Opportunities and Challenges
Pursuing glassblowing as a career can be both rewarding and challenging.
- Opportunities: Selling your art, teaching workshops, working as a studio assistant, designing for manufacturers.
- Challenges: High equipment costs, competition, inconsistent income, physical demands.
29. How to Set Up a Glassblowing Studio
Setting up your own glassblowing studio requires careful planning and significant investment.
- Location: Choose a location with adequate space, ventilation, and access to utilities.
- Equipment: Invest in essential equipment like a furnace, glory hole, annealer, and hand tools.
- Safety: Implement safety measures like fire extinguishers, ventilation systems, and protective gear.
- Regulations: Comply with local zoning regulations and environmental requirements.
30. The Psychological Benefits of Working with Glass
Working with glass can have a profound impact on your mental and emotional well-being.
- Flow State: The focused concentration required in glassblowing can induce a flow state, reducing stress and enhancing creativity.
- Sensory Engagement: The tactile experience of working with molten glass can be grounding and therapeutic.
- Self-Expression: Glassblowing provides a powerful outlet for self-expression and emotional release.
- Mindfulness: The process encourages mindfulness and presence, helping you stay grounded in the moment.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to help you further explore the world of glassblowing. Discover more about glass artistry, glass forming, and hot glass techniques by visiting our website.
Interested in learning more about glassblowing and other artistic skills? Visit learns.edu.vn at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Let us help you unleash your creative potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Learning Glassblowing
1. Is glassblowing difficult to learn?
Glassblowing can be challenging but is achievable with proper instruction and practice. The coordination, timing, and physical demands require dedication, but the rewards are well worth the effort.
2. How much does it cost to get started in glassblowing?
The initial costs can be significant, especially for equipment. Taking classes at a studio is a more affordable way to start, as you’ll have access to all the necessary tools and facilities.
3. What safety precautions should I take when glassblowing?
Always wear protective gear, maintain a safe distance from hot equipment, ensure proper ventilation, and handle tools carefully. Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures and have a first-aid kit readily available.
4. Can I learn glassblowing online?
While some theoretical knowledge can be gained online, hands-on experience is crucial for glassblowing. Online resources can supplement in-person instruction but should not replace it.
5. How long does it take to become proficient in glassblowing?
Proficiency varies depending on individual dedication and practice. It can take several years of consistent effort to develop advanced skills.
6. What type of glass is best for beginners?
Soda-lime glass is generally recommended for beginners due to its lower melting point and ease of use.
7. What are the best resources for learning glassblowing?
Local studio schools, community colleges, craft centers, and universities with art programs are excellent resources. Additionally, books, magazines, and online forums can provide valuable information.
8. Can I make a living as a glassblower?
Making a living as a glassblower is possible but requires dedication, skill, and business acumen. Many artists supplement their income by teaching, selling online, or participating in craft fairs.
9. What is annealing, and why is it important?
Annealing is the process of slowly cooling glass to relieve internal stresses and prevent cracking. It is essential for ensuring the durability and longevity of your glass pieces.
10. How can I develop my own style in glassblowing?
Experiment with different techniques, colors, and forms to create pieces that reflect your personal vision. Draw inspiration from other artists, nature, and your own experiences, and seek feedback from others.