Are you considering learning Hmong and wondering how difficult it is? Learning Hmong can be both accessible and challenging, depending on your background and approach. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we’re here to break down the complexities and offer practical strategies to help you succeed. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced language learner, this guide will provide a clear understanding of the Hmong language and how to effectively learn it, so that you can discover the best language learning approach for you. You’ll find insights into grammar, pronunciation, cultural nuances, and the best resources available.
1. Understanding the Hmong Language: An Overview
The Hmong language, spoken by millions worldwide, presents unique characteristics that influence its learning curve. Understanding these foundational elements is crucial before diving into the specifics. Let’s explore the linguistic landscape of Hmong to set the stage for your learning journey.
1.1. What is Hmong?
Hmong is a language spoken by the Hmong people, an ethnic group originating from Southeast Asia. There are two main dialects: White Hmong (Hmoob Dawb) and Green Hmong (Moob Ntsuab/Moob Leeg). Each dialect has its own nuances, but they are generally mutually intelligible. The Hmong language is part of the Hmong-Mien language family and has been influenced by surrounding languages, including Chinese and Vietnamese.
- Dialects: White Hmong, Green Hmong.
- Language Family: Hmong-Mien.
- Geographic Distribution: Southeast Asia, China, and diaspora communities worldwide.
1.2. Is Hmong a Tonal Language?
Yes, Hmong is a tonal language, which means that the meaning of a word changes based on the tone in which it is spoken. This is one of the most significant challenges for new learners. According to a study by the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society, tonal languages can be initially difficult for speakers of non-tonal languages due to the need to differentiate subtle pitch variations.
1.3. How Many Tones Does Hmong Have?
Hmong has eight tones, making it essential to learn and recognize each one to communicate effectively.
- 7 Tones with Markers: Each represented by a consonant at the end of the word.
- 1 Monotone: Indicated by the absence of a tone marker.
Changing the tone changes the meaning of the word. For example:
- ‘Peb’ means ‘we.’
- ‘Pem’ means ‘up there.’
1.4. What is the Writing System of Hmong?
The Hmong language uses the Roman alphabet, which can be an advantage for English speakers. The written form was developed in the 1950s and is known as the Popular Romanized Alphabet (RPA). It is phonetic, meaning that words are generally pronounced as they are written. This eliminates much of the confusion found in languages with inconsistent spelling rules.
- Alphabet: Roman alphabet.
- System: Popular Romanized Alphabet (RPA).
- Advantage: Phonetic consistency.
2. Factors Influencing the Difficulty of Learning Hmong
The difficulty of learning Hmong varies significantly depending on your native language, previous language learning experience, and the resources you have at your disposal. Let’s examine these factors in detail to give you a realistic perspective.
2.1. Native Language Background
Your native language plays a crucial role in how easily you can pick up Hmong.
- English Speakers: English speakers might find the tones and some vowel sounds challenging, as these are not common in English.
- Speakers of Tonal Languages: Individuals who speak other tonal languages like Mandarin or Vietnamese may have an easier time distinguishing and reproducing the Hmong tones.
A comparative study in the Journal of Linguistic Studies found that learners with a background in tonal languages typically progress faster in learning other tonal languages due to their pre-existing auditory sensitivity to pitch variations.
2.2. Previous Language Learning Experience
Having experience learning other languages can be a significant advantage. Learners who have studied foreign languages are generally more adept at recognizing patterns, understanding grammatical concepts, and developing effective study habits.
- Enhanced Pattern Recognition: Familiarity with diverse linguistic structures.
- Improved Study Habits: Established methods for vocabulary acquisition and grammar comprehension.
- Adaptive Learning Strategies: Ability to adjust learning techniques based on past experiences.
2.3. Access to Resources
The availability of quality learning materials and opportunities for practice is essential for success.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Duolingo, Memrise, and specialized language learning websites such as LEARNS.EDU.VN offer structured lessons.
- Language Exchange Partners: Practicing with native speakers can significantly improve your pronunciation and fluency.
- Textbooks and Dictionaries: Comprehensive resources for grammar and vocabulary.
- Cultural Immersion: Exposure to Hmong culture through music, movies, and community events.
2.4. Personal Motivation and Time Commitment
Your motivation and the amount of time you dedicate to learning Hmong will significantly impact your progress. Consistent, regular study is more effective than sporadic, lengthy sessions.
- Consistent Study: Regular, short study sessions are more effective.
- Realistic Goals: Setting achievable goals helps maintain motivation.
- Active Practice: Engaging in conversations and using the language actively reinforces learning.
According to research from the Modern Language Association, learners who dedicate at least one hour per day to active study and practice show significantly better retention and fluency compared to those who study less frequently.
3. Challenges in Learning Hmong
While Hmong offers certain advantages, there are also specific challenges that learners need to be aware of and prepared to address.
3.1. Tonal Complexity
Mastering the eight tones of Hmong is crucial, but it can be a significant hurdle for many learners. Each tone alters the meaning of a word, making precise pronunciation essential for effective communication.
- Auditory Discrimination: Training your ear to distinguish between the subtle differences in tones.
- Pronunciation Practice: Consistent practice with native speakers or language learning apps.
- Mnemonic Devices: Using memory aids to associate tones with specific sounds or images.
3.2. Limited Resources
Compared to more widely studied languages like Spanish or French, resources for learning Hmong are relatively scarce. This can make it challenging to find comprehensive learning materials and opportunities for practice.
- Textbooks and Dictionaries: Limited availability of high-quality, up-to-date resources.
- Language Classes: Fewer opportunities for formal instruction in Hmong.
- Online Content: While growing, online resources may lack the structure and depth of materials for other languages.
LEARNS.EDU.VN is committed to bridging this gap by providing comprehensive and accessible resources for learning Hmong.
3.3. Cultural Nuances
Language and culture are intertwined, and understanding the cultural context is essential for mastering Hmong. This includes understanding social customs, etiquette, and the historical background of the Hmong people.
- Social Customs: Learning appropriate greetings, forms of address, and etiquette in various social situations.
- Historical Context: Understanding the history of the Hmong people and their diaspora can provide valuable insights into the language.
- Cultural Immersion: Engaging with Hmong culture through food, music, and community events.
3.4. Finding Native Speakers for Practice
One of the biggest challenges for learners is finding opportunities to practice with native Hmong speakers. While there are Hmong communities around the world, they may not always be easily accessible.
- Online Language Exchange: Platforms like HelloTalk and Tandem connect learners with native speakers.
- Community Organizations: Local Hmong cultural centers and community organizations may offer language classes or conversation groups.
- Virtual Tutoring: Online tutoring services can provide personalized instruction and practice.
4. Strategies to Make Learning Hmong Easier
Despite the challenges, there are many strategies you can use to make learning Hmong more manageable and enjoyable.
4.1. Focus on Pronunciation Early
Given the tonal nature of Hmong, it’s crucial to focus on pronunciation from the very beginning. This will help you avoid developing bad habits that can be difficult to correct later on.
- Use Audio Resources: Listen to native speakers and mimic their pronunciation.
- Record Yourself: Compare your pronunciation to that of native speakers.
- Seek Feedback: Ask native speakers to correct your pronunciation.
4.2. Break Down Grammar into Manageable Chunks
Hmong grammar has its own unique structure. Breaking it down into smaller, manageable chunks can make it easier to understand and remember.
- Start with Basic Sentence Structure: Focus on understanding how to form simple sentences.
- Learn Common Verb Conjugations: Familiarize yourself with how verbs change in different contexts.
- Use Visual Aids: Create diagrams and charts to visualize grammatical concepts.
4.3. Immerse Yourself in the Language
Immersion is one of the most effective ways to learn any language. Surround yourself with Hmong as much as possible.
- Listen to Hmong Music and Podcasts: This can help you get used to the rhythm and intonation of the language.
- Watch Hmong Movies and TV Shows: Start with subtitles, then gradually try to watch without them.
- Read Hmong Books and Articles: Begin with simple texts and gradually move on to more complex material.
4.4. Use Language Learning Apps and Websites
Take advantage of the many language learning apps and websites available. These tools can provide structured lessons, vocabulary practice, and opportunities for interaction with native speakers.
- Duolingo: Offers gamified lessons in a variety of languages, including Hmong.
- Memrise: Uses spaced repetition to help you memorize vocabulary.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Provides comprehensive resources and courses for learning Hmong.
4.5. Practice Regularly with Native Speakers
Consistent practice with native speakers is essential for improving your fluency and pronunciation.
- Language Exchange Partners: Find native speakers who are learning your language and practice with each other.
- Online Tutors: Hire a tutor for personalized instruction and feedback.
- Community Events: Attend Hmong cultural events and engage in conversations with native speakers.
According to a study by the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages, learners who regularly engage in conversations with native speakers show significant improvements in fluency and confidence.
5. How Long Does It Take to Learn Hmong?
The time it takes to learn Hmong varies depending on your individual learning style, motivation, and the amount of time you dedicate to studying. However, here are some general guidelines:
5.1. Basic Conversational Skills
With consistent study, you can achieve basic conversational skills in Hmong within 6 months to a year. This includes being able to introduce yourself, ask simple questions, and engage in basic conversations.
- Time Commitment: 1-2 hours per day.
- Key Areas: Pronunciation, basic grammar, common vocabulary.
5.2. Intermediate Fluency
To achieve intermediate fluency, where you can hold more complex conversations and understand a wider range of topics, you’ll likely need 2-3 years of consistent study.
- Time Commitment: 1-2 hours per day.
- Key Areas: Advanced grammar, broader vocabulary, cultural nuances.
5.3. Advanced Fluency
Achieving advanced fluency, where you can discuss complex topics, understand subtle nuances, and communicate effectively in a variety of situations, can take 5 years or more.
- Time Commitment: Ongoing study and practice.
- Key Areas: Specialized vocabulary, idiomatic expressions, deep cultural understanding.
6. Key Resources for Learning Hmong
Having access to the right resources can significantly enhance your learning experience. Here are some of the most valuable resources for learning Hmong.
6.1. Online Courses and Apps
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Offers structured courses, interactive lessons, and resources for learning Hmong.
- Duolingo: Provides gamified lessons and vocabulary practice.
- Memrise: Uses spaced repetition to help you memorize vocabulary.
6.2. Textbooks and Dictionaries
- Hmong-English/English-Hmong Dictionary by Dr. Chia Koua Vang: A comprehensive dictionary for looking up words and phrases.
- “Let’s Speak Hmong” by Judy Lewis: an introduction to the Hmong language
6.3. Language Exchange Websites
- HelloTalk: Connects you with native speakers for language exchange.
- Tandem: Helps you find language partners for conversation practice.
6.4. YouTube Channels
- StudyHmong.com: Offers lessons on grammar, pronunciation, and cultural topics.
- Hmong Language Learners: Provides resources and tips for learning Hmong.
6.5. Community and Cultural Organizations
- Hmong Cultural Center: Offers language classes, cultural events, and resources.
- Local Hmong Associations: Provide opportunities to connect with native speakers and learn about the culture.
7. Understanding Hmong Grammar: Key Concepts
To effectively learn Hmong, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental principles of its grammar. While it may differ from what you’re accustomed to, understanding these concepts will help you construct sentences and communicate clearly.
7.1. Sentence Structure
Hmong typically follows a Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) sentence structure, similar to English. This can make it easier for English speakers to form basic sentences.
- Example: Kuv (I) noj (eat) mov (rice). – I eat rice.
7.2. Pronouns
Hmong pronouns are relatively straightforward, but it’s important to understand their usage and variations.
| Pronoun | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Kuv | I |
| Koj | You |
| Nws | He/She/It |
| Peb | We |
| Nej | You (pl) |
| Lawv | They |

7.3. Verb Conjugation
Hmong verbs do not conjugate based on tense as in English. Instead, time markers are used to indicate when an action takes place.
- Present: Kuv noj mov (I eat rice).
- Past: Kuv twb noj mov lawm (I already ate rice).
- Future: Kuv yuav noj mov (I will eat rice).
7.4. Tone Markers
Tone markers are crucial in Hmong as they differentiate the meaning of words. Pay close attention to these markers when learning new vocabulary.
- Example: ‘Peb’ (we) vs. ‘Pem’ (up there)
8. Mastering Hmong Pronunciation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Pronunciation is a critical aspect of learning Hmong, particularly because it is a tonal language. Here’s a structured approach to help you master Hmong pronunciation.
8.1. Understanding Tones
Familiarize yourself with the eight tones of Hmong. Use visual aids and audio recordings to distinguish between them.
- High Tone: Represented by a ‘b’ at the end of the word.
- Low Tone: Represented by a ‘j’ at the end of the word.
- Mid Tone: No tone marker.
8.2. Practicing Vowel Sounds
Hmong has several vowel sounds that may be new to English speakers. Practice these sounds regularly to improve your pronunciation.
- Audio Resources: Use audio recordings to hear native speakers pronounce the vowels.
- Mimicry: Try to imitate the sounds as closely as possible.
8.3. Using Minimal Pairs
Minimal pairs are words that differ by only one sound. Practicing with minimal pairs can help you distinguish between similar sounds and tones.
- Example: ‘Peb’ (we) vs. ‘Pem’ (up there).
8.4. Getting Feedback
Record yourself speaking Hmong and ask native speakers for feedback. This will help you identify areas where you need to improve.
- Online Tutors: Hire an online tutor for personalized pronunciation lessons.
- Language Exchange Partners: Practice with native speakers and ask for corrections.
9. Cultural Immersion: Enhancing Your Hmong Learning Experience
Immersing yourself in the culture of the Hmong people is an excellent way to enhance your language learning experience. It provides context, makes the learning process more enjoyable, and helps you understand the nuances of the language.
9.1. Engaging with Hmong Music and Cinema
Listening to Hmong music and watching Hmong films can expose you to the language in a natural and engaging way.
- Music: Explore various genres of Hmong music to get accustomed to the rhythm and intonation of the language.
- Cinema: Watch Hmong movies with subtitles initially, and gradually try watching without subtitles.
9.2. Participating in Cultural Events
Attending Hmong cultural events can provide opportunities to interact with native speakers and learn about the customs and traditions of the Hmong people.
- New Year Celebrations: Participate in Hmong New Year celebrations to experience the cultural festivities.
- Community Gatherings: Attend local Hmong community gatherings to meet native speakers and practice your language skills.
9.3. Learning Hmong Cuisine
Learning about Hmong cuisine can provide insights into the culture and language. Try cooking Hmong dishes and learning the names of ingredients and cooking techniques in Hmong.
- Cooking Classes: Take a Hmong cooking class to learn how to prepare traditional dishes.
- Food Markets: Visit local markets that sell Hmong ingredients and learn the names of these ingredients in Hmong.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Learning Hmong
Even with the best strategies, learners often make common mistakes. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid them and improve your learning efficiency.
10.1. Ignoring Tones
One of the most common mistakes is not paying enough attention to tones. Remember that tones are crucial for distinguishing the meaning of words.
- Practice: Dedicate time to practicing tones every day.
- Feedback: Seek feedback from native speakers to ensure you are pronouncing tones correctly.
10.2. Neglecting Pronunciation
Poor pronunciation can hinder communication. Make sure to focus on pronunciation from the beginning.
- Audio Resources: Use audio recordings to mimic native speakers.
- Record Yourself: Compare your pronunciation to that of native speakers.
10.3. Relying Too Heavily on Translation
While translation can be helpful, relying too heavily on it can prevent you from thinking in Hmong.
- Immersion: Try to think in Hmong as much as possible.
- Context: Use context to understand the meaning of words and phrases.
10.4. Giving Up Easily
Learning a new language takes time and effort. Don’t get discouraged by initial challenges.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your learning into smaller, achievable goals.
- Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress to stay motivated.
FAQ Section: Your Burning Questions About Learning Hmong Answered
Is Hmong hard to learn?
Hmong can be easy to learn due to its use of the Roman alphabet and consistent spelling, but the tonal nature of the language poses a challenge. With dedication and the right resources, anyone can learn Hmong effectively.
How long does it take to learn Hmong?
Learning Hmong varies, but basic conversational skills can be achieved in 6 months to a year with consistent study, while fluency may take several years. Your learning pace depends on your dedication and resources.
What are the basic greetings in Hmong?
Basic greetings in Hmong include “Nyob zoo” (Hello) and “Sib ntsib dua” (Goodbye).
How many dialects of Hmong are there?
There are two main dialects: White Hmong (Hmoob Dawb) and Green Hmong (Moob Ntsuab/Moob Leeg).
How many tones does the Hmong language have?
The Hmong language has eight tones, crucial for distinguishing word meanings. Mastering these tones is essential for effective communication.
Is Hmong a dying language?
No, Hmong is not a dying language. It continues to be kept alive by millions of speakers worldwide.
How do you say ‘Yes’ in Hmong?
There is no direct equivalent to ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ in Hmong. Instead, responses are based on the verb in the question.
Do Hmong have a country?
Hmong people are not centralized in one country but are spread throughout Southeast Asia and other parts of the world.
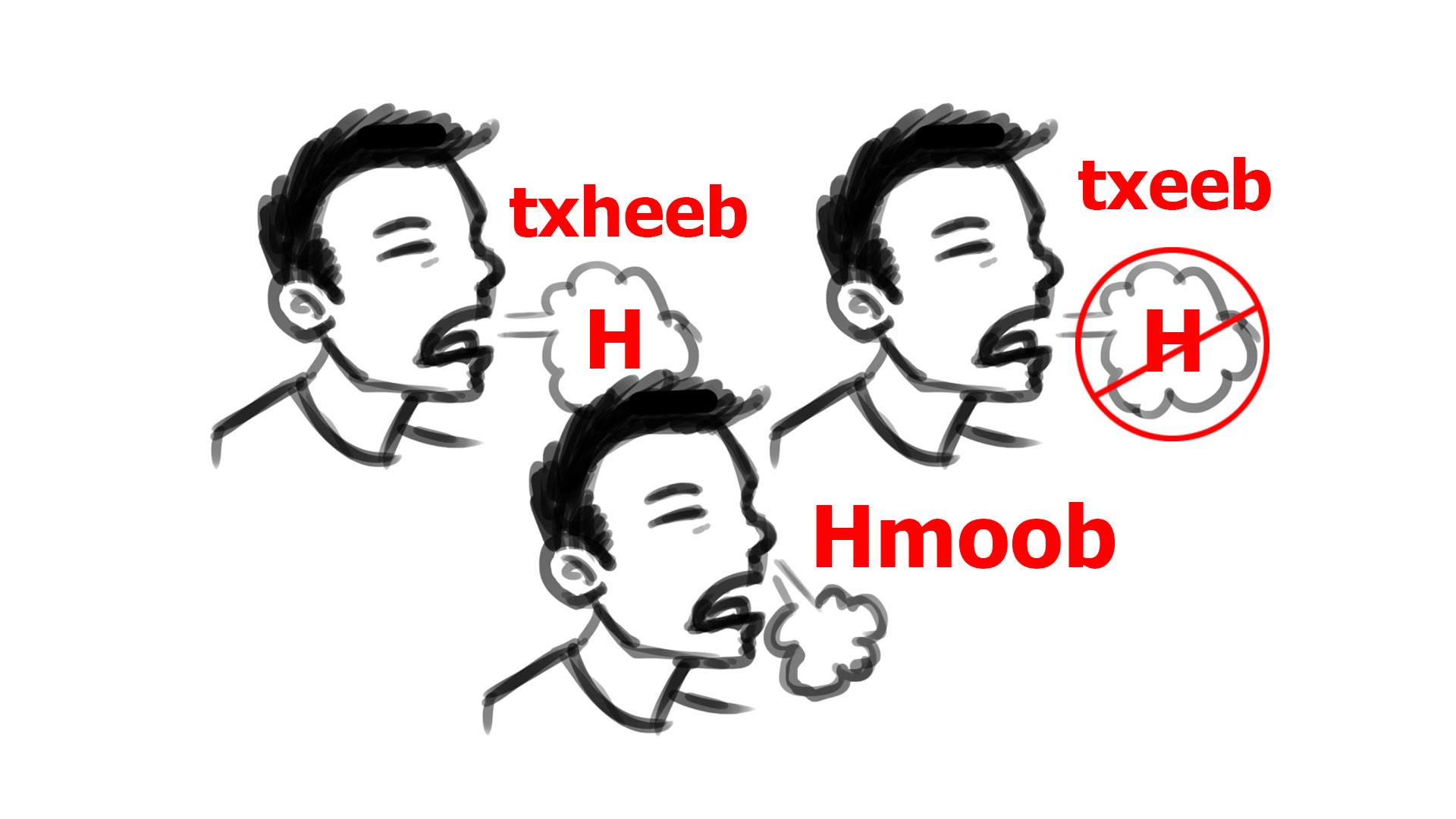
Is the ‘H’ silent in Hmong?
No. In White Hmong, the ‘H’ is aspirated and comes from the nose. In Green Hmong, it is not aspirated and the word is often spelled ‘Mong.’
What are some good resources for learning Hmong?
Resources include online courses like LEARNS.EDU.VN, textbooks, language exchange partners, and cultural organizations.
Conclusion: Embark on Your Hmong Learning Journey with Confidence
Learning Hmong can be a rewarding experience, opening doors to a rich culture and community. While the tonal nature of the language and limited resources may present challenges, with the right strategies, dedication, and resources like those available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can achieve fluency and connect with the Hmong-speaking world.
Ready to start your Hmong learning journey? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive courses and resources. Our expert instructors and interactive lessons will guide you every step of the way. Don’t miss this opportunity to unlock a new language and culture.
Contact us:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: learns.edu.vn
Start learning Hmong today and discover the world of opportunities that await you!