Embark on a journey of knowledge and self-discovery! A Learning Experience is more than just acquiring information; it’s a transformative process that shapes our understanding and perspective. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe that understanding the essence of “a learning experience” is crucial for anyone seeking to enhance their skills, broaden their horizons, or simply cultivate a lifelong love for learning. Discover educational journey, cognitive development, and skill enhancement with LEARNS.EDU.VN!
1. Defining a Learning Experience
At its core, a learning experience is any interaction or event that leads to a change in knowledge, skills, attitudes, or behaviors. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from formal education to informal self-discovery. Understanding the key elements of a learning experience can help educators and learners alike design and engage in more effective and meaningful learning opportunities. To fully grasp what constitutes a learning experience, let’s dissect its fundamental components: situation, time, and impression.
1.1 The Three Pillars of a Learning Experience
According to Niels Floor in “This is Learning Experience Design,” an experience is any situation encountered that takes a certain amount of time and leaves some kind of impression. Let’s explore these elements in detail:
1.1.1 Situation
The situation is the context in which learning occurs. According to the Cambridge Dictionary, it is “the set of things that are happening and the conditions that exist at a particular time and place.” This includes the physical environment, the social dynamics, and the learner’s state of mind.
- Physical Environment: A quiet library versus a bustling coffee shop can significantly impact focus and retention.
- Social Dynamics: Group projects versus solo study sessions offer different opportunities for collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Learner’s State of Mind: A motivated and curious learner will absorb information more effectively than one who is bored or stressed.
The situation can significantly influence what you experience and how you experience things. For example, reading this article at home in a quiet evening setting will provide a different experience compared to reading it on a crowded subway during a busy morning commute.
1.1.2 Time
Time is an essential element of any experience. Learning experiences unfold over time, whether it’s a short burst of insight or a long-term process of skill development.
- Duration: A quick online tutorial versus a semester-long course offers different levels of depth and engagement.
- Pacing: Self-paced learning allows individuals to adjust the speed of instruction to their needs, while structured courses follow a predetermined schedule.
- Timing: Learning new information right before a test versus spacing out study sessions over time can affect long-term retention.
Emotion plays a primary role in influencing how fast time passes. As Albert Einstein explained, time is relative. When you design a learning experience, it is important to consider how much time you ask from the learner and what you offer in return. What the learner gets out of a learning experience should always outweigh the time they spend.
1.1.3 Impression
The impression is the lasting impact of the experience. It encompasses what you remember, what you have learned, and how the experience made you feel. It’s about the extent to which the experience changed your life.
- Knowledge Gain: Did you acquire new information or skills?
- Behavior Change: Did the experience influence your actions or habits?
- Emotional Impact: Did the experience evoke positive or negative feelings?
Learning experience designers aim to have a big impact on the learner, but not every experience can nor should be life-changing.
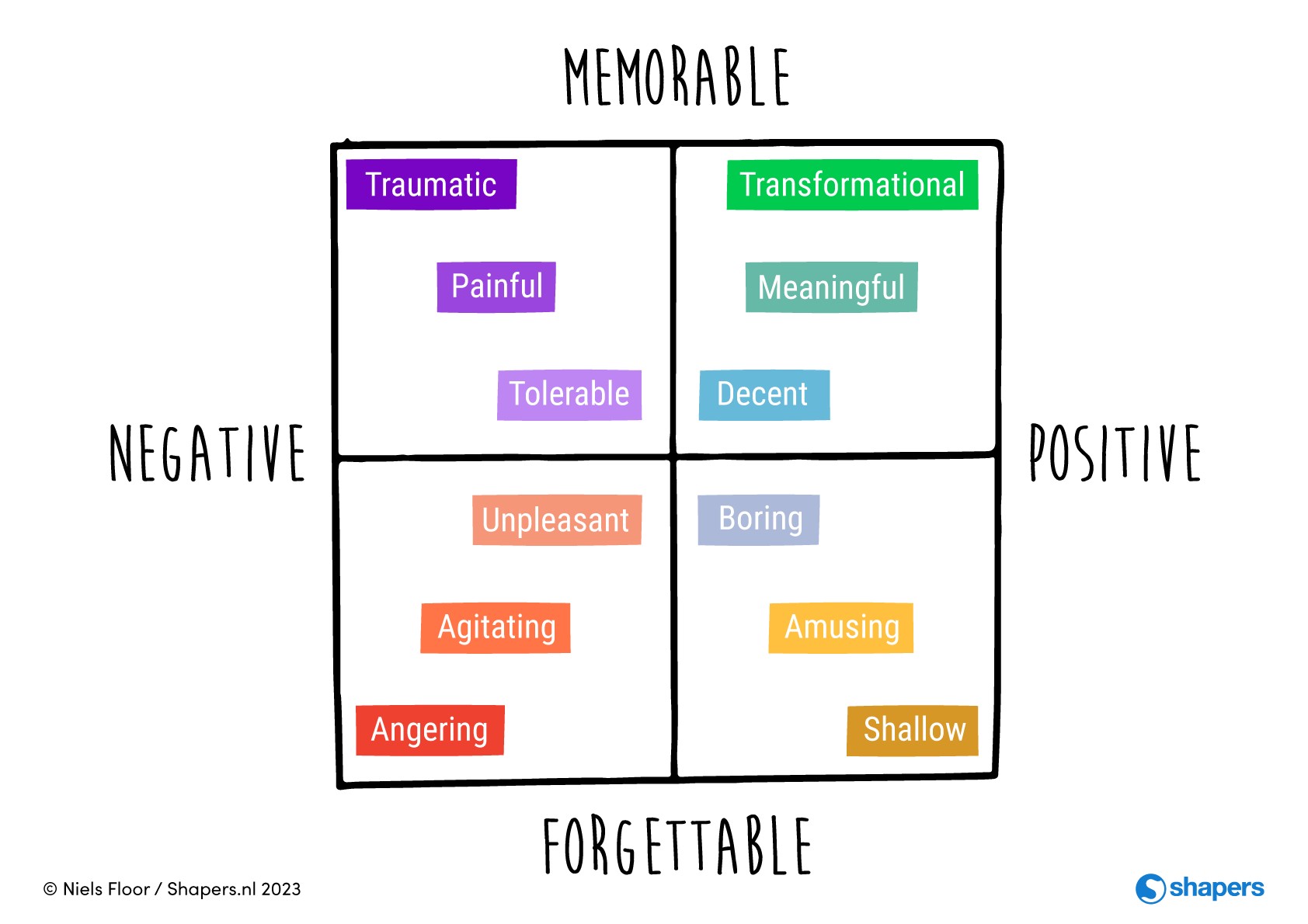
1.2 The Experience Impact Model
The Experience Impact Model, developed by Niels Floor, illustrates how experiences can vary in terms of positive and negative impact. It emphasizes the importance of designing experiences that have a positive and lasting effect on the learner.
Experiences that fall into the upper right corner of the model are the most desirable. They have a big positive impact. However, life doesn’t work that way, and often the most impactful experiences occur outside of our control. Our experiences are subjective. For example, a negative remark by a teacher can have a huge impact on a student, while the teacher may forget the experience almost immediately. On the other hand, there are many examples of painful experiences that can teach valuable lessons and have a lasting positive impact, like entrepreneurs who use rejection and adversity to develop perseverance to become highly successful.
1.3 Spontaneous vs. Designed Learning Experiences
Learning experiences can be either spontaneous or designed. Spontaneous learning experiences happen unexpectedly, while designed learning experiences are intentionally created to achieve specific learning outcomes.
| Feature | Spontaneous Learning Experience | Designed Learning Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Occurrence | Unexpected, unplanned | Intentional, planned |
| Outcome | Unpredictable, may or may not lead to learning | Predefined, aimed at achieving specific learning objectives |
| Control | Learner has more control over the experience | Designer/educator has more control over the experience |
| Examples | Overcoming a challenge while traveling, a conversation with a stranger | Structured course, workshop, online tutorial |
| Primary Goal | Personal growth, exploration | Skill development, knowledge acquisition |
| Design Focus | N/A | Creative design skills, tools and methods are used to shape these experiences with a focus on the overall experience of the learner |
| Learning result | Unintended result of your design | Intended results |

2. Types of Learning Experiences
Learning experiences come in many forms, each with its own unique benefits and challenges. Here are some common types:
2.1 Formal Education
This includes traditional classroom learning, such as attending school or university. Formal education provides a structured curriculum and a credential upon completion.
- Strengths: Structured learning environment, expert instruction, recognized qualifications
- Weaknesses: Can be expensive, may not cater to individual learning styles, rigid curriculum
2.2 Online Learning
Online learning encompasses a wide range of digital educational resources, from online courses to webinars and virtual workshops.
- Strengths: Flexible, accessible, often more affordable than traditional education
- Weaknesses: Requires self-discipline, can feel isolating, may lack face-to-face interaction
2.3 Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities and real-world applications. This can include internships, apprenticeships, and simulations.
- Strengths: Highly engaging, promotes deeper understanding, develops practical skills
- Weaknesses: Can be time-consuming, may require significant resources, difficult to scale
2.4 Informal Learning
Informal learning occurs outside of structured educational settings. It can include reading books, watching documentaries, attending workshops, and engaging in conversations with experts.
- Strengths: Flexible, self-directed, can be tailored to individual interests
- Weaknesses: Requires self-motivation, may lack structure, difficult to assess learning outcomes
2.5 Blended Learning
Blended learning combines online and face-to-face instructional methods, which provide personalized learning experiences and more flexibility for learners.
- Strengths: Combines the benefits of both online and face-to-face learning, personalized learning experiences, and more flexibility for learners
- Weaknesses: Requires careful planning and coordination and may require more resources than traditional learning methods
3. Designing Effective Learning Experiences
Designing effective learning experiences requires careful consideration of the learner’s needs, goals, and preferences. Here are some key principles to keep in mind:
3.1 Start with Clear Learning Objectives
What do you want learners to achieve as a result of the experience? Clearly defined learning objectives provide a roadmap for the design process.
3.2 Consider the Learner’s Perspective
Put yourself in the learner’s shoes. What are their motivations, challenges, and expectations? Understanding the learner’s perspective will help you create a more relevant and engaging experience.
3.3 Incorporate Active Learning Strategies
Engage learners in active learning activities, such as discussions, group projects, and simulations. Active learning promotes deeper understanding and retention.
3.4 Provide Meaningful Feedback
Offer timely and constructive feedback to help learners track their progress and identify areas for improvement. Feedback should be specific, actionable, and focused on the learning objectives.
3.5 Make it Relevant and Engaging
Connect the learning experience to real-world applications and make it personally relevant to the learner. Use multimedia, storytelling, and other techniques to capture their attention and keep them engaged.
3.6 Promote Collaboration and Social Interaction
Encourage learners to collaborate and interact with each other. Social interaction can enhance learning and provide opportunities for peer support.
3.7 Embrace Technology Wisely
Integrate technology to enhance the learning experience. Choose tools that are user-friendly, accessible, and aligned with the learning objectives.
4. The Role of Technology in Learning Experiences
Technology has revolutionized the way we learn, offering new possibilities for creating engaging and effective learning experiences.
4.1 Online Learning Platforms
Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer a vast array of courses on virtually every topic imaginable.
- Benefits: Wide range of courses, flexible scheduling, affordable pricing
- Challenges: Requires self-discipline, may lack personalized support, quality can vary
4.2 Learning Management Systems (LMS)
LMS platforms like Moodle and Canvas provide tools for creating, delivering, and tracking online courses and training programs.
- Benefits: Centralized platform for managing learning content, tracking learner progress, facilitating communication
- Challenges: Can be complex to set up and manage, may require technical expertise, cost can be a barrier for some
4.3 Mobile Learning Apps
Apps like Duolingo and Memrise make learning fun and accessible on the go.
- Benefits: Convenient, gamified learning, personalized feedback
- Challenges: Can be distracting, may not offer in-depth instruction, limited content
4.4 Virtual and Augmented Reality
VR and AR technologies create immersive learning environments that can simulate real-world scenarios.
- Benefits: Highly engaging, promotes deeper understanding, allows for risk-free experimentation
- Challenges: Expensive, requires specialized equipment, can cause motion sickness
5. Real-World Examples of Effective Learning Experiences
Let’s examine some real-world examples of effective learning experiences across different domains.
5.1 The Khan Academy
This non-profit organization provides free online educational resources, including video lessons and practice exercises, covering a wide range of subjects.
- Key Features: Personalized learning paths, mastery-based learning, data-driven insights
5.2 General Assembly
This coding bootcamp offers intensive, immersive programs designed to help individuals launch careers in tech.
- Key Features: Hands-on projects, industry-expert instructors, career coaching
5.3 The Montessori Method
This educational approach emphasizes self-directed learning, hands-on activities, and collaborative problem-solving.
- Key Features: Child-centered learning, mixed-age classrooms, specialized learning materials
5.4 Corporate Training Programs at Google
Google invests heavily in employee training and development, offering a wide range of programs designed to enhance skills and promote innovation.
- Key Features: Experiential learning, peer-to-peer mentoring, hackathons
6. Overcoming Challenges in Learning Experiences
Even the best-designed learning experiences can encounter challenges. Here are some common obstacles and how to overcome them:
6.1 Lack of Motivation
- Challenge: Learners may lack intrinsic motivation to engage in the learning experience.
- Solution: Make the learning experience relevant, engaging, and personally meaningful. Connect it to real-world applications and provide opportunities for learners to pursue their interests.
6.2 Cognitive Overload
- Challenge: Learners may feel overwhelmed by too much information or too complex tasks.
- Solution: Break down complex topics into smaller, more manageable chunks. Provide clear instructions and scaffolding to support learning.
6.3 Learning Styles Differences
- Challenge: Learners have different learning styles and preferences, making it difficult to cater to everyone’s needs.
- Solution: Offer a variety of learning activities and resources to accommodate different learning styles. Provide options for learners to choose how they engage with the material.
6.4 Accessibility Issues
- Challenge: Learners with disabilities may face barriers to accessing the learning experience.
- Solution: Ensure that the learning experience is accessible to all learners, regardless of their abilities. Provide accommodations and assistive technologies as needed.
6.5 Technical Difficulties
- Challenge: Technical glitches and software issues can disrupt the learning experience.
- Solution: Provide technical support and troubleshooting resources. Test technology in advance to ensure that it is working properly.
7. Measuring the Effectiveness of Learning Experiences
How do you know if a learning experience is successful? Here are some key metrics to track:
7.1 Knowledge Gain
Assess whether learners have acquired new knowledge or skills as a result of the experience.
- Methods: Quizzes, tests, projects
7.2 Behavior Change
Evaluate whether the learning experience has influenced learners’ actions or habits.
- Methods: Observation, self-reporting, performance reviews
7.3 Learner Satisfaction
Measure learners’ satisfaction with the learning experience.
- Methods: Surveys, feedback forms, focus groups
7.4 Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculate the financial benefits of the learning experience in relation to the costs.
- Methods: Cost-benefit analysis, performance metrics
7.5 Engagement Metrics
Monitor learner engagement with the learning experience.
- Methods: Tracking participation, completion rates, time spent on tasks
8. The Future of Learning Experiences
The field of learning experience design is constantly evolving. Here are some key trends to watch:
8.1 Personalized Learning
Tailoring learning experiences to individual needs and preferences is becoming increasingly important.
- Example: Adaptive learning platforms that adjust the difficulty of content based on learner performance.
8.2 Microlearning
Delivering learning content in small, bite-sized chunks is becoming more popular.
- Example: Short video tutorials, infographics, and interactive quizzes.
8.3 Gamification
Incorporating game-like elements into learning experiences can increase engagement and motivation.
- Example: Points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges.
8.4 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to personalize learning, automate tasks, and provide intelligent feedback.
- Example: AI-powered chatbots that answer learner questions, AI-driven assessment tools that provide personalized feedback.
8.5 Data Analytics
Using data to track learner progress and improve learning experiences is becoming more common.
- Example: Learning analytics dashboards that provide insights into learner behavior and performance.
9. Learning Experience Design (LXD): A Holistic Approach
Learning Experience Design (LXD) is a discipline that focuses on creating engaging and effective learning experiences. LXD takes a holistic approach, considering all aspects of the learner’s journey, from the initial engagement to the final assessment.
9.1 Key Principles of LXD
- Learner-centered: LXD puts the learner at the center of the design process.
- Goal-oriented: LXD focuses on achieving specific learning outcomes.
- Evidence-based: LXD uses research and data to inform design decisions.
- Iterative: LXD involves continuous testing and refinement.
9.2 The LXD Process
The LXD process typically involves the following steps:
- Needs Analysis: Identify the learning needs and goals of the target audience.
- Design: Create a blueprint for the learning experience, including learning objectives, activities, and assessments.
- Development: Build the learning experience, including creating content and developing interactive elements.
- Implementation: Deliver the learning experience to the target audience.
- Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of the learning experience and make improvements as needed.
9.3 The Skills of a Learning Experience Designer
- Instructional Design: Create effective learning materials.
- User Experience (UX) Design: Design intuitive and engaging interfaces.
- Visual Design: Create visually appealing and effective graphics.
- Project Management: Manage projects and deadlines.
- Communication: Communicate effectively with stakeholders.
10. Unleash Your Learning Potential with LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to create and engage in transformative learning experiences. Whether you’re a student, educator, or lifelong learner, we have something for you.
10.1 Explore Our Resources
Visit our website at LEARNS.EDU.VN to discover a wealth of articles, tutorials, and resources on learning experience design and related topics. From in-depth guides on instructional design to practical tips on creating engaging online courses, we have everything you need to enhance your learning journey.
10.2 Connect with Our Experts
Our team of experienced educators and learning designers is here to help you succeed. Contact us at +1 555-555-1212 or visit our office at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States to connect with our experts and get personalized guidance on your learning goals.
10.3 Join Our Community
Join our vibrant community of learners and educators to share ideas, ask questions, and collaborate on projects. Together, we can create a world where everyone has access to high-quality learning experiences.
10.4 Featured Courses
Take a look at the courses that will provide you with more learning experience:
| Course Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Learning Design | Learn the fundamentals of learning experience design and create your own engaging learning activities. |
| Creating Effective Online Courses | Learn how to design and develop effective online courses that meet the needs of your learners. |
| Gamification in Education | Discover how to use gamification to increase engagement and motivation in your learning experiences. |
| Artificial Intelligence in Education | Explore the potential of AI in education and learn how to use AI tools to personalize learning and provide intelligent feedback. |
| Data Analytics for Learning Design | Learn how to use data analytics to track learner progress and improve your learning experiences. |
| Designing for Accessibility | Understand how to design inclusive learning experiences that are accessible to all learners, regardless of their abilities. |
| Mobile Learning | Learn how to design and develop effective mobile learning experiences that are accessible on any device. |
| Blended Learning | Discover how to combine online and face-to-face instructional methods to create personalized learning experiences and more flexibility for learners. |
| Project-Based Learning | Learn how to create project-based learning experiences that engage learners in real-world problem-solving. |
| Assessment and Evaluation | Explore different assessment and evaluation methods and learn how to use them to measure the effectiveness of your learning experiences. |
| Learning Technologies | Discover the latest learning technologies and learn how to use them to enhance your learning experiences. |
| The Art of Facilitation | Learn how to facilitate effective learning experiences that promote collaboration, critical thinking, and problem-solving. |
| Instructional Design Models | Explore different instructional design models and learn how to apply them to your learning experiences. |
| The Science of Learning | Delve into the science of learning and discover how the brain learns and processes information, and how to apply this knowledge to your learning experiences. |
| Building Learning Communities | Learn how to build online and offline learning communities that foster engagement, collaboration, and a sense of belonging. |
| Creating Engaging Presentations | Discover how to design and deliver engaging presentations that capture your audience’s attention and keep them interested. |
| Storytelling in Learning | Learn how to use storytelling to make your learning experiences more memorable, engaging, and impactful. |
| The Future of Learning | Explore the trends shaping the future of learning and discover how to prepare yourself for the changing landscape of education. |
| Designing Adaptive Learning | Learn how to design adaptive learning experiences that adjust to each learner’s individual needs and pace. |
| Inclusive Design Strategies | Discover strategies for designing inclusive learning experiences that are welcoming and accessible to learners from all backgrounds and abilities. |
| Emotional Intelligence in Learning | Learn how to leverage emotional intelligence to create learning experiences that are more engaging, supportive, and effective. |
| Learning Analytics and Reporting | Explore the power of learning analytics and discover how to use data to track learner progress, measure the impact of your learning experiences, and make data-driven decisions. |
| Building a Culture of Learning | Learn how to create a culture of learning in your organization or community, where everyone is encouraged to learn, grow, and innovate. |
| Personalizing the Learning Journey | Discover how to personalize the learning journey for each learner, creating experiences that are tailored to their individual needs, goals, and learning styles. |
| Social and Collaborative Learning | Explore the benefits of social and collaborative learning and learn how to design experiences that foster interaction, communication, and knowledge sharing among learners. |
| The Art of Feedback and Assessment | Learn how to provide effective feedback and assessment that helps learners improve, grow, and achieve their full potential. |
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Learning Experiences
Q1: What is the difference between learning and training?
A: Learning is a broad term that encompasses any change in knowledge, skills, attitudes, or behaviors. Training is a specific type of learning that focuses on acquiring skills for a particular job or task.
Q2: How can I make my learning experience more engaging?
A: Make it relevant, interactive, and personally meaningful. Connect it to real-world applications and provide opportunities for learners to pursue their interests.
Q3: What are some common mistakes to avoid when designing learning experiences?
A: Overloading learners with too much information, failing to provide clear instructions, and neglecting to address different learning styles.
Q4: How can I measure the effectiveness of a learning experience?
A: Track knowledge gain, behavior change, learner satisfaction, and return on investment.
Q5: What role does technology play in learning experiences?
A: Technology can enhance learning experiences by providing access to information, facilitating communication, and creating immersive learning environments.
Q6: What is the future of learning experiences?
A: The future of learning experiences is personalized, micro, gamified, AI-powered, and data-driven.
Q7: How can I create a learning culture in my organization?
A: Encourage continuous learning, provide opportunities for professional development, and recognize and reward learning achievements.
Q8: What is the best way to learn a new skill?
A: Practice, get feedback, and stay motivated.
Q9: How can I improve my memory?
A: Use mnemonic devices, practice active recall, and get enough sleep.
Q10: What are the benefits of lifelong learning?
A: Improved cognitive function, increased job opportunities, enhanced personal growth, and a greater sense of purpose.
12. Final Thoughts
A learning experience is a transformative journey that can enrich your life in countless ways. By understanding the key principles of learning experience design and embracing the power of technology, you can create and engage in learning experiences that are both effective and enjoyable. Visit learns.edu.vn today to discover a world of knowledge and unlock your full potential! Remember, the journey of learning never ends!
