A Web Based Learning Program Is Called Synchronous When it allows for real-time interaction, mirroring the dynamic exchange of information found in traditional classrooms. This immediate interaction fosters a sense of community and aids in clarifying any misconceptions. LEARNS.EDU.VN is committed to providing valuable insights into how to effectively use synchronous learning for optimal educational results, along with asynchronous and hybrid models. Enhance your understanding with synchronous collaboration, real-time feedback, and interactive sessions for enriched educational technology.
1. Understanding Synchronous Learning Environments
Synchronous learning refers to educational activities where participants interact at the same time, irrespective of their location. This interaction usually happens through web based learning programs that facilitate real-time communication. It is a cornerstone of modern educational strategies, offering a blend of immediacy and engagement that complements other learning methods.
1.1. Key Characteristics of Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning replicates the interactive dynamics of a traditional classroom, but in a digital setting.
- Real-Time Interaction: The defining feature is the ability to interact in real-time.
- Immediate Feedback: Learners receive instant responses to their questions.
- Collaborative Opportunities: Students can work together on projects and discuss ideas.
- Structured Schedules: Classes or sessions occur at set times, promoting routine and discipline.
- Instructor-Led: Often guided by an instructor who facilitates discussions and delivers lectures.
1.2. Examples of Synchronous Activities
Several activities fall under the umbrella of synchronous learning:
- Live Webinars: Presentations delivered live, allowing for Q&A sessions.
- Video Conferencing: Tools like Zoom or Google Meet enable face-to-face interactions.
- Instant Messaging: Platforms such as Slack or Microsoft Teams used for quick communication.
- Virtual Classrooms: Online spaces designed to mimic physical classrooms.
 Students participating in a live webinar, asking questions and interacting with the presenter in real-time
Students participating in a live webinar, asking questions and interacting with the presenter in real-time
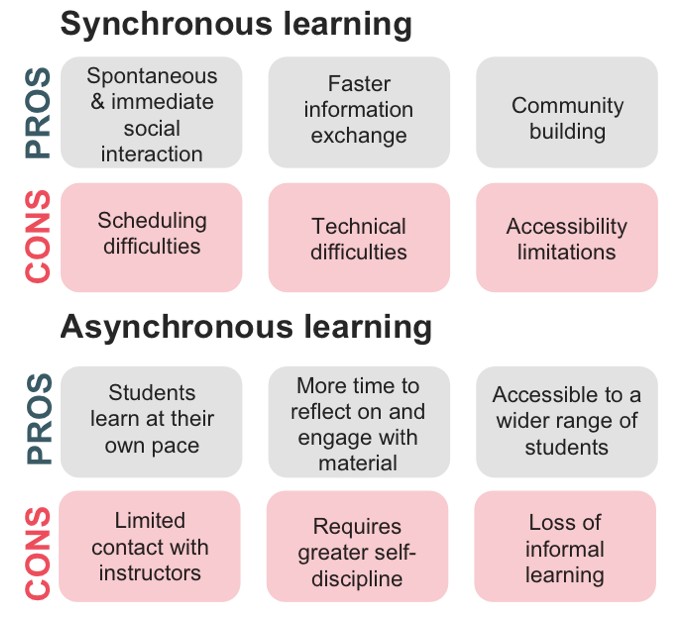
2. Benefits of Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning offers many advantages, making it a valuable component of any comprehensive educational program.
2.1. Enhanced Social Interaction
One of the most significant benefits of synchronous learning is the opportunity for social interaction.
- Community Building: Real-time interactions help build a sense of community among learners.
- Networking Opportunities: Students can connect with peers and instructors.
- Motivation and Engagement: Live interactions can boost motivation and engagement.
2.2. Immediate Clarification
The ability to ask questions and receive immediate answers can greatly enhance understanding.
- Real-Time Problem Solving: Complex problems can be addressed in real-time.
- Reduced Misunderstandings: Instant clarification prevents misconceptions.
- Personalized Learning: Instructors can tailor their teaching based on immediate feedback.
2.3. Structured Learning Environment
Synchronous learning provides a structured environment that can be beneficial for many learners.
- Time Management: Scheduled sessions help students manage their time effectively.
- Routine and Discipline: Regular class times promote routine and discipline.
- Consistent Engagement: Keeps learners consistently engaged with the material.
2.4. Fostering Active Participation
Synchronous sessions encourage active participation, which is critical for effective learning.
- Interactive Discussions: Live discussions encourage critical thinking.
- Collaborative Projects: Group projects enhance teamwork and problem-solving skills.
- Increased Retention: Active participation leads to better retention of information.
3. Challenges of Synchronous Learning
Despite its advantages, synchronous learning also presents several challenges that educators and learners need to address.
3.1. Scheduling Conflicts
One of the primary challenges is coordinating schedules, especially for diverse groups.
- Time Zone Differences: Participants in different time zones may find it difficult to attend live sessions.
- Conflicting Commitments: Students may have other obligations that conflict with scheduled classes.
- Accessibility Issues: Not all students may be available at the designated times due to various reasons.
3.2. Technical Issues
Technical difficulties can disrupt synchronous sessions and frustrate participants.
- Internet Connectivity: Reliable internet access is essential but not always available.
- Software Compatibility: Participants need compatible software and hardware.
- Technical Support: Access to technical support is crucial for resolving issues quickly.
3.3. Accessibility Concerns
Ensuring that synchronous sessions are accessible to all learners is crucial.
- Disability Accommodations: Providing accommodations for students with disabilities.
- Language Barriers: Offering support for non-native speakers.
- Equitable Access: Ensuring all students have equal access to resources.
3.4. Engagement Maintenance
Keeping learners engaged in a virtual environment can be challenging.
- Distractions: Students may face distractions in their learning environment.
- Attention Spans: Maintaining attention during long sessions can be difficult.
- Interactive Strategies: Requires instructors to use engaging teaching methods.
**4. Comparing Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous and asynchronous learning represent two distinct approaches to education, each with its own set of features, benefits, and challenges. Understanding the differences between these modalities can help educators design more effective learning experiences.
4.1. Key Differences
| Feature | Synchronous Learning | Asynchronous Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Real-time, scheduled | Flexible, self-paced |
| Interaction | Immediate, direct | Delayed, indirect |
| Location | Shared virtual space | Individual, varied locations |
| Pace | Uniform, dictated by instructor | Individual, self-determined |
| Feedback | Instant | Delayed |
| Collaboration | Real-time group activities | Forums, discussion boards |
| Technology | Video conferencing, live chat | Pre-recorded videos, email |
| Structure | Highly structured, scheduled | Less structured, more independent |
| Engagement | High potential for engagement but requires active facilitation | Relies on self-motivation and discipline |
| Accessibility | Can be challenging due to scheduling and tech requirements | Generally more accessible due to flexibility |
4.2. Benefits of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning offers several advantages:
- Flexibility: Learners can access materials and complete assignments at their own pace.
- Accessibility: Suitable for students with varied schedules and time zones.
- Self-Paced Learning: Allows students to review materials as needed.
- Reflection Time: Provides time for thoughtful responses and contributions.
4.3. Challenges of Asynchronous Learning
However, asynchronous learning also poses certain challenges:
- Lack of Immediate Feedback: Delayed feedback can hinder understanding.
- Reduced Social Interaction: Fewer opportunities for real-time interaction.
- Procrastination: Requires strong self-discipline to avoid procrastination.
- Technical Issues: Still requires reliable internet access and technical skills.
5. Strategies for Effective Synchronous Learning
To maximize the benefits of synchronous learning, educators should implement specific strategies that address the challenges and enhance engagement.
5.1. Planning and Preparation
Thorough planning is essential for successful synchronous sessions.
- Clear Objectives: Define clear learning objectives for each session.
- Detailed Agenda: Create a detailed agenda and share it with participants.
- Technical Rehearsal: Conduct a technical rehearsal to ensure all systems work properly.
- Backup Plans: Have backup plans in case of technical issues.
5.2. Engagement Techniques
Keeping learners engaged requires using interactive techniques.
- Polls and Quizzes: Use polls and quizzes to check understanding and keep participants involved.
- Breakout Rooms: Divide participants into small groups for discussions and activities.
- Interactive Whiteboards: Use virtual whiteboards for collaborative brainstorming.
- Gamification: Incorporate game-like elements to make learning fun.
5.3. Accessibility Considerations
Ensuring accessibility is crucial for inclusivity.
- Closed Captioning: Provide closed captioning for live sessions.
- Transcripts: Offer transcripts of audio content.
- Screen Reader Compatibility: Ensure materials are compatible with screen readers.
- Alternative Formats: Provide materials in alternative formats (e.g., large print).
5.4. Communication and Feedback
Effective communication is key to successful synchronous learning.
- Clear Instructions: Provide clear instructions for all activities.
- Regular Check-Ins: Regularly check in with participants to gauge understanding.
- Prompt Feedback: Provide prompt feedback on questions and contributions.
- Open Communication Channels: Maintain open communication channels for questions and support.
6. Tools and Technologies for Synchronous Learning
Several tools and technologies can facilitate synchronous learning, each with its own strengths and features.
6.1. Video Conferencing Platforms
Video conferencing platforms are essential for synchronous learning.
- Zoom: Popular for its ease of use and robust features.
- Google Meet: Integrated with Google Workspace, offering seamless collaboration.
- Microsoft Teams: Part of the Microsoft ecosystem, ideal for organizations using Microsoft products.
- Webex: Known for its enterprise-level security and features.
6.2. Virtual Classroom Software
Virtual classroom software provides a comprehensive learning environment.
- Blackboard Collaborate: Designed specifically for education, offering a range of tools.
- Canvas Conference: Integrated with the Canvas learning management system.
- Adobe Connect: Suitable for training and presentations, with interactive features.
6.3. Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools enhance interaction and teamwork.
- Google Docs: Allows real-time collaborative document editing.
- Microsoft Teams: Offers channels for group discussions and file sharing.
- Slack: Popular for instant messaging and team collaboration.
- Miro: A virtual whiteboard for brainstorming and visual collaboration.
6.4. Interactive Whiteboards
Interactive whiteboards facilitate real-time collaboration.
- Miro: Offers a versatile platform for visual collaboration.
- Whiteboard.fi: A simple and easy-to-use virtual whiteboard.
- Explain Everything: An interactive whiteboard with advanced features.
7. Examples of Synchronous Learning in Practice
To illustrate the effectiveness of synchronous learning, consider these practical examples:
7.1. Online Language Classes
Synchronous sessions allow students to practice speaking and listening skills in real-time.
- Interactive Conversations: Students engage in live conversations with instructors and peers.
- Pronunciation Practice: Instructors provide immediate feedback on pronunciation.
- Cultural Exchange: Students learn about different cultures through live interactions.
7.2. Virtual Science Labs
Synchronous labs enable students to conduct experiments and analyze data together.
- Real-Time Guidance: Instructors guide students through experiments in real-time.
- Collaborative Analysis: Students analyze data and discuss findings together.
- Problem-Solving: Students work together to troubleshoot issues and solve problems.
7.3. Online Music Lessons
Synchronous lessons allow instructors to provide personalized feedback and guidance.
- Real-Time Instruction: Instructors provide real-time instruction on technique and performance.
- Immediate Feedback: Students receive immediate feedback on their playing.
- Collaborative Performances: Students can perform together in virtual ensembles.
7.4. Remote Professional Training
Synchronous training sessions allow professionals to learn new skills and network with peers.
- Live Workshops: Professionals participate in live workshops and training sessions.
- Expert Instruction: Experts provide real-time instruction and guidance.
- Networking Opportunities: Professionals connect with peers and build relationships.
8. Synchronous Learning and Neurodiversity
Understanding how synchronous learning environments can be adapted to support neurodiverse learners is crucial for creating inclusive and effective educational experiences. Neurodiversity encompasses a range of neurological differences, including autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and others.
8.1. Challenges Faced by Neurodiverse Learners in Synchronous Settings
- Sensory Overload: Bright screens, loud noises, and rapid visual changes can be overwhelming.
- Attention and Focus: Maintaining focus during long, unstructured sessions can be difficult for individuals with ADHD.
- Social Communication: Real-time social interactions can be challenging for those with autism.
- Processing Speed: Some learners may need more time to process information and respond.
8.2. Strategies for Supporting Neurodiverse Learners
- Provide Clear Structure: Offer detailed agendas, clear instructions, and predictable routines.
- Offer Breaks: Incorporate regular breaks to prevent sensory overload and maintain focus.
- Use Visual Aids: Visual supports can help learners process and retain information.
- Allow Flexible Participation: Offer options for participation, such as chat, written responses, or private messaging.
- Provide Recordings: Offer recordings of sessions so learners can review the material at their own pace.
- Promote a Supportive Environment: Encourage empathy and understanding among all participants.
8.3. Assistive Technologies and Tools
- Text-to-Speech Software: Helps learners with dyslexia or visual impairments access written materials.
- Speech-to-Text Software: Allows learners to participate verbally without typing.
- Noise-Canceling Headphones: Reduces distractions and sensory overload.
- Screen Filters: Reduces glare and blue light, minimizing visual strain.
9. The Future of Synchronous Learning
The future of synchronous learning is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology and pedagogy promising to enhance its effectiveness and accessibility.
9.1. Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are poised to transform synchronous learning.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR can create immersive learning environments.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR can overlay digital information onto the real world.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can personalize learning and provide intelligent feedback.
- 5G Technology: 5G can improve internet connectivity and enable seamless synchronous experiences.
9.2. Personalized Learning
Personalized learning tailors instruction to individual needs and preferences.
- Adaptive Learning Platforms: These platforms adjust the difficulty and content based on learner performance.
- AI-Powered Tutors: AI tutors can provide personalized feedback and guidance.
- Customized Content: Learners can access content that is relevant to their interests and goals.
9.3. Hybrid Learning Models
Hybrid learning combines synchronous and asynchronous activities to create a balanced learning experience.
- Flipped Classrooms: Students review materials asynchronously before attending synchronous sessions for discussions and activities.
- Blended Learning: Combines online and in-person instruction.
- HyFlex Learning: Allows students to choose whether to attend sessions in person or online.
9.4. Continued Professional Development
Continued professional development is essential for educators to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and best practices in synchronous learning.
- Online Courses: Educators can take online courses to learn new skills and strategies.
- Workshops and Conferences: These events provide opportunities for networking and learning from experts.
- Mentoring Programs: Mentoring programs can provide guidance and support for educators.
10. Best Practices for Integrating Synchronous Learning
Integrating synchronous learning effectively requires a strategic approach that considers the needs of learners and the goals of the educational program.
10.1. Aligning Learning Objectives
Ensure that synchronous activities align with overall learning objectives.
- Clear Goals: Define clear learning goals for each session.
- Relevant Content: Select content that is relevant to the learning goals.
- Meaningful Activities: Design activities that help learners achieve the learning goals.
10.2. Creating an Inclusive Environment
Foster an inclusive environment where all learners feel valued and supported.
- Respectful Communication: Encourage respectful communication and collaboration.
- Diverse Perspectives: Value diverse perspectives and experiences.
- Equitable Access: Ensure equitable access to resources and opportunities.
10.3. Providing Technical Support
Offer timely technical support to address any issues that may arise.
- Dedicated Support Team: Provide a dedicated support team to assist learners.
- Help Desk: Offer a help desk for troubleshooting technical issues.
- Training Resources: Provide training resources to help learners use the technology effectively.
10.4. Assessing Learning Outcomes
Assess learning outcomes to measure the effectiveness of synchronous activities.
- Formative Assessments: Use formative assessments to check understanding and provide feedback.
- Summative Assessments: Use summative assessments to measure overall learning.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Gather feedback from learners to improve future sessions.
In conclusion, synchronous learning offers a dynamic and engaging approach to education, providing numerous benefits such as enhanced social interaction, immediate clarification, and a structured learning environment. By understanding its challenges and implementing effective strategies, educators can leverage synchronous learning to create impactful and inclusive educational experiences. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers in-depth articles and resources to help you master the art of synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid learning models.
FAQ: Synchronous Learning
-
What is synchronous learning?
Synchronous learning is an educational approach where students and instructors interact in real-time, often through video conferencing or live chats. -
What are the benefits of synchronous learning?
Benefits include enhanced social interaction, immediate feedback, structured learning environments, and active participation. -
What are the challenges of synchronous learning?
Challenges include scheduling conflicts, technical issues, accessibility concerns, and maintaining engagement. -
How does synchronous learning differ from asynchronous learning?
Synchronous learning is real-time, while asynchronous learning is self-paced and flexible. -
What tools are used for synchronous learning?
Common tools include video conferencing platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams, as well as collaboration tools like Google Docs and Slack. -
How can I make synchronous learning more accessible?
Provide closed captioning, transcripts, screen reader compatibility, and alternative formats for materials. -
What are some engagement techniques for synchronous learning?
Use polls, quizzes, breakout rooms, interactive whiteboards, and gamification to keep learners engaged. -
What is hybrid learning?
Hybrid learning combines synchronous and asynchronous activities to create a balanced learning experience. -
How can I assess learning outcomes in a synchronous environment?
Use formative assessments, summative assessments, and feedback mechanisms to measure learning effectiveness. -
Where can I find more resources on synchronous learning?
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for in-depth articles, guides, and resources on synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid learning models.
Ready to revolutionize your approach to education? Unlock the full potential of synchronous learning with LEARNS.EDU.VN. Explore our comprehensive resources and expert insights to create engaging and effective learning experiences for all. Visit us today at learns.edu.vn, or contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212.