Stress and emotions play a significant role in the learning process, impacting students’ ability to acquire and retain information. This article explores the complex relationship between stress, emotions, and learning, examining how both negative and positive emotions can influence academic performance. We’ll delve into the neurophysiological mechanisms behind these effects and discuss strategies for managing stress and fostering a positive learning environment.
 Key points of stress and learning
Key points of stress and learning
Learning involves cognitive, emotional, and physiological factors, with emotions being integral to knowledge acquisition. Stress, often perceived negatively, is crucial for adaptation and learning when managed effectively. Excessive stress, however, can hinder learning by impairing cognitive functions, attention, and memory retrieval.
The COVID-19 pandemic serves as a stark example of how acute stress can disrupt learning. The abrupt shift to remote learning, disrupted routines, increased workload, social isolation, and uncertainty about the future contributed to heightened stress and anxiety among students. Studies show that students experienced difficulties concentrating, processing information, and retaining new knowledge due to pandemic-related stress.
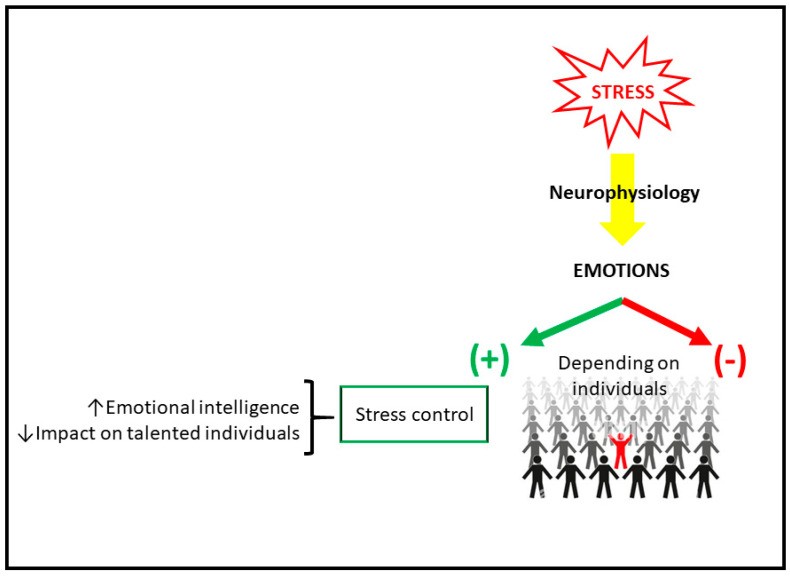
Stress triggers physiological responses, primarily through the sympathetic-adrenal-medullary (SAM) and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axes. These systems release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, influencing brain regions crucial for learning and memory, including the hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex. Moderate stress can enhance learning by increasing dopamine and noradrenaline activity in the prefrontal cortex, but chronic stress can negatively impact these areas, hindering learning.
Emotions, as interpretations of internal and external environments, significantly impact learning. Negative emotions like fear, anxiety, and sadness can impair well-being and hinder learning, while positive emotions like joy, hope, and happiness promote learning by increasing intellectual, physical, and social resources. Emotional regulation, including awareness, understanding, acceptance, and control of emotions, is crucial for successful learning.
The amygdala, a key structure in emotional processing, plays a vital role in learning. It processes and stores emotional reactions, influencing both physiological and psychological responses. The amygdala receives emotional information through fast and slow pathways, contributing to the emotional meaning of situations and influencing memory formation. Dysregulation in the amygdala, particularly related to fear, can negatively affect learning and memory.
Emotional intelligence (EI) significantly influences a student’s ability to learn and adapt. EI encompasses the ability to perceive, process, regulate, and manage emotions, impacting social adaptation, teamwork, performance, and stress management. Key components of EI include self-awareness, self-regulation, social awareness, relationship management, and empathy. Developing these skills helps students manage stress, foster positive relationships, and create a supportive learning environment, ultimately enhancing learning outcomes.
Talented individuals, with their exceptional learning abilities and efficient information processing, often demonstrate effective stress and emotion management in the learning process. They possess a unique capacity to acquire complex patterns and adapt to new knowledge, allowing them to thrive in challenging academic environments.
Further research is needed to explore strategies for mitigating the negative effects of stress and emotions on learning. Techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and relaxation can help students develop emotional regulation, resilience, and coping mechanisms. Investigating the strategies employed by talented individuals to manage stress and emotions can also provide valuable insights for improving learning outcomes for all students. A deeper understanding of the neurophysiological mechanisms involved in stress and emotional regulation can lead to targeted interventions that promote effective learning and enhance academic success.
In conclusion, stress significantly affects learning, impacting memory, cognitive function, and overall academic performance. Managing stress and cultivating positive emotions are crucial for creating an optimal learning environment. By developing emotional intelligence and implementing effective coping strategies, students can navigate academic challenges, improve their well-being, and achieve their full learning potential.