Electronic Learning, commonly referred to as e-learning or web-based training, represents a dynamic approach to education that transcends geographical boundaries and time constraints. Delivered via the internet or corporate intranets, it empowers students and learners to engage in structured educational experiences through web browsers, irrespective of their physical location. Unlike conventional learning methodologies, electronic learning offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling individuals, from students to employees undergoing professional training, to participate in organized learning at their own pace and convenience.
Initially, e-learning platforms primarily facilitated a direct, one-way flow of information from educators to learners. However, the landscape of electronic learning has significantly evolved, fostering multidirectional communication and leveraging increasingly interactive tools. Today’s learners enjoy greater autonomy in choosing how they interact with e-learning content, fostering collaborative environments where peers can actively participate and contribute.
The Growing Importance of Electronic Learning
The significance of electronic learning methodologies and technologies is paramount in contemporary education and professional development. Its relevance spans across educating students in academic settings and enhancing the skill sets of employees in the professional sphere.
The relentless pace of technological advancement necessitates continuous learning and adaptation, making e-learning crucial for workforce development. The anticipated rise of quantum computing, for instance, is poised to fundamentally reshape modern business operations, impacting roles from coders to cybersecurity experts. Electronic learning platforms will be instrumental in retraining and reskilling professionals to navigate these technological shifts.
Moreover, organizations are increasingly adopting online learning solutions for ongoing employee training and upskilling initiatives. Learning Management Systems (LMS) have gained considerable traction within corporate environments. Simultaneously, higher education institutions are integrating online learning methodologies and internet-enabled devices both within and outside traditional classroom settings. A 2022 McKinsey & Company survey involving 7,000 students across 17 countries revealed that a significant 65% of higher education students advocate for retaining elements of online learning in the post-pandemic educational model.
This article is part of a broader discussion on Workplace learning, offering a complete guide for businesses seeking to optimize employee development.
How Electronic Learning Systems Function
Electronic education utilizes a blend of static and interactive methods for content delivery. Static methods encompass learning portals, hyperlinked documents, screen recording tutorials, streamed audio and video content, and live webinars. Conversely, interactive methods include discussion forums, real-time chats, and video conferencing, promoting active engagement and collaboration.
For an e-learning program to be genuinely effective, particularly within an enterprise context, three key criteria are essential:
- Mobile Accessibility: In an era dominated by mobile devices, e-learning must be optimized for smartphone and tablet access. Training notifications, reminders, and achievements should be seamlessly delivered through mobile applications.
- Social Integration: Incorporating social features, akin to social media platforms, can enhance learner engagement by providing avenues for updates, training responses, and communication with peers and supervisors.
- Instructional Design Excellence: Effective e-learning experiences should employ a diverse range of learning resources to cater to varied learning preferences. This includes quizzes, infographics, podcasts, demonstrations, and narrative-driven materials. E-learning authoring tools empower individuals without extensive coding expertise to create these varied and engaging resources.
Exploring the Types of Electronic Learning
Web-based learning systems primarily fall into two categories:
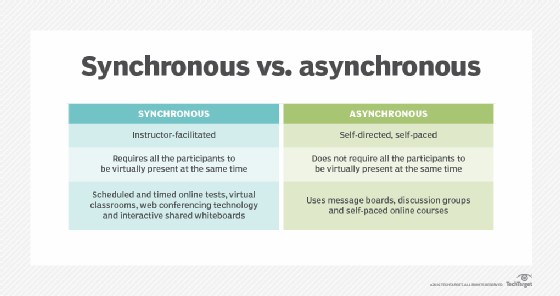
- Synchronous Learning: Often instructor-led, this model necessitates real-time interaction, albeit in a virtual setting.
- Asynchronous Learning: Characterized by self-directed, self-paced learning, offering greater flexibility in terms of schedule.
Synchronous e-learning mandates participants to be virtually present simultaneously, whereas asynchronous e-learning removes this requirement, allowing learners to engage at their own convenience.
Synchronous e-learning methodologies include scheduled online assessments, virtual classrooms, web conferencing, and collaborative digital whiteboards. Asynchronous e-learning examples are discussion boards, online forums, and self-paced courses.
Advantages of Electronic Learning Platforms
Electronic learning offers numerous advantages, widely regarded as outweighing its limitations. Key benefits include:
- On-Demand Accessibility: E-learning resources are typically available 24/7, catering to individuals with demanding schedules. Learners can access online materials anytime, provided they have access to the e-learning platform.
- Elimination of Geographical Constraints: E-learning is particularly effective for cohort learning, enabling groups geographically dispersed individuals to collaboratively acquire new skills or knowledge.
- Cost Efficiency: Compared to traditional classroom settings, e-learning significantly reduces overhead costs associated with physical space, infrastructure, maintenance, and learning materials.
- Enhanced Flexibility: Web-based training and e-learning provide learners with the flexibility to consume information at their own pace, optimizing learning outcomes.
Disadvantages of Electronic Learning Systems
Despite its benefits, e-learning also faces criticisms regarding certain drawbacks:
- Reduced Human Interaction: While suitable for self-motivated learners, the lack of face-to-face interaction can be a limitation for individuals who thrive in more socially interactive learning environments. Asynchronous e-learning, for example, might lack the structure and immediate feedback some learners need.
- Potential Technical Challenges: Online learners often rely on their personal devices and internet connections, which may pose accessibility issues for students without reliable technology or internet access.
- Variable Content Quality and Transparency: The credibility and quality of e-learning content and instructors can sometimes be inconsistent, especially on freely accessible platforms.
Popular Electronic Learning Platforms
A wide array of e-learning platforms exists, supporting both synchronous and asynchronous learning across educational, corporate, and independent learning contexts. These robust software suites facilitate digital learning and online training, offering features such as course delivery, presentation tools, online assessments, and performance analytics. Examples include Anthology for Business, Canvas, Moodle, Sakai, and Schoology in the educational sector.
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are also extensively used in organizations for employee onboarding and training programs. The most effective corporate LMS solutions are scalable, customizable, goal-oriented, and user-friendly. Enterprise-level LMS providers include Adobe Learning Manager, Docebo, eFront, iSpring Learn, Looop by 360Learning, Northpass, and TalentLMS, each offering diverse pricing structures.
Social Media Integration in E-learning
Social media platforms offer valuable tools for enhancing electronic learning. They foster learning communities and facilitate the sharing of e-learning content. Examples of social media applications in e-learning:
- Facebook: Enables the creation of groups for sharing information and collaborative discussions among learners.
- LinkedIn: Provides professional networking groups for e-learning, enhancing credibility through user profiles. LinkedIn Learning, a paid platform, offers a vast library of business-related courses.
- X (Twitter): Connects learners through topic-specific hashtags, facilitating real-time discussions and resource sharing.
- YouTube: Hosts a wealth of free educational content, allowing users to access, comment on, and evaluate learning videos.
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs)
Independent learners can also benefit from Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) available on platforms like Coursera and edX. MOOCs provide free access to course content, often modeled after university-level curricula, to a global audience. While basic access is typically free, certificates of completion may require a fee, as seen with edX’s certificate programs.
Platforms such as Udemy and Skillshare offer similar online learning opportunities but often focus on practical, skill-based learning with a user-pays model, contrasting with the lecture-centric approach of many university-based MOOCs. Regardless of the platform, electronic learning provides a versatile and adaptable pathway for professional and personal skill development.
A Brief History of Electronic Learning
The concept of e-learning predates both the internet and the term itself. In 1983, Ron Gordon, former president of Atari, initiated the Electronic University Network (EUN), an early online education network aimed at facilitating online courses in higher education. EUN was later acquired by KnowledgeNet in 1987.
The advent of the World Wide Web in 1989 initially served as a platform for rapid academic information exchange.
The term “e-learning” emerged in 1999, coinciding with the launch of online course initiatives like MIT’s OpenCourseWare in 2002. By the late 2000s, advancements in technology and course design enabled the scalability of e-learning to accommodate large learner groups, giving rise to MOOCs. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of e-learning across businesses and educational institutions, highlighting its critical role in accessible and flexible education.
Electronic learning has now evolved into a significant market sector with numerous providers specializing in business training solutions. Explore further into e-learning providers to identify resources that can benefit your organization’s training needs.