Want to discover How Can I Learn To Draw Cartoons? This article is for you. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide a comprehensive guide to cartoon drawing, covering everything from basic principles to advanced techniques. Learn to develop your skills and create captivating characters with our expert advice, tutorials, and resources, transforming your artistic aspirations into reality, explore character design, and create comic strips with our easy-to-follow guides.
1. Unveiling the Cartooning World: A Beginner’s Voyage
Cartooning, at its core, is the art of simplifying and exaggerating reality to create humorous or expressive images. It’s a versatile medium, applicable to various fields such as animation, comics, advertising, and even education. Understanding the fundamentals is crucial for anyone eager to learn how can i learn to draw cartoons.
1.1. Grasping the Essence of Cartooning
Before you put pencil to paper, it’s essential to understand what makes a cartoon a cartoon. Here are some key elements:
- Exaggeration: Cartooning often involves exaggerating features, expressions, and actions to create a humorous or dramatic effect. This can range from oversized eyes to exaggerated poses.
- Simplification: Complex objects and characters are often reduced to their most basic shapes and forms. This simplification makes cartoons easier to draw and more visually appealing.
- Caricature: This is the art of distorting or exaggerating specific features of a person or object to create a recognizable likeness. It’s a common technique used in political cartoons and humorous illustrations.
- Expression: Cartoons are excellent at conveying emotions and moods. Through the use of expressive lines, exaggerated features, and dynamic poses, cartoonists can effectively communicate a wide range of feelings.
1.2. Why Cartooning? The Benefits Beyond Art
Learning to draw cartoons isn’t just about acquiring an artistic skill; it offers a wealth of cognitive and creative benefits:
- Enhanced Creativity: Cartooning encourages you to think outside the box and come up with imaginative ideas. It pushes you to see the world in new and creative ways.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: Breaking down complex objects into simple shapes and forms requires problem-solving skills. You learn to analyze and deconstruct visual information.
- Boosted Communication Skills: Cartoons can be a powerful tool for communication. They can convey messages, tell stories, and express emotions in a visually engaging way.
- Stress Relief and Relaxation: Engaging in creative activities like cartooning can be a great way to relieve stress and relax. It allows you to focus on the present moment and express yourself freely.
- Increased Self-Confidence: As you improve your cartooning skills, you’ll gain a sense of accomplishment and increased self-confidence. You’ll be proud of the artwork you create.
1.3. Setting Up Your Creative Space
Creating a conducive environment is crucial for nurturing your cartooning journey. Here’s a breakdown of essential tools and workspace considerations:
- Basic Supplies:
- Pencils: Start with a variety of pencils ranging from 2H to 6B. Harder pencils (2H) are great for light sketching, while softer pencils (6B) are ideal for darker lines and shading.
- Erasers: A good quality eraser is essential for correcting mistakes and refining your drawings. Consider both a standard eraser and a kneaded eraser for different purposes.
- Paper: Choose a smooth, acid-free paper that can withstand erasing and won’t yellow over time. Sketchbooks are great for practicing, while Bristol board is ideal for finished artwork.
- Pens & Markers: Experiment with different types of pens and markers to find what works best for your style. Fine-liners are great for outlining, while brush pens are ideal for creating dynamic lines.
- Drawing Tablet (Optional): If you’re interested in digital cartooning, a drawing tablet can be a valuable tool. Look for one with pressure sensitivity for varying line thickness.
- Workspace Considerations:
- Lighting: Ensure your workspace is well-lit to avoid eye strain. Natural light is ideal, but if that’s not possible, use a bright, adjustable lamp.
- Comfort: Choose a comfortable chair and desk that are the right height for you. This will help you avoid back pain and other discomfort.
- Organization: Keep your supplies organized and within easy reach. This will help you stay focused and productive.
- Inspiration: Surround yourself with things that inspire you, such as books, artwork, or toys. This will help you stay motivated and creative.
With the right tools and a dedicated space, you’ll be well-equipped to embark on your cartooning adventure!
2. Mastering the Foundations: Essential Drawing Techniques
Before diving into cartoon-specific techniques, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental principles of drawing. These foundational skills will provide a solid base upon which you can build your cartooning expertise.
2.1. Line Art: The Language of Cartoons
Lines are the most basic, yet most essential, element of cartooning. They define shapes, create textures, and convey movement. Mastering line control is crucial for creating dynamic and expressive cartoons.
-
Types of Lines:
- Straight Lines: Used for creating rigid shapes, defining edges, and conveying a sense of stability.
- Curved Lines: Used for creating organic shapes, adding softness, and conveying a sense of movement.
- Wavy Lines: Used for creating textures, suggesting movement, and adding a playful touch.
- Dashed Lines: Used for suggesting hidden lines, indicating movement, and adding a sense of incompleteness.
- Varying Line Weight: Line weight refers to the thickness of a line. Varying line weight can add depth, create emphasis, and make your drawings more visually interesting.
-
Line Control Exercises:
- Straight Line Practice: Draw straight lines of varying lengths and angles without using a ruler. Focus on maintaining a consistent line weight and direction.
- Curved Line Practice: Draw smooth, flowing curves of varying sizes and shapes. Focus on maintaining a consistent line weight and avoiding jerky movements.
- Line Weight Practice: Practice varying the thickness of your lines by applying more or less pressure to your pencil or pen. Experiment with creating thick, bold lines and thin, delicate lines.
- Contour Drawing: Draw the outline of an object without lifting your pencil from the paper. Focus on capturing the shape and form of the object with a single, continuous line.
2.2. Shapes and Forms: Building Blocks of Characters
All objects, including cartoon characters, can be broken down into basic shapes: circles, squares, triangles, and rectangles. Understanding how to use these shapes to construct your characters is essential for creating believable and appealing designs.
-
Basic Shapes:
- Circles: Often used for creating heads, bodies, and other rounded forms.
- Squares: Used for creating boxy shapes, defining edges, and conveying a sense of strength.
- Triangles: Used for creating sharp angles, adding dynamism, and conveying a sense of danger.
- Rectangles: Used for creating elongated shapes, defining structures, and conveying a sense of stability.
-
Constructing Characters with Shapes:
- Head Construction: Start by drawing a circle for the head. Then, add guidelines to indicate the placement of the eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Body Construction: Use simple shapes like ovals, rectangles, and cylinders to construct the body. Pay attention to the proportions and how the shapes connect.
- Limb Construction: Use simple shapes like cylinders and cones to construct the limbs. Pay attention to the joints and how the limbs move.
- Clothing Construction: Use simple shapes to represent the folds and wrinkles in the clothing. Pay attention to how the fabric drapes over the body.
-
From 2D to 3D: Understanding Form:
- Form is the three-dimensional quality of an object. To create the illusion of form in your cartoons, you need to understand how light and shadow interact with the object.
- Shading: Use shading to create the illusion of depth and volume. Apply darker tones to areas that are in shadow and lighter tones to areas that are in light.
- Highlights: Add highlights to areas that are directly illuminated by light. This will make your drawings look more realistic and dynamic.
- Cast Shadows: Draw cast shadows to indicate the direction of the light source and to ground your characters in their environment.
2.3. Proportions and Anatomy: The Structure Beneath the Style
While cartooning allows for exaggeration and simplification, understanding basic anatomy and proportions is still crucial. It provides a framework for creating believable and appealing characters.
-
Understanding Basic Anatomy:
- Skeleton: The skeleton is the underlying framework of the body. Understanding the basic structure of the skeleton will help you create more believable poses and movements.
- Muscles: The muscles give the body its shape and allow it to move. Understanding the basic muscle groups will help you create more dynamic and expressive characters.
-
Cartoon Proportions:
- Head Size: Cartoon characters often have larger heads than realistic figures. This can make them look more cute and expressive.
- Eye Size: Cartoon characters often have larger eyes than realistic figures. This can make them look more innocent and appealing.
- Limb Length: Cartoon characters often have shorter limbs than realistic figures. This can make them look more childlike and playful.
-
Exaggeration and Style:
- Once you understand the basic principles of anatomy and proportions, you can start to exaggerate and stylize your characters to create a unique look.
- Experiment with different proportions, shapes, and features to find a style that you enjoy.
- Don’t be afraid to break the rules and create something completely original.
2.4. Perspective: Creating Depth in Your Cartoons
Perspective is the technique of representing three-dimensional objects and space on a two-dimensional surface. Understanding perspective is essential for creating believable and immersive cartoon environments.
-
Types of Perspective:
- One-Point Perspective: All lines converge at a single vanishing point on the horizon line. This is often used for creating simple scenes with a sense of depth.
- Two-Point Perspective: Lines converge at two vanishing points on the horizon line. This is often used for creating more complex scenes with a greater sense of depth.
- Three-Point Perspective: Lines converge at three vanishing points (two on the horizon line and one above or below). This is often used for creating dramatic and dynamic scenes with a strong sense of depth.
-
Applying Perspective to Cartooning:
- Simple Backgrounds: Use one-point perspective to create simple backgrounds for your cartoons. This will help to ground your characters in their environment.
- Complex Environments: Use two- or three-point perspective to create more complex environments for your cartoons. This will add depth and realism to your scenes.
- Exaggerated Perspective: Don’t be afraid to exaggerate the perspective to create a more dynamic and visually interesting scene.
Mastering these fundamental drawing techniques will provide you with a solid foundation for your cartooning journey. Remember to practice regularly and don’t be afraid to experiment with different styles and techniques.
3. Character Design: Crafting Memorable Cartoon Personalities
Character design is the heart and soul of cartooning. It’s about creating visually appealing and engaging characters that resonate with your audience. A well-designed character can tell a story all on its own.
3.1. Understanding Character Archetypes
Before you start designing your characters, it’s helpful to understand the different character archetypes. These are recurring patterns of behavior and personality that can be found in stories across cultures and time periods.
-
Common Archetypes:
- The Hero: The protagonist of the story, who often faces challenges and overcomes obstacles.
- The Villain: The antagonist of the story, who opposes the hero and creates conflict.
- The Sidekick: The hero’s loyal companion, who provides support and comic relief.
- The Mentor: A wise and experienced character who guides the hero on their journey.
- The Innocent: A naive and pure character who often represents hope and goodness.
-
Creating Unique Characters:
- While understanding archetypes is helpful, it’s important to create unique characters that stand out from the crowd.
- Give your characters flaws, quirks, and unique motivations.
- Don’t be afraid to challenge traditional archetypes and create characters that are complex and multi-dimensional.
3.2. Visual Cues: Designing Personality Through Appearance
A character’s appearance can reveal a lot about their personality. Use visual cues to communicate your character’s traits, backstory, and role in the story.
-
Facial Features:
- Eyes: The eyes are the windows to the soul. Use different eye shapes and expressions to convey a range of emotions.
- Nose: The nose can be used to indicate a character’s personality. A large nose might suggest a character is greedy or pompous, while a small nose might suggest a character is delicate or innocent.
- Mouth: The mouth is used for speaking and expressing emotions. Use different mouth shapes and expressions to convey a range of emotions.
-
Body Shape and Posture:
- Body Shape: A character’s body shape can reveal a lot about their personality. A large, muscular character might be strong and aggressive, while a small, thin character might be weak and timid.
- Posture: A character’s posture can also reveal a lot about their personality. A confident character might stand tall and upright, while a shy character might slouch and avoid eye contact.
-
Clothing and Accessories:
- Clothing: A character’s clothing can reveal a lot about their personality, social status, and profession.
- Accessories: Accessories like hats, glasses, and jewelry can add personality and detail to your characters.
3.3. Exaggeration and Caricature: Emphasizing Key Traits
Exaggeration and caricature are powerful tools for emphasizing a character’s key traits and making them more memorable.
-
Exaggerating Features:
- Exaggerate the features that are most characteristic of your character.
- If your character is known for their large nose, make it even larger in your drawing.
- If your character is known for their big eyes, make them even bigger in your drawing.
-
Caricaturing Personality:
- Use caricature to exaggerate your character’s personality traits.
- If your character is greedy, draw them with a large belly and a grasping expression.
- If your character is vain, draw them with an elaborate hairstyle and a self-satisfied smirk.
3.4. Bringing Your Characters to Life: Expression and Posing
Once you’ve designed your characters, it’s time to bring them to life with expressive poses and dynamic actions.
-
Facial Expressions:
- Mastering facial expressions is crucial for conveying emotions in your cartoons.
- Study different emotions and practice drawing them on your characters.
- Pay attention to the subtle changes in the eyes, eyebrows, mouth, and nose that communicate different feelings.
-
Body Language:
- Body language is another important tool for conveying emotions and personality.
- Pay attention to how your characters stand, move, and gesture.
- Use different poses to communicate different emotions and attitudes.
-
Action Poses:
- Dynamic action poses can add excitement and energy to your cartoons.
- Study different action poses and practice drawing them on your characters.
- Pay attention to the lines of action and how they convey movement and force.
Creating memorable and engaging cartoon characters is a process that requires practice, experimentation, and a keen understanding of human psychology. Don’t be afraid to try new things and develop your own unique style.
4. Cartooning Techniques: Elevating Your Artistry
Now that you have a solid foundation in drawing and character design, it’s time to explore specific cartooning techniques that will elevate your artistry and give your cartoons a professional polish.
4.1. Dynamic Posing: Action and Movement
Dynamic posing is all about creating a sense of action and movement in your cartoons. A well-posed character can tell a story without saying a word.
-
Lines of Action:
- The line of action is an imaginary line that runs through the center of a character’s body, indicating the direction of their movement.
- Use curved lines of action to create a sense of fluidity and energy.
- Use straight lines of action to create a sense of strength and stability.
-
Exaggerated Poses:
- Don’t be afraid to exaggerate your character’s poses to create a more dynamic and visually interesting image.
- Bend the limbs, twist the torso, and tilt the head to create a sense of movement and energy.
-
Weight and Balance:
- Pay attention to the weight and balance of your characters.
- Make sure they are grounded in their environment and that their poses feel natural and believable.
4.2. Exaggerated Expressions: Amplifying Emotions
Exaggerated expressions are a key element of cartooning. They allow you to amplify emotions and make your characters more expressive and engaging.
-
Facial Muscles:
- Study the facial muscles and how they create different expressions.
- Pay attention to the subtle changes in the eyes, eyebrows, mouth, and nose that communicate different feelings.
-
Squash and Stretch:
- Use the squash and stretch principle to exaggerate your character’s expressions.
- Squash the face to create a sense of compression and impact.
- Stretch the face to create a sense of anticipation and excitement.
-
Emotional Clarity:
- Make sure your character’s emotions are clear and easily understood.
- Use exaggerated expressions to communicate their feelings in a visually compelling way.
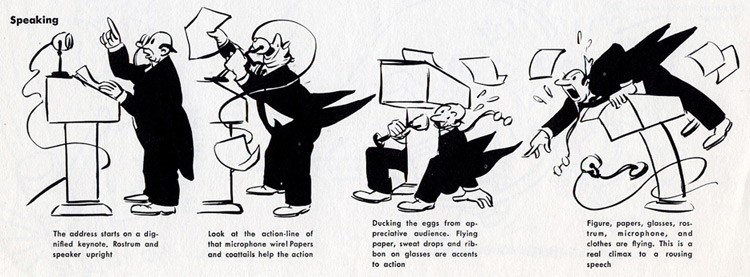 Cartoon Speaking
Cartoon Speaking
4.3. Speed Lines and Motion Effects: Visualizing Movement
Speed lines and motion effects are used to visualize movement and add a sense of energy to your cartoons.
-
Speed Lines:
- Speed lines are lines that are drawn behind or around a moving object to indicate its speed and direction.
- Use different types of speed lines to create different effects.
- Straight speed lines create a sense of speed and power.
- Curved speed lines create a sense of fluidity and grace.
-
Motion Blur:
- Motion blur is used to create the illusion of movement by blurring the edges of a moving object.
- Use motion blur sparingly to avoid making your cartoons look messy or unclear.
-
Dust and Debris:
- Adding dust, debris, and other small particles around a moving object can help to create a sense of speed and impact.
4.4. Inking Techniques: Defining Your Style
Inking is the process of adding dark lines to your drawings to define shapes, add detail, and create a more polished look.
-
Line Weight Variation:
- Use line weight variation to create depth and emphasis in your drawings.
- Use thick lines to define the outlines of objects and thin lines to add detail.
-
Hatching and Cross-Hatching:
- Hatching and cross-hatching are used to create shading and texture in your drawings.
- Hatching involves drawing parallel lines close together to create a darker tone.
- Cross-hatching involves drawing intersecting lines to create a darker tone.
-
Clean Lines:
- Strive for clean, crisp lines in your inking.
- Avoid wobbly or uneven lines.
- Use a variety of pens and brushes to achieve different effects.
Mastering these cartooning techniques will allow you to create more dynamic, expressive, and visually appealing cartoons. Remember to practice regularly and experiment with different styles and techniques to find what works best for you.
5. Digital Cartooning: Embracing the Digital Canvas
Digital cartooning has revolutionized the industry, offering artists a plethora of tools and techniques to create stunning artwork. From digital painting to vector graphics, the possibilities are endless.
5.1. Software and Hardware Essentials
Choosing the right software and hardware is crucial for a smooth and productive digital cartooning experience.
-
Software:
- Adobe Photoshop: Industry-standard software for raster-based painting and image editing.
- Clip Studio Paint: Popular among comic book artists for its drawing and painting tools.
- Procreate: A powerful and intuitive iPad app for digital painting.
- Adobe Illustrator: Industry-standard software for vector-based illustration.
- Affinity Designer: A versatile and affordable alternative to Adobe Illustrator.
-
Hardware:
- Drawing Tablet: A drawing tablet with pressure sensitivity is essential for digital cartooning. Wacom is a popular brand, but there are many other great options available.
- Stylus: A good stylus is just as important as the drawing tablet. Look for one that is comfortable to hold and has good pressure sensitivity.
- Computer: A computer with a fast processor and plenty of RAM is essential for running digital art software smoothly.
- Monitor: A high-resolution monitor will allow you to see your artwork in detail.
5.2. Digital Painting Techniques: Colors, Shading, and Effects
Digital painting offers a wide range of techniques for creating stunning colors, shading, and effects.
-
Color Theory:
- Understanding color theory is essential for creating visually appealing artwork.
- Learn about color harmonies, color values, and color saturation.
-
Layering:
- Use layers to organize your artwork and make it easier to edit.
- Create separate layers for line art, colors, shading, and effects.
-
Blending Modes:
- Experiment with different blending modes to create unique effects.
- Blending modes can be used to create highlights, shadows, and color variations.
-
Digital Brushes:
- Explore the wide range of digital brushes available in your software.
- Use different brushes to create different textures and effects.
5.3. Vector Graphics: Clean Lines and Scalability
Vector graphics are created using mathematical equations rather than pixels. This means they can be scaled to any size without losing quality.
-
Paths and Shapes:
- Vector graphics are created using paths and shapes.
- Learn how to create and manipulate paths and shapes in your vector graphics software.
-
Gradients and Patterns:
- Use gradients and patterns to add depth and detail to your vector graphics.
-
Typography:
- Vector graphics are ideal for creating typography.
- Learn how to create and manipulate text in your vector graphics software.
5.4. Animation Software: Bringing Your Cartoons to Life
If you’re interested in animating your cartoons, there are several animation software options available.
- Toon Boom Harmony: Industry-standard software for 2D animation.
- Adobe Animate: Popular software for creating interactive animations for the web.
- OpenToonz: Free and open-source software for 2D animation.
Exploring digital cartooning can open up a world of creative possibilities. Experiment with different software, hardware, and techniques to find what works best for you.
6. Finding Your Unique Style: Experimentation and Inspiration
Developing your own unique cartooning style is a journey of experimentation, inspiration, and self-discovery. It’s about finding what resonates with you and expressing your own unique voice through your artwork.
6.1. Studying Your Favorite Artists
One of the best ways to find your own style is to study the work of your favorite artists.
-
Analyze Their Techniques:
- Pay attention to the techniques they use, such as line weight, shading, and color palette.
- Try to replicate their techniques in your own artwork.
-
Identify Their Influences:
- Research the artists who influenced your favorite artists.
- This can give you a deeper understanding of their style and help you to find new sources of inspiration.
-
Don’t Copy, Learn:
- It’s important to learn from your favorite artists, but don’t simply copy their work.
- Use their techniques as a starting point and then develop your own unique style.
6.2. Experimenting with Different Mediums
Experimenting with different mediums can help you to discover new techniques and styles.
-
Traditional Mediums:
- Try drawing with pencils, charcoal, ink, or watercolors.
- Each medium has its own unique properties and can produce different effects.
-
Digital Mediums:
- Explore the different digital painting and drawing software available.
- Experiment with different brushes, textures, and effects.
-
Mixed Media:
- Combine traditional and digital mediums to create unique and interesting artwork.
6.3. Drawing from Life: Capturing the Real World
Drawing from life is a great way to improve your drawing skills and develop your own unique style.
-
Observe the World Around You:
- Pay attention to the shapes, forms, and details of the objects and people around you.
- Try to capture the essence of what you see in your drawings.
-
Sketch Regularly:
- Carry a sketchbook with you and sketch whenever you have a spare moment.
- The more you practice drawing from life, the better you will become.
-
Focus on the Fundamentals:
- Remember to focus on the fundamentals of drawing, such as line weight, shading, and perspective.
- These fundamentals will help you to create more realistic and believable drawings.
6.4. Embracing Your Quirks and Imperfections
Your unique style will often emerge from your quirks and imperfections.
-
Don’t Be Afraid to Be Different:
- Embrace your unique perspective and don’t be afraid to be different.
- The world needs more original artwork, not more copies of the same thing.
-
Learn from Your Mistakes:
- Everyone makes mistakes, so don’t be discouraged when you make them.
- Learn from your mistakes and use them as an opportunity to improve.
-
Be Patient:
- Developing your own unique style takes time and effort.
- Be patient and persistent, and you will eventually find your own voice.
Finding your unique style is a lifelong journey. Embrace the process and enjoy the ride!
7. Resources for Aspiring Cartoonists: Learning and Inspiration
The journey of learning how to draw cartoons is greatly enhanced by access to valuable resources. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced artist, these resources can provide guidance, inspiration, and opportunities for growth.
7.1. Online Courses and Tutorials
Online courses and tutorials offer structured learning paths and expert instruction in various aspects of cartooning.
| Platform | Description | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| learns.edu.vn | Offers comprehensive courses on cartooning, character design, and animation. With expert instructors and structured learning paths. | Provides in-depth knowledge and practical skills. Perfect for both beginners and experienced artists looking to enhance their skills. |
| Skillshare | Offers a wide range of cartooning courses taught by experienced artists. | Basic drawing, character design, comic creation. |
| Udemy | Provides a variety of cartooning courses for different skill levels and interests. | Character design, animation, digital painting. |
| YouTube (Free Tutorials) | Many talented artists share free tutorials on YouTube. | Basic drawing, character design, animation techniques. |
| Coursera | Features courses from top universities and institutions on art and design, including cartooning and animation. | Art history, character design, animation principles. |
7.2. Books and Publications
Books and publications offer in-depth knowledge, techniques, and inspiration from renowned cartoonists and illustrators.
| Title | Author(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| “Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain” | Betty Edwards | Teaches you how to see and draw like an artist. |
| “Understanding Comics” | Scott McCloud | Explores the theory and history of comics. |
| “Cartooning: The Ultimate Character Design Book” | Christopher Hart | A comprehensive guide to character design for cartoonists. |
| “Figure Drawing: For All It’s Worth” | Andrew Loomis | A classic guide to figure drawing for artists. |
| “Dynamic Anatomy” | Burne Hogarth | Explores the principles of anatomy for artists. |
7.3. Online Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums provide a supportive environment for cartoonists to connect, share their work, and receive feedback.
| Platform | Description | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| DeviantArt | A popular online community for artists of all kinds, including cartoonists. | Sharing artwork, receiving feedback, connecting with other artists. |
| ArtStation | A professional platform for artists to showcase their work and connect with industry professionals. | Showcasing professional artwork, networking, finding job opportunities. |
| Reddit (r/comics, r/learnart) | Reddit has several subreddits dedicated to comics and art, where you can share your work, ask for advice, and connect with other artists. | Sharing artwork, receiving feedback, learning new techniques. |
| Pencil Kings | A premium online art school with a supportive community. | Learning new techniques, receiving feedback, connecting with other artists. |
| The Concept Art Association | A professional organization for concept artists, illustrators, and animators. | Networking, learning new techniques, finding job opportunities. |
7.4. Museums and Art Galleries
Visiting museums and art galleries can provide inspiration and expose you to different styles and techniques.
- Cartoon Art Museum (San Francisco): A museum dedicated to the art of cartooning.
- The Louvre (Paris): A world-renowned museum with a vast collection of art, including cartoons and illustrations.
- The Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York): Another world-renowned museum with a vast collection of art, including cartoons and illustrations.
These resources can provide you with the knowledge, inspiration, and support you need to succeed as a cartoonist. Take advantage of these resources and continue to learn and grow as an artist.
8. Monetizing Your Cartooning Skills: Turning Passion into Profit
Cartooning can be more than just a hobby; it can be a rewarding career. With the rise of the internet and the increasing demand for visual content, there are more opportunities than ever to monetize your cartooning skills.
8.1. Freelance Illustration and Design
Freelance illustration and design is a popular way to earn money as a cartoonist.
-
Finding Clients:
- Network with potential clients online and in person.
- Create a professional portfolio website to showcase your work.
- Use online freelance platforms to find job opportunities.
-
Types of Projects:
- Book illustrations
- Magazine illustrations
- Web graphics
- Logo design
- Character design
-
Setting Your Rates:
- Research the going rates for freelance illustration and design work.
- Factor in your experience, skill level, and the complexity of the project.
8.2. Creating and Selling Comics
Creating and selling comics is another popular way to earn money as a cartoonist.
-
Self-Publishing:
- Self-publish your comics online or in print.
- Use online platforms like ComiXology and Kindle Direct Publishing.
-
Submitting to Publishers:
- Submit your comics to publishers for consideration.
- Research publishers that specialize in your genre of comics.
-
Selling at Conventions:
- Sell your comics at comic conventions and art fairs.
- Connect with fans and build your audience.
8.3. Online Content Creation: Building a Brand
Creating online content can help you to build a brand and monetize your cartooning skills.
-
YouTube Channel:
- Create a YouTube channel to share your cartooning tutorials, speed drawings, and animations.
- Monetize your channel with ads and sponsorships.
-
Patreon:
- Create a Patreon page to allow fans to support your work with monthly donations.
- Offer exclusive content and rewards to your Patreon supporters.
-
Online Store:
- Create an online store to sell your prints, merchandise, and original artwork.
- Use platforms like Etsy and Shopify.
8.4. Teaching Cartooning: Sharing Your Knowledge
Teaching cartooning can be a rewarding way to share your knowledge and earn money.
-
Online Courses:
- Create online courses on platforms like Udemy and Skillshare.
- Teach students the fundamentals of cartooning and character design.
-
Workshops and Classes:
- Offer in-person workshops and classes at local art centers and schools.
- Provide hands-on instruction and personalized feedback.
-
Private Tutoring:
- Offer private tutoring to students who want to improve their cartooning skills.
- Provide personalized instruction and customized lesson plans.
Monetizing your cartooning skills takes time, effort, and dedication. Be patient, persistent, and don’t be afraid to experiment with different monetization strategies.
9. Overcoming Creative Blocks: Staying Inspired
Creative blocks are a common challenge for artists of all kinds, including cartoonists. It’s important to have strategies for overcoming creative blocks and staying inspired.
9.1. Taking Breaks and Relaxing
Sometimes the best way to overcome a creative block is to take a break and relax.
-
Step Away from Your Work:
- Get up and walk around, stretch, or do something completely unrelated to your work.
-
Engage in Relaxing Activities:
- Read a book, listen to music, watch a movie, or take a nap.
-
Meditate or Practice Mindfulness:
- Meditation and mindfulness can help you to clear your mind and reduce stress.
9.2. Seeking Inspiration from Different Sources
Inspiration can come from many different sources.
-
Visit Museums and Art Galleries:
- Expose yourself to different styles and techniques.
-
Read Books and Watch Movies:
- Look for inspiration in the stories, characters, and visuals.
-
Listen to Music:
- Let the music inspire your creativity.
-
Spend Time in Nature:
- Observe the beauty and complexity of the natural world.
9.3. Trying New Techniques and Styles
Experimenting with new techniques and styles can help you to break out of your creative rut.
-
Try a New Medium:
- Switch from pencils to ink or from digital painting to watercolors.
-
Study a Different Artist:
- Learn from the techniques and styles of artists you admire.
-
Set a Challenge for Yourself: