Learning How Can I Learn Web Designing Online is a rewarding journey. It equips you with the skills to create visually appealing and functional websites. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to guide you, from understanding design principles to mastering coding languages. Embrace this opportunity to develop your creative skills and shape the digital landscape. Learning web design online empowers you to build websites that not only look great but also provide excellent user experiences, incorporating elements of visual artistry and technical knowledge to craft sites that are both engaging and effective.
1. Understanding Web Design Fundamentals
Web design is the art and science of creating websites that are aesthetically pleasing, user-friendly, and effective in achieving their intended purpose. It’s more than just making a website look good; it’s about understanding how users interact with the site and designing it to facilitate a seamless and enjoyable experience. A good web design considers various factors, including visual appeal, usability, accessibility, and search engine optimization. Let’s delve deeper into the core aspects of web design:
1.1. Key Elements of Effective Web Design
Several key elements contribute to an effective web design. These include:
- Visual Hierarchy: Guiding the user’s eye to the most important elements on the page through size, color, and placement.
- User Interface (UI): Designing interactive elements, such as buttons and forms, to be intuitive and easy to use.
- User Experience (UX): Ensuring the overall experience of using the website is positive and satisfying.
- Accessibility: Making the website usable for people with disabilities.
- Responsiveness: Ensuring the website looks and functions well on all devices, from desktops to smartphones.
- Content: Creating compelling and informative content that engages the user.
1.2. The Role of UI, UX, and SEO in Web Design
UI, UX, and SEO are integral subdisciplines within web design. A strong understanding of these areas is crucial for creating websites that not only look good but also perform well and achieve their objectives:
- User Interface (UI): Focuses on the visual elements and interactive components of a website. It involves selecting appropriate colors, fonts, icons, and other design elements to create an engaging and intuitive interface. A well-designed UI makes it easy for users to navigate the website and find the information they need.
- User Experience (UX): Deals with the overall experience a user has while interacting with a website. It involves understanding user needs, conducting user research, and designing the website to meet those needs. A good UX design ensures that the website is easy to use, efficient, and enjoyable.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Focuses on optimizing a website to rank higher in search engine results. It involves using relevant keywords, creating high-quality content, and building backlinks. Good SEO practices help drive traffic to the website and increase its visibility.
1.3. Essential Skills for Web Designers
To create engaging and user-friendly websites, web designers require a diverse set of skills:
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Design | Understanding of design principles like color theory, typography, and layout. |
| UI/UX Design | Knowledge of user interface and user experience design principles. |
| HTML & CSS | Proficiency in HTML for structuring content and CSS for styling. |
| JavaScript | Understanding of JavaScript for adding interactivity and dynamic elements. |
| Graphic Design | Ability to create visual assets such as logos, icons, and images. |
| Problem-Solving | Capacity to identify and solve design and usability issues. |
| Communication | Skill to effectively communicate design ideas and collaborate with clients and developers. |
| Adaptability | Willingness to learn new technologies and adapt to evolving design trends. |
| Attention to Detail | Ability to notice and correct small errors that can impact the user experience. |
| Organization | Skill to manage multiple projects and deadlines effectively. |
2. Understanding the Backend and Frontend of Web Design
Web design involves two main aspects: the backend and the frontend. Understanding the difference between these two is crucial for aspiring web designers.
2.1. The Backend: The Engine Room of a Website
The backend is the behind-the-scenes aspect of a website, responsible for storing and managing data, handling server requests, and ensuring the website functions correctly. It’s like the engine room of a ship, powering everything that happens on the surface. Backend developers use programming languages like PHP, Python, and Java, along with databases like MySQL and MongoDB, to build and maintain the backend of a website. They also work with servers, applications, and APIs to ensure that all the components of the website work together seamlessly.
- Databases: Store and manage website data, such as user information, product details, and blog posts.
- Servers: Host the website and handle requests from users.
- Applications: Perform specific tasks, such as processing payments or sending emails.
- APIs: Allow different systems to communicate with each other.
2.2. The Frontend: What Visitors See and Interact With
The frontend is the user-facing aspect of a website, responsible for displaying content, creating interactive elements, and providing a visually appealing experience. It’s like the deck of a ship, where passengers can enjoy the view and interact with the environment. Frontend developers use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build the frontend of a website. They focus on creating a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and visually appealing.
- HTML: Structures the content of a web page, defining elements like headings, paragraphs, and images.
- CSS: Styles the HTML elements, controlling their appearance, layout, and responsiveness.
- JavaScript: Adds interactivity and dynamic behavior to the website, such as animations, form validation, and AJAX requests.
2.3. The Interplay Between Backend and Frontend
The backend and frontend work together to create a complete website. The frontend sends requests to the backend for data, and the backend processes those requests and sends the data back to the frontend. The frontend then displays the data to the user in a visually appealing and interactive way. For example, when a user submits a form on the frontend, the data is sent to the backend for processing. The backend then stores the data in a database and sends a confirmation message back to the frontend, which displays it to the user.
3. Mastering Visual Design Principles
Visual design principles are the fundamental rules that govern how we perceive and organize visual elements. Understanding these principles is essential for creating websites that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also effective in communicating their message.
3.1. Key Principles of Visual Design
Several key principles of visual design can be applied to web design:
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Balance | Creating a sense of equilibrium and stability in the design, either symmetrically or asymmetrically. |
| Contrast | Using differences in color, size, and shape to create visual interest and highlight important elements. |
| Emphasis | Creating a focal point in the design to draw the user’s attention to the most important element. |
| Proportion | Using the relative size and scale of elements to create a sense of harmony and balance. |
| Rhythm | Creating a sense of movement and visual flow through the repetition of elements. |
| Unity | Creating a sense of coherence and wholeness in the design, ensuring that all the elements work together harmoniously. |
| White Space (Negative Space) | Utilizing the space around elements to create visual breathing room and improve readability. |
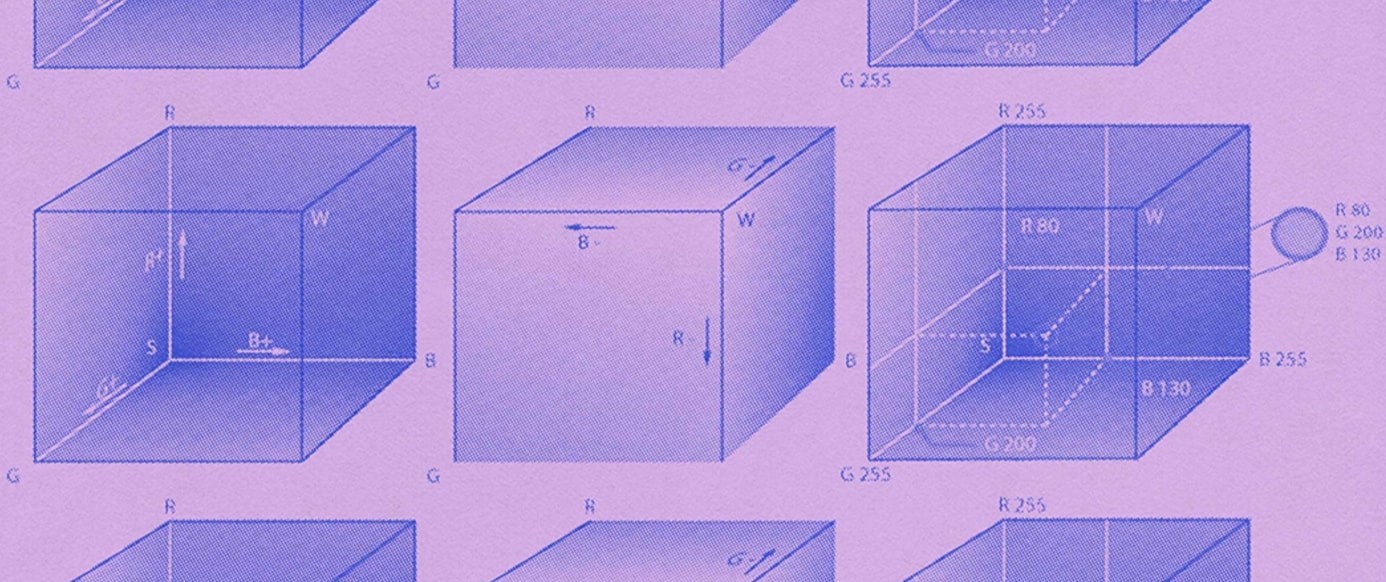
3.2. Applying Color Theory to Web Design
Color is a powerful tool in web design, capable of evoking emotions, creating moods, and influencing user behavior. Understanding color theory is essential for choosing the right colors for your website.
- Color Wheel: A visual representation of the relationships between different colors.
- Complementary Colors: Colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel, creating a high-contrast effect.
- Analogous Colors: Colors that are next to each other on the color wheel, creating a harmonious and balanced effect.
- Triadic Colors: Three colors that are equally spaced on the color wheel, creating a vibrant and energetic effect.
- Color Psychology: The study of how different colors affect human emotions and behavior.
3.3. The Importance of Typography in Web Design
Typography plays a crucial role in web design, affecting readability, legibility, and the overall aesthetic appeal of a website. Choosing the right fonts and using them effectively can significantly enhance the user experience.
- Font Families: Different types of fonts, such as serif, sans-serif, and display fonts.
- Font Size: The size of the text, which should be appropriate for the target audience and the device being used.
- Line Height: The spacing between lines of text, which should be adjusted to improve readability.
- Letter Spacing: The spacing between letters, which can be adjusted to improve legibility.
- Color Contrast: The difference in color between the text and the background, which should be high enough to ensure readability.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: How Can I Learn Web Designing Online?
Learning web design online can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
4.1. Step 1: Laying the Foundation: Key Concepts of Visual Design
Begin by understanding the core principles of visual design. This includes line, shapes, texture and color. These elements, when combined effectively, create visually appealing and user-friendly websites.
- Lines: Lines create structure and separate elements. Vertical lines can define sections, while horizontal lines can divide content.
- Shapes: Basic shapes like squares, circles, and triangles serve different purposes. Squares and rectangles are great for content blocks, circles work well for buttons, and triangles can be used for icons.
- Texture: Textures add depth and realism to a design. They replicate real-world surfaces and can make a design more engaging.
- Color: Color is a powerful tool that evokes emotions and guides the user’s eye. Understanding color theory helps you create visually appealing color schemes.
4.2. Step 2: Diving Into HTML Basics
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the foundation of every website. It provides the structure and content of a web page. Learning HTML basics is essential for understanding how websites are built.
- HTML Tags: HTML uses tags to define elements on a web page. These tags tell the browser how to display the content.
- Headings: Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) create a hierarchy of information, making it easier for users to scan the content.
- Paragraphs: Paragraphs (P) contain the main body of text on a web page.
- Links: Links (A) connect different web pages together, allowing users to navigate the website.
- Images: Images (IMG) add visual interest to a web page.
4.3. Step 3: Styling with CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to style the HTML elements on a web page. It controls the appearance of the website, including colors, fonts, and layout.
- CSS Selectors: CSS uses selectors to target specific HTML elements.
- CSS Properties: CSS properties define the style of an element, such as color, font-size, and margin.
- CSS Classes: CSS classes allow you to apply the same styles to multiple elements.
- CSS Frameworks: CSS frameworks like Bootstrap and Foundation provide pre-built styles and components, making it easier to create responsive websites.
4.4. Step 4: Understanding the Foundations of UX Design
UX (User Experience) design focuses on creating a positive and satisfying experience for users. It involves understanding user needs, conducting user research, and designing the website to meet those needs.
- User Personas: User personas are fictional representations of your target audience.
- Information Architecture: Information architecture is the organization and structure of content on a website.
- User Flows: User flows map out the steps a user takes to complete a task on a website.
- Wireframes: Wireframes are basic layouts of a web page, showing the placement of elements like headings, text, and images.
- Prototyping: Prototypes are interactive mockups of a website, allowing you to test the user experience before development.
4.5. Step 5: UI Design: Making it Interactive
UI (User Interface) design focuses on the visual elements and interactive components of a website. It involves selecting appropriate colors, fonts, icons, and other design elements to create an engaging and intuitive interface.
- Buttons: Buttons are interactive elements that allow users to take actions, such as submitting a form or adding an item to their cart.
- Forms: Forms allow users to input information, such as their name, email address, and password.
- Navigation: Navigation menus allow users to easily navigate the website.
- Icons: Icons are visual representations of actions or concepts.
4.6. Step 6: Grasping the Basics of Layouts
Understanding different layout patterns can help you create websites that are easy to navigate and visually appealing.
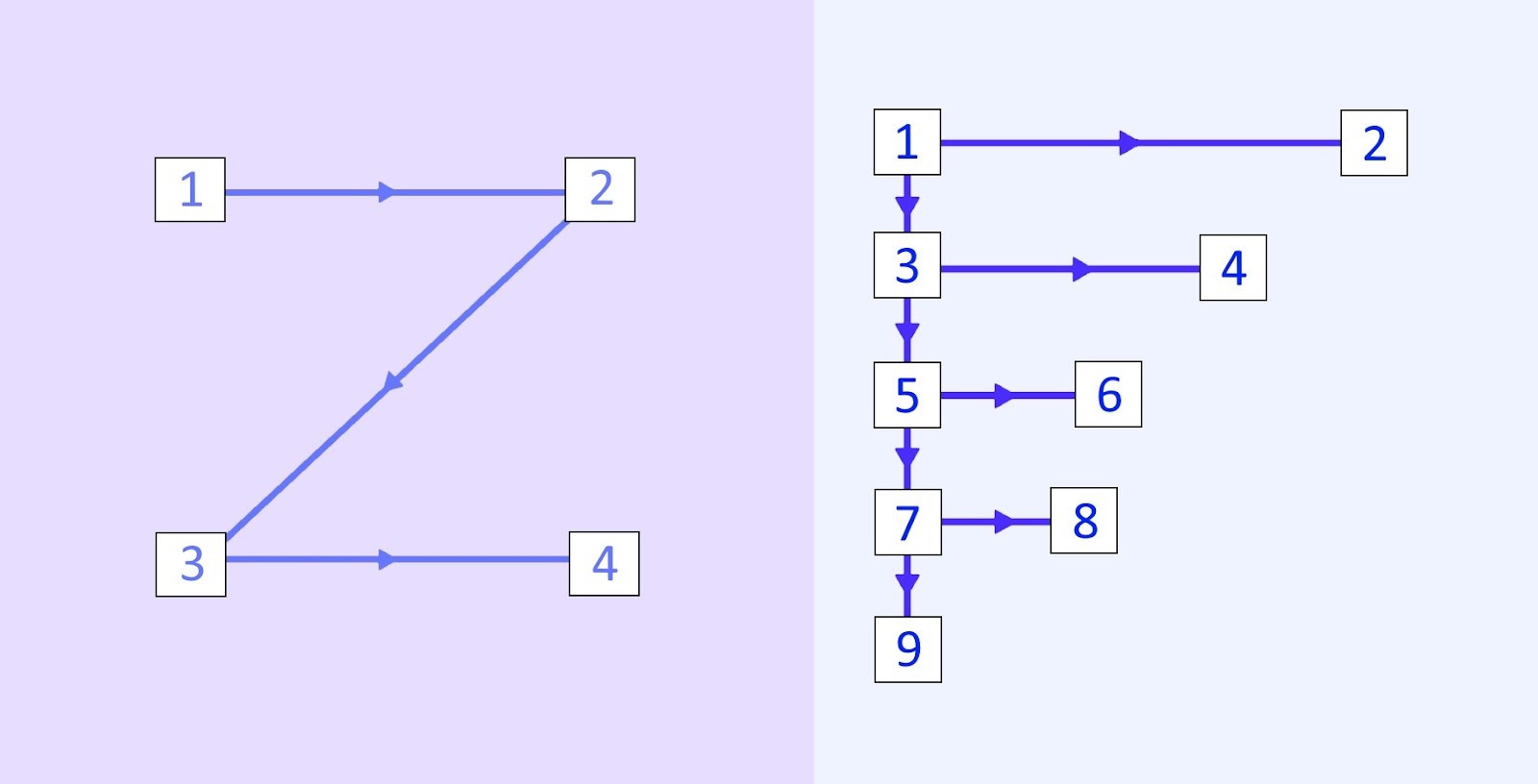
- Z-Pattern: The Z-pattern is effective for landing pages and websites with generous amounts of negative space.
- F-Pattern: The F-pattern is common for websites with a lot of text, such as blogs and online publications.
- Responsive Web Design: Responsive web design ensures that a website looks and functions well on all devices, from desktops to smartphones.
4.7. Step 7: The Art of Typography
Typography plays a crucial role in web design, affecting readability, legibility, and the overall aesthetic appeal of a website.
- Serif Fonts: Serif fonts have small decorative strokes at the end of each letter.
- Sans-Serif Fonts: Sans-serif fonts do not have these strokes and are often used for body text.
- Display Fonts: Display fonts are often used for headings and can be more decorative and attention-grabbing.
4.8. Step 8: Practice Makes Perfect: Build Something
The best way to learn web design is to start building websites. Begin with small projects, such as a blog or a simple landing page.
- Content Management System (CMS): A CMS like WordPress or Webflow makes it easy to create and manage website content.
4.9. Step 9: Seek Guidance: Find a Mentor
A mentor can provide valuable guidance and feedback as you learn web design.
- Networking: Attend industry events and connect with other designers.
- Online Communities: Join online communities and forums where you can ask questions and get feedback on your work.
5. The Importance of Staying Updated with Trends and Technologies
The web design landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, trends, and best practices emerging regularly. Staying updated with these changes is crucial for web designers to remain competitive and create cutting-edge websites. This continuous learning approach ensures that your skills remain relevant and that your designs leverage the latest advancements in the field.
5.1. Emerging Trends in Web Design
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to personalize user experiences, automate design tasks, and improve website accessibility.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR are creating immersive and interactive experiences for users.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is being used to create secure and transparent websites.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Dark Mode | Using dark color schemes to reduce eye strain and save battery life. |
| Micro-Interactions | Small animations and feedback that enhance the user experience. |
| 3D Elements | Using 3D graphics and animations to create more immersive and engaging designs. |
| Abstract Illustrations | Using abstract and unconventional illustrations to add visual interest and personality. |
| Neumorphism | A design style that uses soft shadows and highlights to create a sense of depth and realism. |
| Voice User Interface (VUI) | Designing websites and applications that can be controlled by voice commands. |
| Scroll-Triggered Animations | Animations that are triggered as the user scrolls down the page, creating a more interactive and engaging experience. |
| Minimalist Design | Focusing on simplicity and functionality, using only essential elements to create a clean and uncluttered design. |
| Mobile-First Design | Designing websites for mobile devices first, then adapting them for larger screens, ensuring a seamless experience on all devices. |
| Inclusive and Accessible Design | Designing websites that are usable by people with disabilities, following accessibility guidelines and standards. |
5.2. Essential Tools and Technologies
- Design Software: Adobe Photoshop, Adobe XD, Sketch, Figma
- Code Editors: Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, Atom
- Version Control: Git, GitHub, GitLab
- Web Frameworks: React, Angular, Vue.js
- Testing Tools: BrowserStack, Lighthouse
5.3. Resources for Staying Updated
- Blogs and Publications: Smashing Magazine, A List Apart, CSS-Tricks, Webflow Blog
- Online Courses and Tutorials: LEARNS.EDU.VN, Coursera, Udemy, edX
- Conferences and Workshops: Web Summit, SmashingConf, UX London
- Social Media: Twitter, LinkedIn, Dribbble, Behance
6. Building Your Portfolio and Finding Opportunities
Once you’ve acquired the necessary skills and knowledge, building a strong portfolio and finding opportunities are crucial steps in launching your web design career. A well-crafted portfolio showcases your abilities and style, while effective job-seeking strategies can help you land your dream job.
6.1. Creating a Web Design Portfolio
- Showcase Your Best Work: Select your most impressive and diverse projects to demonstrate your skills.
- Highlight Your Process: Describe the challenges you faced, the solutions you implemented, and the results you achieved.
- Tailor Your Portfolio: Customize your portfolio to match the specific requirements of the jobs you’re applying for.
- Seek Feedback: Ask mentors, peers, and potential employers for feedback on your portfolio.
- Keep It Updated: Regularly update your portfolio with your latest projects.
6.2. Networking and Building Connections
- Attend Industry Events: Network with other designers and potential employers at conferences, workshops, and meetups.
- Join Online Communities: Connect with other designers in online forums, social media groups, and professional networks.
- Contribute to Open Source Projects: Collaborate with other developers on open-source projects to gain experience and build your reputation.
- Volunteer Your Services: Offer your web design services to non-profit organizations to gain experience and build your portfolio.
6.3. Finding Web Design Jobs
- Online Job Boards: Indeed, LinkedIn, Glassdoor, Behance
- Company Websites: Check the career pages of companies you’re interested in working for.
- Freelance Platforms: Upwork, Fiverr, Toptal
- Networking: Leverage your network of contacts to find job opportunities.
7. Why Choose LEARNS.EDU.VN for Your Web Design Journey?
LEARNS.EDU.VN is a comprehensive online education platform that provides a wide range of resources and courses to help you learn web design. With LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can access high-quality educational content, learn from experienced instructors, and connect with a community of fellow learners.
7.1. Comprehensive Web Design Courses
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a variety of web design courses that cover everything from the fundamentals to advanced techniques. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced designer, you can find courses that match your skill level and interests.
7.2. Expert Instructors
Our instructors are experienced web designers and educators who are passionate about sharing their knowledge and skills. They provide clear and concise instruction, along with real-world examples and practical exercises.
7.3. Interactive Learning Environment
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides an interactive learning environment that allows you to engage with the course content, ask questions, and receive feedback from instructors and fellow learners.
7.4. Community Support
Join a community of fellow learners where you can share your experiences, ask for help, and collaborate on projects.
8. Conclusion: Your Path to Web Design Mastery Starts Now
Learning web design is an exciting and rewarding journey that can lead to a fulfilling career. By understanding the fundamentals, mastering the essential skills, staying updated with trends and technologies, and building a strong portfolio, you can achieve your web design goals. Remember, the field of web design is ever-evolving, so keep exploring, learning, and creating. With dedication and a passion for design, you can create websites that not only look great but also provide exceptional user experiences.
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our web design courses and resources. Take the first step towards becoming a successful web designer. Unleash your creativity and start building the websites of tomorrow. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
9. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Learning Web Design Online
Here are some frequently asked questions about learning web design online:
-
Is it possible to learn web design online without any prior experience?
Yes, it’s definitely possible. Many online courses and resources cater to beginners with no prior experience. -
How long does it take to learn web design?
The time it takes varies depending on your learning speed, dedication, and the depth of knowledge you want to acquire. However, you can gain a solid foundation in a few months with consistent effort. -
What are the essential skills I need to learn?
Essential skills include HTML, CSS, JavaScript, UI/UX design principles, and graphic design basics. -
What tools and software do web designers use?
Common tools include Adobe Photoshop, Adobe XD, Sketch, Figma, Visual Studio Code, and web development frameworks like React and Angular. -
How can I build a web design portfolio?
Create personal projects, volunteer your services, and showcase your best work in an online portfolio. -
How can I stay updated with the latest web design trends?
Follow industry blogs, attend online conferences, and join web design communities on social media. -
What are the job opportunities for web designers?
Job opportunities include frontend developer, UX designer, UI designer, web designer, and freelance web designer. -
How much can I earn as a web designer?
Earnings vary depending on experience, location, and type of job. However, experienced web designers can earn a comfortable salary. -
What are the differences between UI and UX design?
UI design focuses on the visual elements and interactive components of a website, while UX design focuses on the overall user experience and usability. -
How can LEARNS.EDU.VN help me learn web design?
learns.edu.vn offers comprehensive web design courses, expert instructors, an interactive learning environment, and a supportive community to help you achieve your web design goals.
