Learning How Can You Learn To Sing Better is a journey attainable by anyone with dedication and the right guidance. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand the aspirations of vocalists at every level. Whether you’re looking for singing tips, vocal exercises, or want to improve your vocal abilities, this guide provides actionable steps for vocal improvement. Discover the secrets to improve singing skills and develop your unique vocal abilities.
1. Understanding the Foundation: Can Everyone Learn to Sing Better?
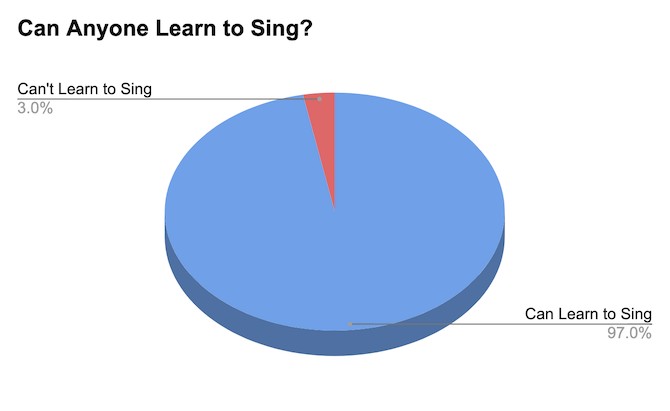
Before diving into specific techniques, it’s essential to address a fundamental question: Can everyone learn how to sing better? The answer is a resounding yes, with a few caveats.
1.1 Talent vs. Skill: The Singing Equation
Many people believe that singing is purely a talent, an innate gift that some possess and others don’t. However, while some individuals may have a natural inclination toward music, singing is primarily a learned skill. Professional vocalists hone their abilities through years of dedicated practice and training.
1.2 The Science of Singing in Tune
Studies indicate that approximately 97% of the population can learn to sing in tune, provided they do not have tone deafness (amusia). This means that whether you’re a beginner or someone looking to refine your technique, there’s a high likelihood you can improve your vocal abilities.
1.3 Age Is Just a Number
It’s never too late to start singing. Whether you’re wondering, “Can I learn to sing at 40?” or even older, the answer is yes. While working with a vocal coach is ideal, you can train yourself to sing through dedicated practice, regardless of your age.
2. Laying the Groundwork: Essential Techniques for Singing Improvement
Now that we’ve established that singing is a skill that can be learned, let’s explore essential techniques for improving your voice.
2.1 Posture Perfection: The Tall Posture
Correct posture is one of the fastest and easiest ways to enhance your singing voice. Singing with the right posture, known as the Tall Posture, provides your diaphragm and throat with the support you need to sing better.
How to Find Tall Posture:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Align your shoulders with your hips and your hips with your feet.
- Comfortably lift your chest, ensuring you’re not leaning forward or backward.
- Allow your knees to bend slightly.
2.2 Breathing from the Diaphragm
Breathing correctly is the foundation of good singing. Rather than breathing from your shoulders or chest, you should inhale from the diaphragm.
How to Breathe from the Diaphragm:
- Stand in front of a mirror to see your torso.
- Place your hands on the sides of your stomach.
- Open your mouth and inhale, allowing your stomach to expand outward.
- Exhale, allowing your stomach to contract inward.
2.3 Farinelli Breathing Exercise
The Farinelli breathing exercise is an effective method for building breath control.
How to Do the Farinelli Breath:
- Set a metronome to 60 BPM.
- Inhale from the diaphragm for 4 counts.
- Hold the breath for 4 counts.
- Exhale for 4 counts.
- Increase the count by 1 each round.
2.4 The Scared Breath
The Scared Breath is a quick way to take a breath from the diaphragm, especially useful when performing on stage.
How to Practice the Scared Breath:
- Stand in front of a mirror and turn to the side.
- Take a quick, silent inhale with your diaphragm as if you’re scared.
- Ensure your stomach expands on each inhale.
3. Training Your Ear: Developing Pitch Accuracy
3.1 The Importance of Ear Training
Ear training is the ability to hear a note and sing it back accurately. This is crucial for singing on pitch. Cupping your ears with your hands can help you hear your voice better.
3.2 Learning to Play an Instrument
Playing an instrument, such as the piano or guitar, can significantly improve your ear training and musicality, making you a better singer.
4. Vocal Warm-Ups: Preparing Your Voice for Optimal Performance
4.1 Warming Up Your Voice Properly
Vocal warm-ups increase blood flow to the vocal cords and help clear mucus, improving vocal performance.
4.2 The Lip Trill
The lip trill is a safe and effective vocal warm-up that helps eliminate vocal breaks and expand your range.
5. Vocal Tone: Achieving a Rich and Balanced Sound
5.1 Avoiding Breathiness
Singing with a breathy tone can weaken your sound. To fix this, speak phrases at a strong volume and then sing them with the same power, focusing on using your chest voice.
5.2 Eliminating Nasality
Nasal singing occurs when your vocal tone resonates in your nasal cavity. To correct this, pinch your nose while singing; if you feel vibration, direct the sound more out of your mouth.
6. Vocal Registers: Exploring Chest, Head, and Mix Voices
6.1 Understanding Vocal Registers
A vocal register is a series of notes that share a consistent sound and vibratory pattern in the vocal folds. The main registers are:
- Vocal Fry
- Chest Voice
- Head Voice
- Whistle Register
6.2 Chest Voice
Chest voice is produced by short, thick vocal folds and gives singers a strong, projected sound.
6.3 Head Voice
Head voice is produced by long, stretched vocal folds and is essential for singing high notes.
6.4 Mix Voice
Singing with a mix involves connecting your chest and head voices to hit high notes with power.
6.5 Fixing Your Vocal Break
Singing with a mix helps fix vocal breaks by connecting your chest and head voice registers.
6.6 Expanding Your Vocal Range
Vocal range is the measurement of how low or high a vocalist can sing. To expand your range, practice exercises like the “ng” sound.
7. Vocal Techniques: Mastering Advanced Singing Skills
7.1 Practicing Singing Exercises and Techniques
The best vocal techniques teach you to sing with a mix of your chest and head voices.
7.2 Avoiding Force
Never force your voice. If something hurts, you’re doing it wrong.
7.3 Singing Higher
Add a bit of press to reduce strain when singing high notes, using a “Cry” sound.
7.4 Singing Intervals
Learn to sing the most common musical intervals using the Italian solfeggio system (Do, Re, Mi, etc.).
7.5 Practicing Scales
Scales are progressions of musical notes. Practice major and minor scales to improve your vocal control.
7.6 Staccato Exercises
Sing exercises staccato (attacking each note separately) to improve vocal fold compression and depth.
7.7 Utilizing Vowels
Different vowels can help you sing better. Experiment with “Ee,” “Ae,” “Oh,” and “Uh” to see which works best for your voice.
7.8 Maintaining a Neutral Larynx Position
Keep your larynx in a neutral position as you sing to avoid a squeezed or pressed tone.
8. Vocal Effects: Adding Style and Flair to Your Singing
8.1 Transitioning to Legato
Move from staccato to legato (smooth) singing to connect notes easily.
8.2 Vibrato
Add vibrato (a rapid, slight variation in pitch) to make notes shimmer. The Diaphragm Pulse exercise can help.
9. Practical Tips for Beginners: Starting Your Singing Journey
9.1 Daily Practice
Practice for 30-60 minutes a day, focusing on exercises and songs.
9.2 Online Video Lessons
Learn from online video lessons, but be aware that information can be confusing.
9.3 Singing Courses
Invest in a singing course for structured vocal training.
9.4 Vocal Coach
Work with a vocal coach for personalized feedback.
9.5 Joining a Choir
Join a choir to sing with others and perform in public.
9.6 Joining a Band
Join a band to perform on stage and gain experience.
10. Becoming an Artist: Developing Your Unique Vocal Identity
10.1 Finding Your Style
Find your unique singing style by experimenting and working with a vocal teacher.
10.2 Inspiration
Get inspired by listening to great singers in your genre.
10.3 Memorizing Lyrics
Learn lyrics thoroughly so you can focus on your singing.
10.4 Microphone Techniques
Learn microphone techniques to perform like a pro.
10.5 Choosing Songs
Choose songs that fit your voice and range.
10.6 Patience
Be patient. Learning to sing takes time and practice.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About Singing
1. How long does it take to learn how to sing?
The time it takes to learn how to sing varies depending on individual factors such as natural ability, dedication, and practice frequency. However, with consistent effort and proper guidance, noticeable improvements can be seen within a few months.
2. Can I teach myself how to sing, or do I need a vocal coach?
While it’s possible to teach yourself how to sing using online resources and practice, working with a vocal coach offers personalized feedback and guidance, accelerating progress and preventing the development of bad habits.
3. What are some common mistakes that singers make?
Common mistakes include poor posture, improper breathing, singing from the throat, not warming up properly, and forcing the voice beyond its natural range.
4. How do I find my vocal range?
To find your vocal range, start by singing the lowest note you can comfortably produce and gradually work your way up to the highest note you can sing without straining. Use a piano or online tool to identify the notes and determine your range.
5. How do I develop a stronger singing voice?
Developing a stronger singing voice involves consistent practice, proper breathing techniques, vocal exercises to strengthen the vocal cords, and maintaining good vocal health through hydration and rest.
6. What is the difference between chest voice, head voice, and mix voice?
Chest voice is the lower register of the voice, characterized by a strong, resonant sound. Head voice is the higher register, producing a lighter, more ethereal tone. Mix voice is a blend of both, allowing singers to access higher notes with power and control.
7. How can I improve my pitch accuracy?
Improving pitch accuracy requires ear training exercises, such as singing scales and intervals, listening to music actively, and using tools like pitch correction software to identify and correct inaccuracies.
8. What are some good vocal warm-up exercises?
Effective vocal warm-up exercises include lip trills, humming scales, tongue twisters, and gentle vocal slides. These exercises help to prepare the vocal cords for singing and prevent strain or injury.
9. How important is posture for singing?
Posture is crucial for singing as it affects breathing, resonance, and overall vocal performance. Proper posture allows for optimal lung capacity and airflow, resulting in a stronger, more controlled sound.
10. How do I deal with stage fright while singing?
Dealing with stage fright involves preparation, practice, deep breathing exercises, visualization techniques, and focusing on connecting with the audience. Over time, exposure to performing can help to reduce anxiety and build confidence.
Conclusion: Your Path to Vocal Excellence Begins Here
Learning how can you learn to sing better is an exciting journey that combines technique, practice, and passion. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to unlock your vocal potential.
Ready to take your singing to the next level?
- Explore our comprehensive articles for in-depth guidance.
- Discover personalized vocal exercises tailored to your needs.
- Connect with our expert vocal coaches for one-on-one support.
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and start your journey towards vocal excellence.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
Remember, every great singer starts somewhere. With dedication, the right techniques, and the support of learns.edu.vn, you can achieve your vocal dreams.