Continuous learning is vital to professional development, representing an ongoing journey of knowledge and skill enhancement. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we champion this approach, offering resources to help individuals and organizations embrace continual growth. By integrating learning agility and knowledge retention, professionals can unlock their full potential and achieve sustained success.
1. Understanding Continuous Learning
Continuous learning is the persistent pursuit of knowledge and skills. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from formal education to informal self-improvement, and plays a crucial role in professional development. This ongoing process is key to adapting to evolving industry demands and fostering innovation.
1.1. Defining Continuous Learning
Continuous learning can be defined as the perpetual, proactive acquisition of knowledge and skills. It is a mindset and a practice, integrating learning into daily routines and career paths.
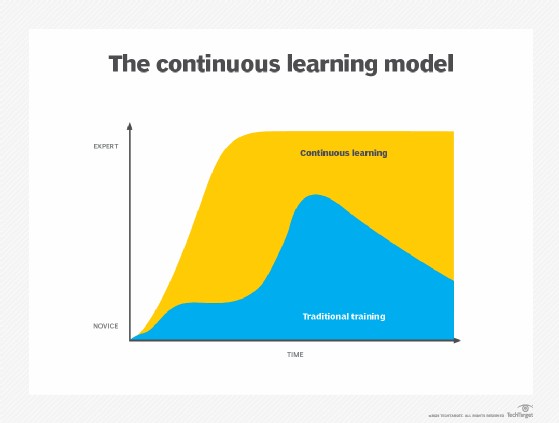
1.2. Continuous Learning vs. Traditional Training
| Feature | Continuous Learning | Traditional Training |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Ongoing, iterative | One-time event |
| Focus | Sustained growth, adaptability | Specific skill acquisition |
| Timeline | Long-term, lifelong | Short-term, focused |
| Knowledge | Continuous improvement upon skill sets | Learning considered finished at some point. |
| Reinforcement | Multiple learning events that reinforce one another. | Peaks right after a training course, then gradually falls off from a lack of reinforcement. |

1.3. The Importance of Continuous Learning in Today’s World
In today’s rapidly changing professional landscape, continuous learning is no longer optional—it’s essential. It enables individuals and organizations to stay competitive, innovative, and relevant. According to a study by the Pew Research Center, approximately 87% of workers believe it will be essential for them to get training and develop new skills throughout their work life to keep up with changes in the workplace.
2. The Link Between Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Continuous learning is inextricably linked to professional development. It’s the engine that drives career growth, enhances expertise, and builds resilience in the face of change.
2.1. Enhancing Skills and Knowledge
Continuous learning directly enhances an individual’s skill set and knowledge base. By staying updated with the latest industry trends and technologies, professionals can improve their performance and productivity. A report by the Association for Talent Development (ATD) found that companies with comprehensive training programs have 24% higher profit margins than those without.
2.2. Fostering Adaptability and Resilience
The modern workplace requires adaptability and resilience. Continuous learning equips professionals with the tools to navigate change, overcome challenges, and thrive in dynamic environments.
2.3. Promoting Innovation and Creativity
Continuous learning fuels innovation and creativity. By exposing themselves to new ideas and perspectives, professionals can develop novel solutions and drive organizational growth. Research from Harvard Business Review indicates that employees who engage in continuous learning are more likely to generate innovative ideas.
2.4. Career Advancement
Continuous learning opens doors to career advancement opportunities. Demonstrating a commitment to ongoing growth signals ambition and competence, making professionals more attractive to employers.
3. Principles of Continuous Learning
Several core principles underpin effective continuous learning. Understanding and applying these principles can maximize the benefits of ongoing education and skill development.
3.1. Accessibility
Learning opportunities should be readily accessible, allowing professionals to learn whenever and wherever they need.
3.2. Application
Learners should have continuous opportunities to apply their knowledge and test new skills in real-world scenarios.
3.3. Culture
A supportive culture that fosters learning, collaboration, and knowledge-sharing is essential for continuous learning to thrive.
3.4. Collaboration
Collaboration opportunities enable learners to share knowledge, perspectives, and experiences, enhancing their understanding and skills.
3.5. Feedback
Regular feedback mechanisms from instructors and peers provide valuable insights and support continuous improvement.
3.6. Key elements to create a continuous learning environment
- Readily accessible learning opportunities for whenever the need arises.
- Continuous opportunities for learners to apply their knowledge and test their new skills.
- A culture that fosters learning with repeatable, sustainable practices.
- Collaboration opportunities so learners share knowledge and perspectives.
- Regular feedback mechanisms from both instructors and students.
4. Benefits of Continuous Learning
The benefits of continuous learning are far-reaching, impacting individuals, teams, and organizations.
4.1. Benefits for Individuals
- Career Development: Helps achieve career development goals.
- Professional Licenses and Certifications: Facilitates obtaining or updating professional licenses and certifications.
- Exploration of New Opportunities: Encourages exploring new opportunities and perspectives in work and personal development.
- Marketable Skills: Enables developing marketable professional skills through upskilling and reskilling.
- Increased Earning Potential: According to a study by Georgetown University, individuals with a bachelor’s degree earn approximately $1 million more over their lifetime than those with only a high school diploma. Continuous learning can further increase earning potential.
4.2. Benefits for Organizations
- Achieving Organizational Goals: Contributes to achieving organizational goals.
- Forward-Thinking Culture: Encourages a forward-thinking, innovation culture.
- Employee Value: Makes employees feel valued.
- Cost Efficiency: Keeps costs down because it’s less expensive to invest in the ongoing development of current employees than to train new employees.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Enhances competitiveness as employees become more skilled and productive.
- Higher Employee Engagement: A study by Gallup found that engaged employees are more productive, profitable, and customer-focused. Continuous learning initiatives can boost employee engagement.
5. Challenges of Continuous Learning
Despite its many benefits, continuous learning can present several challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.
5.1. Resistance to New Skills
Employees may resist learning new skills if they find the topic uninteresting or difficult. Alternative training methods and tools should be explored.
5.2. Evolving Requirements
Business needs change frequently, so having employees learn skills that may become irrelevant isn’t productive.
5.3. Time Constraints
Employees may find it difficult to fit additional training into their schedules. Courses that are broken into smaller, manageable lessons are easier to incorporate.
5.4. Budget Issues
Employers may have limited budgets for training and software, which can restrict the quality and duration of training.
5.5. Lack of Personalized Learning
Employees learn differently, but continuous learning courses often aren’t designed to be personalized. Flexible and personalized upskilling programs are the best approach.
5.6. Additional challenges
- Difficulty in staying motivated.
- Lack of immediate application opportunities.
- Information overload.
6. Continuous Learning Models
Several models provide frameworks for implementing continuous learning effectively.
6.1. Deloitte’s Continuous Learning Model
Deloitte’s Continuous Learning Model features three different categories for learners’ needs:
- Immediate: Learning needed to be successful today.
- Intermediate: Learning needed to expand skill sets and grow in current positions.
- Transitional: Learning needed to reach long-term organizational goals, advance up the career ladder, or make a career switch.
6.2. Paradigms of Learning
Paradigms are the different ways employees learn, consisting of:
- Education: Traditional learning and development often done in classrooms or e-learning experiences.
- Experience: Learning through workplace events, such as special projects, job rotations, and stretch assignments.
- Exposure: Learning through social relationships and interactions.
- Environment: The tools and systems that support employee learning in the workplace.
7. Continuous Learning Strategies
Various strategies can be employed to implement continuous learning techniques effectively.
7.1. Structured Learning
Formal learning methods are preorganized for specific goals and purposes, including school courses, online courses, workshops, seminars, webinars, conferences, and employee and managerial training programs.
7.2. Social Learning
The ways people learn through interacting and observing others, including discussion, coworking, collaborative problem-solving, mentoring, and on-the-job training.
7.3. Self-Directed Learning
Independently administered approaches that employees can use to expand their skills and knowledge, including research, reading, experimentation, and practice testing.
7.4. Detailed examples of Learning
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Microlearning | Delivering content in small, easily digestible chunks, such as short videos or infographics. | Increases engagement, knowledge retention, and flexibility. |
| Mentorship | Pairing experienced professionals with less experienced ones to provide guidance and support. | Fosters knowledge transfer, skill development, and career growth. |
| Job Rotation | Moving employees between different roles or departments to broaden their skills and experiences. | Enhances adaptability, cross-functional collaboration, and organizational understanding. |
| Online Courses | Providing access to a wide range of courses on platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning. | Offers flexibility, affordability, and access to expert knowledge. |
| Webinars | Delivering live or recorded presentations and discussions on specific topics. | Enables real-time interaction, knowledge sharing, and accessibility. |
| Conferences | Attending industry events to learn about new trends, network with peers, and gain insights from experts. | Provides exposure to cutting-edge knowledge, networking opportunities, and professional development. |
| Lunch and Learns | Hosting informal learning sessions during lunchtime, where employees can share knowledge and learn from each other. | Promotes a culture of learning, collaboration, and knowledge sharing. |
| Book Clubs | Creating groups where employees read and discuss books related to their field or personal development. | Enhances critical thinking, communication skills, and knowledge sharing. |
| Hackathons | Organizing events where employees collaborate to solve problems and develop innovative solutions. | Fosters creativity, problem-solving skills, and teamwork. |
| Simulations | Using simulated environments to allow employees to practice new skills and make decisions in a risk-free setting. | Enhances skill development, decision-making abilities, and confidence. |
8. Building a Continuous Learning Strategy
A continuous learning strategy begins with business leadership or those tasked with training employees developing long-term goals for their continuous learning plans. Then, a learning infrastructure is implemented that includes various courses and tools to achieve those goals.
8.1. Planning
Map out a course of action to show employees that the organization is investing effort and resources into continuous learning. This should include who the learning plans are for, such as individual employees, teams, departments, and the entire organization. There should be ongoing dialogue between management and employees to clarify objectives and priorities.
8.2. Leadership
A continuous learning culture starts from the top, so it’s important for management to communicate their full support for these activities.
8.3. Sustainability
Provide ongoing resources to support and maintain a continuous learning culture.
9. Building a Culture of Continuous Learning
Once the scope of a continuous learning strategy is determined and a plan devised, the following components will help to ensure employees take full advantage of it:
9.1. Flexibility
Flexibility is key to accommodating as many employees as possible and ensuring their participation. Flexible approaches include accounting for people’s busy schedules and personal lives by allotting sufficient time to complete assignments. Another example would be providing easily accessible forums or discussion boards for collaboration and interaction among learners who live far apart.
9.2. Technology Tools and Resources
Learning management systems (LMSes) and other types of learning platforms are particularly useful for cohort learning, which helps train or educate multiple employees at the same time. Systems that enable virtual and hybrid learning are also useful.
9.3. Collaborative Efforts
LMSes have capabilities that foster collaboration and interactive assignments with features such as forums and gamification. When learners engage in fun activities and interactions, they’re more likely to retain what they’re learning.
9.4. Steps to build
- Assess Learning Needs: Identify skill gaps and learning needs through surveys, performance reviews, and business goals.
- Set Clear Learning Objectives: Define what employees should know or be able to do after completing the learning activity.
- Provide Diverse Learning Opportunities: Offer a variety of learning formats (e.g., online courses, workshops, mentoring) to cater to different learning styles.
- Encourage Self-Directed Learning: Empower employees to take ownership of their learning by providing access to resources and support.
- Recognize and Reward Learning: Acknowledge and reward employees who actively participate in learning activities and demonstrate skill improvement.
- Measure the Impact of Learning: Evaluate the effectiveness of learning initiatives by tracking key metrics such as skill improvement, job performance, and employee engagement.
10. Continuous Learning for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The concept of continuous learning applies to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) systems. Ongoing learning is a key part of these systems. ML systems use algorithms to learn to analyze data on their own. Algorithms help them distinguish important insights and learn what predictions they can make from that information.
10.1. ML models
In a static learning process, once an ML algorithm is trained on a specific data set, it assumes every future data set it analyzes is similar. However, the world and knowledge aren’t static. Therefore, in the same way humans are retrained and reskilled through continuous and constant learning, ML systems also undergo continuous training as part of the ML operations process.
10.2. Ongoing Learning
An ML model is deployed once and then continuously monitored and retrained to adapt to constantly changing data. There are different techniques and tools that developers use to automate this retraining process.
10.3. Periodic Oversight
The continuous learning process for ML requires periodic oversight from a human developer. There are also drawbacks to this type of retraining, as it requires expensive technology and can be time-consuming. However, the ongoing learning process is important to ensure the efficiency of AI and ML systems.
10.4. Key Considerations
- Data Quality: Ensure the data used for training is accurate, relevant, and representative of the real-world environment.
- Model Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the performance of ML models to identify areas for improvement.
- Feedback Loops: Implement feedback loops to allow models to learn from their mistakes and adapt to changing conditions.
- Ethical Considerations: Address ethical concerns such as bias and fairness in ML models.
11. Continuous vs. Lifelong Learning
The term lifelong learning is often used interchangeably with continuous learning, yet there are differences.
11.1. Continuous Learning
Continuous learning applies to employers or institutions that offer courses to improve a person’s knowledge or skill sets, including both hard and soft skills.
11.2. Lifelong Learning
Lifelong learning instead focuses on an employee’s or student’s personal development as they cultivate skills and obtain new knowledge that isn’t necessarily required or useful for career development.
11.3. Examples
For example, a person working in a field that doesn’t require coding skills might take e-learning courses on computer languages, such as HTML5, for web development side projects and to fill skill gaps. This type of structureless personal development qualifies as lifelong learning. When similar courses are offered through an employer with set dates and sessions, and the course content pertains to the employee’s day-to-day tasks and competencies, this exemplifies continuous learning.
12. Practical Tips for Embracing Continuous Learning
Implementing continuous learning effectively requires a strategic approach and a commitment to ongoing growth.
12.1. Set Clear Goals
Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for learning and development.
12.2. Allocate Time
Schedule dedicated time for learning activities, treating it as a non-negotiable part of the workday.
12.3. Utilize Technology
Leverage technology tools and platforms to access learning resources, track progress, and collaborate with peers.
12.4. Seek Feedback
Actively solicit feedback from mentors, peers, and supervisors to identify areas for improvement and refine learning strategies.
12.5. Stay Curious
Cultivate a curious mindset, always seeking new knowledge and perspectives.
12.6. Additonal Tips
- Create a Personal Learning Plan: Develop a structured plan with clear objectives, timelines, and resources.
- Join Professional Organizations: Engage with industry peers, attend events, and access learning resources.
- Read Widely: Stay informed about industry trends, best practices, and new technologies through books, articles, and blogs.
- Attend Workshops and Seminars: Participate in hands-on learning experiences to develop specific skills.
- Network with Experts: Connect with thought leaders, mentors, and experts in your field to gain insights and guidance.
- Reflect on Learning: Take time to reflect on what you have learned, how you can apply it, and what further learning you need.
13. The Role of LEARNS.EDU.VN in Fostering Continuous Learning
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to fostering continuous learning and professional development. Our platform offers a wide range of resources and tools to support learners at every stage of their journey.
13.1. Comprehensive Learning Resources
We provide access to a vast library of courses, articles, and tutorials covering diverse topics and skill sets.
13.2. Personalized Learning Paths
Our personalized learning paths help learners identify their strengths, weaknesses, and goals, and create customized learning plans.
13.3. Expert Guidance
Our team of experienced educators and industry experts provides guidance, support, and feedback to help learners achieve their full potential.
13.4. Community Engagement
We foster a vibrant community of learners, providing opportunities for collaboration, knowledge sharing, and networking.
13.5. Our commitment
- Curated Content: High-quality, relevant resources tailored to specific learning needs.
- Interactive Learning Experiences: Engaging formats such as quizzes, simulations, and case studies.
- Progress Tracking: Tools to monitor learning progress, identify areas for improvement, and celebrate achievements.
- Certification Programs: Industry-recognized certifications to validate skills and knowledge.
- Career Support: Resources and guidance to help learners advance their careers.
14. Case Studies: Continuous Learning in Action
Real-world examples illustrate the transformative power of continuous learning in professional development.
14.1. Case Study 1: Google’s 20% Time
Google’s famous “20% Time” policy allows employees to spend 20% of their time working on projects of their own choosing. This has led to the development of innovative products like Gmail and AdSense, demonstrating the power of continuous learning and exploration.
14.2. Case Study 2: IBM’s Skills Gateway
IBM’s Skills Gateway is an internal platform that provides employees with access to a wide range of learning resources and opportunities. This has helped IBM employees stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and develop new skills, contributing to the company’s success.
14.3. Case Study 3: AT&T’s Future Ready Program
AT&T’s Future Ready program is a massive reskilling initiative aimed at preparing employees for the jobs of the future. The program provides employees with access to online courses, workshops, and mentoring, helping them develop the skills they need to succeed in a rapidly changing industry.
15. Future Trends in Continuous Learning
The future of continuous learning is dynamic, shaped by emerging technologies and evolving learner needs.
15.1. Personalized Learning
AI-powered personalized learning platforms will tailor learning experiences to individual needs, preferences, and goals.
15.2. Microlearning
Bite-sized learning modules will deliver targeted knowledge and skills in a convenient, engaging format.
15.3. Immersive Learning
Virtual and augmented reality technologies will create immersive learning experiences that enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
15.4. Social Learning
Collaborative learning platforms will foster knowledge sharing, peer support, and community engagement.
15.5. Adaptive Learning
Learning systems will adapt to learner performance, providing customized feedback and guidance.
15.6. The future
- AI-Driven Learning: Personalized content, adaptive assessments, and intelligent tutoring systems.
- Gamification: Learning through game-like elements to increase engagement and motivation.
- Mobile Learning: Accessing learning resources on smartphones and tablets for on-the-go learning.
- VR/AR in Education: Immersive learning experiences that simulate real-world scenarios.
16. Embracing Continuous Learning for a Brighter Future
Continuous learning is the cornerstone of professional development, enabling individuals and organizations to thrive in a rapidly changing world. By embracing a culture of continuous learning, we can unlock our full potential and create a brighter future.
FAQ
- What is continuous learning?
Continuous learning is the ongoing, voluntary, and self-motivated pursuit of knowledge for either personal or professional reasons. - Why is continuous learning important for professional development?
It enhances skills, fosters adaptability, promotes innovation, and opens doors to career advancement. - What are the key principles of continuous learning?
Accessibility, application, culture, collaboration, and feedback. - What are the benefits of continuous learning for individuals?
Career development, professional certifications, exploration of new opportunities, and marketable skills. - What are the benefits of continuous learning for organizations?
Achieving organizational goals, fostering a forward-thinking culture, valuing employees, cost efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness. - What are the challenges of continuous learning?
Resistance to new skills, evolving requirements, time constraints, budget issues, and lack of personalized learning. - How can organizations build a culture of continuous learning?
By implementing flexible learning plans, providing useful technology tools, and fostering collaborative efforts. - What is the difference between continuous learning and lifelong learning?
Continuous learning focuses on improving specific skills, while lifelong learning is broader and includes personal development. - What strategies can be used to implement continuous learning?
Structured learning, social learning, and self-directed learning. - How can LEARNS.EDU.VN help in fostering continuous learning?
By providing comprehensive learning resources, personalized learning paths, expert guidance, and community engagement.
Ready to unlock your full potential? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and explore our extensive range of courses and resources. Our team of experienced educators and industry experts are here to guide you on your journey. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. Let learns.edu.vn be your partner in continuous growth and professional success!