How Do Artists Learn To Draw? Discover proven techniques and methods on LEARNS.EDU.VN to master drawing, from basic shapes to advanced concepts, and unlock your artistic potential. Explore fundamental skills and practical tips to enhance your drawing abilities.
1. Understanding the Core Principles of Drawing
Drawing is a fundamental skill that anyone can learn with dedication and the right approach. It’s not about inherent talent but rather about understanding core principles and practicing consistently. Aspiring artists often wonder how professional artists hone their skills. The answer lies in a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical application, and continuous learning. Understanding these principles forms the bedrock of artistic development, allowing learners to progress from simple sketches to complex, detailed artworks.
1.1 The Importance of Observation Skills
Observation is the cornerstone of drawing. It involves training your eye to see beyond the surface and to perceive the underlying structure, form, and relationships within a subject. Artists need to be able to accurately observe shapes, sizes, proportions, and the interplay of light and shadow. Developing keen observation skills is paramount for accurately representing the world around you.
1.1.1 Exercises to Improve Observation
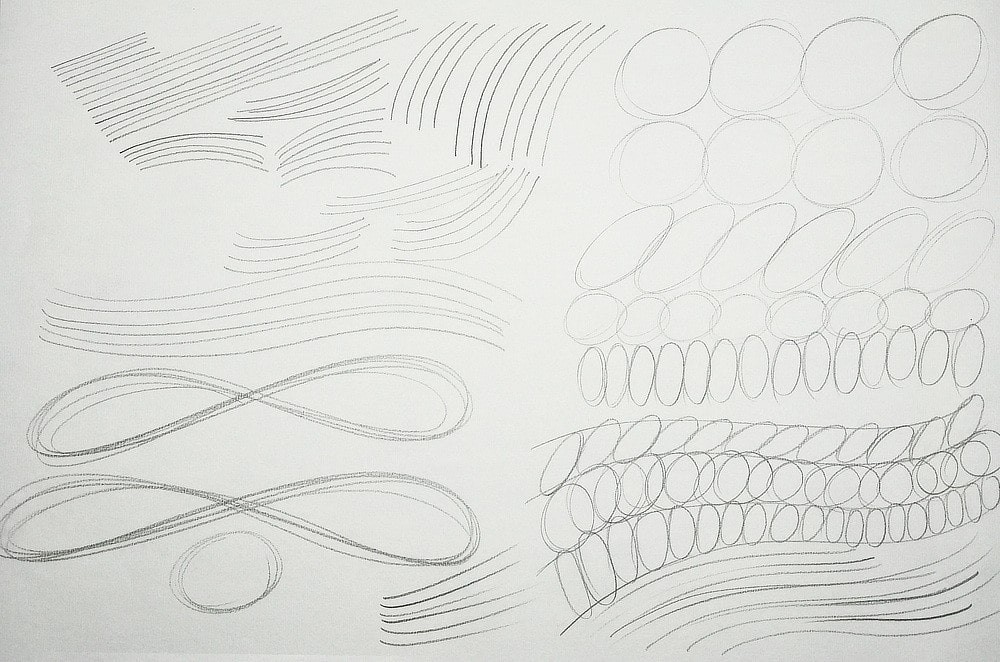
- Contour Drawing: Focus on drawing the outline of a subject without lifting your pencil. This helps train your eye to follow edges and understand form.
- Blind Contour Drawing: Similar to contour drawing, but you don’t look at your paper while drawing. This forces you to rely entirely on your sense of touch and observation.
- Gesture Drawing: Quickly capture the essence of a subject’s form and movement with loose, energetic lines. This exercise emphasizes capturing the overall impression rather than precise details.
1.2 Mastering Basic Shapes and Forms
All complex objects can be broken down into basic shapes such as circles, squares, triangles, cylinders, and cones. Mastering these shapes is essential for constructing more intricate drawings. Artists often begin by simplifying subjects into these fundamental forms before adding details.
1.2.1 Practicing Shape Decomposition
- Object Breakdown: Choose a complex object and try to identify the basic shapes that make up its structure. Practice drawing these shapes individually and then assemble them to recreate the object.
- Geometric Construction: Use geometric shapes as a framework for your drawings. Start with a simple object and gradually add details and refine the shapes to create a more realistic representation.
1.3 Understanding Perspective
Perspective is the technique used to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional surface. It involves understanding how objects appear to shrink and converge as they recede into the distance. Mastering perspective is crucial for creating realistic and believable drawings.
1.3.1 Types of Perspective
- One-Point Perspective: All lines converge at a single vanishing point on the horizon line. This is commonly used for drawing roads, hallways, and other linear scenes.
- Two-Point Perspective: Lines converge at two vanishing points on the horizon line. This is used for drawing objects viewed from an angle, such as buildings or boxes.
- Three-Point Perspective: Lines converge at three vanishing points, including one above or below the horizon line. This is used for drawing objects viewed from a high or low angle, such as skyscrapers or deep canyons.
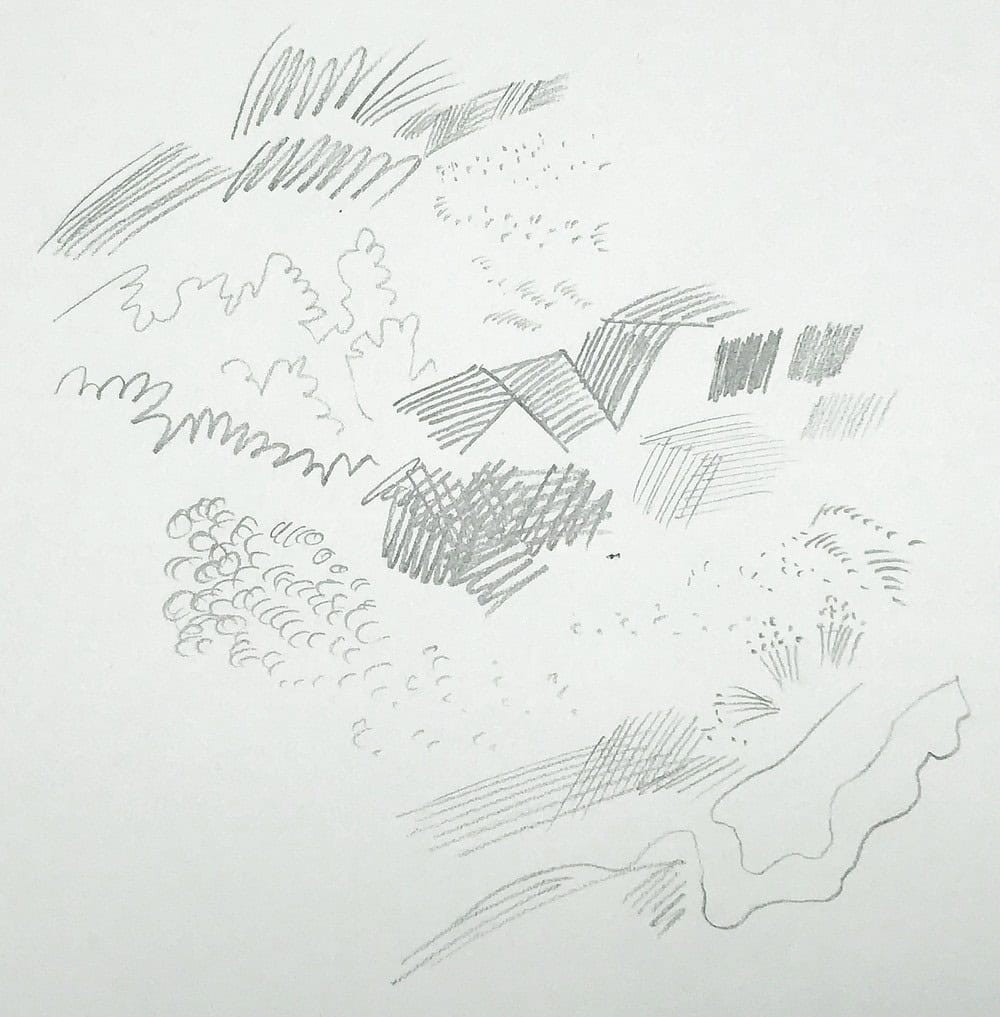
1.4 Value and Shading Techniques
Value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. Shading is the technique of using value to create the illusion of form and depth in a drawing. Understanding how light interacts with surfaces is essential for creating realistic and compelling drawings.
1.4.1 Shading Techniques
| Technique | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Hatching | Creating value with parallel lines. | Suggesting texture and form. |
| Cross-Hatching | Creating value with intersecting lines. | Creating darker values. |
| Stippling | Creating value with dots. | Building up subtle value. |
| Blending | Smoothing values together with a tool like a blending stump or your finger. | Creating smooth transitions. |

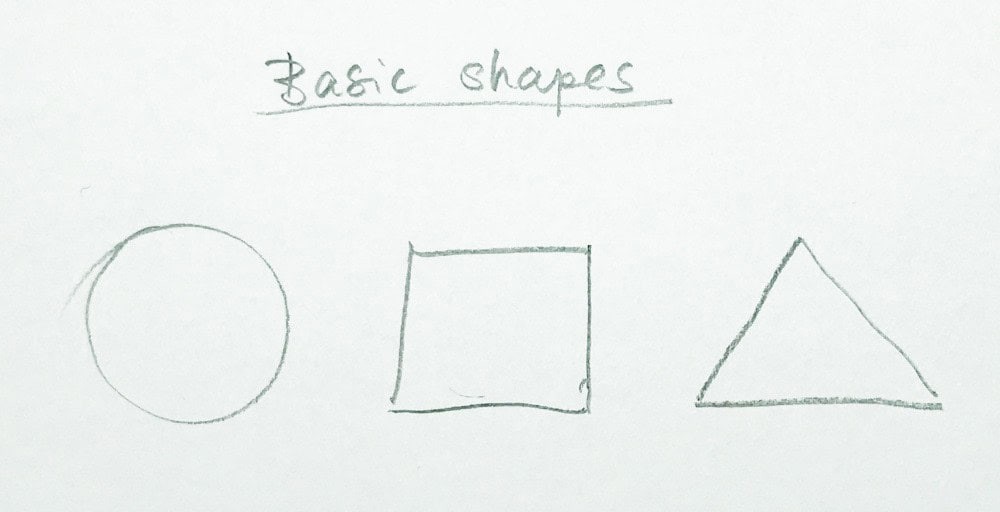




2. Building a Strong Foundation in Drawing Fundamentals
To excel in drawing, a strong foundation in fundamental skills is essential. This involves consistent practice, understanding of basic techniques, and a willingness to learn from mistakes. Aspiring artists should focus on mastering these fundamentals before moving on to more advanced techniques. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources and courses to help you build a solid foundation in drawing.
2.1 Regular Practice and Consistency
Consistent practice is the key to improving your drawing skills. Set aside dedicated time each day or week to practice drawing, even if it’s just for a few minutes. Regular practice helps reinforce your skills and build muscle memory.
2.1.1 Creating a Practice Schedule
- Set Realistic Goals: Start with small, achievable goals, such as drawing for 15-30 minutes each day.
- Variety: Include a variety of drawing exercises in your practice routine to keep things interesting and challenging.
- Track Progress: Keep a sketchbook or digital journal to track your progress and identify areas for improvement.
2.2 Understanding Composition
Composition refers to the arrangement of elements within a drawing. A well-composed drawing is visually appealing and effectively conveys the artist’s intended message. Understanding principles of composition can greatly enhance the impact of your artwork.
2.2.1 Principles of Composition
- Rule of Thirds: Divide your canvas into nine equal parts with two horizontal and two vertical lines. Place key elements of your drawing along these lines or at their intersections to create a balanced and visually interesting composition.
- Leading Lines: Use lines to guide the viewer’s eye through your drawing. Leading lines can create a sense of depth and movement.
- Balance: Distribute elements evenly throughout your drawing to create a sense of equilibrium. Balance can be symmetrical or asymmetrical.
2.3 Studying Anatomy
For artists interested in drawing the human figure, studying anatomy is essential. Understanding the underlying bone structure and muscle groups helps you create more realistic and dynamic figures.
2.3.1 Resources for Studying Anatomy
- Anatomy Books: Consult anatomy books specifically designed for artists. These books provide detailed illustrations and explanations of the human anatomy.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources such as websites, videos, and 3D models to study anatomy.
- Life Drawing Classes: Attend life drawing classes to practice drawing the human figure from observation.
2.4 Experimenting with Different Mediums
Experimenting with different drawing mediums can help you discover your preferences and expand your artistic skills. Each medium has its own unique properties and techniques.
2.4.1 Common Drawing Mediums
- Pencil: Versatile and widely accessible, pencils are great for sketching, shading, and detailed work.
- Charcoal: Creates rich, dark values and is ideal for expressive drawings.
- Ink: Used for precise lines and bold contrasts.
- Colored Pencils: Allow for vibrant color and detailed rendering.
- Digital Drawing: Offers a wide range of tools and effects, allowing for experimentation and easy corrections.
3. Advanced Techniques to Elevate Your Drawing Skills
Once you have a solid foundation in the fundamentals, you can begin to explore more advanced techniques to elevate your drawing skills. These techniques involve refining your understanding of light, shadow, and form, and developing your own unique artistic style.
3.1 Mastering Light and Shadow
Understanding how light interacts with surfaces is crucial for creating realistic and compelling drawings. Advanced techniques involve studying the properties of light and shadow and applying them to your drawings.
3.1.1 Properties of Light and Shadow
- Highlight: The brightest area on a surface, where light is directly hitting.
- Midtone: The area between the highlight and shadow, where the surface is partially lit.
- Shadow: The area on a surface that is not directly lit.
- Core Shadow: The darkest area within the shadow, where light is completely blocked.
- Reflected Light: Light that bounces off surrounding surfaces and illuminates the shadow area.
- Cast Shadow: The shadow that an object casts onto surrounding surfaces.
3.2 Rendering Textures
Rendering textures involves creating the illusion of different surface qualities in your drawings. This can be achieved by using a variety of techniques, such as hatching, stippling, and blending.
3.2.1 Techniques for Rendering Textures
- Hatching: Use parallel lines to create the illusion of texture. Vary the spacing and thickness of the lines to create different effects.
- Stippling: Use dots to create the illusion of texture. Vary the density of the dots to create different values.
- Blending: Use a blending stump or your finger to smooth values and create soft textures.
3.3 Color Theory and Application
For artists working with color, understanding color theory is essential. Color theory involves studying the properties of colors and how they interact with each other.
3.3.1 Basic Color Concepts
- Hue: The pure color, such as red, blue, or green.
- Saturation: The intensity or purity of a color.
- Value: The lightness or darkness of a color.
- Color Harmony: The pleasing arrangement of colors.
- Complementary Colors: Colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel, such as red and green.
- Analogous Colors: Colors that are next to each other on the color wheel, such as blue and green.
3.4 Developing Your Unique Style
As you gain experience and confidence in your drawing skills, you can begin to develop your own unique artistic style. This involves experimenting with different techniques, mediums, and subjects, and finding what resonates with you.
3.4.1 Steps to Develop Your Style
- Experiment: Try different techniques and mediums to see what you enjoy and what works best for you.
- Study Artists You Admire: Analyze the work of artists whose style you admire and identify the elements that you find appealing.
- Practice: Continue to practice and refine your skills, focusing on the techniques and subjects that you are most passionate about.
- Be Authentic: Don’t try to imitate other artists. Instead, focus on expressing your own unique vision and perspective.
4. Learning Resources and Educational Paths
Learning to draw can be a self-directed process, but there are also many resources and educational paths available to help you develop your skills. Whether you prefer to learn on your own or through formal instruction, there are options to suit your needs and preferences.
4.1 Online Courses and Tutorials
Online courses and tutorials offer a convenient and affordable way to learn drawing from the comfort of your own home. There are many platforms that offer courses on a wide range of topics, from basic drawing fundamentals to advanced techniques.
4.1.1 Popular Online Learning Platforms
| Platform | Description |
|---|---|
| Coursera | Offers courses from top universities and institutions. |
| Udemy | Provides a vast library of courses taught by independent instructors. |
| Skillshare | Focuses on creative skills, with courses taught by industry professionals. |
| LEARNS.EDU.VN | Offers comprehensive education resources, including drawing courses. |
4.2 Books and Publications
Books and publications are a valuable resource for learning drawing. There are many books available that cover a wide range of topics, from basic drawing techniques to advanced concepts.
4.2.1 Recommended Drawing Books
- “Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain” by Betty Edwards
- “Keys to Drawing” by Bert Dodson
- “Figure Drawing: For All It’s Worth” by Andrew Loomis
- “Color and Light: A Guide for the Realist Painter” by James Gurney
4.3 Art Schools and Workshops
For a more structured and immersive learning experience, consider attending art schools or workshops. These programs offer formal instruction from experienced artists and provide opportunities to work alongside other aspiring artists.
4.3.1 Benefits of Art Schools and Workshops
- Structured Curriculum: Provides a clear path for learning and skill development.
- Expert Instruction: Learn from experienced artists who can provide personalized feedback and guidance.
- Community: Connect with other aspiring artists and build a supportive network.
- Resources: Access to specialized equipment, materials, and facilities.
4.4 Local Art Groups and Communities
Joining local art groups and communities can provide valuable opportunities for learning, networking, and sharing your work. These groups often organize workshops, exhibitions, and other events.
4.4.1 Benefits of Joining Art Groups
- Learning: Learn from other artists and share your own knowledge and experiences.
- Networking: Connect with other artists and build professional relationships.
- Exposure: Showcase your work in exhibitions and other events.
- Support: Receive encouragement and support from a community of like-minded individuals.
5. Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Learning to draw can be challenging, and it’s normal to experience setbacks and frustrations along the way. Overcoming these challenges and staying motivated is essential for continued progress and success.
5.1 Dealing with Frustration and Setbacks
It’s important to remember that everyone experiences frustration and setbacks when learning to draw. Don’t let these challenges discourage you. Instead, view them as opportunities for learning and growth.
5.1.1 Strategies for Dealing with Frustration
- Take Breaks: Step away from your drawing and do something else to clear your mind.
- Seek Feedback: Ask for constructive criticism from other artists or instructors.
- Focus on Progress: Celebrate your accomplishments and focus on how far you’ve come.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Be kind to yourself and remember that it’s okay to make mistakes.
5.2 Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is essential for staying motivated and avoiding burnout. Set small, achievable goals that you can accomplish on a regular basis.
5.2.1 Tips for Setting Realistic Goals
- Start Small: Begin with simple goals, such as drawing for 15 minutes each day.
- Be Specific: Set specific goals, such as mastering a particular technique or drawing a specific subject.
- Be Measurable: Set goals that you can track and measure your progress.
- Be Achievable: Set goals that are challenging but realistic.
5.3 Finding Inspiration
Finding inspiration is crucial for staying motivated and creative. Surround yourself with art that you admire and seek out new sources of inspiration.
5.3.1 Sources of Inspiration
- Art Museums and Galleries: Visit art museums and galleries to see works by master artists.
- Online Art Communities: Explore online art communities to discover new artists and styles.
- Nature: Spend time in nature and observe the beauty of the natural world.
- Everyday Life: Find inspiration in everyday objects, people, and experiences.
5.4 Joining a Supportive Community
Joining a supportive community of artists can provide encouragement, feedback, and motivation. Connect with other artists online or in person to share your work and learn from others.
5.4.1 Benefits of Joining a Community
- Encouragement: Receive support and encouragement from other artists.
- Feedback: Get constructive criticism on your work.
- Learning: Learn from the experiences and knowledge of other artists.
- Networking: Connect with other artists and build professional relationships.
6. Drawing as a Lifelong Journey
Learning to draw is a lifelong journey. There is always more to learn, and there are always new challenges to overcome. Embrace the journey and enjoy the process of continuous learning and growth.
6.1 Embracing Continuous Learning
The most successful artists are those who embrace continuous learning. Stay curious, explore new techniques and mediums, and never stop challenging yourself.
6.1.1 Strategies for Continuous Learning
- Take Workshops and Classes: Continue to take workshops and classes to learn new skills and techniques.
- Read Books and Articles: Stay up-to-date on the latest trends and developments in the art world.
- Experiment: Try new techniques and mediums to expand your artistic skills.
- Seek Feedback: Continue to seek feedback from other artists and instructors.
6.2 Exploring Different Art Styles
Exploring different art styles can help you broaden your artistic horizons and develop your own unique style. Study the works of artists from different periods and cultures and experiment with different techniques and approaches.
6.2.1 Popular Art Styles
- Realism: Aims to depict subjects as accurately and realistically as possible.
- Impressionism: Focuses on capturing the fleeting impressions of light and color.
- Expressionism: Emphasizes emotional expression over realistic representation.
- Surrealism: Explores the realm of dreams and the subconscious.
- Abstract Art: Non-representational art that focuses on form, color, and composition.
6.3 Sharing Your Art with the World
Sharing your art with the world can be a rewarding experience. It allows you to connect with others, receive feedback, and contribute to the artistic community.
6.3.1 Ways to Share Your Art
- Online Platforms: Share your work on online platforms such as Instagram, DeviantArt, and ArtStation.
- Exhibitions: Participate in local and national art exhibitions.
- Art Fairs: Sell your work at art fairs and festivals.
- Commissions: Offer your services as a commissioned artist.
6.4 The Benefits of Drawing for Personal Growth
Drawing can be a powerful tool for personal growth. It can help you develop your creativity, improve your observation skills, and express your emotions.
6.4.1 Personal Benefits of Drawing
- Creativity: Drawing can help you unleash your creativity and explore new ideas.
- Observation: Drawing can improve your observation skills and help you see the world in new ways.
- Emotional Expression: Drawing can be a powerful tool for expressing your emotions and processing your experiences.
- Mindfulness: Drawing can be a meditative practice that helps you focus on the present moment.
7. Integrating Digital Tools in Your Drawing Journey
In today’s digital age, integrating digital tools into your drawing practice can open up new possibilities and enhance your workflow. Digital drawing offers unique advantages, such as easy correction, a wide range of tools, and the ability to share your work instantly.
7.1 Advantages of Digital Drawing
Digital drawing provides several benefits that traditional methods may lack. These include:
- Undo Function: Easily correct mistakes without leaving any marks.
- Versatility: Access a wide range of brushes, pencils, and effects in one place.
- Portability: Carry your entire art studio on a tablet or laptop.
- Sharing: Easily share your work online and get instant feedback.
- Experimentation: Try out new techniques and styles without wasting materials.
7.2 Essential Digital Drawing Tools
To get started with digital drawing, you’ll need a few essential tools:
- Drawing Tablet: A graphics tablet with a stylus is crucial for creating digital art. Popular options include Wacom, iPad Pro with Apple Pencil, and Huion tablets.
- Drawing Software: Choose a drawing software that suits your needs and preferences. Some popular options include Adobe Photoshop, Procreate, Clip Studio Paint, and Autodesk Sketchbook.
- Computer or Tablet: A computer or tablet with sufficient processing power and storage space is necessary for running drawing software smoothly.
7.3 Learning Digital Drawing Techniques
Digital drawing requires learning new techniques and workflows. Here are some tips for mastering digital drawing:
- Practice Pen Pressure: Learn to control the pressure of your stylus to create different line weights and effects.
- Use Layers: Take advantage of layers to separate different elements of your drawing and make adjustments easily.
- Experiment with Brushes: Explore different brushes and settings to achieve various textures and effects.
- Use Reference Images: Keep reference images handy to help you draw accurately.
- Watch Tutorials: Learn from online tutorials and courses to improve your digital drawing skills.
7.4 Combining Traditional and Digital Techniques
Many artists find it beneficial to combine traditional and digital techniques. You can start with a traditional sketch and then scan it into your computer for digital enhancements. Alternatively, you can print out your digital drawings and add traditional media on top.
8. Exploring Different Drawing Subjects and Styles
Expanding your repertoire of drawing subjects and styles is a great way to challenge yourself and grow as an artist. Experimenting with different subjects and styles can help you discover new techniques, develop your own unique style, and keep your drawing practice fresh and exciting.
8.1 Drawing from Life
Drawing from life involves drawing what you see in front of you, rather than relying on photographs or imagination. This is an excellent way to improve your observation skills and develop a deeper understanding of form, light, and shadow.
8.1.1 Tips for Drawing from Life
- Choose Simple Subjects: Start with simple objects, such as fruits, vegetables, or household items.
- Set Up Good Lighting: Position your subject in good lighting to create interesting shadows and highlights.
- Observe Carefully: Take your time to observe the subject carefully before you start drawing.
- Focus on Shapes and Proportions: Pay attention to the shapes and proportions of the subject.
- Use a Viewfinder: Use a viewfinder to help you frame your composition.
8.2 Drawing from Reference Photos
Drawing from reference photos can be a convenient way to practice drawing subjects that are difficult to draw from life, such as animals, landscapes, or portraits. However, it’s important to use reference photos wisely and avoid simply copying them.
8.2.1 Tips for Drawing from Reference Photos
- Choose High-Quality Photos: Use photos that are clear, well-lit, and in focus.
- Understand Anatomy: Study the anatomy of your subject to draw it accurately.
- Focus on Form and Value: Pay attention to the form and value of the subject, rather than just copying the lines.
- Add Your Own Style: Don’t be afraid to add your own personal touches to your drawings.
- Use Multiple References: Use multiple reference photos to get a better understanding of your subject.
8.3 Exploring Different Art Styles
Experimenting with different art styles can help you expand your artistic horizons and develop your own unique style. Here are some popular art styles to explore:
- Realism: Aims to depict subjects as accurately and realistically as possible.
- Impressionism: Focuses on capturing the fleeting impressions of light and color.
- Expressionism: Emphasizes emotional expression over realistic representation.
- Surrealism: Explores the realm of dreams and the subconscious.
- Abstract Art: Non-representational art that focuses on form, color, and composition.
- Cartooning: Emphasizes simplified and exaggerated forms.
- Manga: A Japanese comic book style characterized by distinctive characters and storytelling.
8.4 Finding Your Niche
As you gain experience and confidence in your drawing skills, you may want to consider finding your niche. This involves specializing in a particular subject or style that you are passionate about.
8.4.1 Benefits of Finding Your Niche
- Expertise: Develop expertise in a particular area of drawing.
- Recognition: Become known for your unique style or subject matter.
- Marketability: Increase your marketability and attract clients who are looking for your specific skills.
- Passion: Focus on what you love and enjoy your drawing practice even more.
9. Building a Portfolio and Showcasing Your Work
Creating a professional portfolio and showcasing your work is essential for advancing your career as an artist. A portfolio is a collection of your best work that demonstrates your skills, style, and versatility.
9.1 Curating Your Best Work
Selecting the right pieces for your portfolio is crucial. Choose your strongest and most representative works to showcase your skills effectively.
9.1.1 Tips for Curating Your Portfolio
- Showcase Variety: Include a variety of subjects, styles, and mediums to demonstrate your versatility.
- Highlight Your Strengths: Focus on pieces that highlight your strengths and unique abilities.
- Choose High-Quality Images: Use high-resolution images that are well-lit and accurately represent your work.
- Seek Feedback: Ask for feedback from other artists or mentors to help you select the best pieces.
- Update Regularly: Keep your portfolio up-to-date with your latest and best work.
9.2 Creating a Professional Website
A professional website is an essential tool for showcasing your work online. Your website should be visually appealing, easy to navigate, and mobile-friendly.
9.2.1 Essential Elements of an Art Website
- Portfolio Gallery: A gallery showcasing your best work with high-quality images.
- About Page: A page providing information about you, your background, and your artistic philosophy.
- Contact Page: A page with your contact information, including email, phone number, and social media links.
- Blog: A blog where you can share your thoughts, insights, and process with your audience.
- Shop (Optional): An online store where you can sell your original artwork, prints, or merchandise.
9.3 Utilizing Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms are a powerful tool for showcasing your work, connecting with other artists, and building your audience.
9.3.1 Popular Social Media Platforms for Artists
- Instagram: A visual platform ideal for sharing your artwork and connecting with other artists.
- Facebook: A versatile platform for sharing your work, connecting with friends and family, and promoting your art business.
- Twitter: A microblogging platform for sharing your thoughts, insights, and promoting your work.
- Pinterest: A visual discovery platform for sharing your artwork and finding inspiration.
- ArtStation: A portfolio platform for professional artists in the game, film, and animation industries.
9.4 Participating in Art Competitions and Exhibitions
Participating in art competitions and exhibitions can provide valuable exposure for your work and help you gain recognition in the art world.
9.4.1 Benefits of Participating in Competitions and Exhibitions
- Exposure: Showcase your work to a wider audience.
- Recognition: Gain recognition for your skills and talent.
- Validation: Receive validation from art professionals and peers.
- Networking: Connect with other artists, curators, and collectors.
- Sales: Sell your artwork to new buyers.
10. Staying Inspired and Avoiding Burnout
Maintaining inspiration and avoiding burnout is essential for long-term success as an artist. It’s important to find ways to keep your drawing practice fresh, exciting, and sustainable.
10.1 Taking Breaks and Practicing Self-Care
Taking regular breaks and practicing self-care is crucial for preventing burnout. Make sure to schedule time for rest, relaxation, and activities that you enjoy.
10.1.1 Self-Care Tips for Artists
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
- Eat Healthy Foods: Fuel your body with nutritious foods that will support your energy and focus.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in physical activity to relieve stress and boost your mood.
- Spend Time in Nature: Connect with nature to recharge your batteries and find inspiration.
- Practice Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, to reduce stress and improve focus.
10.2 Setting Boundaries and Managing Time
Setting boundaries and managing your time effectively can help you avoid feeling overwhelmed and stressed.
10.2.1 Time Management Tips for Artists
- Create a Schedule: Create a daily or weekly schedule to allocate time for drawing, marketing, and other tasks.
- Prioritize Tasks: Identify your most important tasks and focus on those first.
- Set Deadlines: Set deadlines for your projects to stay on track.
- Avoid Multitasking: Focus on one task at a time to improve your efficiency and focus.
- Learn to Say No: Don’t be afraid to say no to projects or requests that don’t align with your goals or values.
10.3 Seeking Inspiration from Other Artists
Seeking inspiration from other artists can help you stay motivated and inspired.
10.3.1 Ways to Find Inspiration
- Visit Art Museums and Galleries: Immerse yourself in the works of master artists.
- Attend Art Events: Connect with other artists and see their work in person.
- Read Art Books and Magazines: Stay up-to-date on the latest trends and developments in the art world.
- Follow Artists on Social Media: Discover new artists and see their latest work.
- Join Online Art Communities: Connect with other artists and share your work.
10.4 Taking on New Challenges
Taking on new challenges can help you grow as an artist and keep your drawing practice fresh and exciting.
10.4.1 Ways to Challenge Yourself
- Try New Subjects: Draw subjects that you’ve never drawn before.
- Experiment with New Styles: Explore different art styles and techniques.
- Work with New Mediums: Try new drawing mediums, such as charcoal, ink, or digital drawing.
- Set Personal Projects: Set personal projects that challenge you creatively.
- Participate in Art Challenges: Join art challenges, such as Inktober or Mermay, to push your limits and connect with other artists.
By following these comprehensive steps and continuously seeking knowledge and practice, anyone can learn how to draw and develop their artistic skills. Remember to visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for more resources, courses, and expert guidance to support your artistic journey.
Ready to take your drawing skills to the next level? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today for comprehensive courses, expert guidance, and a supportive community to help you unlock your artistic potential. Explore our drawing fundamentals, advanced techniques, and personalized learning paths. Don’t wait, start your artistic journey now! Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212, or visit our website at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
FAQ: How Do Artists Learn to Draw?
-
What are the fundamental skills needed to learn drawing?
- Fundamental skills include observation, understanding basic shapes, perspective, and value shading. Consistent practice and a willingness to learn from mistakes are also crucial.
-
How important is it to study anatomy for drawing?
- Studying anatomy is essential, especially for artists interested in drawing the human figure. It helps in creating realistic and dynamic figures by understanding the underlying bone structure and muscle groups.
-
What are some effective exercises to improve observation skills?
- Effective exercises include contour drawing (drawing outlines without lifting the pencil), blind contour drawing (drawing without looking at the paper), and gesture drawing (capturing the essence of a subject’s form quickly).
-
How can I stay motivated while learning to draw?
- Stay motivated by setting realistic goals, joining a supportive community, finding inspiration from other artists, and taking on new challenges.
-
What role do online courses and tutorials play in learning to draw?
- Online courses and tutorials offer a convenient and affordable way to learn drawing from home. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, Skillshare, and learns.edu.vn provide courses ranging from basic fundamentals to advanced techniques.
-
What are the benefits of learning digital drawing techniques?
- Digital drawing offers advantages like easy correction, versatility with a wide range of tools, portability, easy sharing, and experimentation without wasting materials.
-
How can I develop my unique artistic style?
- Develop your unique style by experimenting with different techniques, studying artists you admire, practicing consistently, and focusing on expressing your own unique vision and perspective.
-
Why is composition important in drawing?
- Composition refers to the arrangement of elements within a drawing and is crucial for creating visually appealing and effectively conveying the artist’s intended message.
-
What are some common challenges faced while learning to draw, and how can they be overcome?
- Common challenges include frustration, setbacks, and lack of motivation. These can be overcome by taking breaks, seeking feedback, focusing on progress, and practicing self-compassion.
-
How can I build a portfolio and showcase my work effectively?
- Build a portfolio by curating your best work, creating a professional website, utilizing social media platforms, and participating in art competitions and exhibitions.
