Learning gender is a multifaceted process shaped by societal influences, cultural norms, and personal experiences. This guide, brought to you by LEARNS.EDU.VN, explores the various factors influencing gender development, offering insights into how we internalize gender roles and expectations. Discover effective learning strategies and resources to navigate this complex topic and foster a deeper understanding of gender identity and expression.
1. Decoding Gender Roles: Societal Blueprints
Gender roles are society’s expectations of how individuals should behave, think, and feel based on their perceived sex. These roles are not fixed but are fluid social constructs that vary across cultures and evolve over time. Understanding gender roles is crucial for recognizing how societal norms influence our perceptions and behaviors.
1.1 The Foundation: Socialization and Gender Roles
Socialization plays a pivotal role in shaping our understanding and performance of gender. From early childhood, individuals are exposed to messages about what it means to be “male” or “female,” influencing their self-perception and interactions with others.
1.2 Examples of Gender Roles in Society:
| Gender | Expected Traits | Common Occupations |
|---|---|---|
| Masculine | Strength, assertiveness, independence, dominance, emotional restraint | Law enforcement, military, politics, engineering, construction |
| Feminine | Nurturing, passivity, emotional expressiveness, submissiveness, interpersonal sensitivity | Childcare, healthcare, social work, teaching, nursing, customer service |



1.3. Challenging Traditional Gender Roles:
Traditional gender roles can be limiting and harmful, perpetuating stereotypes and inequalities. It is essential to recognize the diversity of gender expressions and identities and to challenge rigid expectations that prevent individuals from realizing their full potential.
2. The Socialization Process: From Cradle to Adulthood
Socialization is the lifelong process through which individuals learn the norms, values, and behaviors appropriate for their culture. It is a crucial mechanism for transmitting gender roles and expectations from one generation to the next.
2.1 Agents of Socialization: Influencing Gender Development
Several agents of socialization contribute to gender development, including family, schools, peer groups, and mass media. Each agent reinforces gender roles and stereotypes, shaping individuals’ understanding of gender.
2.2 The Role of Family in Gender Socialization:
Family is the first and most influential agent of socialization. Parents often treat sons and daughters differently, reinforcing gender stereotypes through their expectations, behaviors, and the toys and activities they provide.
2.3 The Role of Schools in Gender Socialization:
Schools also play a significant role in gender socialization. Teachers may reinforce gender stereotypes through their interactions with students, the curriculum they teach, and the ways they organize the classroom.
2.4 The Role of Peer Groups in Gender Socialization:
Peer groups are powerful agents of socialization, particularly during adolescence. Peers often reinforce gender norms and expectations through their interactions, behaviors, and the social pressures they exert.
2.5 The Role of Mass Media in Gender Socialization:
Mass media, including television, movies, and the internet, is a pervasive agent of socialization. Media often reinforces gender stereotypes through its portrayal of characters, roles, and relationships.
3. Gender Stereotypes: Oversimplified Beliefs
Gender stereotypes are oversimplified and often inaccurate beliefs about the characteristics, traits, and behaviors of men and women. These stereotypes can have negative consequences, limiting individuals’ opportunities and reinforcing inequalities.
3.1 The Impact of Gender Stereotypes on Individuals:
Gender stereotypes can affect individuals’ self-esteem, career choices, and relationships. They can also lead to discrimination and prejudice.
3.2 Challenging Gender Stereotypes:
It is essential to challenge gender stereotypes and promote more accurate and nuanced understandings of gender. This can be done through education, awareness campaigns, and by challenging sexist language and behavior.
4. Sexism: Prejudice and Discrimination
Sexism is prejudice, stereotyping, or discrimination based on sex. It can manifest in various forms, from individual attitudes and behaviors to institutional policies and practices.
4.1 The Manifestations of Sexism in Society:
Sexism can be seen in various aspects of society, including the workplace, education, politics, and the media. It often results in unequal treatment and opportunities for women.
4.2 The Effects of Sexism on Individuals and Society:
Sexism can have negative consequences for individuals, including lower self-esteem, limited career opportunities, and increased risk of violence and harassment. It also harms society by perpetuating inequalities and limiting the potential of women.
4.3 Combating Sexism:
Combating sexism requires a multi-faceted approach, including education, awareness campaigns, and legal and policy reforms. It also requires individuals to challenge their own biases and prejudices.
5. Gender Identity: Understanding Your True Self
Gender identity is an individual’s internal sense of being male, female, both, or neither, regardless of their assigned sex at birth. It is a fundamental aspect of self-identity and can have a profound impact on individuals’ lives.
5.1 The Development of Gender Identity:
Gender identity typically develops during childhood, although it can continue to evolve throughout life. The development of gender identity is influenced by various factors, including biological, psychological, and social factors.
5.2 Gender Expression: Communicating Gender Identity
Gender expression is how individuals outwardly present their gender through clothing, hairstyle, behavior, and other means. Gender expression may or may not align with an individual’s gender identity.
5.3 Transgender and Gender Non-Conforming Identities:
Transgender individuals are those whose gender identity differs from their assigned sex at birth. Gender non-conforming individuals are those whose gender expression does not conform to traditional gender norms.
5.4 Supporting Transgender and Gender Non-Conforming Individuals:
It is essential to support transgender and gender non-conforming individuals by respecting their gender identity, using their preferred pronouns, and advocating for their rights.
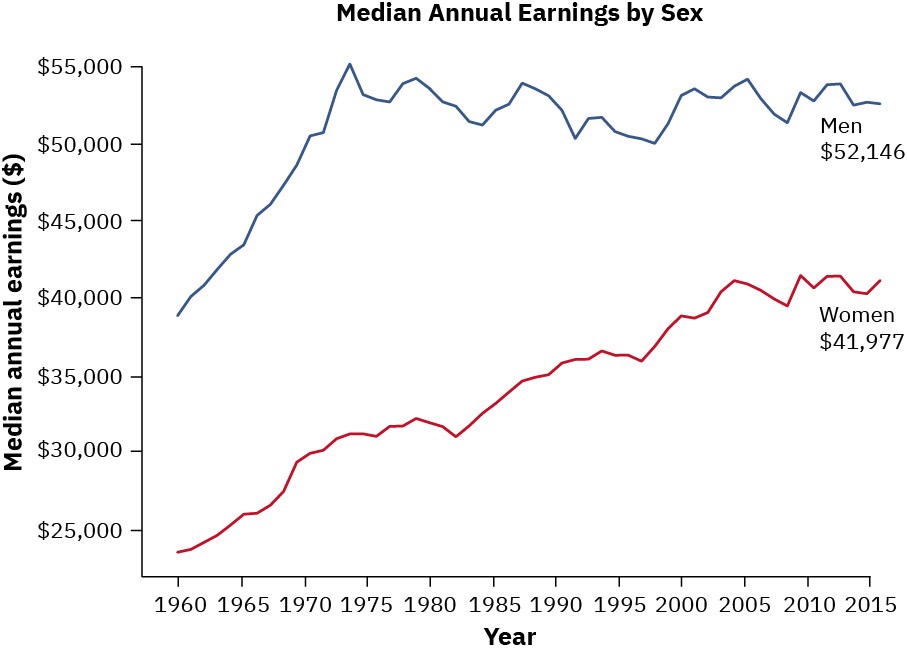
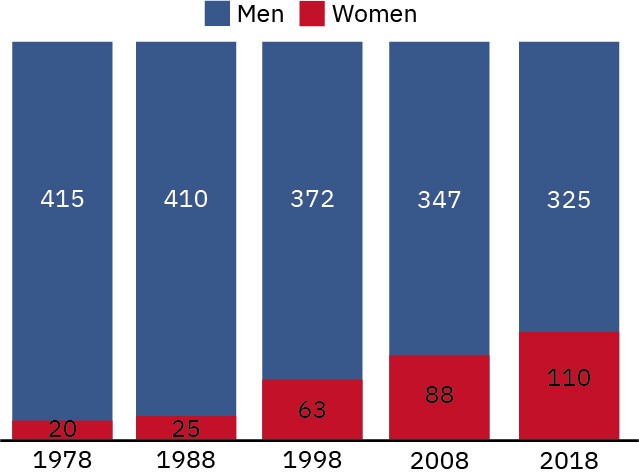
6. The Gender Pay Gap: A Persistent Inequality
The gender pay gap is the difference between the average earnings of men and women. It is a persistent inequality that affects women in virtually every industry and occupation.
6.1 Factors Contributing to the Gender Pay Gap:
Several factors contribute to the gender pay gap, including discrimination, occupational segregation, and the unequal distribution of caregiving responsibilities.
6.2 The Impact of the Gender Pay Gap on Women:
The gender pay gap can have significant financial consequences for women, affecting their retirement savings, economic security, and overall well-being.
6.3 Addressing the Gender Pay Gap:
Addressing the gender pay gap requires a multi-faceted approach, including equal pay laws, policies that support work-life balance, and efforts to combat discrimination and occupational segregation.
7. Gender Equality: A Vision for the Future
Gender equality is the state in which everyone enjoys the same rights, opportunities, and access to resources, regardless of their gender. It is a fundamental human right and a prerequisite for a just and equitable society.
7.1 The Benefits of Gender Equality:
Gender equality benefits individuals, families, communities, and society as a whole. It leads to improved health outcomes, increased economic growth, and greater social harmony.
7.2 Strategies for Promoting Gender Equality:
Promoting gender equality requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of gender inequality. This includes education, awareness campaigns, legal and policy reforms, and efforts to challenge harmful gender norms and stereotypes.
7.3 The Role of Education in Promoting Gender Equality:
Education plays a crucial role in promoting gender equality by challenging gender stereotypes, empowering girls and women, and promoting critical thinking and awareness of gender issues.
8. Navigating Gender Dynamics in the Workplace
Understanding gender dynamics in the workplace is essential for creating a fair and inclusive environment where everyone can thrive. This involves recognizing and addressing gender biases, promoting equal opportunities, and fostering a culture of respect and inclusion.
8.1 Common Gender Biases in the Workplace:
Gender biases can manifest in various forms, including hiring decisions, performance evaluations, and promotion opportunities. These biases can disadvantage women and perpetuate inequalities.
8.2 Strategies for Mitigating Gender Biases:
Mitigating gender biases requires awareness, training, and the implementation of fair and transparent policies and practices. This includes blind resume reviews, structured interviews, and diversity and inclusion training programs.
8.3 Creating a Gender-Inclusive Workplace:
Creating a gender-inclusive workplace requires a commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion at all levels of the organization. This includes providing equal opportunities, fostering a culture of respect and inclusion, and addressing gender-based discrimination and harassment.
9. Resources for Learning More About Gender
Numerous resources are available for learning more about gender, including books, articles, websites, and organizations. These resources can provide valuable insights into gender identity, gender roles, sexism, and gender equality.
9.1 Recommended Books on Gender:
- “Gender Trouble” by Judith Butler
- “We Should All Be Feminists” by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
- “The Second Sex” by Simone de Beauvoir
- “Like a Girl: A Celebration of Today’s Girls” by Karen Mockler
9.2 Useful Websites and Organizations:
- LEARNS.EDU.VN
- The United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women)
- The National Women’s Law Center (NWLC)
- The Human Rights Campaign (HRC)
9.3 Academic Journals and Research on Gender Studies:
- “Gender & Society”
- “Feminist Studies”
- “Journal of Gender Studies”
- “Sex Roles”
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Learning Gender
10.1 What is gender identity?
Gender identity is an individual’s internal sense of being male, female, both, or neither, regardless of their assigned sex at birth.
10.2 What are gender roles?
Gender roles are society’s expectations of how individuals should behave, think, and feel based on their perceived sex.
10.3 What is sexism?
Sexism is prejudice, stereotyping, or discrimination based on sex.
10.4 What is gender equality?
Gender equality is the state in which everyone enjoys the same rights, opportunities, and access to resources, regardless of their gender.
10.5 How can I challenge gender stereotypes?
You can challenge gender stereotypes by questioning your own biases, challenging sexist language and behavior, and promoting more accurate and nuanced understandings of gender.
10.6 How can I support transgender and gender non-conforming individuals?
You can support transgender and gender non-conforming individuals by respecting their gender identity, using their preferred pronouns, and advocating for their rights.
10.7 What are the causes of the gender pay gap?
The causes of the gender pay gap include discrimination, occupational segregation, and the unequal distribution of caregiving responsibilities.
10.8 What are the benefits of gender equality?
The benefits of gender equality include improved health outcomes, increased economic growth, and greater social harmony.
10.9 How can education promote gender equality?
Education can promote gender equality by challenging gender stereotypes, empowering girls and women, and promoting critical thinking and awareness of gender issues.
10.10 Where can I find more resources for learning about gender?
You can find more resources for learning about gender on LEARNS.EDU.VN and through the organizations and publications listed in Section 9 of this guide.
Gender studies is an evolving field, with new insights and perspectives constantly emerging. Stay curious, keep learning, and be open to new ideas. This journey of understanding gender will not only enrich your own life but also contribute to a more just and equitable world for everyone.
Unveiling Implicit Biases: A Journey of Self-Discovery
Recognizing and understanding our own implicit biases is a fundamental step towards fostering gender equality. Implicit biases are unconscious attitudes and stereotypes that can influence our perceptions, decisions, and behaviors without us even realizing it.
Strategies for Uncovering Implicit Biases:
- Take Implicit Association Tests (IATs): Project Implicit offers a variety of IATs that can help you identify unconscious biases related to gender, race, and other social categories.
- Reflect on your Thoughts and Actions: Pay attention to your reactions and assumptions about people based on their gender. Ask yourself why you think or feel a certain way.
- Seek Feedback from Others: Ask trusted friends, family members, or colleagues for feedback on your behavior and communication. Be open to hearing their perspectives, even if they challenge your own.
Resources for Understanding and Overcoming Implicit Biases:
- Project Implicit: This Harvard-based project offers resources and tools for exploring implicit biases.
(https://implicit.harvard.edu/implicit/takeatest.html) - The Kirwan Institute for the Study of Race and Ethnicity: This institute conducts research and provides training on implicit bias.
(http://kirwaninstitute.osu.edu/) - Books on Implicit Bias:
- “Blindspot: Hidden Biases of Good People” by Mahzarin R. Banaji and Anthony G. Greenwald
- “Subliminal: How Your Unconscious Mind Rules Your Behavior” by Leonard Mlodinow
Gender and Intersectionality: A Multifaceted Lens
Intersectionality is a framework that recognizes that individuals can experience multiple forms of oppression and discrimination based on the intersection of various social identities, such as gender, race, class, sexual orientation, and disability.
Understanding the Interplay of Gender and Other Identities:
- Gender and Race: Women of color often face unique challenges due to the intersection of sexism and racism.
- Gender and Class: Women from low-income backgrounds may face additional barriers to education, employment, and healthcare.
- Gender and Sexual Orientation: LGBTQ+ individuals may experience discrimination and prejudice based on both their gender identity and their sexual orientation.
Resources for Learning More About Intersectionality:
- Kimberlé Crenshaw’s Work on Intersectionality: Crenshaw is a leading scholar on intersectionality and has written extensively on the topic.
- The Intersectional Feminist Collective: This organization provides resources and support for intersectional feminists.
(https://www.intersectionalfeministcollective.org/) - Books on Intersectionality:
- “Intersectionality” by Patricia Hill Collins and Sirma Bilge
- “Ain’t I a Woman: Black Women and Feminism” by bell hooks
Gender-Affirming Language: Respecting Identity
Using gender-affirming language is a sign of respect and inclusivity. It involves using the pronouns and names that individuals use to express themselves, reflecting a commitment to diversity and recognition of self-identified individuality.
Tips for Using Gender-Affirming Language:
- Ask for Pronouns: When you meet someone new, ask them what pronouns they use.
- Use Gender-Neutral Language: Use gender-neutral language when referring to people in general.
- Avoid Assumptions: Avoid making assumptions about someone’s gender based on their appearance.
Resources for Learning More About Gender-Affirming Language:
- GLAAD’s Media Reference Guide: This guide provides information on using accurate and respectful language when referring to LGBTQ+ people.
(https://www.glaad.org/reference) - The National Center for Transgender Equality: This organization offers resources and support for transgender people.
(https://transequality.org/) - MyPronouns.org: This website provides resources for learning about and using pronouns.
(https://www.mypronouns.org/)
Continuous Learning: A Lifelong Commitment
Learning about gender is a lifelong journey. New insights and perspectives are constantly emerging, and it is essential to stay curious and open to learning. Take an active role in acquiring knowledge, dismantling bias, and promoting diversity in your sphere of influence, and encourage others to do the same.
Tips for Continuous Learning:
- Read Books and Articles on Gender: Stay up-to-date on the latest research and scholarship on gender.
- Attend Workshops and Conferences: Participate in workshops and conferences to learn from experts and connect with others who are passionate about gender equality.
- Engage in Conversations with People from Diverse Backgrounds: Listen to and learn from the experiences of people from different gender identities, races, classes, and sexual orientations.
Ready to delve deeper into the fascinating world of gender studies? LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources, articles, and courses to expand your understanding. Visit our website at LEARNS.EDU.VN to explore a comprehensive collection of educational materials designed to empower you with knowledge and skills. Our platform provides detailed guidance, expert insights, and practical tools to support your learning journey. For personalized assistance, contact us at +1 555-555-1212 or visit our campus at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Start your exploration today and unlock the potential of lifelong learning with learns.edu.vn.
