How Does Alcohol Affect Memory And Learning? Discover the intricate connection between alcohol consumption and its effects on cognitive functions with LEARNS.EDU.VN. Delve into the science behind how alcohol influences memory consolidation and learning processes, and find effective strategies to mitigate these impacts. Explore resources for enhancing cognitive health and academic success.
Introduction to Alcohol’s Impact on Memory and Learning
How does alcohol affect memory and learning, and what can we do to protect our cognitive abilities? At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of a sharp mind for effective learning and personal growth. Alcohol, even in moderate amounts, can significantly impair cognitive functions, including memory consolidation and the ability to learn new information. This comprehensive guide will explore how alcohol interferes with these processes, offering insights and practical advice to safeguard your cognitive health. You’ll discover the long-term and short-term effects, including conditions like alcohol-induced amnesia and the impact on brain structures critical for memory.
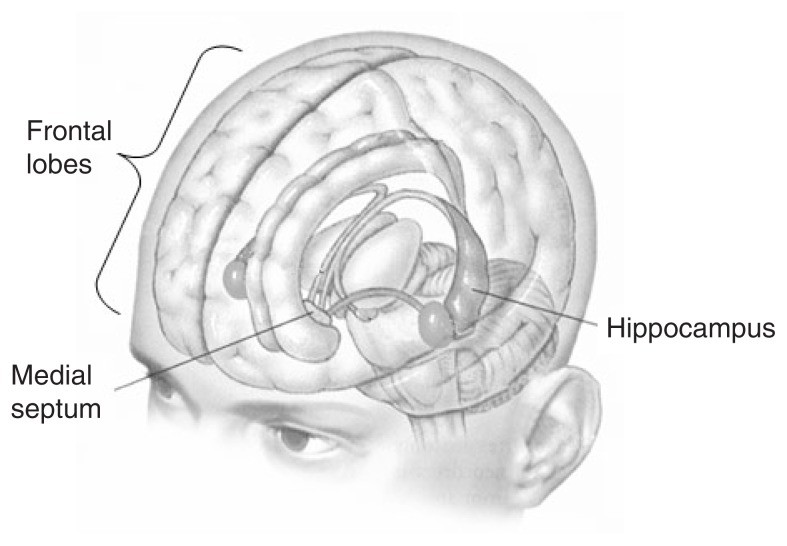 Brain with hippocampus highlighted
Brain with hippocampus highlighted
1. Understanding the Basics of Memory and Learning
To truly understand how alcohol affects memory and learning, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of these cognitive processes. Memory isn’t a single entity but rather a complex system involving different types of memory and stages of processing. Learning, on the other hand, is the process by which we acquire new knowledge and skills.
1.1 Types of Memory
Memory can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving different functions and relying on distinct brain regions:
| Memory Type | Description | Brain Regions Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Sensory Memory | Brief storage of sensory information (e.g., visual, auditory) | Sensory cortex |
| Short-Term Memory (STM) | Temporary storage of information needed for immediate tasks | Prefrontal cortex |
| Working Memory | Active maintenance and manipulation of information in STM | Prefrontal cortex, parietal cortex |
| Long-Term Memory (LTM) | Storage of information over extended periods | Hippocampus, neocortex |
| Explicit Memory (Declarative) | Conscious recall of facts and events | Hippocampus, prefrontal cortex |
| Implicit Memory (Non-Declarative) | Unconscious recall of skills and habits | Cerebellum, basal ganglia |
1.2 Stages of Memory Processing
The process of forming and retrieving memories involves three main stages:
- Encoding: Converting sensory information into a form that can be stored in the brain.
- Storage: Retaining encoded information over time.
- Retrieval: Accessing stored information when needed.
1.3 The Learning Process
Learning involves acquiring new knowledge, skills, behaviors, or preferences through experience, study, or instruction. It’s a complex process that relies on neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections.
Key Elements of Effective Learning
- Attention: Focusing on relevant information.
- Motivation: Having a desire to learn.
- Active Engagement: Participating actively in the learning process.
- Feedback: Receiving information about performance to improve.
- Repetition: Practicing and reviewing material to reinforce learning.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we design our courses and materials to optimize these key elements, ensuring an effective and engaging learning experience. We provide tools and strategies to help you focus, stay motivated, and actively participate in your learning journey.
2. How Alcohol Affects the Brain
Alcohol’s impact on the brain is multifaceted, affecting various neurotransmitter systems and brain regions. Understanding these effects is crucial for comprehending how alcohol disrupts memory and learning.
2.1 Neurotransmitter Systems Affected by Alcohol
Alcohol primarily affects the following neurotransmitter systems:
| Neurotransmitter | Effect of Alcohol | Cognitive Impact |
|---|---|---|
| GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) | Enhances GABA activity (inhibitory) | Sedation, reduced anxiety, impaired motor control |
| Glutamate | Inhibits glutamate activity (excitatory) | Impaired learning and memory |
| Dopamine | Increases dopamine release | Reward and reinforcement |
| Serotonin | Affects serotonin levels | Mood changes, altered behavior |
2.2 Brain Regions Vulnerable to Alcohol’s Effects
Several brain regions are particularly vulnerable to alcohol’s effects:
- Hippocampus: Critical for forming new long-term memories.
- Cerebellum: Involved in motor coordination and balance.
- Prefrontal Cortex: Responsible for executive functions, decision-making, and working memory.
- Amygdala: Processes emotions, including fear and anxiety.
Alcohol’s ability to disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters and impair the function of these brain regions is central to understanding its negative effects on memory and learning.
2.3 Short-Term vs. Long-Term Effects
- Short-Term Effects: These include impaired judgment, reduced attention span, and difficulty forming new memories. They are typically reversible once alcohol is metabolized.
- Long-Term Effects: Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain, resulting in persistent cognitive deficits and an increased risk of neurological disorders.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources to help you understand the science of addiction and provides guidance on making informed decisions about alcohol consumption.
3. The Impact of Alcohol on Memory Formation
Alcohol’s most pronounced effect on memory is its ability to disrupt the formation of new long-term memories. This section delves into the specific ways alcohol interferes with memory consolidation and retrieval.
3.1 Disrupting Encoding
Encoding is the first step in forming a memory, and alcohol can significantly impair this process. By interfering with neurotransmitter systems and reducing neuronal activity in the hippocampus, alcohol makes it harder for the brain to convert sensory information into a durable memory trace.
3.2 Impairing Consolidation
Consolidation is the process by which short-term memories are transformed into long-term memories. Alcohol disrupts this process by:
- Interfering with Long-Term Potentiation (LTP): LTP is a cellular mechanism that strengthens synaptic connections and is crucial for memory consolidation. Alcohol inhibits LTP, making it harder for memories to become স্থায়ী.
- Disrupting Sleep Architecture: Sleep is vital for memory consolidation. Alcohol disrupts normal sleep patterns, reducing the amount of time spent in deep sleep stages that are most important for memory processing.
3.3 Affecting Retrieval
While alcohol primarily affects memory encoding and consolidation, it can also impair memory retrieval. Intoxication can make it difficult to access stored information, leading to temporary memory lapses.
State-Dependent Memory
One interesting phenomenon is state-dependent memory, where recall is best when the individual is in the same state (e.g., intoxicated) as when the memory was formed. However, this effect is unreliable and doesn’t negate the overall impairment of memory caused by alcohol.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we emphasize the importance of creating optimal learning conditions, free from the influence of substances that impair cognitive function.
4. Alcohol-Induced Amnesia: Blackouts Explained
Blackouts, or alcohol-induced amnesia, are periods of memory loss for events that occurred while a person was intoxicated. They can be either fragmentary or complete, and understanding the mechanisms behind them is essential.
4.1 Fragmentary vs. En Bloc Blackouts
- Fragmentary Blackouts: Partial memory loss where some details of events can be recalled, often with prompting.
- En Bloc Blackouts: Complete memory loss for a period of time, with no ability to recall any details.
4.2 Factors Contributing to Blackouts
Several factors increase the risk of experiencing a blackout:
- Rapid Alcohol Consumption: Drinking quickly leads to a rapid rise in blood alcohol concentration (BAC).
- High BAC Levels: Higher BAC levels are associated with a greater risk of blackouts.
- Empty Stomach: Drinking on an empty stomach increases the rate of alcohol absorption.
- Gender: Women are more susceptible to blackouts due to physiological differences in alcohol metabolism.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to experiencing blackouts.
4.3 Brain Mechanisms Underlying Blackouts
Blackouts are primarily caused by alcohol’s disruptive effects on the hippocampus. By inhibiting LTP and impairing neuronal activity, alcohol prevents the formation of lasting memories.
Research Insights
Research has shown that even moderate levels of alcohol can significantly reduce hippocampal activity, leading to impaired memory formation. Additionally, the combination of alcohol with other drugs can further increase the risk of blackouts.
LEARNS.EDU.VN encourages responsible behavior and provides resources to help you understand the risks associated with alcohol consumption.
5. Alcohol’s Impact on Learning Abilities
Beyond memory, alcohol also affects various aspects of learning, including attention, executive functions, and motor skills. These effects can have significant consequences for academic and professional performance.
5.1 Impaired Attention and Concentration
Alcohol reduces the ability to focus and maintain attention, making it harder to absorb new information. This can lead to decreased learning efficiency and poor academic outcomes.
5.2 Reduced Executive Functions
Executive functions, such as planning, problem-solving, and decision-making, are essential for effective learning. Alcohol impairs these functions by disrupting activity in the prefrontal cortex.
5.3 Motor Skill Impairment
Learning new motor skills requires practice and coordination. Alcohol impairs motor control and coordination, making it difficult to acquire and refine motor skills.
Real-World Examples
- Students: Reduced ability to study and perform well on exams.
- Professionals: Impaired performance in tasks requiring attention, problem-solving, and motor skills.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers courses and resources to enhance cognitive skills and improve learning outcomes.
6. Long-Term Effects of Alcohol on Cognitive Function
Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to lasting damage to the brain, resulting in persistent cognitive deficits and an increased risk of neurological disorders.
6.1 Alcohol-Related Brain Damage
Long-term alcohol abuse can cause structural changes in the brain, including:
- Brain Atrophy: Reduction in brain volume, particularly in the frontal lobes and hippocampus.
- White Matter Damage: Damage to the nerve fibers that connect different brain regions, disrupting communication between them.
6.2 Cognitive Deficits
Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to a range of cognitive deficits, including:
- Memory Impairment: Difficulty forming new memories and recalling old ones.
- Executive Dysfunction: Impaired planning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Visuospatial Deficits: Difficulty with spatial orientation and visual perception.
6.3 Neurological Disorders
Long-term alcohol abuse increases the risk of developing neurological disorders, such as:
- Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome: A severe neurological disorder caused by thiamine deficiency, characterized by confusion, memory loss, and impaired coordination.
- Alcoholic Dementia: A progressive cognitive decline associated with chronic alcohol abuse.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing long-term cognitive damage from alcohol requires moderation or abstinence. Treatment options for alcohol-related cognitive deficits include:
- Thiamine Supplementation: Essential for individuals with Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Therapies to improve cognitive function and compensate for deficits.
- Abstinence: Stopping alcohol consumption to prevent further brain damage.
LEARNS.EDU.VN supports cognitive health by promoting responsible behavior and providing resources for those seeking help with alcohol-related issues.
7. Strategies to Mitigate Alcohol’s Effects on Memory and Learning
While abstinence is the most effective way to prevent alcohol’s negative effects on memory and learning, there are strategies to mitigate its impact if you choose to consume alcohol.
7.1 Responsible Drinking Habits
- Moderation: Limiting alcohol consumption to moderate levels.
- Pacing: Drinking slowly to avoid rapid increases in BAC.
- Eating: Consuming food while drinking to slow alcohol absorption.
- Hydration: Drinking water to stay hydrated and dilute alcohol.
7.2 Nutritional Support
- Thiamine: Ensuring adequate thiamine intake through diet or supplements.
- B Vitamins: Supporting overall brain health with a balanced B vitamin complex.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promoting brain function with omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil or flaxseed oil.
7.3 Cognitive Enhancement Techniques
- Mindfulness Meditation: Improving attention and focus through mindfulness practices.
- Cognitive Training: Engaging in brain training exercises to enhance cognitive skills.
- Memory Strategies: Using mnemonic devices and other memory strategies to improve encoding and retrieval.
The Role of Education
Education is key to promoting responsible behavior and mitigating the harmful effects of alcohol. By understanding the risks and implementing preventive strategies, individuals can protect their cognitive health and well-being.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive resources and guidance on responsible behavior and cognitive enhancement.
8. Resources for Enhancing Cognitive Health
LEARNS.EDU.VN is committed to supporting your cognitive health and providing resources to help you learn effectively and maintain a sharp mind.
8.1 Courses and Workshops
We offer a variety of courses and workshops designed to enhance cognitive skills, improve memory, and promote effective learning strategies.
8.2 Articles and Guides
Our website features a wealth of articles and guides on topics related to cognitive health, learning, and responsible behavior.
8.3 Expert Insights
We collaborate with experts in the fields of neuroscience, psychology, and education to provide you with the latest research and insights.
8.4 Community Support
Join our community of learners to connect with others, share experiences, and support each other on your learning journeys.
Explore LEARNS.EDU.VN
Visit our website today to discover the many resources we offer to support your cognitive health and enhance your learning potential.
9. Latest Research and Updates on Alcohol and Memory
Stay informed with the most current findings on how alcohol influences memory and learning. This section will continuously update with new research, studies, and insights into the impact of alcohol on cognitive functions.
9.1 Cutting-Edge Studies
| Topic | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol’s Impact on Synaptic Plasticity | Research showing how even moderate alcohol consumption can disrupt synaptic plasticity, essential for memory formation. | Journal of Neuroscience |
| Long-Term Cognitive Effects | Longitudinal studies tracking the long-term cognitive effects of chronic alcohol use, revealing the extent of brain damage. | Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research |
| Gender Differences | Investigations into gender differences in alcohol metabolism and susceptibility to memory impairments, providing insights into why women are more vulnerable. | Psychopharmacology |
| Rehabilitation Strategies | Studies exploring the effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation techniques for individuals recovering from alcohol-related brain damage. | Neuropsychological Rehabilitation |
9.2 Neuroimaging Techniques
Modern neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), offer unprecedented opportunities to investigate alcohol’s impact on brain function during cognitive tasks. These techniques provide valuable insights into the neural mechanisms underlying alcohol-induced memory impairments.
9.3 Future Directions
Future research will likely focus on:
- Genetic Factors: Identifying genetic factors that influence susceptibility to alcohol-related cognitive deficits.
- Preventive Strategies: Developing effective preventive strategies to mitigate alcohol’s harmful effects on the brain.
- Treatment Innovations: Exploring new treatment options for individuals with alcohol-related cognitive impairments.
Stay tuned to LEARNS.EDU.VN for the latest updates and research findings on alcohol and memory.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Alcohol and Memory
10.1 Can moderate alcohol consumption affect my memory?
Yes, even moderate alcohol consumption can impair memory formation and retrieval, especially when it comes to new information.
10.2 How long does it take for alcohol’s effects on memory to wear off?
The effects of alcohol on memory can last for several hours, depending on the amount consumed and individual factors. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to persistent cognitive deficits.
10.3 Are blackouts a sign of alcoholism?
While blackouts are more common among individuals with alcoholism, they can also occur in social drinkers who consume large amounts of alcohol rapidly.
10.4 Can I improve my memory after drinking alcohol?
While there’s no quick fix, engaging in healthy habits such as getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and practicing cognitive enhancement techniques can support memory recovery.
10.5 Are women more susceptible to alcohol-related memory problems?
Yes, women are generally more susceptible to alcohol-related memory problems due to physiological differences in alcohol metabolism.
10.6 Does combining alcohol with other drugs increase the risk of memory problems?
Yes, combining alcohol with other drugs can significantly increase the risk of memory impairments and blackouts.
10.7 How does alcohol affect the hippocampus?
Alcohol disrupts activity in the hippocampus, a brain region critical for forming new long-term memories. It inhibits LTP and impairs neuronal activity.
10.8 Can chronic alcohol abuse lead to dementia?
Yes, chronic alcohol abuse increases the risk of developing alcoholic dementia, a progressive cognitive decline associated with long-term alcohol exposure.
10.9 What are some strategies to mitigate alcohol’s effects on memory?
Strategies include drinking in moderation, pacing alcohol consumption, eating while drinking, staying hydrated, and practicing cognitive enhancement techniques.
10.10 Where can I find more resources on cognitive health and responsible behavior?
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for courses, articles, guides, and expert insights on cognitive health, learning, and responsible behavior.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Cognitive Health
Understanding how alcohol affects memory and learning is crucial for making informed decisions and protecting your cognitive health. By adopting responsible drinking habits, supporting your brain with proper nutrition, and engaging in cognitive enhancement techniques, you can mitigate alcohol’s negative effects and maintain a sharp mind.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the resources and support you need to achieve your learning goals and enhance your cognitive potential. Explore our courses, articles, and community to embark on a journey of lifelong learning and cognitive wellness.
Remember, your cognitive health is an investment in your future. Make informed choices, prioritize your well-being, and unlock your full learning potential with LEARNS.EDU.VN.
Take Action Today
Visit learns.edu.vn to explore our courses, articles, and community resources. Enhance your cognitive skills, improve your memory, and unlock your full learning potential. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. We’re here to support you on your journey to cognitive wellness and lifelong learning.