Understanding how a switch learns MAC addresses is crucial for anyone involved in network administration or studying for certifications like CCNA. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by LEARNS.EDU.VN, will explore the MAC address learning process of a network switch, providing detailed explanations, real-world examples, and practical tips. Learn about address learning, forward/filter decisions, and loop avoidance, ensuring effective network communication and optimized network performance. Dive in to discover how switches build their MAC address tables, prevent network loops, and enhance network efficiency.
1. Understanding MAC Addresses and Network Communication
The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier assigned to each network interface card (NIC). It acts as a physical address, facilitating communication between devices within a Local Area Network (LAN). Before devices can exchange data, they need to know each other’s MAC addresses. This foundational knowledge is essential for understanding the role of switches in network communication.
1.1. The Role of MAC Addresses in LANs
MAC addresses play a vital role in enabling communication within a LAN. Each device uses the MAC address to identify itself and other devices on the same network segment. This identification process is crucial for sending and receiving data packets efficiently.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniqueness | Every NIC has a unique MAC address. |
| Layer 2 Addressing | MAC addresses operate at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. |
| Local Communication | Used for direct communication between devices within the same network segment. |
| ARP Dependency | Devices use the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to discover the MAC address associated with an IP address. |
1.2. Why Devices Need to Know Each Other’s MAC Addresses
Devices need to know each other’s MAC addresses to ensure that data packets are delivered to the correct destination within the LAN. Without this knowledge, packets would be broadcasted to every device, leading to network congestion and inefficiency.
1.3. The Significance of the MAC Address Table
Switches use MAC address tables to make intelligent forwarding decisions. This table stores the association between MAC addresses and switch ports, enabling the switch to direct traffic only to the port connected to the destination device. This targeted approach significantly reduces unnecessary network traffic.
2. How Switches Learn MAC Addresses: The Learning Process
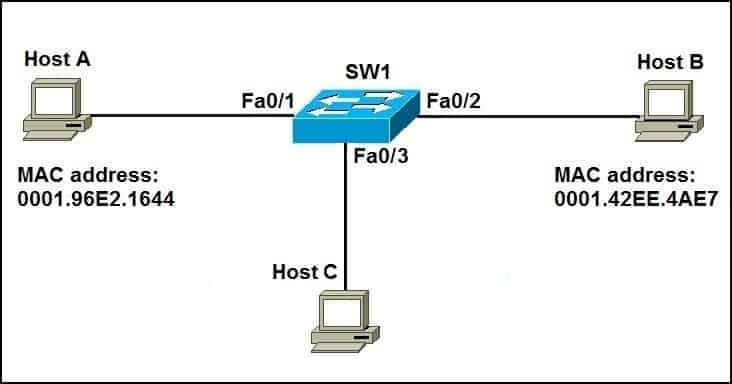
Switches automatically learn MAC addresses by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames. When a frame arrives at a switch port, the switch records the source MAC address and the port number in its MAC address table. This process is known as MAC address learning and is fundamental to the switch’s operation.
2.1. Examining the Source MAC Address
Every frame that passes through a switch contains a source MAC address. This address identifies the sending device. The switch inspects this address and uses it to update its MAC address table.
2.2. Associating MAC Addresses with Ports
When a switch receives a frame, it associates the source MAC address with the port on which the frame was received. This association is stored in the MAC address table, allowing the switch to know which devices are connected to each of its ports.
2.3. Building the MAC Address Table
The MAC address table is a dynamic database that stores the MAC address-to-port mappings. As the switch learns new MAC addresses, it adds them to the table. This table is crucial for making forwarding decisions.
Alt: Network diagram illustrating how a switch learns MAC addresses by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames and associating them with the corresponding port, highlighting the efficiency of targeted data delivery.
3. The Three Main Functions of a Switch in a LAN
Switches perform three primary functions in a LAN: address learning, forward/filter decisions, and loop avoidance. These functions work together to ensure efficient and reliable network communication.
3.1. Address Learning
As discussed earlier, address learning is the process by which a switch discovers and records MAC addresses. This learning process is continuous, allowing the switch to adapt to changes in the network.
3.2. Forward/Filter Decisions
Based on the destination MAC address of a frame, a switch decides whether to forward or filter the frame. If the destination MAC address is known (i.e., it exists in the MAC address table), the switch forwards the frame only to the corresponding port. If the destination MAC address is unknown, the switch floods the frame to all ports except the one on which it was received.
3.3. Loop Avoidance
Network loops can cause broadcast storms and disrupt network communication. Switches use the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent these loops while still allowing for redundancy. STP ensures that there is only one active path between any two network devices.
4. A Practical Example: Host A Communicating with Host B
Consider a scenario where Host A wants to communicate with Host B for the first time. Host A knows Host B’s IP address but needs to discover its MAC address using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
4.1. Initial Communication Setup
Host A initiates the communication by sending an ARP request to find Host B’s MAC address. This ARP request is broadcasted to all devices on the network segment.
4.2. The ARP Process
The ARP process involves Host A broadcasting an ARP request containing Host B’s IP address. The switch forwards this request to all ports except the one connected to Host A.
4.3. Host B’s Response
Host B receives the ARP request and responds with its MAC address. This response is sent directly to Host A.
4.4. Switch Learning During ARP
During the ARP process, the switch learns the MAC addresses of both Host A and Host B. It records these addresses in its MAC address table, associating them with the respective ports.
5. How the Switch Forwards Unicast Frames
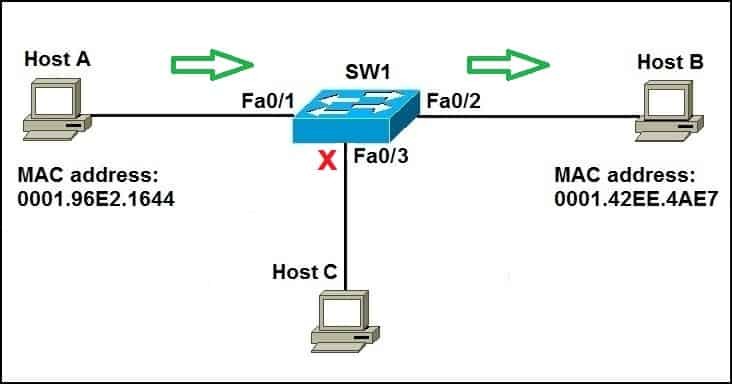
Once the switch has learned the MAC addresses of Host A and Host B, it can forward unicast frames efficiently. When Host A sends a packet to Host B, the switch looks up the destination MAC address in its MAC address table and forwards the frame only to the port connected to Host B.
5.1. Looking Up the MAC Address in the Table
The switch searches its MAC address table for the destination MAC address. If the address is found, the switch knows exactly which port to use for forwarding the frame.
5.2. Forwarding the Frame to the Correct Port
The frame is forwarded only to the port associated with the destination MAC address. This targeted forwarding reduces unnecessary network traffic and improves network performance.
5.3. Excluding Other Hosts on the Network
Because the switch knows the correct port for the destination MAC address, it does not involve other hosts in the communication. This exclusivity ensures that network resources are used efficiently.
Alt: Diagram illustrating how a switch forwards unicast frames by looking up the destination MAC address in its table and directing the frame only to the port connected to the destination device, optimizing network performance.
6. The Aging Time of MAC Addresses
By default, MAC addresses remain in the switch’s MAC address table for a limited time, typically 5 minutes. This aging mechanism ensures that the table remains up-to-date and accurate.
6.1. Default Aging Time
The default aging time for MAC addresses is usually set to 5 minutes. This means that if a MAC address is not seen within 5 minutes, it is removed from the MAC address table.
6.2. Why Aging is Necessary
Aging is necessary to remove stale entries from the MAC address table. Devices may be moved to different ports, or they may be taken offline. Without aging, the MAC address table would become filled with outdated information.
6.3. Impact on Network Communication
If a MAC address is aged out, the switch will need to relearn the address when the device next sends a frame. This relearning process can cause a brief delay in communication, but it ensures the accuracy of the MAC address table.
7. Displaying the MAC Address Table
Network administrators can use the show mac-address-table command to view the contents of the MAC address table. This command provides valuable information about the MAC addresses that the switch has learned and the ports to which they are associated.
7.1. Using the show mac-address-table Command
The show mac-address-table command is a fundamental tool for network administrators. It allows them to see which MAC addresses the switch has learned, which VLANs they belong to, and which ports they are connected to.
7.2. Interpreting the Output
The output of the show mac-address-table command typically includes the following information:
- VLAN: The VLAN to which the MAC address belongs.
- MAC Address: The MAC address that the switch has learned.
- Type: The type of entry (e.g., Dynamic or Static).
- Ports: The port(s) associated with the MAC address.
7.3. Understanding Dynamic vs. Static Entries
MAC address table entries can be either dynamic or static. Dynamic entries are learned automatically by the switch, while static entries are manually configured by the network administrator.
8. The Importance of VLANs in MAC Address Management
Virtual LANs (VLANs) segment a physical network into multiple logical networks. Each VLAN maintains its own MAC address table, which helps to isolate traffic and improve network security.
8.1. How VLANs Segment Networks
VLANs divide a physical network into multiple logical networks, allowing administrators to group devices based on function, department, or other criteria.
8.2. VLAN-Specific MAC Address Tables
Each VLAN has its own MAC address table. This means that a switch maintains separate MAC address mappings for each VLAN, which helps to isolate traffic and prevent broadcast storms.
8.3. Benefits of Using VLANs
Using VLANs offers several benefits, including improved security, better network performance, and simplified network management.
9. Troubleshooting MAC Address Table Issues
Issues with the MAC address table can lead to network connectivity problems. Common issues include MAC address flooding, MAC address spoofing, and incorrect MAC address mappings.
9.1. Common Issues
- MAC Address Flooding: Occurs when a switch is overwhelmed with different source MAC addresses, leading to performance degradation.
- MAC Address Spoofing: A malicious device impersonates another device by using its MAC address.
- Incorrect MAC Address Mappings: The MAC address table contains incorrect associations between MAC addresses and ports.
9.2. Diagnostic Tools
Several tools can be used to diagnose MAC address table issues, including the show mac-address-table command, packet sniffers, and network analyzers.
9.3. Mitigation Strategies
Mitigation strategies for MAC address table issues include implementing port security, using VLANs, and regularly monitoring the MAC address table.
10. Advanced Topics in MAC Address Learning
Several advanced topics relate to MAC address learning, including MAC address security features, MAC address filtering, and the impact of virtualization on MAC address management.
10.1. MAC Address Security Features
Switches offer several security features related to MAC addresses, such as port security, which limits the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a port.
10.2. MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering allows administrators to control which devices can access the network based on their MAC addresses.
10.3. Virtualization and MAC Address Management
Virtualization can complicate MAC address management, as virtual machines (VMs) may have multiple MAC addresses. Switches need to be configured to handle these scenarios correctly.
11. Practical Tips for Managing MAC Address Tables
Effective management of MAC address tables is essential for maintaining network performance and security. Here are some practical tips:
11.1. Regular Monitoring
Regularly monitor the MAC address table to identify any anomalies or potential security threats.
11.2. Implementing Port Security
Implement port security to limit the number of MAC addresses learned on each port, preventing MAC address flooding and spoofing.
11.3. Using VLANs Effectively
Use VLANs to segment the network and isolate traffic, improving security and performance.
12. Integrating Security Measures with MAC Address Learning
Integrating security measures with MAC address learning is crucial for protecting the network from unauthorized access and attacks.
12.1. Implementing Port Security
Port security restricts the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a specific port, preventing unauthorized devices from connecting to the network.
12.2. DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping prevents rogue DHCP servers from assigning IP addresses to clients, ensuring that only authorized devices can access the network.
12.3. Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
DAI prevents ARP spoofing attacks by validating ARP packets against the DHCP snooping database.
13. How Newer Technologies Impact MAC Address Learning
Newer technologies like cloud computing, software-defined networking (SDN), and network function virtualization (NFV) are transforming how MAC address learning is managed and secured.
13.1. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing introduces new challenges for MAC address management, as virtual machines (VMs) can be created and destroyed dynamically.
13.2. Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN centralizes network control, allowing administrators to manage MAC address learning and security policies from a single console.
13.3. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
NFV virtualizes network functions, such as firewalls and load balancers, which can impact MAC address learning and forwarding decisions.
14. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of MAC Address Learning
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into how MAC address learning works in practice.
14.1. Enterprise Network
In an enterprise network, MAC address learning is crucial for ensuring that traffic is forwarded efficiently between different departments and devices.
14.2. Data Center
In a data center, MAC address learning is essential for supporting virtualization and cloud computing environments.
14.3. Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) Network
In a SOHO network, MAC address learning helps to ensure that devices can communicate with each other and access the internet.
15. Common Misconceptions About MAC Address Learning
Several misconceptions exist about MAC address learning. Addressing these misconceptions can help to clarify the concepts and improve understanding.
15.1. MAC Addresses are Globally Unique
While MAC addresses are intended to be globally unique, MAC address collisions can occur, especially in large networks.
15.2. MAC Addresses Never Change
MAC addresses can be changed, either intentionally (e.g., for privacy reasons) or unintentionally (e.g., due to hardware failure).
15.3. MAC Address Learning is Always Secure
MAC address learning can be vulnerable to security threats, such as MAC address spoofing, if proper security measures are not implemented.
16. MAC Address Learning and the OSI Model
Understanding how MAC address learning relates to the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model can provide a deeper understanding of the process.
16.1. Layer 2 Operations
MAC address learning operates at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, which is responsible for providing reliable data transfer between two directly connected nodes.
16.2. Interaction with Higher Layers
While MAC address learning operates at Layer 2, it interacts with higher layers, such as the Network Layer (Layer 3), through protocols like ARP.
16.3. The Role of the Physical Layer
The Physical Layer (Layer 1) provides the physical medium for transmitting data, while the Data Link Layer uses MAC addresses to ensure that data is delivered to the correct destination.
17. Step-by-Step Guide to Configuring MAC Address Learning
Configuring MAC address learning involves setting up the switch to properly learn and manage MAC addresses. This includes enabling MAC address learning, setting aging times, and configuring port security.
17.1. Enabling MAC Address Learning
MAC address learning is typically enabled by default on most switches. However, it’s important to verify that it is enabled and properly configured.
17.2. Setting Aging Times
The aging time determines how long a MAC address remains in the MAC address table. Adjusting the aging time can help to optimize network performance.
17.3. Configuring Port Security
Port security limits the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a port, preventing unauthorized devices from connecting to the network.
18. The Future of MAC Address Learning
The future of MAC address learning is likely to be shaped by emerging technologies and evolving security threats. Innovations in SDN, NFV, and artificial intelligence (AI) are expected to play a significant role.
18.1. Innovations in SDN and NFV
SDN and NFV are expected to provide more flexible and scalable solutions for MAC address management and security.
18.2. The Role of AI
AI can be used to analyze MAC address traffic patterns and detect anomalies, helping to prevent security threats.
18.3. Addressing Evolving Security Threats
As security threats become more sophisticated, new techniques will be needed to protect MAC address learning from attacks.
19. How to Improve Network Performance with Efficient MAC Address Learning
Efficient MAC address learning is crucial for optimizing network performance. By properly managing MAC address tables and implementing security measures, network administrators can improve network speed, reliability, and security.
19.1. Optimizing MAC Address Tables
Optimizing MAC address tables involves regularly monitoring the tables, removing stale entries, and implementing port security.
19.2. Reducing Broadcast Traffic
Reducing broadcast traffic can improve network performance by preventing unnecessary data from being transmitted across the network.
19.3. Enhancing Security
Enhancing security can prevent unauthorized devices from accessing the network, protecting against security threats and improving overall network performance.
20. Resources for Further Learning on MAC Addresses
Several resources are available for those who want to learn more about MAC addresses and network communication. These resources include online courses, books, and technical documentation.
20.1. Online Courses
Online courses offer a structured learning experience and can provide valuable insights into MAC addresses and network communication.
20.2. Books
Books offer a comprehensive overview of MAC addresses and network communication, covering both theoretical concepts and practical applications.
20.3. Technical Documentation
Technical documentation provides detailed information about MAC addresses and network communication, including specifications, standards, and best practices.
21. The Impact of MAC Address Learning on Network Scalability
MAC address learning has a significant impact on network scalability. As the network grows, the switch must be able to efficiently learn and manage a large number of MAC addresses.
21.1. Scaling MAC Address Tables
As the network grows, the MAC address table must be able to scale to accommodate a large number of entries.
21.2. Handling Increased Traffic
The switch must be able to handle increased traffic volumes as the network grows, forwarding packets efficiently to the correct destinations.
21.3. Maintaining Performance
Maintaining performance as the network grows requires careful planning and optimization of the MAC address learning process.
22. Best Practices for MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering is a security technique that allows network administrators to control which devices can access the network based on their MAC addresses. Here are some best practices for implementing MAC address filtering:
22.1. Creating a Whitelist
Create a whitelist of authorized MAC addresses and only allow those devices to access the network.
22.2. Regularly Updating the List
Regularly update the whitelist to remove devices that are no longer authorized and add new devices as needed.
22.3. Monitoring for Unauthorized Access
Monitor the network for unauthorized access attempts and take appropriate action to prevent them.
23. Maximizing Network Security with MAC Address Management
Effective MAC address management is crucial for maximizing network security. By implementing security measures such as port security, DHCP snooping, and DAI, network administrators can protect the network from unauthorized access and attacks.
23.1. Implementing Port Security
Port security limits the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a port, preventing unauthorized devices from connecting to the network.
23.2. Using DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping prevents rogue DHCP servers from assigning IP addresses to clients, ensuring that only authorized devices can access the network.
23.3. Applying DAI
DAI prevents ARP spoofing attacks by validating ARP packets against the DHCP snooping database.
24. The Role of MAC Addresses in IoT Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding, with billions of devices connecting to the internet. MAC addresses play a crucial role in identifying and managing these devices on the network.
24.1. Identifying IoT Devices
MAC addresses are used to uniquely identify IoT devices on the network.
24.2. Managing IoT Device Access
MAC address filtering can be used to control which IoT devices can access the network, preventing unauthorized devices from connecting.
24.3. Securing IoT Networks
Securing IoT networks requires careful planning and implementation of security measures such as port security, DHCP snooping, and DAI.
25. How to Monitor MAC Address Activity for Security Threats
Monitoring MAC address activity is essential for detecting and preventing security threats. By analyzing MAC address traffic patterns, network administrators can identify anomalies and take appropriate action.
25.1. Using Network Analyzers
Network analyzers can be used to capture and analyze MAC address traffic, providing valuable insights into network activity.
25.2. Analyzing Traffic Patterns
Analyzing traffic patterns can help to identify anomalies, such as sudden increases in traffic from a particular MAC address.
25.3. Setting Up Alerts
Set up alerts to notify network administrators when suspicious MAC address activity is detected.
26. Best Practices for Securing Wireless Networks with MAC Addresses
Securing wireless networks requires careful planning and implementation of security measures. MAC address filtering can be used to control which devices can access the network, preventing unauthorized access.
26.1. Enabling MAC Address Filtering
Enable MAC address filtering on the wireless access point to control which devices can connect to the network.
26.2. Creating a Whitelist
Create a whitelist of authorized MAC addresses and only allow those devices to access the network.
26.3. Regularly Updating the List
Regularly update the whitelist to remove devices that are no longer authorized and add new devices as needed.
27. The Benefits of Centralized MAC Address Management
Centralized MAC address management can simplify network administration and improve security. By managing MAC addresses from a central location, network administrators can ensure that security policies are consistently applied across the network.
27.1. Simplifying Administration
Centralized MAC address management simplifies network administration by providing a single point of control for managing MAC addresses.
27.2. Improving Security
Centralized MAC address management improves security by ensuring that security policies are consistently applied across the network.
27.3. Reducing Costs
Centralized MAC address management can reduce costs by automating tasks and improving efficiency.
28. Tools and Technologies for Efficient MAC Address Learning
Several tools and technologies are available to help network administrators efficiently manage MAC address learning. These tools include network management systems, packet sniffers, and network analyzers.
28.1. Network Management Systems
Network management systems provide a centralized platform for managing MAC addresses and monitoring network activity.
28.2. Packet Sniffers
Packet sniffers can be used to capture and analyze MAC address traffic, providing valuable insights into network activity.
28.3. Network Analyzers
Network analyzers can be used to analyze network traffic and identify anomalies, helping to prevent security threats.
29. Key Takeaways for Effective MAC Address Learning
Effective MAC address learning is crucial for maintaining network performance and security. Key takeaways include understanding how switches learn MAC addresses, implementing security measures such as port security and DHCP snooping, and regularly monitoring MAC address activity.
29.1. Understanding the Learning Process
Understand how switches learn MAC addresses by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames and associating them with the corresponding port.
29.2. Implementing Security Measures
Implement security measures such as port security and DHCP snooping to protect the network from unauthorized access and attacks.
29.3. Monitoring Network Activity
Regularly monitor MAC address activity to detect and prevent security threats.
30. Future Trends in MAC Address Technology
The future of MAC address technology is likely to be shaped by emerging technologies and evolving security threats. Innovations in SDN, NFV, and AI are expected to play a significant role.
30.1. SDN and NFV
SDN and NFV are expected to provide more flexible and scalable solutions for MAC address management and security.
30.2. Artificial Intelligence
AI can be used to analyze MAC address traffic patterns and detect anomalies, helping to prevent security threats.
30.3. Evolving Security Threats
As security threats become more sophisticated, new techniques will be needed to protect MAC address learning from attacks.
By understanding these concepts and best practices, network administrators can effectively manage MAC addresses and ensure the performance and security of their networks.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About MAC Addresses
Q1: What is a MAC address?
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface card (NIC) for communication within a network segment.
Q2: How does a switch learn MAC addresses?
A switch learns MAC addresses by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames and associating it with the port on which the frame was received.
Q3: Why do devices need to know each other’s MAC addresses?
Devices need to know each other’s MAC addresses to ensure that data packets are delivered to the correct destination within the local network.
Q4: What is a MAC address table?
A MAC address table is a table stored in a switch that maps MAC addresses to the ports on which they were learned, enabling the switch to forward traffic efficiently.
Q5: How long does a MAC address stay in the MAC address table?
By default, a MAC address stays in the switch’s MAC address table for approximately 5 minutes.
Q6: What is VLAN and how does it relate to MAC addresses?
VLAN (Virtual LAN) is a logical grouping of network devices that allows them to communicate as if they were on the same physical segment. Each VLAN maintains its own MAC address table.
Q7: What is port security?
Port security is a feature that limits the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a switch port, preventing unauthorized access and mitigating MAC address flooding attacks.
Q8: What is MAC address spoofing?
MAC address spoofing is a technique used to disguise a device by falsifying its MAC address, often used in network attacks.
Q9: How can I view the MAC address table on a Cisco switch?
You can view the MAC address table on a Cisco switch by using the show mac-address-table command in the command-line interface.
Q10: What are the benefits of managing MAC addresses effectively?
Effectively managing MAC addresses enhances network security, improves performance by reducing unnecessary traffic, and simplifies network administration.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in acquiring new skills and deepening your understanding of complex topics like network management. That’s why we offer comprehensive resources designed to simplify learning and help you achieve your educational and professional goals.
Ready to dive deeper into network management or explore other fascinating topics? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover our extensive collection of articles and courses tailored to meet your needs.
Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. For immediate assistance, reach out via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Start your journey towards expertise with learns.edu.vn!