How Does The Brain Learn Best? Understanding the science behind learning can dramatically improve your study habits and overall cognitive function. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we delve into effective learning methods, memory enhancement techniques, and strategies to optimize your brain’s learning potential. Discover the best approaches for knowledge retention and cognitive skill development with us.
1. Understanding Neuroplasticity: The Brain’s Adaptability
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This dynamic process allows the brain to adjust in response to experiences, learning, and environmental changes. Essentially, it’s the brain’s way of rewiring itself. Neuroplasticity operates on a “use it or lose it” principle, meaning that frequently used neural pathways strengthen, while those used less often weaken and may eventually disappear.
- Definition: Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s capacity to change structurally and functionally as a result of input from the environment.
- Mechanism: It involves the formation of new synaptic connections and the elimination of old ones.
- Significance: It is vital for learning, memory, and recovery from brain injuries.
 Neuroplasticity Explained: Brain's Ability to Adapt
Neuroplasticity Explained: Brain's Ability to Adapt
1.1. Leveraging Neuroplasticity for Enhanced Learning
To enhance learning through neuroplasticity, repetition and consistent practice are crucial. When you repeatedly engage with new material, you strengthen the neural pathways associated with that information, making it easier to recall. This principle is particularly effective when learning new languages, musical instruments, or complex concepts.
- Repetition: Regular repetition reinforces neural connections, improving recall.
- Practice: Consistent practice solidifies learning and enhances skill development.
- Application: Applying learned material in real-world scenarios deepens understanding and retention.
1.2. Real-World Example: London Cab Drivers and Spatial Memory
A classic example of neuroplasticity in action is the study of London cab drivers. These drivers undergo rigorous training to memorize the intricate map of London, a process known as “the Knowledge.” Brain scans have shown that their hippocampi, the region of the brain associated with spatial memory, are larger than those of average individuals. Moreover, the size of the hippocampus correlates with the amount of time they have spent on the job, demonstrating how sustained learning and practice can lead to structural changes in the brain.
| Study Finding | Description |
|---|---|
| Larger Hippocampus | Brain scans revealed that London cab drivers have a significantly larger hippocampus compared to individuals in control groups. |
| Correlation with Time on the Job | The size of the hippocampus directly correlates with the amount of time the drivers have spent navigating and memorizing London’s streets. |
| Structural Changes Accommodating “the Knowledge” | Scientists observed structural changes in the hippocampus, allowing drivers to store and process complex spatial information. |
1.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Harness Neuroplasticity
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we offer resources and courses designed to help you leverage neuroplasticity for optimal learning. Our materials emphasize repetition, practice, and real-world application to ensure that you strengthen neural connections and enhance your cognitive abilities. Explore our website to discover techniques for mastering new skills and improving your memory.
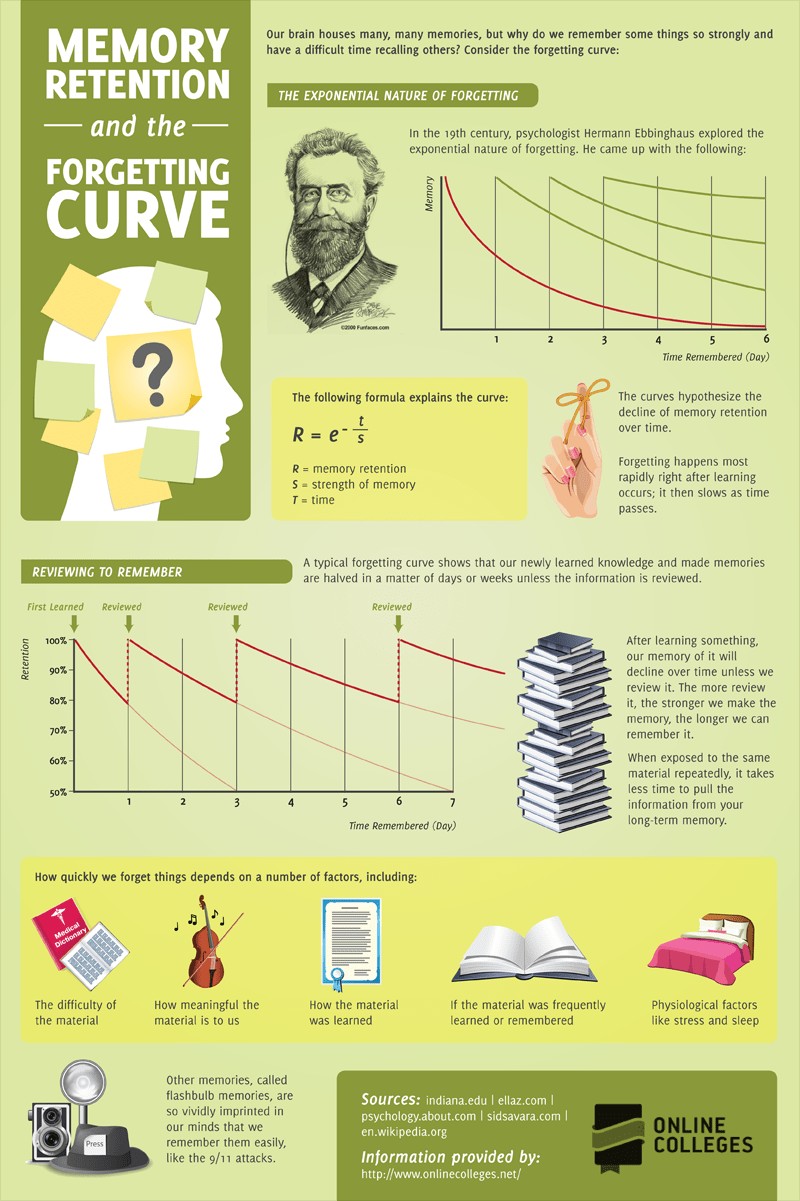
2. The Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve: Understanding Memory Decay
The Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve, developed by German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, illustrates how information is lost over time if no attempt is made to retain it. Ebbinghaus’s research indicated that a significant portion of newly learned information is forgotten within the first hour if not reinforced. This curve highlights the importance of active recall and spaced repetition in combating memory decay.
- Initial Memory Loss: According to Ebbinghaus, about 50% of new information is forgotten within the first hour.
- Rate of Forgetting: The rate of forgetting slows down over time, but without intervention, memory continues to decline.
- Implications: Understanding this curve is crucial for designing effective learning strategies.
2.1. Factors Influencing the Rate of Forgetting
Several factors influence how quickly we forget information. The difficulty of the material, its meaningfulness, and the learning method all play a role. Additionally, physiological factors such as stress and sleep deprivation can significantly impact memory retention.
| Factor | Impact on Forgetting Rate |
|---|---|
| Difficulty of Material | More complex and challenging material tends to be forgotten more quickly. |
| Meaningfulness | Information that is personally relevant or meaningful is retained more effectively. |
| Learning Method | Active learning techniques, such as teaching the material to someone else, improve retention compared to passive reading. |
| Physiological Factors (Stress & Sleep) | Stress and lack of sleep impair memory consolidation and increase the rate of forgetting. |
2.2. Strategies to Combat the Forgetting Curve
To combat the forgetting curve, employ strategies such as spaced repetition, active recall, and elaboration. Spaced repetition involves reviewing material at increasing intervals, reinforcing memory over time. Active recall, such as testing yourself, strengthens neural connections. Elaboration involves connecting new information to existing knowledge, making it more meaningful and memorable.
- Spaced Repetition: Reviewing material at increasing intervals to reinforce memory.
- Active Recall: Testing yourself on the material to strengthen neural connections.
- Elaboration: Connecting new information to existing knowledge to make it more meaningful.
2.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Improve Memory Retention
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to help you combat the forgetting curve. Our courses incorporate spaced repetition techniques and active recall exercises to enhance memory retention. Explore our articles and resources to discover how to optimize your learning and remember more effectively.
3. The Impact of Stress on Memory
Stress significantly affects memory and cognitive function. When stressed, the body releases cortisol, a hormone that, in small amounts, helps us respond to immediate threats. However, chronic stress leads to prolonged cortisol release, which can damage cells in the hippocampus, the brain region critical for memory formation and retrieval.
- Cortisol Release: Stress triggers the release of cortisol, which can be harmful in excess.
- Hippocampal Damage: Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can damage cells in the hippocampus.
- Cognitive Impairment: Stress impairs attention, perception, short-term memory, learning, and word finding.
3.1. Managing Stress for Optimal Learning
To mitigate the negative effects of stress on memory, it’s essential to implement effective stress management techniques. Mindfulness practices, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help regulate cortisol levels and protect the hippocampus.
- Mindfulness Practices: Meditation and mindfulness exercises reduce stress and improve focus.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps lower cortisol levels and enhances cognitive function.
- Adequate Sleep: Sufficient sleep is crucial for memory consolidation and stress reduction.
3.2. Practical Stress-Reduction Techniques
Incorporating simple stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine can significantly improve your cognitive performance. Deep breathing exercises, time management strategies, and engaging in relaxing hobbies can help manage stress and enhance learning.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Practicing deep, slow breaths to calm the nervous system and reduce stress. |
| Time Management | Organizing tasks and setting realistic goals to reduce feelings of overwhelm. |
| Relaxing Hobbies | Engaging in activities you enjoy, such as reading, painting, or listening to music, to promote relaxation. |
| Social Support | Spending time with friends and family to foster a sense of connection and reduce feelings of isolation. |
| Progressive Relaxation | Tensing and releasing different muscle groups to reduce physical tension and promote relaxation. |
3.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Manage Stress
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources on stress management to help you maintain optimal cognitive function. Our articles provide practical tips and techniques for reducing stress and improving your learning environment. Visit our website to learn how to balance your studies with effective stress-reduction strategies.
4. The Importance of Sleep for Memory Consolidation
Sleep is crucial for memory consolidation, the process by which the brain transfers information from short-term to long-term memory. During sleep, the brain replays and strengthens neural connections, making it easier to recall information later. A lack of sleep impairs both the ability to pay attention and learn effectively, as well as the consolidation of memories.
- Memory Consolidation: Sleep facilitates the transfer of information from short-term to long-term memory.
- Attention and Learning: Lack of sleep impairs attention and reduces the ability to learn efficiently.
- Cognitive Performance: Sleep deprivation negatively impacts cognitive performance and memory retention.
4.1. How Sleep Enhances Memory
Sleep enhances memory through several mechanisms. During sleep, the brain reactivates neural pathways associated with recent learning experiences, strengthening these connections. Sleep also allows the brain to clear out toxins and waste products that can interfere with cognitive function.
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Neural Reactivation | The brain replays and strengthens neural pathways associated with recent learning experiences. |
| Synaptic Pruning | Sleep allows the brain to prune weaker synaptic connections, strengthening the most important ones. |
| Toxin Clearance | During sleep, the brain clears out toxins and waste products that can impair cognitive function. |
| Hippocampal Processing | Sleep is crucial for the hippocampus to process and consolidate memories, transferring them to the neocortex for long-term storage. |
4.2. Strategies for Improving Sleep Quality
Improving sleep quality can significantly enhance memory and cognitive function. Establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimize your sleep environment to promote restful sleep.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day to regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities, such as reading or taking a warm bath, to prepare your body for sleep.
- Optimize Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool to promote restful sleep.
4.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Improve Sleep Habits
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources on improving sleep habits to enhance memory and cognitive function. Our articles offer practical tips and strategies for optimizing your sleep schedule and creating a conducive sleep environment. Visit our website to learn how to prioritize sleep and improve your learning outcomes.
5. Repetition and Review: Key to Long-Term Memory
Repetition and review are essential for transferring learned material from short-term to long-term memory. Repeated exposure to information strengthens neural connections, making it easier to recall information later. Spaced Learning, a method of increasing retention, relies on this principle.
- Memory Transfer: Repetition helps move information from short-term to long-term memory.
- Neural Strengthening: Repeated exposure strengthens neural connections associated with the learned material.
- Spaced Learning: A method that leverages repetition at optimal intervals to enhance retention.
5.1. The Power of Spaced Learning
Spaced Learning involves reviewing material at increasing intervals after the initial learning session. This technique takes advantage of the forgetting curve by reinforcing memory just before the information is likely to be forgotten.
| Interval | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Initial | Review the material shortly after the initial learning session to reinforce the information. |
| Subsequent | Increase the intervals between reviews to strengthen memory over time. |
| Maintenance | Periodically review the material to maintain long-term retention. |
5.2. Practical Tips for Effective Repetition and Review
To implement effective repetition and review, create a study schedule that incorporates regular review sessions. Use flashcards, quizzes, and other active recall techniques to reinforce memory and identify areas that need further review.
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan regular review sessions to reinforce learned material.
- Use Flashcards: Flashcards are a convenient tool for active recall and spaced repetition.
- Take Quizzes: Quizzes and self-tests help identify areas that need further review.
- Teach the Material: Explaining the material to someone else reinforces your understanding and memory.
5.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Implement Repetition and Review
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers tools and resources to help you implement effective repetition and review strategies. Our courses include built-in review sessions and active recall exercises to enhance memory retention. Explore our website to discover how to optimize your study habits and achieve long-term learning success.
6. Cultivating a Growth Mindset for Enhanced Learning
A growth mindset, the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work, is crucial for enhanced learning. Encourage a growth mindset by embracing challenges, persevering through difficulties, and viewing failure as an opportunity for growth.
- Belief in Development: A growth mindset involves believing that abilities can be developed.
- Embracing Challenges: Viewing challenges as opportunities for growth and learning.
- Perseverance: Persisting through difficulties and setbacks.
- Learning from Failure: Seeing failure as a valuable part of the learning process.
6.1. Fostering a Growth Mindset in Learners
To foster a growth mindset, encourage learners to challenge themselves, persevere through difficulties, and view failure as a learning opportunity. Praise effort and progress, rather than innate ability, to reinforce the belief that hard work leads to improvement.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Encourage Challenges | Encourage learners to take on new challenges and step outside their comfort zones. |
| Promote Perseverance | Teach learners the importance of perseverance and persistence in the face of difficulties. |
| Emphasize Effort and Progress | Praise effort and progress, rather than innate ability, to reinforce the value of hard work. |
| View Failure as a Learning Tool | Encourage learners to see failure as an opportunity for growth and improvement. |
6.2. The Benefits of a Growth Mindset
A growth mindset leads to numerous benefits, including increased motivation, greater resilience, and improved learning outcomes. Individuals with a growth mindset are more likely to embrace challenges, persist through setbacks, and achieve their full potential.
- Increased Motivation: A growth mindset enhances motivation to learn and improve.
- Greater Resilience: Individuals with a growth mindset are more resilient in the face of setbacks.
- Improved Learning Outcomes: A growth mindset leads to better learning outcomes and academic achievement.
6.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Develop a Growth Mindset
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to help you develop a growth mindset and unlock your full learning potential. Our articles offer practical tips and strategies for cultivating a growth mindset in yourself and others. Visit our website to learn how to embrace challenges, persevere through difficulties, and achieve your learning goals.
7. Active Learning: Engaging the Brain for Deeper Understanding
Active learning involves engaging with the material, participating in class, and collaborating with others. This approach enhances the learning experience by helping students create stronger memories and develop a deeper understanding of the material covered.
- Engagement: Active learning requires active engagement with the material.
- Participation: Participation in class discussions and activities.
- Collaboration: Working with peers to solve problems and understand concepts.
- Deeper Understanding: Active learning promotes a deeper and more meaningful understanding of the material.
7.1. Strategies for Promoting Active Learning
To promote active learning, incorporate strategies such as case-based problem-solving exercises, debates, group discussions, and peer instruction. These activities encourage students to think critically, apply their knowledge, and engage with the material in a meaningful way.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Case-Based Problem-Solving | Present students with real-world cases and ask them to apply their knowledge to solve problems. |
| Debates | Organize debates on relevant topics to encourage critical thinking and argumentation. |
| Group Discussions | Facilitate group discussions to allow students to share ideas and learn from each other. |
| Peer Instruction | Have students teach the material to each other to reinforce their understanding. |
| Brainstorm Learning Objectives | Involve students in brainstorming learning objectives to increase their investment and motivation. |
7.2. The Benefits of Active Learning
Active learning offers numerous benefits, including improved memory retention, enhanced critical thinking skills, and increased motivation. By actively engaging with the material, students develop a deeper understanding and are better able to apply their knowledge in real-world situations.
- Improved Memory Retention: Active learning enhances memory retention by creating stronger neural connections.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: Active learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Increased Motivation: Active learning increases student investment and motivation in the learning process.
7.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Implement Active Learning
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to help you implement active learning strategies in your educational settings. Our articles offer practical tips and techniques for engaging students and promoting deeper understanding. Visit our website to learn how to transform your teaching methods and enhance the learning experience for your students.
8. Optimizing Your Learning Environment
Creating an optimal learning environment is crucial for maximizing your brain’s ability to learn and retain information. A conducive learning environment should be free from distractions, comfortable, and well-organized.
- Distraction-Free Zone: Minimize distractions such as noise, social media, and interruptions.
- Comfortable Setting: Ensure your learning space is comfortable and conducive to focus.
- Organization: Keep your learning materials organized and easily accessible.
8.1. Key Elements of an Effective Learning Space
An effective learning space should incorporate several key elements, including good lighting, comfortable seating, and proper ventilation. Additionally, consider incorporating plants or other natural elements to create a calming and inspiring atmosphere.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Good Lighting | Adequate lighting reduces eye strain and promotes focus. |
| Comfortable Seating | Ergonomic seating supports good posture and prevents discomfort during long study sessions. |
| Proper Ventilation | Good ventilation ensures a fresh and comfortable environment. |
| Natural Elements | Incorporating plants or natural elements can create a calming and inspiring atmosphere. |
| Minimal Clutter | Keeping the space tidy and free from unnecessary items reduces distractions and promotes focus. |
8.2. The Role of Technology in Learning Environments
Technology plays a significant role in modern learning environments. Utilize digital tools and resources to enhance your learning experience, but be mindful of potential distractions. Balance the use of technology with traditional learning methods to optimize your learning environment.
- Digital Resources: Utilize online resources, educational apps, and digital textbooks to enhance learning.
- Distraction Management: Be mindful of potential distractions from social media and other online activities.
- Balanced Approach: Combine technology with traditional learning methods for optimal results.
8.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Create an Optimal Learning Environment
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to help you create an optimal learning environment that supports your cognitive function and enhances your learning outcomes. Our articles offer practical tips and strategies for designing a conducive learning space, managing distractions, and leveraging technology effectively. Visit our website to learn how to optimize your learning environment and achieve your full potential.
9. Nutrition and Hydration: Fueling Your Brain for Optimal Performance
Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for fueling your brain and supporting optimal cognitive performance. A balanced diet rich in nutrients, vitamins, and antioxidants can enhance memory, focus, and overall brain health.
- Balanced Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Nutrients and Vitamins: Ensure you are getting adequate nutrients and vitamins essential for brain health.
- Antioxidants: Incorporate antioxidant-rich foods to protect your brain from oxidative stress.
- Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated to support optimal cognitive function.
9.1. Key Nutrients for Brain Health
Several key nutrients are particularly beneficial for brain health, including omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants. Incorporate foods rich in these nutrients into your diet to support optimal cognitive function.
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts | Supports brain cell structure, improves memory, and reduces inflammation. |
| B Vitamins | Whole grains, lean meats, eggs, leafy green vegetables | Supports nerve function, enhances energy production, and improves mood. |
| Antioxidants | Berries, dark chocolate, spinach, kale | Protects brain cells from oxidative stress, improves cognitive function, and reduces the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Vitamin D | Fortified foods, fatty fish, sunlight | Supports cognitive function, enhances mood, and protects against cognitive decline. |
| Choline | Eggs, beef, chicken, fish | Supports memory and learning by aiding in the production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. |
9.2. The Impact of Hydration on Cognitive Function
Hydration plays a crucial role in cognitive function. Dehydration can lead to decreased attention, impaired memory, and reduced cognitive performance. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day to stay adequately hydrated.
- Attention and Focus: Dehydration can impair attention and reduce focus.
- Memory and Cognition: Proper hydration supports memory and overall cognitive function.
- Physical Health: Staying hydrated helps maintain overall physical health, which indirectly benefits brain function.
9.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Optimize Your Nutrition and Hydration
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to help you optimize your nutrition and hydration for optimal brain performance. Our articles offer practical tips and strategies for incorporating brain-boosting foods into your diet and staying adequately hydrated. Visit our website to learn how to fuel your brain and enhance your learning outcomes.
10. Personalized Learning: Tailoring Your Approach for Maximum Impact
Personalized learning involves tailoring your learning approach to your individual needs, preferences, and learning style. Understanding your learning style and identifying your strengths and weaknesses can help you optimize your learning experience and achieve better outcomes.
- Individual Needs: Personalized learning caters to individual needs and preferences.
- Learning Styles: Understanding your learning style can help you optimize your approach.
- Strengths and Weaknesses: Identifying your strengths and weaknesses allows you to focus on areas that need improvement.
10.1. Identifying Your Learning Style
Identifying your learning style is a crucial step in personalizing your learning approach. Common learning styles include visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and read/write. Experiment with different learning methods to determine which approach works best for you.
| Learning Style | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual | Learners who prefer to learn through visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and videos. |
| Auditory | Learners who prefer to learn through listening to lectures, discussions, and audio recordings. |
| Kinesthetic | Learners who prefer to learn through hands-on activities, experiments, and physical movement. |
| Read/Write | Learners who prefer to learn through reading and writing, such as taking notes, writing summaries, and creating outlines. |
10.2. Setting Achievable Learning Goals
Setting achievable learning goals is essential for staying motivated and focused. Break down larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks and track your progress along the way. Celebrate your successes to stay motivated and reinforce positive learning habits.
- Break Down Goals: Divide larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks.
- Track Progress: Monitor your progress to stay motivated and on track.
- Celebrate Successes: Acknowledge and celebrate your achievements to reinforce positive learning habits.
10.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Personalize Your Learning
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to help you personalize your learning approach and achieve your full potential. Our articles offer practical tips and strategies for identifying your learning style, setting achievable goals, and tailoring your learning experience to your individual needs. Visit our website to learn how to personalize your learning and unlock your cognitive potential.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to optimize your learning potential. By understanding how the brain learns best and implementing effective learning strategies, you can unlock your cognitive potential and achieve your academic and professional goals.
FAQ: How Does the Brain Learn Best?
1. What is neuroplasticity, and how does it affect learning?
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life, allowing it to adapt to new experiences and learning.
2. How does the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve impact memory retention?
The Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve shows how information is lost over time if no attempt is made to retain it, highlighting the importance of active recall and spaced repetition.
3. How does stress affect memory and learning?
Stress releases cortisol, which, in excess, can damage the hippocampus, impairing attention, perception, short-term memory, and learning.
4. Why is sleep important for memory consolidation?
Sleep is crucial for transferring information from short-term to long-term memory, strengthening neural connections, and clearing out toxins that can interfere with cognitive function.
5. What is spaced learning, and how does it improve memory retention?
Spaced learning involves reviewing material at increasing intervals, reinforcing memory just before the information is likely to be forgotten, thereby improving retention.
6. What is a growth mindset, and how does it enhance learning?
A growth mindset is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work, leading to increased motivation, resilience, and improved learning outcomes.
7. What is active learning, and how does it promote deeper understanding?
Active learning involves engaging with the material, participating in class, and collaborating with others, enhancing the learning experience and promoting deeper understanding.
8. How does the learning environment affect cognitive performance?
An optimal learning environment, free from distractions and well-organized, is crucial for maximizing the brain’s ability to learn and retain information.
9. How do nutrition and hydration impact brain function?
Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for fueling the brain, supporting optimal cognitive performance, enhancing memory, focus, and overall brain health.
10. What is personalized learning, and how does it maximize learning impact?
Personalized learning involves tailoring your learning approach to your individual needs, preferences, and learning style, optimizing your learning experience and achieving better outcomes.
Ready to unlock your learning potential? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover a wealth of resources, courses, and expert guidance designed to help you learn smarter, not harder. Explore our website to find articles, tools, and personalized learning plans tailored to your unique needs. Don’t wait – start your journey to lifelong learning and success with LEARNS.EDU.VN now!
Contact Information:
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: learns.edu.vn