Is learning to play the drums difficult? That’s a question many aspiring musicians ask. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe that with the right approach and resources, anyone can learn to drum. We’ll break down the realities of learning drums, offering insights and strategies to make your musical journey a success. Discover practice techniques, skill development, and the joys of drumming through tailored learning paths.
1. Understanding the Drumming Landscape
Learning any musical instrument involves a commitment of time and effort, and the drums are no exception. However, the perception of difficulty can be subjective and depend on individual goals, learning styles, and practice habits. Let’s explore the various factors that influence the drumming learning curve.
1.1. Initial Accessibility vs. Long-Term Mastery
One of the appealing aspects of drumming is the initial accessibility. Unlike some instruments that require months to produce a decent sound, beginners can often play basic beats within a few weeks. The immediate gratification can be highly motivating. However, achieving mastery requires a deeper understanding of rhythm, coordination, musicality, and technique.
1.2. Physical Demands
Drumming is a physically demanding activity. It requires coordination between all four limbs, which can be challenging at first. Developing the necessary muscle memory, stamina, and control takes time and consistent practice.
1.3. Musical Knowledge
While it’s possible to start drumming without extensive musical knowledge, a basic understanding of music theory, rhythm, and timing can significantly enhance the learning process. This knowledge helps drummers understand song structures, anticipate changes, and play more musically.
2. Factors Influencing the Learning Curve
Several factors can affect how quickly and effectively someone learns to play the drums. Understanding these factors can help you optimize your learning journey.
2.1. Natural Aptitude and Musical Background
Some people may have a natural aptitude for rhythm and coordination, giving them a head start. Prior musical experience, even on a different instrument, can also be beneficial. However, aptitude and background are not the only determinants of success.
2.2. Quality of Instruction
The quality of instruction plays a crucial role. A good teacher can provide personalized guidance, correct bad habits early on, and introduce effective practice techniques. Whether you opt for in-person lessons, online courses, or self-study, make sure the resources you use are reputable and well-structured.
2.3. Practice Habits
Consistent, focused practice is essential for progress. Short, regular practice sessions are generally more effective than infrequent, marathon sessions. It’s also important to practice with intention, focusing on specific skills or techniques rather than simply playing mindlessly.
2.4. Goals and Expectations
Having realistic goals and expectations is vital. If your goal is to play complex jazz rhythms or intricate progressive rock patterns, it will naturally take longer than if you simply want to play basic rock beats. Adjust your expectations accordingly and celebrate small victories along the way.
2.5. Overcoming Challenges
Every drummer faces challenges, such as mastering difficult rhythms, improving coordination, or overcoming performance anxiety. The ability to persevere through these challenges is crucial. Embrace mistakes as learning opportunities and don’t be afraid to seek help when needed.
3. Debunking the Myths About Learning Drums
Many misconceptions surround the process of learning drums. Separating fact from fiction can help you approach your drumming journey with a more realistic and positive mindset.
3.1. Myth: You Need Natural Talent to Play Drums
Reality: While some people may have a natural aptitude for rhythm, drumming is primarily a skill that can be developed through practice and dedication. Anyone can learn to play drums, regardless of their perceived talent. Passion and persistence are far more important.
3.2. Myth: You Need an Expensive Drum Set to Start
Reality: You don’t need a top-of-the-line drum set to begin learning. A basic, affordable kit is sufficient for beginners. Alternatively, you can start with a practice pad or even use household items to develop your technique before investing in a full drum set.
3.3. Myth: You Need to Read Music to Play Drums
Reality: While reading music can be helpful, it’s not essential, especially for playing popular music genres like rock, pop, and blues. Many famous drummers don’t read music. However, learning to read drum notation can expand your musical horizons and improve your understanding of rhythm.
3.4. Myth: Drumming Is Too Loud and Disruptive
Reality: While drums can be loud, there are ways to mitigate the noise. You can use practice pads, electronic drum sets, or soundproofing materials to reduce the volume. Additionally, many practice spaces and studios are available for drummers who want to play without disturbing others.
4. Setting Realistic Goals and Timelines
Setting realistic goals is crucial for maintaining motivation and tracking progress. Here are some general timelines for achieving different levels of drumming proficiency.
4.1. Beginner Level (3-6 Months)
- Goal: Learn basic drum beats and fills.
- Skills: Play simple rock, pop, and blues grooves.
- Practice: 30-60 minutes per day, 3-5 days per week.
4.2. Intermediate Level (1-2 Years)
- Goal: Develop coordination, timing, and technique.
- Skills: Play more complex rhythms, fills, and rudiments.
- Practice: 60-90 minutes per day, 5-7 days per week.
4.3. Advanced Level (2+ Years)
- Goal: Master a wide range of musical styles and techniques.
- Skills: Improvise, compose, and perform at a professional level.
- Practice: 2+ hours per day, 5-7 days per week.
Table: Drumming Skill Levels and Expected Timelines
| Skill Level | Timeframe | Goals | Skills | Practice Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | 3-6 Months | Learn basic drum beats and fills. | Play simple rock, pop, and blues grooves. | 30-60 minutes/day, 3-5 days/week |
| Intermediate | 1-2 Years | Develop coordination, timing, and technique. | Play more complex rhythms, fills, and rudiments. | 60-90 minutes/day, 5-7 days/week |
| Advanced | 2+ Years | Master a wide range of musical styles and techniques. | Improvise, compose, and perform at a professional level. | 2+ hours/day, 5-7 days/week |


5. Effective Practice Techniques for Drumming
To make the most of your practice time, it’s important to use effective techniques that target specific skills and areas for improvement. Here are some proven practice strategies for drummers.
5.1. Warm-Up Exercises
Before diving into your main practice routine, start with warm-up exercises to prepare your muscles and improve blood flow. Simple rudiments, stretching, and limb independence exercises can help prevent injuries and improve performance.
5.2. Rudiment Practice
Rudiments are the building blocks of drumming. Mastering the 40 essential rudiments can significantly improve your technique, coordination, and creativity. Practice rudiments with a metronome at various tempos to develop precision and consistency.
5.3. Groove Development
Grooves are the rhythmic patterns that form the foundation of most songs. Practice playing different grooves in various styles, focusing on timing, feel, and dynamics. Experiment with variations and embellishments to add your personal touch.
5.4. Fill Practice
Fills are short rhythmic phrases that add interest and excitement to a song. Practice playing different fills in various styles, focusing on creativity, technique, and timing. Learn to seamlessly integrate fills into your grooves.
5.5. Song Play-Along
Playing along with your favorite songs is a fun and effective way to improve your drumming skills. Choose songs that challenge you but are still within your ability level. Focus on locking in with the groove, matching the dynamics, and playing the fills accurately.
5.6. Recording and Analysis
Recording yourself playing can provide valuable insights into your strengths and weaknesses. Listen back to your recordings and analyze your timing, technique, and musicality. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and adjust your practice routine accordingly.
6. Essential Skills to Develop as a Drummer
Becoming a well-rounded drummer requires developing a range of skills beyond just playing basic beats. Here are some essential skills to focus on as you progress.
6.1. Timing and Tempo Control
Accurate timing and consistent tempo control are fundamental to drumming. Practice with a metronome regularly to develop your internal clock. Learn to play in different time signatures and tempos with precision.
6.2. Coordination and Limb Independence
Drumming requires coordinating all four limbs independently. Practice exercises that challenge your coordination and limb independence, such as playing different rhythms with your hands and feet simultaneously.
6.3. Dynamics and Control
Dynamics refer to the loudness and softness of your playing. Developing dynamic control allows you to add expression and nuance to your drumming. Practice playing at different volume levels and transitioning smoothly between them.
6.4. Reading Drum Notation
Learning to read drum notation can expand your musical horizons and improve your understanding of rhythm. Start with basic notation and gradually work your way up to more complex charts.
6.5. Improvisation and Creativity
Improvisation involves creating your own rhythms and fills on the spot. Practice improvising over different grooves and chord progressions to develop your creativity and spontaneity.
6.6. Musicality and Expression
Musicality refers to the ability to play with feeling and emotion. Focus on listening to the music and responding to it with your drumming. Experiment with different sounds, textures, and dynamics to add expression to your playing.
7. Overcoming Common Challenges in Drumming
Learning drums is not always easy. Here are some common challenges that drummers face, along with strategies for overcoming them.
7.1. Coordination Difficulties
Coordinating all four limbs can be challenging, especially for beginners. Break down complex patterns into smaller, more manageable parts. Practice slowly and gradually increase the tempo as you improve.
7.2. Timing Issues
Inconsistent timing is a common problem for drummers. Practice with a metronome regularly to develop your internal clock. Focus on playing precisely on the beat and maintaining a steady tempo.
7.3. Lack of Motivation
Losing motivation is a natural part of the learning process. Set realistic goals, track your progress, and reward yourself for achieving milestones. Find a practice buddy or join a drumming community to stay motivated.
7.4. Plateaus
Hitting a plateau is frustrating, but it’s a sign that you’re pushing your limits. Try new practice techniques, explore different musical styles, or seek guidance from a teacher to break through the plateau.
7.5. Performance Anxiety
Performance anxiety is a common issue for musicians. Practice performing in front of others to build your confidence. Visualize success and focus on enjoying the music.
8. Resources for Learning Drums
Numerous resources are available to help you learn drums, including books, videos, websites, and teachers. Here are some of the best resources for drummers.
8.1. Books and Method Books
- “Stick Control for the Snare Drummer” by George Lawrence Stone: A classic book for developing hand technique and control.
- “The Art of Bop Drumming” by John Riley: A comprehensive guide to jazz drumming.
- “Progressive Steps to Syncopation for the Modern Drummer” by Ted Reed: A versatile book for improving rhythm and coordination.
8.2. Online Video Courses and Tutorials
- Drumeo: A popular online drumming platform with a vast library of lessons and tutorials.
- MikesLessons.com: A comprehensive online drumming resource with lessons from top drummers.
- YouTube Channels: Many drummers and educators offer free drumming lessons and tutorials on YouTube.
8.3. Drum Teachers and Coaches
- Local Music Schools: Many music schools offer drum lessons for students of all ages and skill levels.
- Private Instructors: Hiring a private drum teacher can provide personalized instruction and guidance.
- Online Coaching: Some drummers offer online coaching services via video conferencing.
8.4. Drumming Communities and Forums
- Drummerworld: A popular online forum for drummers to connect, share tips, and ask questions.
- Reddit Drumming: A subreddit dedicated to all things drumming.
- Local Drumming Groups: Joining a local drumming group can provide opportunities to jam with other drummers and learn from each other.
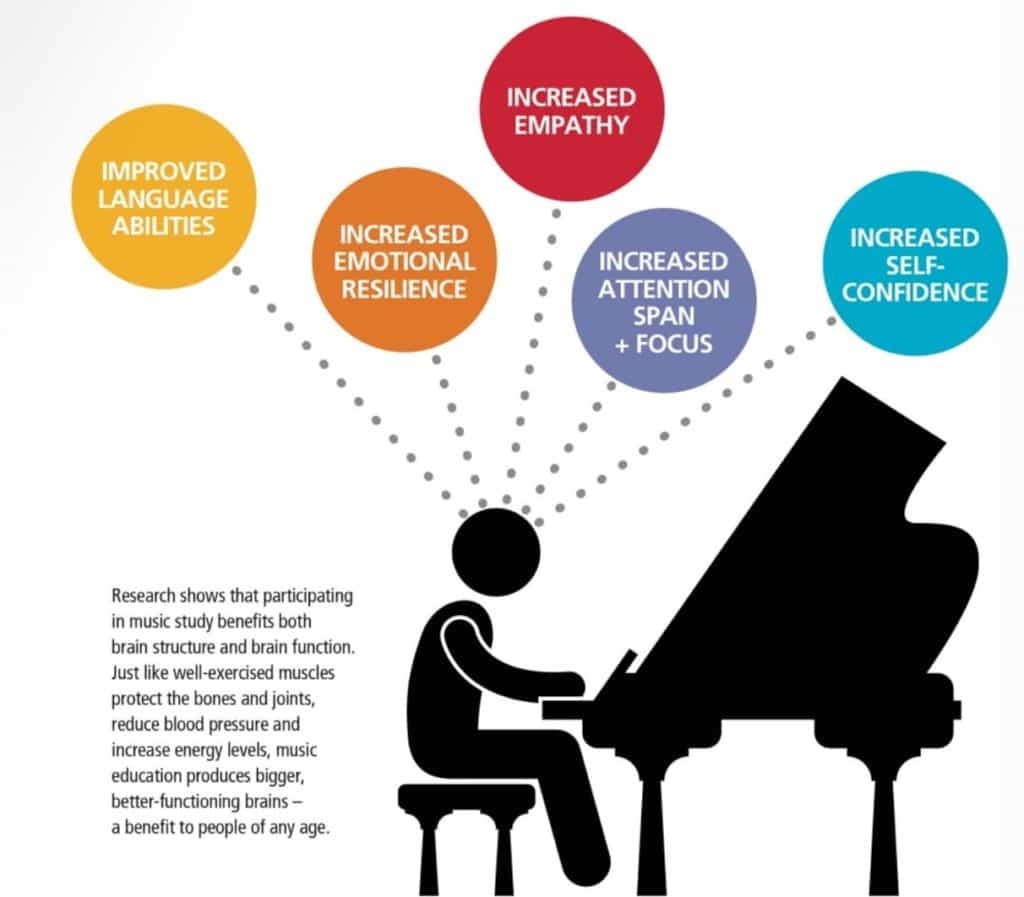
9. Benefits of Learning to Play Drums
Learning to play the drums offers numerous benefits beyond just musical enjoyment. Here are some of the advantages of drumming.
9.1. Improved Coordination and Motor Skills
Drumming requires coordinating all four limbs independently, which can significantly improve your motor skills and coordination. This can translate to other areas of life, such as sports, dancing, and everyday tasks.
9.2. Enhanced Cognitive Function
Drumming has been shown to improve cognitive function, including memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. The complex rhythms and patterns involved in drumming stimulate different parts of the brain, leading to improved cognitive performance.
9.3. Stress Relief and Emotional Expression
Drumming can be a powerful form of stress relief and emotional expression. The physical act of drumming releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Drumming can also provide an outlet for expressing emotions and releasing pent-up energy.
9.4. Increased Confidence and Self-Esteem
Learning to play the drums can boost your confidence and self-esteem. As you master new skills and overcome challenges, you’ll develop a sense of accomplishment and pride. Performing in front of others can also help you build confidence and overcome stage fright.
9.5. Social Connection and Community
Drumming can be a social activity that connects you with other musicians and music lovers. Joining a band, drumming group, or online community can provide opportunities to collaborate, share your passion, and build lasting friendships.
9.6. Physical Fitness
Drumming can be a great workout. The repetitive movements and physical exertion involved in drumming can improve your cardiovascular health, strengthen your muscles, and increase your stamina.
10. Maximizing Your Drumming Learning Experience
To make your drumming journey as enjoyable and rewarding as possible, here are some tips for maximizing your learning experience.
10.1. Set Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is essential for maintaining motivation and tracking progress. Start with small, achievable goals and gradually work your way up to more ambitious ones.
10.2. Practice Consistently
Consistent practice is key to improving your drumming skills. Aim to practice regularly, even if it’s just for a short period of time. Short, focused practice sessions are generally more effective than infrequent, marathon sessions.
10.3. Find a Good Teacher or Mentor
A good teacher or mentor can provide personalized guidance, correct bad habits early on, and introduce effective practice techniques. Look for a teacher who is experienced, knowledgeable, and passionate about drumming.
10.4. Join a Drumming Community
Joining a drumming community can provide opportunities to connect with other drummers, share tips, and ask questions. Look for local drumming groups, online forums, or social media communities.
10.5. Record Yourself Playing
Recording yourself playing can provide valuable insights into your strengths and weaknesses. Listen back to your recordings and analyze your timing, technique, and musicality.
10.6. Be Patient and Persistent
Learning drums takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and don’t get discouraged by setbacks. Celebrate small victories along the way and keep practicing consistently.
11. Advanced Drumming Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can start exploring advanced drumming techniques to expand your skills and creativity. Here are some advanced techniques to consider.
11.1. Double Bass Drumming
Double bass drumming involves using two bass drums to create fast, intricate rhythms. This technique is commonly used in heavy metal, rock, and other genres.
11.2. Odd Time Signatures
Odd time signatures are time signatures that have an odd number of beats per measure, such as 5/4 or 7/8. Playing in odd time signatures can add complexity and interest to your drumming.
11.3. Polyrhythms
Polyrhythms involve playing two or more different rhythms simultaneously. This technique can create complex and intriguing rhythmic textures.
11.4. Linear Drumming
Linear drumming involves playing patterns where no two limbs play at the same time. This technique can create a clean, precise sound.
11.5. Brush Playing
Brush playing involves using wire brushes to create soft, textured sounds on the drums. This technique is commonly used in jazz, blues, and other genres.
11.6. Drum Soloing
Drum soloing involves improvising a solo on the drums. This technique requires a high level of skill, creativity, and musicality.
12. Choosing the Right Drumming Gear
Selecting the right drumming gear can significantly impact your playing experience. Here are some factors to consider when choosing drums and accessories.
12.1. Drum Set
- Shell Material: Different shell materials (e.g., maple, birch, mahogany) produce different sounds.
- Drum Sizes: Drum sizes affect the tone and resonance of the drums.
- Hardware: Sturdy, reliable hardware is essential for stability and durability.
12.2. Cymbals
- Type: Different types of cymbals (e.g., hi-hats, crashes, rides) produce different sounds.
- Size: Cymbal size affects the tone and sustain of the cymbals.
- Material: Cymbal material (e.g., bronze, brass) affects the tone and brightness of the cymbals.
12.3. Drumheads
- Type: Different types of drumheads (e.g., coated, clear, muffled) produce different sounds.
- Thickness: Drumhead thickness affects the tone and durability of the drumheads.
- Tuning: Proper drumhead tuning is essential for achieving the desired sound.
12.4. Sticks
- Material: Different stick materials (e.g., hickory, maple, oak) affect the weight and durability of the sticks.
- Size: Stick size affects the feel and balance of the sticks.
- Tip Shape: Stick tip shape affects the sound and articulation of the drums.
12.5. Accessories
- Drum Throne: A comfortable drum throne is essential for good posture and comfort.
- Metronome: A metronome is essential for developing timing and tempo control.
- Practice Pad: A practice pad is a quiet, portable way to practice drumming technique.
13. Drumming as a Career
While many people play drums as a hobby, it is possible to pursue drumming as a career. Here are some career options for drummers.
13.1. Session Drummer
Session drummers are hired to play on recordings and live performances for other artists. This requires a high level of skill, versatility, and professionalism.
13.2. Touring Drummer
Touring drummers travel with bands and perform at concerts and festivals. This requires a high level of stamina, adaptability, and social skills.
13.3. Drum Teacher
Drum teachers provide instruction to students of all ages and skill levels. This requires a high level of knowledge, patience, and communication skills.
13.4. Drum Clinician
Drum clinicians travel to music stores and schools to demonstrate drumming techniques and promote drum products. This requires a high level of skill, knowledge, and presentation skills.
13.5. Studio Owner/Engineer
Some drummers own or work in recording studios, where they record and produce music for themselves and other artists. This requires a high level of technical knowledge and musical skills.
13.6. Composer/Arranger
Some drummers compose or arrange music for themselves and other artists. This requires a high level of musical creativity and knowledge of music theory.
14. Latest Trends in Drumming Education
The field of drumming education is constantly evolving with new technologies, techniques, and approaches. Here are some of the latest trends in drumming education.
14.1. Online Drum Lessons
Online drum lessons have become increasingly popular in recent years. Online lessons offer convenience, flexibility, and access to a wide range of teachers and resources.
14.2. Drumming Apps
Numerous drumming apps are available for mobile devices. These apps can be used for practicing rudiments, learning grooves, and improving timing.
14.3. E-Drum Kits
Electronic drum kits have become more sophisticated and affordable in recent years. E-drum kits offer quiet practice, realistic sounds, and MIDI connectivity.
14.4. Hybrid Drumming
Hybrid drumming involves combining acoustic drums with electronic elements, such as triggers, samplers, and effects. This technique allows drummers to create unique and innovative sounds.
14.5. Drum Circles
Drum circles are group drumming events where participants play drums and percussion instruments together in a non-competitive, improvisational setting. Drum circles can promote stress relief, social connection, and creativity.
14.6. Drumming Therapy
Drumming therapy is a therapeutic approach that uses drumming to promote emotional, cognitive, and physical well-being. Drumming therapy can be used to treat a variety of conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
Table: Trends in Drumming Education
| Trend | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Online Drum Lessons | Drum lessons delivered via the internet, often through video conferencing or pre-recorded videos. | Convenience, flexibility, access to a wide range of teachers and resources. |
| Drumming Apps | Mobile applications designed to help drummers practice rudiments, learn grooves, and improve timing. | Portable practice tool, gamified learning, access to a variety of exercises and resources. |
| E-Drum Kits | Electronic drum kits that offer quiet practice, realistic sounds, and MIDI connectivity. | Quiet practice, versatile sounds, MIDI integration for recording and production. |
| Hybrid Drumming | Combining acoustic drums with electronic elements, such as triggers, samplers, and effects. | Unique and innovative sounds, expanded sonic possibilities, integration of technology. |
| Drum Circles | Group drumming events where participants play drums and percussion instruments together. | Stress relief, social connection, creativity, community building. |
| Drumming Therapy | Therapeutic approach that uses drumming to promote emotional, cognitive, and physical well-being. | Treatment for anxiety, depression, PTSD, improved emotional regulation and cognitive function. |
15. FAQs About Learning Drums
Here are some frequently asked questions about learning drums, along with answers to help you on your journey.
Q1: Is it hard to learn drums if I have no musical experience?
A: Not at all! Many successful drummers started with no prior musical experience. The key is to be patient, persistent, and willing to learn.
Q2: How much practice is needed to become a good drummer?
A: The amount of practice needed varies depending on your goals and skill level. However, consistent practice is essential. Aim for at least 30 minutes of focused practice most days of the week.
Q3: Can I learn drums online, or do I need a teacher?
A: You can learn drums online, but having a teacher can provide personalized guidance and correct bad habits early on. A combination of online resources and in-person lessons can be ideal.
Q4: What’s the best age to start learning drums?
A: There’s no best age to start learning drums. Children, teenagers, and adults can all learn to play. The most important thing is to have the desire and motivation to learn.
Q5: Do I need an expensive drum set to start learning?
A: No, you don’t need an expensive drum set to start. A basic, affordable kit is sufficient for beginners. You can also start with a practice pad or electronic drum set.
Q6: How long does it take to become a professional drummer?
A: Becoming a professional drummer can take several years of dedicated practice and study. It also requires networking, marketing, and business skills.
Q7: Is drumming a good way to relieve stress?
A: Yes, drumming can be a powerful form of stress relief. The physical act of drumming releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
Q8: Can drumming improve my coordination?
A: Yes, drumming requires coordinating all four limbs independently, which can significantly improve your motor skills and coordination.
Q9: What are the most important skills for a drummer to develop?
A: The most important skills for a drummer to develop include timing, coordination, dynamics, reading drum notation, improvisation, and musicality.
Q10: Where can I find other drummers to play with?
A: You can find other drummers to play with by joining local drumming groups, online forums, or social media communities.
Conclusion
So, How Hard Is It To Learn Drums? It requires dedication, practice, and the right resources. But with consistent effort and a positive attitude, anyone can achieve their drumming goals. Whether you dream of playing in a band, recording in a studio, or simply enjoying the personal satisfaction of making music, the drums offer a rewarding and fulfilling experience.
Ready to start your drumming journey? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN to explore our comprehensive drumming courses and resources. Unlock your musical potential and join a community of passionate drummers. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Let learns.edu.vn help you achieve your musical dreams.
