Is learning to play the drums a challenge? Absolutely! But with the right approach, resources, and guidance from LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can master drumming skills and achieve your musical goals. This comprehensive guide explores the realities of learning drums, addresses common concerns, and provides actionable steps to help you become a proficient drummer, emphasizing rhythm development, coordination exercises, and musical expression. Discover a wealth of knowledge that includes instruction on how to develop rhythm, practice coordination, and express yourself musically.
1. Understanding the Drumming Learning Curve
The difficulty of learning drums depends on your goals. Are you aiming to play basic rock beats or complex jazz rhythms? Let’s break down the learning curve:
-
Initial Stages (First Few Weeks):
- What to Expect: Learning basic drum beats, understanding rhythm, and developing basic coordination.
- Challenges: Coordination between hands and feet can be tricky initially. Developing a consistent tempo is essential.
- Tips: Focus on simple exercises. Practice with a metronome. Keep sessions short and frequent.
-
Intermediate Stages (6 Months – 2 Years):
- What to Expect: Playing a wider range of rhythms, learning different drumming styles, and playing along with songs.
- Challenges: Developing stamina, improving technique, and learning to read drum notation.
- Tips: Join a band or ensemble. Take lessons from an experienced instructor. Explore different genres of music.
-
Advanced Stages (2+ Years):
- What to Expect: Mastering complex rhythms, improvising, creating original drum parts, and performing professionally.
- Challenges: Developing a unique style, maintaining motivation, and navigating the music industry.
- Tips: Network with other musicians. Record your playing. Seek out mentorship from established drummers.
2. Dispelling Common Myths About Learning Drums
Many misconceptions can discourage aspiring drummers. Let’s debunk some common myths:
- Myth: You need natural talent to play drums.
- Reality: While some individuals may have a natural aptitude for rhythm, drumming is a skill that can be developed through practice and dedication. Talent is less important than passion and perseverance.
- Myth: You have to start playing drums as a child to become good.
- Reality: It’s never too late to start learning drums. While younger learners may have an advantage in terms of neuroplasticity, adults can still acquire drumming skills with focused effort.
- Myth: Drumming is too loud and disruptive.
- Reality: There are ways to mitigate noise. Electronic drum sets are a great option for quiet practice. You can also use practice pads to work on technique without disturbing others.
- Myth: Drumming is too expensive.
- Reality: While a full drum set can be an investment, you can start with a practice pad and sticks. Many affordable online resources, like those available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, can help you get started.
- Myth: Drumming is only for certain types of people.
- Reality: Drumming is for everyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. It’s a fun and rewarding activity that can be enjoyed by anyone with an interest in music.
3. Essential Skills to Master as a Beginner Drummer
To succeed as a drummer, you need to develop a range of fundamental skills:
-
Rhythm and Timing:
- Importance: The foundation of drumming.
- Exercises: Practice with a metronome. Play along with simple songs. Focus on maintaining a steady beat.
-
Coordination:
- Importance: Coordinating your hands and feet is crucial for playing drum beats.
- Exercises: Start with basic patterns. Gradually increase the complexity. Practice slowly and deliberately.
-
Technique:
- Importance: Proper technique prevents injuries and improves your sound.
- Exercises: Focus on grip, posture, and stroke technique. Watch videos of experienced drummers.
-
Listening Skills:
- Importance: Listening to music and analyzing drum parts is essential for learning new rhythms and styles.
- Exercises: Transcribe drum beats from your favorite songs. Listen to different genres of music.
-
Reading Drum Notation:
- Importance: Being able to read drum notation opens up a world of possibilities.
- Resources: Use online resources and books to learn the basics. Practice reading simple drum charts.
4. The Role of Practice in Drumming Proficiency
Consistent practice is the key to improving your drumming skills. Here’s how to make the most of your practice sessions:
-
Set Realistic Goals:
- Start with achievable goals. Gradually increase the difficulty as you progress.
- Example: “I will practice rudiments for 15 minutes every day.”
-
Create a Practice Schedule:
- Establish a consistent practice routine. Stick to it as much as possible.
- Example: “I will practice drums for 30 minutes every evening after work.”
-
Focus on Fundamentals:
- Spend time working on basic techniques and rudiments. These are the building blocks of more advanced playing.
- Example: Practice single stroke rolls, double stroke rolls, and paradiddles.
-
Vary Your Practice:
- Mix up your practice routine to keep things interesting.
- Example: Alternate between rudiments, drum beats, and playing along with songs.
-
Record Yourself:
- Recording your playing allows you to identify areas for improvement.
- Example: Record a drum beat and listen back to check your timing and technique.
-
Seek Feedback:
- Ask a drum teacher or experienced drummer for feedback on your playing.
- Example: Share a recording of your playing with a friend who is a drummer and ask for their opinion.
-
Stay Patient and Persistent:
- Learning drums takes time and effort. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks.
- Example: If you’re struggling with a particular drum beat, break it down into smaller parts and practice each part slowly.
5. Choosing the Right Drumming Resources and Learning Methods
Selecting the right resources can significantly impact your learning experience. Consider these options:
-
Drum Teachers:
- Benefits: Personalized instruction, expert feedback, and structured learning.
- Considerations: Cost, location, and teaching style.
- Finding a Teacher: Ask for recommendations, search online directories, and attend local music events.
-
Online Courses:
- Benefits: Convenience, affordability, and a wide range of topics.
- Considerations: Quality of instruction, level of interaction, and course structure.
- Platforms: LEARNS.EDU.VN offers excellent online drumming courses, along with platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and Skillshare.
-
Books and DVDs:
- Benefits: Comprehensive information, detailed explanations, and visual aids.
- Considerations: Relevance to your goals, clarity of instruction, and availability.
- Recommendations: “Stick Control” by George Lawrence Stone, “The Art of Bop Drumming” by John Riley, and “Modern Drummer” magazine.
-
Practice Pads:
- Benefits: Quiet practice, portability, and affordability.
- Considerations: Size, feel, and durability.
- Types: Rubber pads, mesh pads, and electronic pads.
-
Drum Sets:
- Benefits: Authentic drumming experience, versatility, and expressive potential.
- Considerations: Cost, space, and noise level.
- Types: Acoustic drum sets, electronic drum sets, and hybrid drum sets.
6. Overcoming Challenges and Plateaus in Drumming
Every drummer faces challenges. Here’s how to overcome them:
-
Identify the Problem:
- Determine the specific area you’re struggling with.
- Example: “I’m having trouble with double bass drumming.”
-
Break It Down:
- Divide the problem into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Example: “I will practice double bass drumming at a slow tempo and gradually increase the speed.”
-
Seek Help:
- Consult a drum teacher, watch instructional videos, or ask for advice from other drummers.
- Example: “I will ask my drum teacher for tips on improving my double bass technique.”
-
Change Your Approach:
- Try a different practice method or exercise.
- Example: “I will try practicing double bass drumming with different foot techniques.”
-
Stay Positive:
- Don’t get discouraged by setbacks. Focus on your progress and celebrate your achievements.
- Example: “I will remind myself that everyone struggles with drumming at times and that I will eventually overcome this challenge.”
-
Take Breaks:
- Sometimes, taking a break can help you come back to the problem with a fresh perspective.
- Example: “I will take a day off from practicing double bass drumming and come back to it tomorrow.”
7. The Importance of Rhythm and Timing Exercises
Rhythm and timing are the cornerstones of drumming. Here are some exercises to improve these skills:
-
Metronome Practice:
- Play basic drum beats with a metronome. Start at a slow tempo and gradually increase the speed.
- Focus on maintaining a steady beat and avoiding rushing or dragging.
-
Subdivision Exercises:
- Subdivide each beat into smaller units (e.g., eighth notes, sixteenth notes).
- This helps you develop a more precise sense of timing.
-
Polyrhythm Practice:
- Play different rhythms simultaneously with your hands and feet.
- This improves your coordination and rhythmic independence.
-
Groove Analysis:
- Listen to your favorite songs and analyze the drum parts.
- Try to identify the underlying rhythms and grooves.
-
Improvisation:
- Improvise over different time signatures and tempos.
- This helps you develop your creativity and rhythmic feel.
8. Developing Coordination and Independence on the Drums
Coordination and independence are essential for playing complex drum beats and fills. Here’s how to develop these skills:
-
Start with Basic Patterns:
- Begin with simple exercises that involve coordinating your hands and feet.
- Example: Play a basic rock beat with your right hand on the hi-hat, left hand on the snare drum, and right foot on the bass drum.
-
Gradually Increase Complexity:
- As you become more comfortable with the basic patterns, gradually increase the complexity by adding new elements.
- Example: Add a left foot hi-hat pattern to the basic rock beat.
-
Practice Rudiments:
- Rudiments are the building blocks of drumming. Practicing rudiments can improve your technique, coordination, and independence.
- Example: Practice single stroke rolls, double stroke rolls, and paradiddles with your hands and feet.
-
Use a Practice Pad:
- Practice pads are a great way to work on your technique and coordination without disturbing others.
- Example: Practice rudiments on a practice pad while watching TV.
-
Play Along with Music:
- Playing along with music is a fun and effective way to develop your coordination and independence.
- Example: Play along with your favorite songs and try to match the drum parts.
-
Record Yourself:
- Recording yourself allows you to identify areas for improvement.
- Example: Record yourself playing a drum beat and listen back to check your coordination and independence.
9. Exploring Different Drumming Styles and Genres
Expanding your knowledge of different drumming styles can make you a more versatile and in-demand drummer. Consider these genres:
| Genre | Characteristics | Key Drummers |
|---|---|---|
| Rock | Strong backbeat, emphasis on snare and bass drum, powerful fills | John Bonham (Led Zeppelin), Dave Grohl (Nirvana, Foo Fighters), Neil Peart (Rush) |
| Jazz | Swing rhythms, complex syncopation, improvisation, use of cymbals | Buddy Rich, Elvin Jones, Max Roach |
| Funk | Syncopated rhythms, emphasis on groove, use of ghost notes | Clyde Stubblefield (James Brown), David Garibaldi (Tower of Power), Chad Smith (Red Hot Chili Peppers) |
| Metal | Fast tempos, double bass drumming, aggressive fills, use of blast beats | Lars Ulrich (Metallica), Dave Lombardo (Slayer), Mike Portnoy (Dream Theater) |
| Latin | Complex rhythms, use of percussion instruments, clave patterns | Tito Puente, Giovanni Hidalgo, Horacio “El Negro” Hernandez |
| Electronic | Use of drum machines and electronic drums, repetitive patterns, emphasis on sound design | Aphex Twin, Squarepusher, The Chemical Brothers |
| World Music | Incorporates rhythms and styles from different cultures, use of traditional instruments | Zakir Hussain (Indian tabla), Stewart Copeland (The Police), Mickey Hart (Grateful Dead) |
10. The Mental Aspects of Learning Drums
Mental preparation is just as important as physical practice. Here’s how to cultivate a positive mindset:
-
Set Realistic Expectations:
- Understand that learning drums takes time and effort. Don’t expect to become a virtuoso overnight.
- Example: “I will set a goal to learn one new drum beat per week.”
-
Focus on Progress, Not Perfection:
- Celebrate your achievements, no matter how small.
- Example: “I will be proud of myself for learning a new rudiment, even if it’s not perfect yet.”
-
Stay Motivated:
- Find ways to stay motivated and engaged in your practice.
- Example: “I will listen to my favorite drummers and try to emulate their playing.”
-
Be Patient:
- Learning drums can be frustrating at times. Be patient with yourself and don’t give up.
- Example: “I will remind myself that everyone struggles with drumming at times and that I will eventually overcome the challenges.”
-
Enjoy the Process:
- Drumming should be fun. If you’re not enjoying it, you’re less likely to stick with it.
- Example: “I will focus on the joy of making music and expressing myself through drumming.”
11. Tools and Technologies That Aid Drum Learning
Modern technology provides numerous tools to enhance your drumming journey:
-
Metronome Apps:
- Function: Helps you develop a steady sense of time.
- Features: Adjustable tempo, time signature settings, and visual cues.
- Examples: Pro Metronome, Tempo, and Drum Metronome.
-
Drumming Apps:
- Function: Provides interactive lessons, drum beats, and exercises.
- Features: Drum notation, video tutorials, and progress tracking.
- Examples: Real Drum, Drum Guru, and GarageBand.
-
Recording Software:
- Function: Allows you to record and analyze your playing.
- Features: Multitrack recording, editing tools, and audio effects.
- Examples: Audacity, GarageBand, and Pro Tools.
-
Online Drumming Communities:
- Function: Connects you with other drummers for support, feedback, and collaboration.
- Features: Forums, chat rooms, and social media groups.
- Examples: Drummerworld, Reddit’s r/drums, and Facebook drumming groups.
-
Electronic Drum Sets:
- Function: Provides a quiet and versatile practice option.
- Features: Multiple drum sounds, headphone output, and USB connectivity.
- Examples: Roland V-Drums, Yamaha DTX, and Alesis Nitro Mesh.
12. The Benefits of Joining a Drumming Community
Being part of a drumming community can greatly enhance your learning experience:
-
Support and Encouragement:
- Connect with other drummers who share your passion.
- Receive support and encouragement when you’re struggling.
-
Feedback and Advice:
- Get feedback on your playing from experienced drummers.
- Receive advice on how to improve your technique, coordination, and independence.
-
Learning Opportunities:
- Learn from other drummers’ experiences.
- Discover new techniques, styles, and genres.
-
Networking:
- Meet other musicians and build relationships.
- Find opportunities to play in bands, ensembles, and jam sessions.
-
Motivation:
- Stay motivated and engaged in your drumming practice.
- See other drummers’ progress and achievements.
13. Tips for Maintaining Motivation and Enjoyment
Staying motivated is crucial for long-term success. Here’s how to keep drumming fun:
-
Set Realistic Goals:
- Start with achievable goals. Gradually increase the difficulty as you progress.
- Example: “I will learn one new drum beat per week.”
-
Choose Music You Enjoy:
- Play songs that you love. This will make practice more enjoyable.
- Example: “I will play along with my favorite rock songs.”
-
Vary Your Practice:
- Mix up your practice routine to keep things interesting.
- Example: Alternate between rudiments, drum beats, and playing along with songs.
-
Join a Band or Ensemble:
- Playing with other musicians is a great way to stay motivated and have fun.
- Example: “I will join a local rock band.”
-
Perform for Others:
- Performing for others can be a rewarding experience.
- Example: “I will play drums at a local open mic night.”
-
Record Yourself:
- Recording your playing allows you to track your progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Example: “I will record myself playing a drum beat and listen back to check my timing and technique.”
-
Take Breaks:
- Sometimes, taking a break can help you come back to drumming with a fresh perspective.
- Example: “I will take a day off from practicing drums and come back to it tomorrow.”
14. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Learning Drums
Avoid these common pitfalls to accelerate your progress:
-
Poor Technique:
- Using incorrect grip, posture, or stroke technique can lead to injuries and limit your progress.
- Solution: Focus on developing proper technique from the beginning. Watch instructional videos, consult a drum teacher, and practice slowly and deliberately.
-
Neglecting Fundamentals:
- Skipping over basic techniques and rudiments can hinder your ability to play more complex rhythms and fills.
- Solution: Dedicate time to practicing fundamentals every day. These are the building blocks of more advanced playing.
-
Rushing Through Practice:
- Practicing too quickly or without focus can lead to mistakes and bad habits.
- Solution: Practice slowly and deliberately. Focus on accuracy and consistency.
-
Ignoring Rhythm and Timing:
- Neglecting to practice with a metronome or develop a steady sense of time can make it difficult to play in time with other musicians.
- Solution: Practice with a metronome regularly. Play along with simple songs and focus on maintaining a steady beat.
-
Comparing Yourself to Others:
- Comparing yourself to more experienced drummers can lead to discouragement and frustration.
- Solution: Focus on your own progress and celebrate your achievements. Remember that everyone learns at their own pace.
-
Giving Up Too Easily:
- Learning drums can be challenging at times. Giving up too easily can prevent you from reaching your full potential.
- Solution: Stay persistent and patient. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks. Remember why you started playing drums in the first place.
15. How to Practice Effectively When Short on Time
Even with a busy schedule, you can make progress with efficient practice:
-
Prioritize Practice:
- Make drumming a priority in your life. Schedule time for practice and stick to it as much as possible.
- Example: “I will practice drums for 30 minutes every evening after work.”
-
Break It Down:
- Divide your practice into smaller, more manageable chunks.
- Example: “I will practice rudiments for 15 minutes and drum beats for 15 minutes.”
-
Focus on Fundamentals:
- Spend time working on basic techniques and rudiments. These are the building blocks of more advanced playing.
- Example: Practice single stroke rolls, double stroke rolls, and paradiddles.
-
Use a Practice Pad:
- Practice pads are a great way to work on your technique and coordination without disturbing others.
- Example: Practice rudiments on a practice pad while watching TV.
-
Listen to Music:
- Listen to your favorite songs and analyze the drum parts.
- This can help you learn new rhythms and styles.
-
Visualize:
- Visualize yourself playing drums. This can help you improve your technique and coordination.
16. Essential Drum Rudiments for Skill Development
Rudiments are the foundational exercises that improve your stick control, coordination, and creativity. Here are some essential ones:
-
Single Stroke Roll:
- Alternating strokes between your right and left hands.
- Helps develop speed, control, and evenness.
-
Double Stroke Roll:
- Two strokes with each hand in quick succession.
- Essential for smooth and fluid playing.
-
Paradiddle:
- A combination of single and double strokes (RLRR LRLL).
- Enhances coordination and independence.
-
Flam:
- Two strokes played almost simultaneously.
- Adds flavor and texture to your playing.
-
Drag:
- Two grace notes followed by a main note.
- Creates a unique rhythmic effect.
17. Strategies for Memorizing Drum Beats and Fills
Memorizing drum patterns is crucial for performing confidently. Here’s how:
-
Break It Down:
- Divide the drum beat or fill into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Example: “I will break down the drum beat into the bass drum pattern, snare drum pattern, and hi-hat pattern.”
-
Practice Slowly:
- Practice the drum beat or fill slowly and deliberately.
- Focus on accuracy and consistency.
-
Use Visual Aids:
- Write out the drum beat or fill in drum notation.
- This can help you visualize the pattern.
-
Listen Repeatedly:
- Listen to the drum beat or fill repeatedly.
- This can help you internalize the pattern.
-
Play Along with Music:
- Play along with the song that contains the drum beat or fill.
- This can help you memorize the pattern in context.
-
Visualize:
- Visualize yourself playing the drum beat or fill.
- This can help you improve your muscle memory.
-
Practice Regularly:
- Practice the drum beat or fill regularly.
- This will help you retain the pattern over time.
18. Tips for Playing Drums in a Band or Ensemble
Playing with other musicians requires different skills than solo practice:
-
Listen Carefully:
- Pay attention to the other musicians in the band.
- Listen to their dynamics, phrasing, and timing.
-
Keep Time:
- Your primary job as a drummer is to keep time.
- Focus on maintaining a steady beat and avoiding rushing or dragging.
-
Support the Music:
- Play drum parts that complement the music.
- Avoid overplaying or distracting from the other musicians.
-
Communicate Effectively:
- Communicate with the other musicians about tempos, dynamics, and song arrangements.
- Use hand signals or verbal cues to indicate changes.
-
Be Flexible:
- Be willing to adapt your playing to the needs of the band.
- Be open to suggestions from the other musicians.
-
Have Fun:
- Playing in a band should be a fun and rewarding experience.
- Relax, enjoy the music, and let your personality shine through.
19. Drumming Exercises to Improve Speed and Endurance
Speed and stamina are crucial for playing demanding drum parts:
-
Endurance Practice:
- Play a simple drum beat for an extended period of time.
- Focus on maintaining a steady beat and avoiding fatigue.
-
Interval Training:
- Alternate between periods of fast playing and periods of rest.
- This can help you build your speed and endurance.
-
Hand Exercises:
- Practice hand exercises to improve your strength and dexterity.
- Examples: Squeezing a stress ball, using a hand gripper, and doing wrist curls.
-
Foot Exercises:
- Practice foot exercises to improve your bass drum technique.
- Examples: Heel-toe technique, swivel technique, and constant spring technique.
-
Warm-Up:
- Warm up your muscles before each practice session.
- This can help prevent injuries.
-
Cool-Down:
- Cool down your muscles after each practice session.
- This can help prevent soreness.
20. How to Record Your Drums for Self-Assessment and Improvement
Recording your drumming allows you to analyze your performance objectively:
-
Choose the Right Equipment:
- Select a microphone that is appropriate for recording drums.
- Use a recording interface to connect the microphone to your computer.
- Choose recording software that is easy to use and has the features you need.
-
Set Up Your Recording Space:
- Choose a quiet room with good acoustics.
- Position the microphone correctly.
- Adjust the levels to avoid clipping.
-
Record Your Playing:
- Record yourself playing drum beats, fills, and solos.
- Be sure to record for several minutes at a time.
-
Listen Back Carefully:
- Listen back to your recording and identify areas for improvement.
- Pay attention to your timing, technique, and sound.
-
Make Notes:
- Make notes on what you need to work on.
- Use these notes to guide your future practice sessions.
21. The Importance of Ear Protection for Drummers
Protecting your hearing is essential for a long and healthy drumming career:
-
Use Earplugs:
- Wear earplugs whenever you’re playing drums or attending loud concerts.
- Choose earplugs that are designed for musicians.
-
Limit Exposure:
- Limit your exposure to loud noise.
- Take breaks from playing drums.
-
Turn Down the Volume:
- Turn down the volume of your drums and other instruments.
- Use a volume control pedal to adjust the volume of your headphones.
-
Get Regular Checkups:
- Get your hearing checked regularly by an audiologist.
- This can help you detect hearing loss early on.
22. Advanced Drumming Techniques to Explore
Once you’ve mastered the basics, consider exploring these advanced techniques:
-
Moeller Technique:
- A technique that uses the natural rebound of the drumstick to generate power and speed.
- Allows you to play faster and with less effort.
-
Heel-Toe Technique:
- A technique for playing double bass drum that involves using both the heel and toe of your foot.
- Allows you to play faster and more complex double bass drum patterns.
-
Swivel Technique:
- A technique for playing double bass drum that involves swiveling your foot from side to side.
- Allows you to play with more power and control.
-
Ghost Notes:
- Very soft notes played on the snare drum.
- Adds a subtle rhythmic texture to your playing.
-
Odd Time Signatures:
- Time signatures that are not divisible by two or four.
- Adds a unique and challenging element to your playing.
23. The Role of Drum Tuning in Achieving Optimal Sound
Proper drum tuning is crucial for achieving the desired sound:
-
Understanding Drum Anatomy:
- Learn the different parts of a drum (e.g., head, shell, hoops, lugs).
- Understand how each part affects the sound.
-
Choosing the Right Heads:
- Select drumheads that are appropriate for your playing style and the sound you want to achieve.
- Consider the thickness, material, and coating of the drumhead.
-
Tuning the Drums:
- Tune the drums to the correct pitch.
- Use a drum key to adjust the tension of the drumheads.
-
Experimenting with Different Tunings:
- Experiment with different tunings to find the sound that you like best.
- Listen to recordings of your favorite drummers and try to emulate their sound.
-
Replacing Heads:
- Replace the drumheads when they become worn out or damaged.
- New drumheads will improve the sound of your drums.
24. How to Customize Your Drum Set to Fit Your Style
Customizing your drum set allows you to create a unique sound and playing experience:
-
Choose the Right Drums:
- Select drums that are appropriate for your playing style and the sound you want to achieve.
- Consider the size, material, and construction of the drums.
-
Choose the Right Cymbals:
- Select cymbals that are appropriate for your playing style and the sound you want to achieve.
- Consider the size, weight, and material of the cymbals.
-
Choose the Right Hardware:
- Select hardware that is sturdy, reliable, and easy to adjust.
- Consider the type of stands, pedals, and throne that you need.
-
Choose the Right Accessories:
- Select accessories that will enhance your playing experience.
- Consider the type of sticks, brushes, and mallets that you need.
-
Experiment with Different Setups:
- Experiment with different setups to find the configuration that works best for you.
- Consider the placement of the drums, cymbals, and hardware.
25. Career Paths for Professional Drummers
If you’re serious about drumming, here are some potential career paths:
-
Session Drummer:
- Record drums for other musicians in the studio.
- Requires versatility, adaptability, and professionalism.
-
Touring Drummer:
- Play drums for a band on tour.
- Requires stamina, reliability, and a willingness to travel.
-
Drum Teacher:
- Teach drums to students of all ages and levels.
- Requires patience, communication skills, and a passion for teaching.
-
Drum Technician:
- Maintain and repair drums for other musicians.
- Requires technical knowledge and attention to detail.
-
Drum Retailer:
- Sell drums and other drumming equipment.
- Requires knowledge of drums and excellent customer service skills.
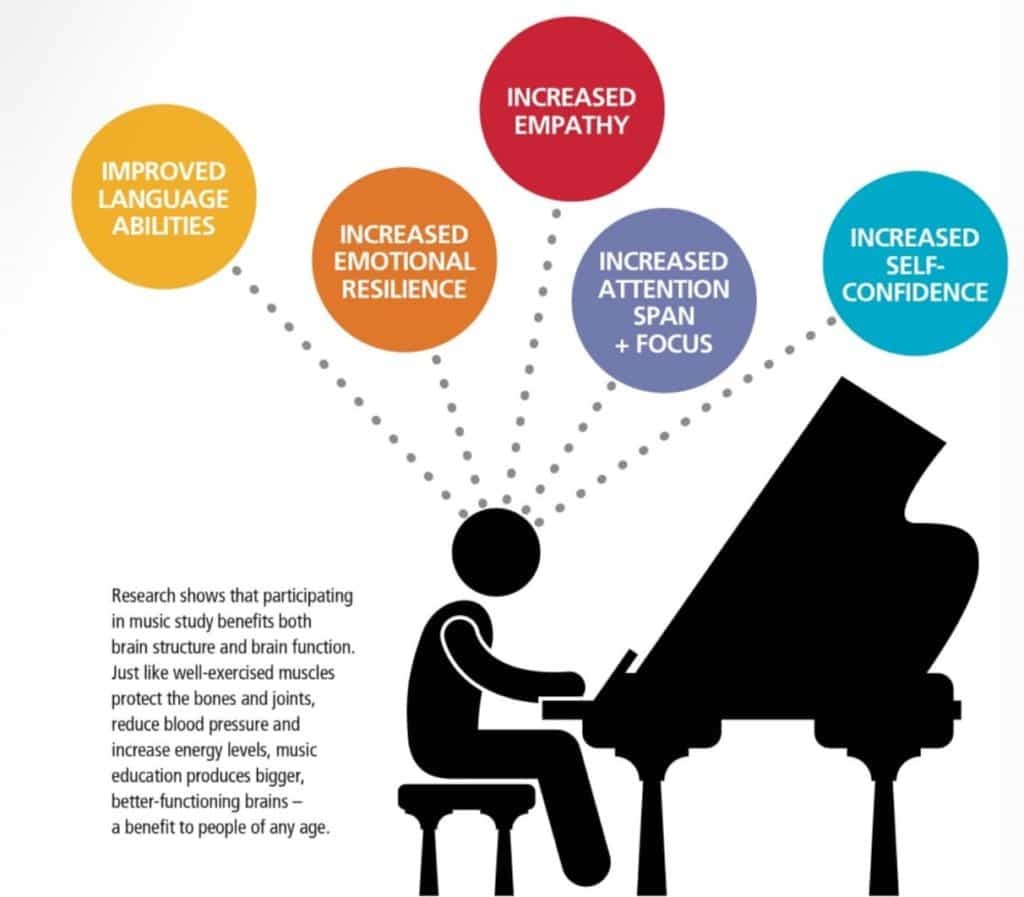
26. Drumming and Cognitive Benefits
Playing drums offers numerous cognitive benefits beyond musical skill:
-
Improved Coordination:
- Drumming requires coordinating your hands and feet, which can improve your overall coordination.
-
Enhanced Memory:
- Memorizing drum beats and fills can improve your memory.
-
Increased Focus:
- Drumming requires focus and concentration, which can improve your ability to focus on other tasks.
-
Reduced Stress:
- Drumming can be a great way to relieve stress and tension.
-
Improved Mood:
- Drumming can release endorphins, which can improve your mood.
-
Enhanced Creativity:
- Drumming can stimulate your creativity and imagination.
27. Drumming for Therapeutic Purposes
Drumming is used as a therapeutic tool to address various conditions:
-
Stress Reduction:
- Drumming can help reduce stress hormones and promote relaxation.
-
Emotional Release:
- Drumming can provide a safe and healthy way to express emotions.
-
Improved Social Interaction:
- Group drumming can improve social interaction and communication skills.
-
Cognitive Enhancement:
- Drumming can improve cognitive function and memory.
-
Physical Rehabilitation:
- Drumming can improve motor skills and coordination.
28. The Evolution of Drumming Throughout History
Drumming has a rich and diverse history spanning cultures and centuries:
-
Ancient Civilizations:
- Drums have been used in rituals, ceremonies, and warfare for thousands of years.
- Examples: African drums, Native American drums, and Asian drums.
-
The Birth of the Drum Set:
- The modern drum set evolved in the early 20th century.
- Drummers began to combine different percussion instruments into a single kit.
-
The Rise of Popular Music:
- Drumming played a key role in the development of jazz, blues, rock, and other popular genres.
- Famous drummers like Gene Krupa, Buddy Rich, and Ringo Starr helped shape the sound of popular music.
-
The Electronic Revolution:
- The invention of electronic drums and drum machines revolutionized drumming in the 1980s.
- Drummers began to experiment with new sounds and rhythms.
-
The Modern Era:
- Drumming continues to evolve in the 21st century.
- Drummers are incorporating new technologies and techniques into their playing.
29. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Learning Drums
- Is it hard to learn drums as an adult?
- Not at all! Adults can learn drums effectively with focused effort and the right resources, such as those available on learns.edu.vn.
- How long does it take to become a proficient drummer?
- Proficiency varies based on your goals. Basic skills can be learned in a few months, while mastery takes several years of dedicated practice.
- Do I need a drum set to start learning?
- No, you can begin with a practice pad and sticks to develop fundamental techniques before investing in a full drum set.
- Are electronic drums a good option for beginners?
- Yes,