Learning How I Learned To Sing can be an exciting and rewarding journey. Whether you’re dreaming of gracing the stage or simply want to improve your vocal skills, this guide, brought to you by LEARNS.EDU.VN, offers a comprehensive approach to self-taught singing, covering fundamental techniques and providing practical exercises for vocal development. Discover how to train your voice and unlock your singing potential!
1. Embracing the Journey: How I Learned To Sing
The desire to sing beautifully is a common one, and fortunately, it’s a skill that can be developed with practice and dedication. Many people wonder, “Can I learn to sing on my own?” or “How can I teach myself to sing?”. The answer is a resounding yes. The internet offers numerous resources, from apps to online tutorials, making it easier than ever to embark on your singing journey.
1.1. Setting the Stage: Why Learn to Sing?
Singing offers numerous benefits, both personally and professionally. It boosts confidence, reduces stress, and provides a creative outlet. For many, singing is a lifelong passion. Sites like LEARNS.EDU.VN can help you understand music theory and vocal exercises to improve your performance. Whether you aspire to sing professionally or simply enjoy singing in the shower, developing your vocal skills can significantly enhance your life. The ability to express yourself through song is a powerful and fulfilling experience.
1.2. Addressing Common Concerns: Can Anyone Learn to Sing?
One of the most frequently asked questions is whether singing is a natural talent or a learned skill. While some individuals may have a natural predisposition for singing, anyone can learn to sing with the right guidance and consistent practice. Overcoming the belief that you lack talent is the first step. LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources and support to help you unlock your vocal potential. Remember, even legendary singers started somewhere, often with self-taught techniques.
2. Laying the Foundation: Essential Singing Techniques
Before diving into specific exercises, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental techniques that underpin good singing. These techniques include posture, breath control, pitch accuracy, and vocal projection. Mastering these basics will provide a solid foundation for your vocal development and help you avoid common pitfalls.
2.1. The Power of Posture: Stand Tall and Sing Strong
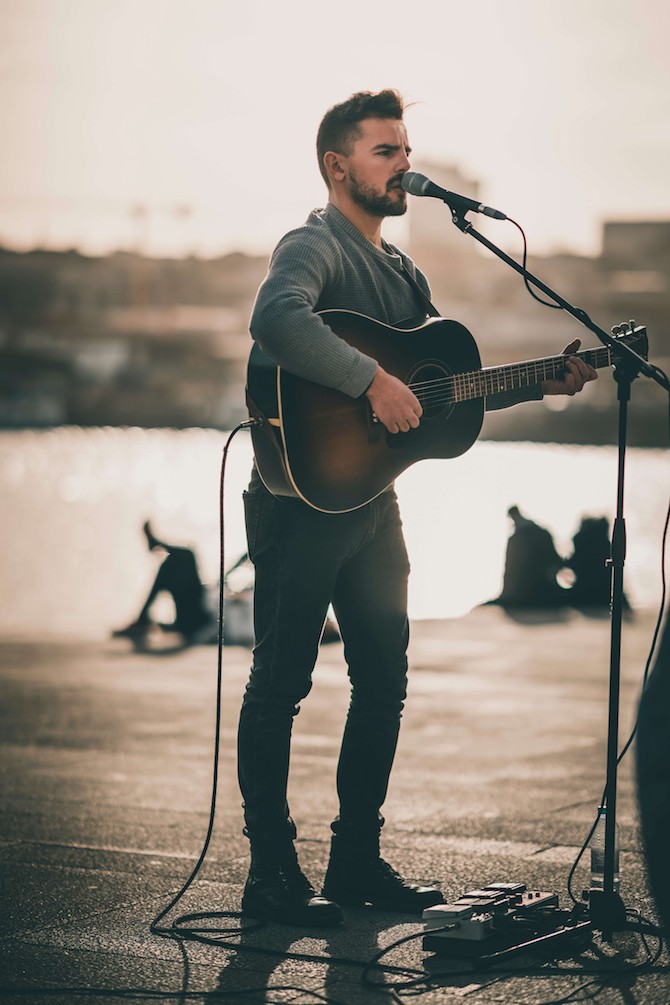 Person singing with correct posture and breathing techniques
Person singing with correct posture and breathing techniques
Posture plays a vital role in singing. Proper posture allows for optimal breath control and vocal resonance. The “tall posture” is ideal for singing, ensuring that your body is aligned to support your vocal cords.
2.1.1. Achieving the Tall Posture: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart: This provides a stable base of support.
- Align your shoulders with your hips and feet: Avoid slouching or leaning forward.
- Lift your chest comfortably: This opens up your ribcage and allows for fuller breaths.
- Keep your neck and chin straight: Avoid tilting your head up or down, as this can strain your vocal cords.
Practicing in front of a mirror can help you ensure that you are maintaining the correct posture. Regular practice will make the tall posture feel natural and improve your overall vocal performance.
2.2. Breath Control: The Engine of Your Voice
Breath control is arguably the most important aspect of singing. Proper breath support allows you to sustain notes, control your vocal dynamics, and avoid vocal fatigue. Diaphragmatic breathing, or breathing from your stomach, is the key to efficient breath control.
2.2.1. Mastering Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Simple Exercise
- Stand in front of a mirror: This allows you to observe your chest and stomach movements.
- Place your hands on your stomach: This helps you feel the movement of your diaphragm.
- Inhale deeply, allowing your stomach to expand: Your chest should remain relatively still.
- Exhale slowly, allowing your stomach to contract: Maintain a steady and controlled exhalation.
Practice this exercise regularly to develop your diaphragmatic breathing. You can also practice while lying down to further enhance your awareness of your diaphragm.
2.3. Pitch Perfect: Singing in Tune
Singing on pitch is essential for creating a pleasing and harmonious sound. Many aspiring singers struggle with pitch accuracy, but it’s a skill that can be improved with practice and feedback.
2.3.1. Improving Pitch Accuracy: A Practical Exercise
- Use a piano or pitch app: These tools provide a reference point for your pitch.
- Sing simple scales: Start with five-note scales and gradually increase the range.
- Record yourself singing: This allows you to identify areas where you are off-pitch.
- Listen critically to your recording: Pay attention to the notes that are sharp or flat.
Repeat this exercise regularly, focusing on matching your pitch to the reference notes. Consider using a vocal coach or online resources for additional guidance and feedback.
2.4. Projecting Your Voice: Be Heard and Be Confident
Vocal projection is the ability to sing loudly and clearly without straining your voice. Proper projection ensures that your voice reaches your audience and conveys your message effectively.
2.4.1. Enhancing Vocal Projection: A Simple Technique
- Choose a phrase from a song: Select a phrase that you want to sing with more power.
- Speak the phrase aloud: Imagine you are addressing a large audience and need to be heard clearly.
- “Speak-sing” the phrase: Maintain the same feeling of projection while singing the notes.
This technique helps you apply the natural resonance and projection of your speaking voice to your singing. Practice regularly to develop your vocal projection and confidence.
3. Exploring Vocal Registers: Chest, Head, and Mixed Voice
Understanding your vocal registers is crucial for expanding your vocal range and achieving a balanced and controlled sound. The three primary vocal registers are chest voice, head voice, and mixed voice.
3.1. Chest Voice: The Power of Your Lower Range
Chest voice refers to the notes in the lower part of your vocal range. It’s characterized by a strong and resonant sound, similar to your speaking voice.
3.1.1. Developing Your Chest Voice: An Exercise
- Place your hand on your chest: This helps you feel the vibrations of your chest voice.
- Say the word “Gug” aloud: Use a strong and projected volume.
- Sing the word “Gug” on a comfortable note: Maintain the same strength and projection.
- Sing the “Gug” on a five-note scale: This helps you develop your chest voice across a range of notes.
Focus on maintaining a strong and resonant sound throughout the exercise. Regular practice will help you strengthen and develop your chest voice.
3.2. Head Voice: The Lightness of Your Upper Range
Head voice refers to the notes in the upper part of your vocal range. It’s characterized by a lighter and more ethereal sound, often described as floating or airy.
3.2.1. Accessing Your Head Voice: An Exercise
- Place your hand on the back of your neck: This helps you feel the vibrations of your head voice.
- Sing the vowel “ooh” as in “oops”: Use a light and relaxed tone.
- Sing a vocal siren: Start on a low note and glide up to the top of your range and back down.
Focus on maintaining a light and relaxed sound throughout the exercise. Regular practice will help you access and develop your head voice.
3.3. Mixed Voice: Bridging the Gap
Mixed voice is the blend of chest and head voice that allows you to sing seamlessly across your entire vocal range. It’s characterized by a balanced and controlled sound, without any noticeable breaks or shifts in register.
3.3.1. Developing Your Mixed Voice: An Exercise
- Say the word “Gee” as in “Geese” aloud: Use a comfortable volume.
- Sing the word “Gee” on a comfortable note: Maintain the same power as when you spoke it.
- Sing the word “Gee” on an octave and a half scale: Replace each note of the scale with the word “Gee”.
Focus on maintaining a consistent sound throughout the scale, without any noticeable breaks or shifts in register. Regular practice will help you develop your mixed voice and bridge the gap between your chest and head voice.
4. Adding Flair: Vibrato and Belting
Once you have a solid foundation in the fundamental techniques and vocal registers, you can start exploring more advanced techniques like vibrato and belting.
4.1. Vibrato: The Shimmering Effect
Vibrato is a slight, rapid variation in pitch that adds warmth and expressiveness to your voice. It’s a natural phenomenon that occurs when your vocal cords are relaxed and your breath is controlled.
4.1.1. Developing Your Vibrato: An Exercise
- Place your fingers on your solar plexus: This helps you feel the movement of your diaphragm.
- Sing and hold an “ee” vowel (like “eat”) on a comfortable note: Maintain a relaxed and controlled breath.
- Pulse into your stomach with your fingers: This creates a slight variation in pitch.
Focus on maintaining a relaxed and controlled breath throughout the exercise. Regular practice will help you develop your vibrato and add a shimmering effect to your voice.
4.2. Belting: The Powerful High Notes
Belting is a technique that allows you to sing high notes with the power and intensity of your chest voice. It’s often used in musical theater and pop music to create a dramatic and exciting effect.
4.2.1. Learning to Belt Safely: An Exercise
- Say the word “Nae” as in “Nasty” aloud in a bratty way: This helps you engage the muscles needed for belting.
- Sing the “bratty Nae” on a comfortable note: Maintain the same bright and brassy sound.
- Sing the “bratty Nae” on an octave repeat scale: Repeat the top note four times.
Focus on maintaining a bright and brassy sound throughout the exercise. Avoid pushing or straining your voice. Regular practice will help you develop your belting technique and sing high notes with power and confidence.
5. Putting It All Together: Singing Songs
The ultimate goal of vocal training is to sing songs beautifully. Once you have a solid foundation in the fundamental techniques and advanced techniques, you can start applying them to your favorite songs.
5.1. Breaking Down Songs: A Simple Exercise
- Select a phrase of a song that’s been difficult for you: Choose a phrase that challenges your vocal skills.
- Sing the melody of the phrase, replacing each word with the vocal exercise “Gee”: This helps you focus on the melody and vocal technique without the distraction of the lyrics.
- Go back to the lyrics and sing the words with the same feeling that you got with the “Gee” exercise: This helps you apply the improved vocal technique to the actual song.
This exercise helps you isolate and address specific challenges in a song. Regular practice will help you improve your overall singing ability and perform your favorite songs with confidence.
6. Advanced Techniques for Vocal Mastery
As you progress in your singing journey, incorporating advanced techniques can elevate your performance. These include vocal agility, ornamentation, and stylistic interpretation.
6.1. Vocal Agility: Navigating Melodic Runs
Vocal agility is the ability to move quickly and smoothly between notes, often seen in complex melodic runs. Developing vocal agility requires precise coordination of breath control, vocal cord engagement, and articulation.
6.1.1. Enhancing Vocal Agility: Scale Variations
- Practice staccato scales: Singing each note short and detached helps in developing precise control.
- Incorporate trills and mordents: These ornaments enhance the fluidity between notes.
- Use a metronome: Gradually increase the tempo to improve speed without sacrificing accuracy.
Regular practice with these exercises builds the necessary muscle memory and coordination for executing rapid melodic runs with ease.
6.2. Ornamentation: Adding Personal Flourishes
Ornamentation involves adding decorative notes and flourishes to a melody, enhancing its expressiveness. Common ornaments include appoggiaturas, grace notes, and turns.
6.2.1. Mastering Ornamentation: Embellishing Melodies
- Study recordings of skilled vocalists: Pay attention to how they incorporate ornaments.
- Start with simple ornaments: Add grace notes before main notes to create a subtle embellishment.
- Experiment with different ornaments: Try adding turns or trills to sustained notes.
Effective ornamentation adds depth and character to your singing, making your performance more engaging and personal.
6.3. Stylistic Interpretation: Conveying Emotion and Meaning
Stylistic interpretation involves understanding and conveying the emotional and contextual nuances of a song. This includes dynamics, phrasing, and emotional expression.
6.3.1. Developing Stylistic Interpretation: Deep Dive into Music
- Analyze song lyrics and context: Understand the story and emotions the song conveys.
- Experiment with dynamics: Vary the volume to highlight emotional peaks and valleys.
- Focus on phrasing: Shape melodies with pauses and breaths to enhance meaning.
Understanding and conveying the stylistic elements of a song brings it to life, connecting with the audience on a deeper emotional level.
7. Maintaining Vocal Health: A Singer’s Lifestyle
Maintaining good vocal health is essential for any singer. This includes proper hydration, avoiding irritants, and getting adequate rest.
7.1. Hydration: Fueling Your Voice
Hydration is crucial for keeping your vocal cords lubricated and functioning optimally.
7.1.1. Staying Hydrated: Practical Tips
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day: Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily.
- Avoid sugary and caffeinated beverages: These can dehydrate your vocal cords.
- Use a humidifier: This helps keep your vocal cords moist, especially in dry environments.
Proper hydration ensures that your vocal cords remain healthy and resilient.
7.2. Avoiding Irritants: Protecting Your Voice
Certain substances can irritate your vocal cords and negatively impact your singing.
7.2.1. Minimizing Irritants: Smart Choices
- Avoid smoking: Smoking is a major irritant that can damage your vocal cords.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Alcohol can dehydrate your vocal cords and impair your coordination.
- Avoid excessive throat clearing: This can irritate your vocal cords.
Minimizing irritants protects your vocal cords and helps you maintain a clear and healthy voice.
7.3. Rest and Recovery: Recharging Your Voice
Rest is essential for allowing your vocal cords to recover from strain and fatigue.
7.3.1. Prioritizing Rest: Essential Habits
- Get adequate sleep: Aim for at least seven to eight hours of sleep per night.
- Avoid overusing your voice: Take breaks during long rehearsals or performances.
- Listen to your body: If your voice feels tired or strained, rest it.
Prioritizing rest and recovery ensures that your vocal cords remain healthy and strong.
8. Tools and Resources for Self-Taught Singers
Numerous tools and resources can assist you in your self-taught singing journey. These include online courses, vocal exercises, and feedback platforms.
8.1. Online Courses: Structured Learning
Online courses provide a structured and comprehensive approach to learning how to sing.
8.1.1. Choosing the Right Course: Key Considerations
- Look for courses taught by experienced vocal coaches: Ensure that the instructor has a proven track record.
- Check the course curriculum: Ensure that it covers the fundamental techniques and advanced techniques that you want to learn.
- Read reviews from other students: Get an idea of the course’s quality and effectiveness.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a variety of online courses designed to help you develop your singing skills.
8.2. Vocal Exercises: Targeted Practice
Vocal exercises help you target specific areas of your voice and improve your technique.
8.2.1. Incorporating Vocal Exercises: Effective Routines
- Warm-up exercises: Prepare your voice for singing.
- Technique-focused exercises: Improve your posture, breath control, and vocal registers.
- Cool-down exercises: Relax your vocal cords after singing.
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides a range of vocal exercises to help you develop your singing skills.
8.3. Feedback Platforms: Constructive Criticism
Feedback is essential for identifying areas where you can improve your singing.
8.3.1. Seeking Feedback: Valuable Insights
- Record yourself singing: This allows you to hear your voice objectively.
- Share your recordings with other singers: Get their feedback on your technique and performance.
- Consider working with a vocal coach: A vocal coach can provide personalized feedback and guidance.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a platform for sharing your recordings and receiving feedback from other singers and vocal coaches.
9. Overcoming Challenges: Common Obstacles and Solutions
Learning to sing can be challenging, and you may encounter obstacles along the way. It’s important to identify these challenges and develop strategies for overcoming them.
9.1. Vocal Fatigue: Managing Strain
Vocal fatigue is a common challenge for singers, especially those who are new to vocal training.
9.1.1. Addressing Vocal Fatigue: Practical Solutions
- Warm-up your voice before singing: This prepares your vocal cords for the demands of singing.
- Use proper breath control: This helps you avoid straining your voice.
- Take breaks during long rehearsals or performances: This allows your vocal cords to recover.
If you experience persistent vocal fatigue, consult with a vocal coach or medical professional.
9.2. Stage Fright: Building Confidence
Stage fright is a common anxiety experienced by performers. It can manifest as nervousness, trembling, and difficulty focusing.
9.2.1. Conquering Stage Fright: Effective Strategies
- Prepare thoroughly: Practice your material until you feel confident and comfortable.
- Visualize success: Imagine yourself performing well and receiving positive feedback.
- Use relaxation techniques: Deep breathing and meditation can help calm your nerves.
With practice and preparation, you can overcome stage fright and perform with confidence.
9.3. Plateauing: Breaking Through
Plateaus are periods where you feel like you’re not making progress in your singing.
9.3.1. Breaking Through Plateaus: Innovative Approaches
- Try new vocal exercises: Introduce new challenges to stimulate your voice.
- Work with a vocal coach: Get personalized feedback and guidance.
- Focus on different genres of music: Explore new styles to expand your vocal skills.
By trying new approaches and seeking expert guidance, you can break through plateaus and continue to improve your singing.
10. Continuing Education: Lifelong Learning
The journey of learning to sing is a lifelong endeavor. There’s always something new to learn and explore.
10.1. Advanced Vocal Techniques: Polishing Your Skills
As you progress, you can explore more advanced vocal techniques, such as improvisation and vocal effects.
10.1.1. Exploring Advanced Techniques: Expanding Horizons
- Study different vocal styles: Learn from singers in various genres.
- Experiment with improvisation: Create your own melodies and harmonies.
- Learn about vocal effects: Use technology to enhance your voice.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources and guidance to help you explore advanced vocal techniques.
10.2. Joining Vocal Communities: Connecting with Others
Connecting with other singers can provide valuable support and inspiration.
10.2.1. Engaging with Vocal Communities: Shared Experiences
- Join a choir or vocal ensemble: Sing with other people and learn from their experiences.
- Attend vocal workshops and conferences: Network with other singers and learn from experts.
- Participate in online vocal communities: Share your experiences and get feedback from other singers.
LEARNS.EDU.VN hosts an online vocal community where you can connect with other singers and share your experiences.
10.3. Setting New Goals: Continuous Improvement
Setting new goals is essential for maintaining motivation and continuing to improve your singing.
10.3.1. Defining New Goals: Personal Growth
- Identify areas where you want to improve: Focus on specific skills or techniques.
- Set realistic and achievable goals: Break down your goals into smaller steps.
- Track your progress: Monitor your improvement and celebrate your successes.
By setting new goals and tracking your progress, you can continue to grow as a singer and achieve your full potential.
The journey of how I learned to sing is one of continuous growth and discovery. Embrace the challenges, celebrate the successes, and never stop learning.
Ready to start your singing journey?
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for more resources, courses, and expert guidance. Our comprehensive materials and supportive community will help you unlock your vocal potential and achieve your singing goals.
Contact us today:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: learns.edu.vn
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Learning to Sing
Here are some frequently asked questions about learning to sing:
- Can anyone learn to sing, or is it a natural talent? While some people have a natural aptitude, anyone can learn to sing with proper training and practice.
- How long does it take to learn to sing well? It varies, but consistent practice can yield noticeable improvements in a few months.
- Is it better to take singing lessons or learn on my own? Singing lessons offer personalized feedback, but self-study can be effective with the right resources.
- What are the most important things to focus on when learning to sing? Posture, breath control, pitch accuracy, and vocal projection are key.
- How often should I practice singing? Aim for at least 30-60 minutes of practice most days of the week.
- What are some good vocal warm-up exercises? Humming, lip trills, and scale exercises are great for warming up.
- How can I improve my vocal range? Practice exercises that target your chest and head voice and gradually expand your range.
- How can I sing higher notes without straining? Use proper breath support and engage your mixed voice to avoid straining.
- What should I do if my voice feels tired or strained? Rest your voice and avoid singing until it recovers.
- What resources are available to help me learn to sing? Online courses, vocal exercises, feedback platforms, and vocal communities are all valuable resources.