How Long To Learn Guitar Basics is a common question, and at LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand the eagerness to start playing your favorite tunes. This guide offers a realistic timeline, effective strategies, and resources to help you master the fundamentals, making your guitar journey enjoyable and rewarding. Discover invaluable insights to accelerate your learning, improve your musical skills and embark on a fulfilling experience on LEARNS.EDU.VN.
1. Understanding the Guitar Learning Timeline
Learning to play the guitar is a journey, not a destination. There’s no magic number of hours or weeks that will suddenly transform you into a guitar hero. The time it takes to learn guitar basics varies significantly from person to person, influenced by factors like practice frequency, learning style, and prior musical experience. Let’s delve into a realistic timeline, breaking down the different phases and what you can expect at each stage.
1.1. Factors Influencing Learning Speed
Several factors play a crucial role in determining how quickly you grasp the guitar basics:
- Practice Consistency: Regular practice, even in short bursts, is more effective than infrequent, long sessions. Aim for daily practice, even if it’s just for 15-30 minutes.
- Learning Style: Some individuals learn best through visual aids, while others prefer auditory or kinesthetic approaches. Identifying your learning style can help you tailor your practice methods for optimal results.
- Prior Musical Experience: Having previous experience with other instruments or music theory can give you a head start in understanding musical concepts and developing coordination.
- Quality of Instruction: A good teacher or a well-structured online course can provide clear guidance, personalized feedback, and effective learning strategies. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wide range of courses to suit your needs.
- Motivation and Dedication: Your passion for playing the guitar and your commitment to practicing regularly will significantly impact your progress.
1.2. The Importance of Realistic Expectations
It’s crucial to set realistic expectations when starting your guitar journey. Avoid comparing yourself to others, as everyone learns at their own pace. Focus on your individual progress and celebrate small victories along the way. Remember, even the most accomplished guitarists started as beginners.
According to a study by the National Association for Music Education, setting achievable goals can significantly increase motivation and persistence in learning a musical instrument.
2. The Beginner Phase: Laying the Foundation (1-3 Months)
The initial phase of learning guitar basics typically lasts for 1-3 months. This is a critical period for establishing a solid foundation in fundamental techniques and musical concepts.
2.1. Essential Skills to Master
During the beginner phase, focus on mastering the following essential skills:
- Holding the Guitar Correctly: Proper posture and hand positioning are crucial for comfort, efficiency, and preventing injuries. Ensure the guitar is resting comfortably against your body, with your fretting hand relaxed and your picking hand positioned for smooth strumming or fingerpicking.
- Basic Chord Shapes: Learning a handful of basic open chords, such as A, D, E, G, C, and Am, will allow you to play a wide variety of songs. Focus on accuracy and clean transitions between chords.
- Strumming Patterns: Develop a consistent strumming pattern, starting with simple downstrokes and gradually incorporating upstrokes and variations. Practice strumming along to your favorite songs to improve your timing and rhythm.
- Finger Exercises: Finger exercises help build strength, dexterity, and coordination in your fretting hand. Practice scales, arpeggios, and chromatic exercises to improve your finger independence and accuracy.
- Basic Music Theory: Understanding basic music theory concepts, such as rhythm, time signatures, and chord progressions, will enhance your understanding of music and accelerate your learning.
2.2. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Beginners often face challenges such as:
- Finger Pain: Developing calluses on your fingertips is a natural part of learning guitar. Play in short bursts and gradually increase your practice time to allow your fingers to adjust.
- Chord Transitions: Switching smoothly between chords requires practice and coordination. Slow down your transitions and focus on accuracy before gradually increasing your speed.
- Frustration: Learning guitar can be challenging at times. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks. Celebrate your progress, focus on your goals, and seek support from teachers, online communities, or fellow guitarists.
2.3. Tips for Effective Practice
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your learning into smaller, manageable goals. Focus on mastering one chord or technique at a time.
- Practice Regularly: Aim for daily practice, even if it’s just for 15-30 minutes. Consistency is key to developing muscle memory and making progress.
- Use a Metronome: A metronome helps you develop a sense of timing and rhythm. Start with a slow tempo and gradually increase it as you improve.
- Record Yourself: Recording your practice sessions allows you to identify areas for improvement. Listen back to your playing and focus on correcting mistakes.
- Find a Practice Buddy: Practicing with a friend or fellow guitarist can be motivating and provide valuable feedback.
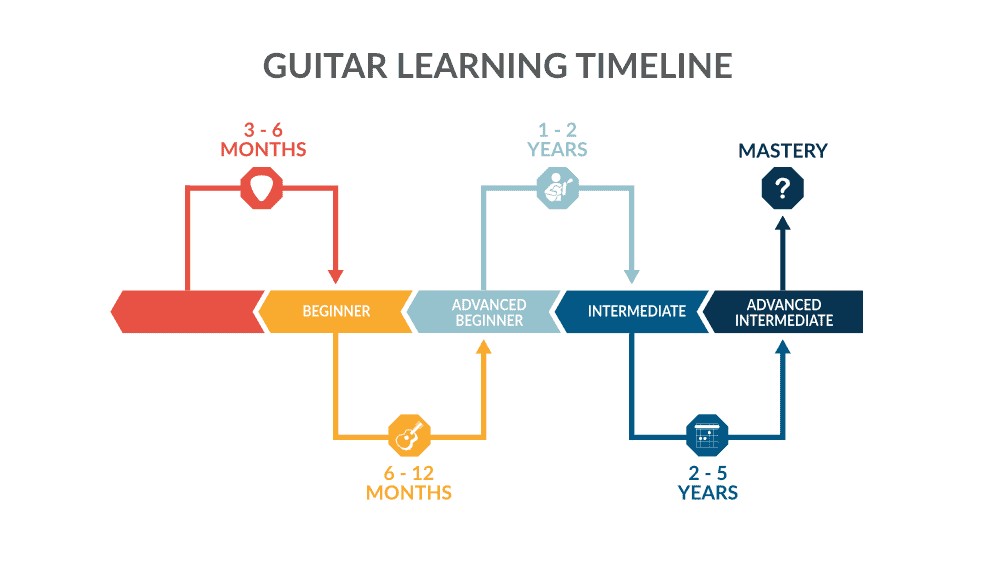
Guitar learning timeline showcasing the different phases of learning guitar and their respective timeframes.
3. The Intermediate Phase: Expanding Your Skills (3-12 Months)
After mastering the basics, you’ll enter the intermediate phase, which typically lasts from 3 to 12 months. This is where you’ll expand your skills, learn more complex techniques, and develop your musical expression.
3.1. Learning New Chords and Chord Progressions
Expand your chord vocabulary by learning barre chords, minor chords, seventh chords, and other variations. Experiment with different chord progressions and learn to play songs in different keys.
3.2. Developing Fingerpicking Techniques
Fingerpicking involves using your fingers instead of a pick to pluck the strings. This technique allows for greater control, nuance, and complexity in your playing. Learn basic fingerpicking patterns and gradually incorporate more advanced techniques.
3.3. Exploring Scales and Melodies
Learning scales is essential for understanding melody and improvisation. Start with basic scales like the major scale, minor scale, and pentatonic scale. Practice playing scales along to backing tracks and experiment with creating your own melodies.
3.4. Introduction to Music Theory
Delve deeper into music theory concepts such as:
- Key Signatures: Understanding key signatures will help you identify the notes and chords that are commonly used in a particular key.
- Chord Inversions: Chord inversions involve changing the order of the notes in a chord. This can create different voicings and add variety to your playing.
- Harmonic Progressions: Harmonic progressions are sequences of chords that create a sense of musical movement and direction. Learning common harmonic progressions will help you write your own songs and understand the structure of existing ones.
3.5. Developing Your Own Style
As you progress, start exploring different genres of music and experimenting with your own style. Listen to a wide variety of guitarists and identify elements of their playing that you admire. Incorporate these elements into your own playing and develop your unique voice on the guitar.
4. The Advanced Phase: Mastering the Instrument (12+ Months)
The advanced phase begins after approximately 12 months of dedicated practice. This is where you’ll refine your skills, master advanced techniques, and develop your own musical identity.
4.1. Advanced Techniques
Explore advanced techniques such as:
- Sweep Picking: Sweep picking involves using a single downstroke or upstroke to play multiple notes across adjacent strings. This technique allows for fast and fluid arpeggios.
- Tapping: Tapping involves using your fingers to tap notes on the fretboard. This technique allows for complex and unconventional melodies.
- Hybrid Picking: Hybrid picking combines the use of a pick and fingers to pluck the strings. This technique allows for greater versatility and control.
4.2. Improvisation
Improvisation is the art of creating music spontaneously. Learn to improvise over chord progressions using scales, modes, and your own musical ideas.
4.3. Songwriting
Songwriting is the process of creating original songs. Learn to write your own melodies, chord progressions, and lyrics. Experiment with different song structures and arrangements.
4.4. Performance
Performing in front of an audience is a great way to hone your skills and share your music with others. Start by performing for friends and family, and gradually work your way up to playing in public venues.
4.5. Continued Learning
Even advanced guitarists never stop learning. Continue to challenge yourself by learning new techniques, exploring different genres of music, and collaborating with other musicians.
A young man playing guitar, showcasing the dedication and passion required to progress from beginner to advanced levels.
5. Optimizing Your Guitar Learning Experience
To make the most of your guitar learning journey, consider the following tips:
5.1. Choose the Right Guitar
Selecting the right guitar is crucial for comfort, playability, and motivation. Consider factors such as:
- Guitar Type: Acoustic, electric, or classical guitar, depending on your musical preferences.
- Body Size: Smaller body sizes are generally easier for beginners to hold and play.
- Neck Profile: The shape and thickness of the neck can affect comfort and playability.
- String Action: Lower string action (the distance between the strings and the fretboard) makes it easier to press down the strings.
5.2. Find a Qualified Instructor
A qualified instructor can provide personalized guidance, effective learning strategies, and valuable feedback. Look for a teacher who is experienced, knowledgeable, and passionate about teaching guitar. LEARNS.EDU.VN can help you find the perfect instructor.
5.3. Utilize Online Resources
Numerous online resources are available to supplement your guitar learning, including:
- Online Courses: Structured online courses can provide comprehensive instruction and track your progress.
- Tutorial Videos: Tutorial videos offer step-by-step guidance on specific techniques and songs.
- Tablature Websites: Tablature websites provide simplified notations of songs, making them easier to learn.
- Guitar Apps: Guitar apps offer a variety of features such as tuners, metronomes, chord dictionaries, and practice games.
5.4. Join a Guitar Community
Connecting with other guitarists can provide motivation, support, and opportunities for collaboration. Join a local guitar club, online forum, or social media group.
5.5. Practice Mindfully
Mindful practice involves focusing your attention on the present moment and paying close attention to your technique, sound, and musical expression. Avoid distractions and practice with intention and purpose.
6. Common Pitfalls to Avoid
To ensure a smooth and successful guitar learning journey, be aware of these common pitfalls:
6.1. Neglecting the Fundamentals
Building a solid foundation in the fundamentals is essential for long-term progress. Don’t rush through the basics or skip important techniques.
6.2. Practicing Without a Plan
Randomly practicing without a plan can be inefficient and frustrating. Create a structured practice routine that addresses your specific goals and weaknesses.
6.3. Comparing Yourself to Others
Comparing yourself to other guitarists can lead to discouragement and self-doubt. Focus on your own progress and celebrate your achievements.
6.4. Giving Up Too Easily
Learning guitar takes time, effort, and dedication. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks or challenges. Persevere through the tough times and remember why you started playing guitar in the first place.
6.5. Ignoring Physical Discomfort
Playing guitar can put stress on your hands, wrists, and back. Pay attention to your body and take breaks when needed. Practice proper posture and hand positioning to prevent injuries.
7. The Benefits of Learning Guitar
Learning guitar offers numerous benefits, both musical and personal:
- Creativity and Self-Expression: Playing guitar allows you to express your creativity and emotions through music.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Learning guitar improves cognitive skills such as memory, attention, and problem-solving.
- Stress Relief: Playing guitar can be a relaxing and therapeutic activity that helps reduce stress and anxiety.
- Social Connection: Playing guitar provides opportunities for social connection and collaboration with other musicians.
- Personal Fulfillment: Learning guitar can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience that enhances your life in many ways.
According to a study by the University of California, San Francisco, playing a musical instrument can improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of dementia.
8. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the guitar learning timeline, let’s consider some real-world examples:
- Case Study 1: Sarah, the Busy Professional: Sarah, a full-time marketing manager, dedicated 30 minutes each day to practicing guitar. Within six months, she could play basic chords and strum along to her favorite songs. After a year, she joined a local band and started performing regularly.
- Case Study 2: David, the Aspiring Musician: David, a college student with a passion for music, practiced guitar for several hours each day. Within a year, he had mastered advanced techniques and started writing his own songs. He is now pursuing a career as a professional musician.
- Case Study 3: Emily, the Senior Citizen: Emily, a retired teacher, decided to learn guitar as a new hobby. She practiced at her own pace and focused on enjoying the process. Within a year, she could play simple melodies and chords, bringing joy to herself and others.
These examples demonstrate that anyone can learn guitar, regardless of their age, background, or level of experience.
9. Accelerating Your Learning with LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the resources and support you need to achieve your guitar learning goals. Our comprehensive platform offers:
- Structured Online Courses: Our courses are designed to guide you through the guitar learning process, from beginner to advanced levels.
- Expert Instructors: Our instructors are experienced, knowledgeable, and passionate about teaching guitar.
- Personalized Feedback: Receive personalized feedback on your playing from our instructors.
- Interactive Exercises: Practice your skills with our interactive exercises and track your progress.
- Community Support: Connect with other guitarists in our online community and share your experiences.
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN to explore our courses and start your guitar learning journey today.
10. The Role of Technology in Guitar Learning
Technology has revolutionized the way we learn guitar, offering a wide range of tools and resources to enhance the learning experience:
10.1. Guitar Learning Apps
Guitar learning apps provide interactive lessons, chord diagrams, scale charts, and other useful features. Many apps also offer personalized feedback and track your progress.
10.2. Online Guitar Tuners
Online guitar tuners make it easy to tune your guitar accurately. Simply play a string into your microphone and the tuner will tell you whether it’s in tune.
10.3. Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
DAWs are software programs that allow you to record, edit, and mix your guitar playing. DAWs are useful for songwriting, practicing improvisation, and creating professional-quality recordings.
10.4. Video Conferencing Tools
Video conferencing tools like Zoom and Skype make it easy to take online guitar lessons from anywhere in the world.
10.5. Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram are valuable resources for finding guitar tutorials, connecting with other guitarists, and sharing your music.
11. Maintaining Motivation and Avoiding Burnout
Learning guitar can be challenging at times, and it’s important to maintain motivation and avoid burnout. Here are some tips:
11.1. Set Achievable Goals
Setting achievable goals will help you stay motivated and track your progress. Break down your learning into smaller, manageable steps.
11.2. Celebrate Your Progress
Acknowledge and celebrate your accomplishments, no matter how small. This will help you stay positive and motivated.
11.3. Take Breaks When Needed
Don’t push yourself too hard. Take breaks when you feel tired or frustrated.
11.4. Find a Practice Buddy
Practicing with a friend or fellow guitarist can be motivating and fun.
11.5. Explore Different Genres
Experiment with different genres of music to keep your learning fresh and exciting.
11.6. Learn Your Favorite Songs
Learning your favorite songs will make practicing more enjoyable and rewarding.
11.7. Set Realistic Expectations
Learning guitar takes time and effort. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks.
According to research by Stanford University, having a growth mindset (believing that your abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work) can significantly improve your motivation and persistence in learning new skills.
12. The Importance of Ear Training
Ear training is the ability to identify notes, chords, and intervals by ear. Developing your ear is essential for understanding music, improvising, and writing your own songs.
12.1. How to Train Your Ear
There are several ways to train your ear:
- Interval Recognition: Practice identifying intervals (the distance between two notes) by ear.
- Chord Recognition: Practice identifying chords by ear.
- Melody Dictation: Practice writing down melodies that you hear.
- Transcription: Practice transcribing (writing down) songs that you hear.
12.2. Resources for Ear Training
Numerous online resources are available for ear training, including websites, apps, and courses.
13. Exploring Different Guitar Genres
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore different guitar genres, such as:
13.1. Rock
Rock guitar is characterized by distorted guitars, heavy drums, and catchy melodies.
13.2. Blues
Blues guitar is characterized by soulful melodies, improvisational solos, and a distinctive chord progression known as the 12-bar blues.
13.3. Country
Country guitar is characterized by twangy guitars, fingerpicking, and a focus on storytelling.
13.4. Jazz
Jazz guitar is characterized by complex chords, improvisation, and a sophisticated harmonic vocabulary.
13.5. Classical
Classical guitar is characterized by fingerpicking, a focus on melody, and a refined technique.
14. Choosing the Right Equipment and Accessories
Having the right equipment and accessories can enhance your guitar playing experience:
14.1. Guitar Picks
Guitar picks come in different thicknesses and materials. Experiment with different picks to find the one that suits your playing style.
14.2. Guitar Strings
Guitar strings come in different gauges (thicknesses) and materials. The right strings can improve your guitar’s tone and playability.
14.3. Guitar Amplifiers
Guitar amplifiers are essential for electric guitars. Choose an amplifier that suits your playing style and budget.
14.4. Guitar Effects Pedals
Guitar effects pedals can add a variety of sounds to your guitar playing, such as distortion, reverb, and delay.
14.5. Guitar Cases
Guitar cases protect your guitar from damage during transport and storage.
15. Advanced Practice Techniques for Accelerated Learning
To accelerate your progress and achieve a deeper understanding of the guitar, consider incorporating these advanced practice techniques into your routine:
- Deliberate Practice: This involves identifying specific weaknesses in your playing and focusing intently on improving them through targeted exercises and drills. For example, if you struggle with barre chords, dedicate a practice session solely to mastering them, breaking down the technique into smaller steps and gradually increasing the speed and accuracy.
- Spaced Repetition: This technique involves reviewing material at increasing intervals over time. This helps to reinforce learning and improve long-term retention. Use flashcards or a spaced repetition software to review chords, scales, and music theory concepts.
- Active Recall: This involves actively retrieving information from memory rather than passively rereading notes or watching videos. Try to recall chords, scales, or songs from memory without looking at the tablature or sheet music. This strengthens neural connections and improves your ability to apply knowledge in real-time.
- Varied Practice: Mixing up your practice routine can prevent boredom and improve your overall learning. Instead of always practicing the same scales and chords, try exploring different genres, learning new songs, or improvising over backing tracks. This challenges your brain in new ways and helps you develop a more well-rounded musical skillset.
- Mental Practice: This involves mentally rehearsing your guitar playing without actually physically playing the instrument. Visualize yourself playing a difficult passage or improvising a solo. This can help to improve your muscle memory, coordination, and focus.
16. Overcoming Plateaus and Maintaining Progress
It’s common to experience plateaus in your guitar learning journey, where progress seems to stall. Here’s how to overcome them:
- Identify the Cause: Determine the root cause of the plateau. Are you lacking motivation, struggling with a specific technique, or simply not practicing enough?
- Set New Goals: Set new, challenging goals to reignite your passion and push you beyond your comfort zone.
- Seek Feedback: Ask a teacher, mentor, or fellow guitarist for feedback on your playing. They may be able to identify areas for improvement that you haven’t noticed.
- Change Your Routine: Introduce new exercises, techniques, or genres to your practice routine to stimulate learning and prevent boredom.
- Take a Break: Sometimes, the best way to overcome a plateau is to take a break from practicing altogether. A few days or even a week away from the guitar can help you to return with a fresh perspective and renewed energy.
17. The Importance of Music Theory and Aural Skills
While it’s possible to learn guitar without studying music theory, understanding the fundamentals of music theory can significantly accelerate your progress and deepen your understanding of music:
- Chord Construction: Learn how chords are built from scales and intervals. This will help you to understand chord progressions and create your own original music.
- Scales and Modes: Explore different scales and modes and learn how they relate to chords. This will enable you to improvise solos and create melodies that fit the harmonic context of a song.
- Key Signatures and Time Signatures: Understanding key signatures and time signatures will help you to read music, transpose songs, and communicate effectively with other musicians.
Aural skills, the ability to recognize pitches, intervals, chords, and rhythms by ear, are also essential for any aspiring musician:
- Interval Training: Practice identifying intervals by ear to improve your ability to transcribe melodies and improvise solos.
- Chord Recognition: Learn to identify different types of chords by ear. This will help you to understand chord progressions and create your own original music.
- Rhythm Dictation: Practice writing down rhythms that you hear. This will improve your sense of timing and enable you to transcribe drum parts and bass lines.
18. Exploring Different Guitar Styles and Techniques
The world of guitar playing is vast and diverse, with countless styles and techniques to explore:
- Fingerstyle Guitar: This technique involves using your fingers to pluck the strings, creating complex and intricate arrangements.
- Slide Guitar: This technique involves using a slide (a metal or glass tube) to glide along the strings, creating a distinctive sound that is often used in blues and country music.
- Alternate Tunings: Experimenting with different guitar tunings can open up new sonic possibilities and inspire creativity.
- Harmonics: Learn how to create harmonics (high-pitched, bell-like tones) on your guitar.
- Tremolo Picking: This technique involves rapidly picking a single note or chord to create a tremolo effect.
19. Developing a Repertoire of Songs
Learning to play songs is one of the most rewarding aspects of learning guitar. It’s important to develop a repertoire of songs that you enjoy playing and that showcase your skills:
- Start Simple: Begin with easy songs that use basic chords and strumming patterns.
- Choose Songs You Love: Select songs that you are passionate about. This will make practicing more enjoyable and motivating.
- Learn Songs in Different Genres: Explore songs in different genres to broaden your musical horizons and challenge yourself.
- Transcribe Songs: Transcribing songs by ear is a great way to improve your aural skills and deepen your understanding of music.
- Perform Songs for Others: Performing songs for friends, family, or in public is a great way to build confidence and share your love of music.
20. Building a Community of Guitarists
Connecting with other guitarists can provide support, motivation, and inspiration:
- Join a Guitar Club: Local guitar clubs offer opportunities to meet other guitarists, share tips and tricks, and jam together.
- Take Guitar Lessons: Private or group guitar lessons can provide personalized instruction and a supportive learning environment.
- Attend Guitar Workshops and Clinics: Workshops and clinics offer opportunities to learn from experienced guitarists and improve your skills.
- Join Online Guitar Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities provide a platform for guitarists to connect, share information, and ask questions.
- Attend Live Music Performances: Attending live music performances can inspire you and expose you to new styles and techniques.
Learning guitar is a rewarding journey that can enrich your life in countless ways. By setting realistic expectations, practicing consistently, and utilizing the resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can achieve your guitar learning goals and unlock your musical potential.
Remember, the journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step. Start your guitar learning journey today, and enjoy the process of discovery, growth, and musical expression.
For further assistance and a wide array of courses designed to elevate your guitar skills, visit LEARNS.EDU.VN. Our address is 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Let us help you unlock your musical potential.
FAQ: How Long to Learn Guitar Basics
Here are some frequently asked questions about learning guitar basics:
- How long does it take to learn basic chords on guitar? Typically, with consistent practice (30 minutes a day), you can learn basic chords in about 1-3 months.
- What’s the fastest way to learn guitar basics? The fastest way involves consistent daily practice, a structured learning plan, and personalized feedback from a qualified instructor.
- Can I learn guitar basics online? Yes, many online resources, including LEARNS.EDU.VN, offer comprehensive courses and tutorials for learning guitar basics.
- How much practice is needed to learn guitar basics effectively? Aim for at least 30 minutes of focused practice each day to make consistent progress.
- What are the most important things to learn as a beginner guitarist? Focus on mastering basic chords, strumming patterns, finger exercises, and basic music theory.
- Is it harder to learn acoustic or electric guitar for beginners? Acoustic guitars can be slightly more challenging initially due to higher string tension, but both are suitable for beginners.
- What should I do if I feel frustrated or stuck while learning guitar? Take a break, review your goals, seek guidance from a teacher or online community, and celebrate small victories.
- How can I stay motivated while learning guitar? Set achievable goals, learn your favorite songs, join a guitar community, and track your progress.
- Are there any shortcuts to learning guitar basics? There are no real shortcuts, but consistent practice, a structured learning plan, and personalized feedback can accelerate your progress.
- What resources does LEARNS.EDU.VN offer for learning guitar basics? learns.edu.vn provides structured online courses, expert instructors, personalized feedback, interactive exercises, and community support to help you master guitar basics efficiently.