Creating a VR learning course offers unparalleled opportunities for immersive and engaging education. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe in harnessing the power of technology to revolutionize learning experiences. This guide will provide you with a step-by-step approach on How To Create A Vr Learning Course that captivates learners and enhances knowledge retention. By integrating VR into your curriculum, you can offer dynamic and effective educational experiences, leveraging cutting-edge techniques and resources.
1. Understanding the Fundamentals of VR Learning
Virtual Reality (VR) learning courses immerse learners in simulated environments, allowing them to interact with digital content in a realistic and engaging manner. These courses can be designed to teach a wide range of subjects, from technical skills to soft skills, offering a hands-on approach that traditional methods often lack.
1.1. Defining Virtual Reality in Education
Virtual Reality in education uses VR technology to create immersive, interactive learning environments. This technology transports learners to a virtual space where they can engage with the material in a way that mimics real-world experiences.
1.2. Benefits of VR Learning Courses
VR learning courses provide a variety of advantages that enhance the educational experience and improve learning outcomes.
- Increased Engagement: VR captures learners’ attention and keeps them involved in the learning process.
- Improved Knowledge Retention: Immersive experiences lead to better memory encoding and recall.
- Practical Skill Development: VR allows for hands-on practice in a safe, controlled environment.
- Enhanced Accessibility: VR can provide access to educational experiences that might otherwise be unavailable due to geographical or physical limitations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While initial setup costs may exist, VR can reduce expenses related to travel, equipment, and physical resources in the long run.
1.3. Key Components of an Effective VR Learning Course
To create an effective VR learning course, consider these essential elements:
- Clear Learning Objectives: Define what learners should know or be able to do after completing the course.
- Engaging Content: Develop immersive, interactive content that captures learners’ attention.
- Intuitive Navigation: Design a user-friendly interface that allows learners to move through the virtual environment with ease.
- Realistic Simulations: Create simulations that accurately mimic real-world scenarios and provide opportunities for practice.
- Performance Feedback: Provide learners with immediate feedback on their performance to guide improvement.
- Accessibility: Ensure the VR course is accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities.
1.4. Types of VR Learning Experiences
Different types of VR experiences can be used in education, each offering unique benefits:
- Simulations: Recreate real-world scenarios for hands-on practice.
- Virtual Tours: Explore historical sites, museums, or other locations from anywhere in the world.
- Interactive Lessons: Engage with learning materials through interactive games and activities.
- Collaborative Learning: Connect with other learners in a virtual environment to share ideas and work together.
2. Identifying Learning Objectives
The first step in creating a VR learning course is to clearly define the learning objectives. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
2.1. Defining Specific Learning Outcomes
Clearly outline what learners should know or be able to do upon completing the course. For example, instead of “understanding project management,” a specific learning outcome could be “applying critical path analysis to project scheduling.”
2.2. Aligning Objectives with Learner Needs
Ensure that the learning objectives align with the needs and goals of the target audience. Conduct a needs assessment to identify gaps in knowledge and skills.
2.3. Setting Measurable Goals
Establish measurable goals to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the course. This could include test scores, project completion rates, or performance metrics within the VR environment.
2.4. Creating Achievable and Relevant Objectives
Make sure that the objectives are realistic and achievable within the scope of the course. They should also be relevant to the learners’ current or future roles.
2.5. Establishing a Timeline
Set a timeline for achieving the learning objectives. This helps to structure the course and keep learners on track.
3. Selecting the Right VR Platform and Tools
Choosing the right VR platform and tools is crucial for developing a successful VR learning course.
3.1. Overview of VR Platforms
Several VR platforms are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Popular options include:
- Unity: A versatile game engine that supports VR development across multiple platforms.
- Unreal Engine: Another powerful game engine known for its high-quality graphics and advanced features.
- WebVR: A web-based platform that allows VR experiences to be accessed through a browser.
- A-Frame: An open-source web framework for building VR experiences with HTML.
3.2. Evaluating Platform Features
When selecting a VR platform, consider the following features:
- Ease of Use: How easy is it to learn and use the platform?
- Development Tools: What tools are available for creating VR content?
- Platform Compatibility: Which VR devices and platforms does the platform support?
- Cost: What are the licensing fees and development costs?
- Community Support: How active and helpful is the platform’s community?
3.3. Choosing Development Tools
Select development tools that align with your skills and the requirements of your course. This might include:
- 3D Modeling Software: Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max for creating 3D assets.
- VR Development Kits: Oculus SDK, SteamVR SDK, or Google VR SDK for integrating VR functionality.
- Programming Languages: C# (for Unity), C++ (for Unreal Engine), or JavaScript (for WebVR).
- No-Code VR Creation Tools: Tools like CoPilot Designer offer drag-and-drop interfaces to build VR experiences without coding.
3.4. Ensuring Compatibility
Make sure that the VR platform and development tools are compatible with the VR devices that your learners will be using. This might include headsets like the Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, or Valve Index.
3.5. Leveraging LEARNS.EDU.VN Resources
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources and guidance to help you select the best VR platform and tools for your course. Our platform offers tutorials, reviews, and expert advice to support your development efforts.
4. Designing Immersive Learning Environments
Creating immersive learning environments is key to engaging learners and maximizing the impact of your VR course.
4.1. Principles of Immersive Design
Follow these principles to create truly immersive VR experiences:
- Presence: Make learners feel like they are actually in the virtual environment.
- Interaction: Allow learners to interact with the environment and objects in a natural and intuitive way.
- Engagement: Create compelling content that captures learners’ attention and motivates them to explore.
- Realism: Strive for realism in the visuals, sounds, and interactions within the VR environment.
- Accessibility: Design the environment to be accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities.
4.2. Creating Realistic Scenarios
Develop realistic scenarios that mimic real-world situations. This allows learners to practice skills in a safe and controlled environment.
4.3. Incorporating Interactive Elements
Include interactive elements that encourage learners to explore and experiment. This could include puzzles, simulations, or role-playing exercises.
4.4. Using 3D Modeling and Animation
Utilize 3D modeling and animation to create visually appealing and realistic environments. Pay attention to details like lighting, textures, and sound effects.
4.5. Optimizing Performance
Optimize the VR environment to ensure smooth performance on VR devices. This might involve reducing polygon counts, optimizing textures, or using level of detail (LOD) techniques.
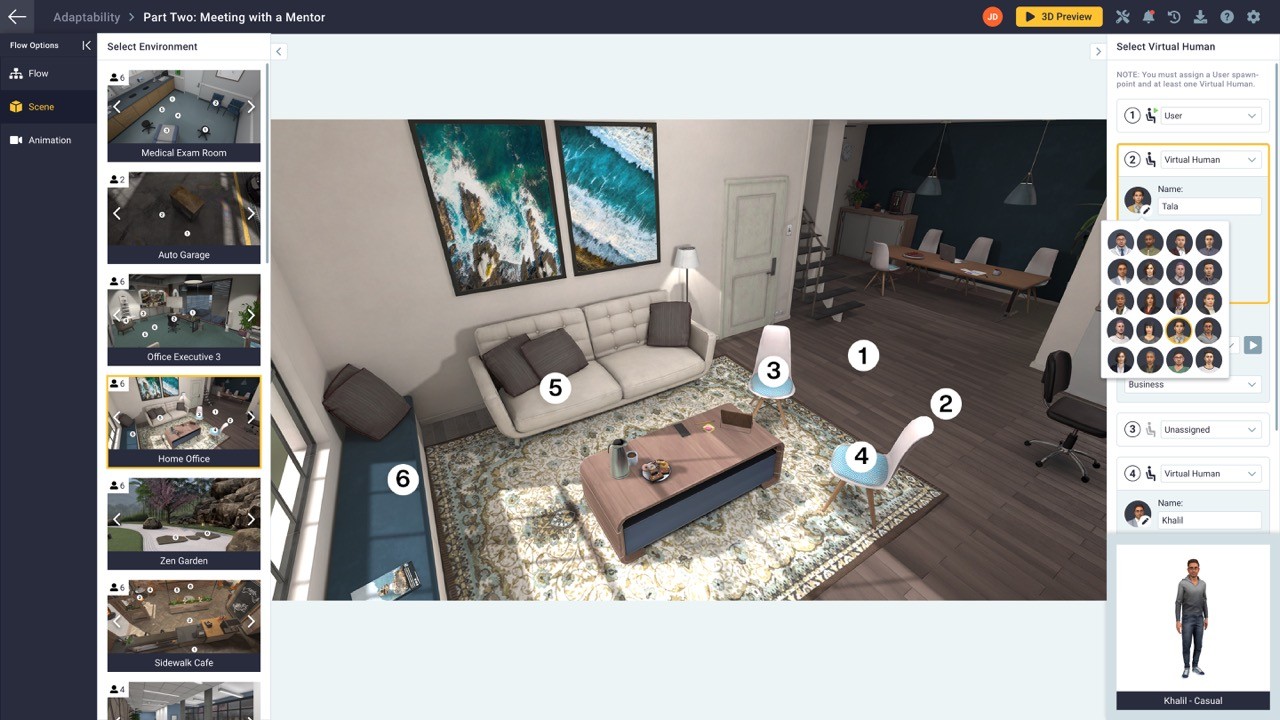
4.6. Leveraging Virtual Human Characters
Virtual human characters can serve as role-play partners, guides, and mentors for learners. Tools like CoPilot Designer offer libraries of diverse virtual characters to enhance the learning experience.
5. Developing Engaging VR Content
Engaging VR content is essential for capturing learners’ attention and promoting knowledge retention.
5.1. Storytelling in VR
Use storytelling techniques to create compelling narratives that immerse learners in the VR environment. This could involve creating a plot, characters, and conflicts that resonate with the learners.
5.2. Designing Interactive Lessons
Develop interactive lessons that encourage learners to participate actively in the learning process. This could include quizzes, games, or simulations.
5.3. Incorporating Multimedia Elements
Integrate multimedia elements like videos, audio, and images to enhance the learning experience. Use these elements to provide additional context, explanations, or examples.
5.4. Providing Performance Feedback
Provide learners with immediate feedback on their performance to guide improvement. This could include scores, grades, or personalized recommendations.
5.5. Gamification Techniques
Gamification techniques can enhance engagement and motivation by incorporating game-like elements such as points, badges, and leaderboards.
5.6. Utilizing CoPilot Designer’s Flow Editor
Tools like CoPilot Designer feature “Flow Editors” to write branched narratives and dialogue options, enhancing the interactive elements of VR learning modules.
6. Implementing Assessment and Evaluation
Assessment and evaluation are crucial for measuring the effectiveness of your VR learning course.
6.1. Designing VR Assessments
Create VR assessments that evaluate learners’ knowledge and skills in a realistic and engaging way. This could include simulations, quizzes, or problem-solving exercises.
6.2. Tracking Learner Progress
Track learners’ progress throughout the course to identify areas where they may need additional support. This could involve monitoring their performance on assessments, tracking their engagement with the content, or gathering feedback through surveys.
6.3. Providing Personalized Feedback
Provide learners with personalized feedback on their performance to guide improvement. This feedback should be specific, constructive, and actionable.
6.4. Analyzing Course Effectiveness
Analyze the results of assessments and evaluations to determine the effectiveness of the VR learning course. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to the content or delivery method.
6.5. Utilizing Data Analytics
Use data analytics tools to gain insights into learners’ behavior and performance. This can help you to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
7. Testing and Iteration
Testing and iteration are essential for refining your VR learning course and ensuring that it meets the needs of your learners.
7.1. Conducting User Testing
Conduct user testing with a representative sample of your target audience. This will help you to identify any usability issues, bugs, or areas for improvement.
7.2. Gathering Feedback
Gather feedback from learners, instructors, and other stakeholders. This feedback should be used to make improvements to the content, design, and delivery of the VR learning course.
7.3. Iterating on the Design
Iterate on the design of the VR learning course based on the results of testing and feedback. This might involve making changes to the content, interface, or interactions within the VR environment.
7.4. Optimizing Performance
Continuously optimize the performance of the VR learning course to ensure a smooth and engaging experience for learners. This might involve reducing loading times, improving frame rates, or optimizing graphics.
7.5. Addressing Accessibility
Ensure that the VR learning course is accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities. This might involve providing alternative input methods, captioning videos, or designing the environment to be navigable by learners with mobility impairments.
8. Deploying Your VR Learning Course
Deploying your VR learning course involves making it available to your target audience and providing them with the support they need to succeed.
8.1. Choosing a Deployment Method
Select a deployment method that aligns with the needs of your learners and the capabilities of your organization. This might include:
- VR Headsets: Distributing the VR learning course on VR headsets like the Oculus Quest or HTC Vive.
- Desktop Computers: Allowing learners to access the VR learning course on their desktop computers using a VR emulator.
- Web Browsers: Hosting the VR learning course on a web server and allowing learners to access it through a web browser.
- Learning Management System (LMS): Integrating the VR learning course with a learning management system to track learner progress and manage enrollment.
8.2. Providing Technical Support
Provide learners with technical support to help them resolve any issues they may encounter while using the VR learning course. This might involve creating a help desk, providing online documentation, or offering remote support.
8.3. Training Instructors
Train instructors on how to use and support the VR learning course. This might involve providing them with training materials, conducting workshops, or offering ongoing coaching.
8.4. Promoting the Course
Promote the VR learning course to your target audience. This might involve creating marketing materials, hosting webinars, or attending industry events.
8.5. Monitoring Usage
Monitor usage of the VR learning course to identify trends and patterns. This can help you to optimize the course and improve the learning experience.
9. Maintaining and Updating Your VR Learning Course
Maintaining and updating your VR learning course is essential for ensuring that it remains relevant and effective.
9.1. Regularly Reviewing Content
Regularly review the content of the VR learning course to ensure that it is accurate, up-to-date, and aligned with the learning objectives.
9.2. Updating Technology
Update the technology used in the VR learning course to take advantage of new features and capabilities. This might involve upgrading the VR platform, development tools, or VR devices.
9.3. Incorporating Feedback
Incorporate feedback from learners, instructors, and other stakeholders to make improvements to the VR learning course.
9.4. Addressing Technical Issues
Address any technical issues that may arise while using the VR learning course. This might involve fixing bugs, optimizing performance, or improving compatibility.
9.5. Planning for Future Enhancements
Plan for future enhancements to the VR learning course. This might involve adding new content, incorporating new technologies, or expanding the scope of the course.
10. Resources and Further Learning at LEARNS.EDU.VN
LEARNS.EDU.VN is your ultimate destination for resources and insights into creating effective VR learning courses. We offer a wealth of materials to enhance your skills and knowledge in this exciting field.
10.1. Accessing Tutorials and Guides
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides a range of tutorials and guides that cover various aspects of VR learning course creation. These resources are designed to help you navigate the complexities of VR development and implementation.
10.2. Exploring Case Studies
Dive into real-world examples with our collection of case studies. Learn how different organizations have successfully implemented VR learning courses and the impact it has had on their training programs.
10.3. Engaging with Experts
Connect with industry experts and fellow educators through our forums and webinars. Share your experiences, ask questions, and collaborate on innovative ideas to advance VR learning.
10.4. Utilizing Templates and Frameworks
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers templates and frameworks to streamline your VR learning course development. These tools can save you time and effort while ensuring that your course is well-structured and effective.
10.5. Staying Updated with Industry Trends
Stay informed about the latest trends and developments in VR learning with our news and articles section. We provide regular updates on new technologies, best practices, and emerging opportunities in the field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Creating a VR Learning Course
1. What is a VR learning course?
A VR learning course uses virtual reality technology to create immersive, interactive learning environments that simulate real-world scenarios, enhancing engagement and knowledge retention.
2. What are the benefits of using VR in education?
VR in education offers increased engagement, improved knowledge retention, practical skill development, enhanced accessibility, and cost-effectiveness.
3. What are the key components of an effective VR learning course?
Key components include clear learning objectives, engaging content, intuitive navigation, realistic simulations, performance feedback, and accessibility.
4. How do I choose the right VR platform for my course?
Consider factors like ease of use, development tools, platform compatibility, cost, and community support when selecting a VR platform.
5. What is immersive design and why is it important?
Immersive design focuses on creating a sense of presence, interaction, engagement, realism, and accessibility in the VR environment to maximize the learning experience.
6. How do I create engaging VR content?
Use storytelling, interactive lessons, multimedia elements, performance feedback, and gamification techniques to create engaging VR content.
7. How do I assess learner progress in a VR course?
Design VR assessments, track learner progress, provide personalized feedback, and analyze course effectiveness using data analytics tools.
8. What is the importance of testing and iteration in VR course development?
Testing and iteration help refine the VR learning course by identifying usability issues, gathering feedback, optimizing performance, and addressing accessibility.
9. What are the different deployment methods for a VR learning course?
Deployment methods include VR headsets, desktop computers, web browsers, and learning management systems (LMS).
10. How do I maintain and update my VR learning course?
Regularly review content, update technology, incorporate feedback, address technical issues, and plan for future enhancements to maintain and update your VR learning course.
Conclusion: The Future of Learning with VR
Creating a VR learning course offers a transformative approach to education, providing immersive and engaging experiences that enhance knowledge retention and skill development. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to supporting educators and learners in harnessing the power of VR to revolutionize the learning landscape.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create effective VR learning experiences that meet the specific needs and objectives of your programs. From defining clear learning objectives to designing immersive environments and implementing robust assessment methods, each stage is critical to the success of your VR course.
As technology continues to evolve, the potential for VR in education is limitless. Stay connected with LEARNS.EDU.VN for the latest insights, resources, and support to help you navigate the exciting world of VR learning. Together, we can create a future where education is more engaging, accessible, and effective than ever before.
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive resources and discover how you can start creating your own VR learning course. Unlock the potential of immersive education and transform the way your students learn.
For more information, contact us at:
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
Let learns.edu.vn be your partner in creating the future of education through virtual reality.