Learning how to write in cursive is a valuable skill that can enhance your writing abilities and cognitive development. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe that mastering cursive handwriting is within reach for everyone with the right guidance and practice. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the knowledge and practical steps necessary to learn cursive effectively, improving penmanship and fostering creativity. Let’s explore cursive writing techniques, penmanship practice, and handwriting development.
1. Understanding the Importance of Cursive Writing
Cursive writing, also known as joined-up writing, is a style of handwriting where the letters are connected to allow for a faster and more fluid writing process. While digital communication has become prevalent, cursive writing retains significant educational and cognitive benefits.
1. 1 Cognitive Advantages of Cursive
Research suggests that learning cursive can improve cognitive skills such as memory, focus, and fine motor skills. The continuous flow of cursive writing engages different parts of the brain compared to printing or typing.
| Cognitive Skill | Benefit from Cursive Writing |
|---|---|
| Memory | The act of forming cursive letters helps reinforce memory pathways in the brain. |
| Focus | The deliberate and continuous nature of cursive writing promotes concentration and attention to detail. |
| Fine Motor Skills | Cursive writing requires precise hand movements, enhancing dexterity and coordination, especially beneficial for children’s development. |
| Reading Comprehension | Understanding cursive helps in reading historical documents and handwritten notes, improving overall literacy. |


1. 2 Educational Benefits for Students
For students, learning cursive can enhance their overall academic performance. It provides an alternative method of note-taking, which can be faster than printing. It also helps in better understanding and appreciation of historical documents written in cursive.
1. 3 Therapeutic Applications
Cursive writing has been shown to have therapeutic benefits, particularly for individuals with dyslexia. The continuous strokes of cursive can help improve letter recognition and reduce letter reversals, making it easier for dyslexic individuals to read and write.
2. Setting the Stage for Learning Cursive
Before diving into the specifics of cursive letter formation, it’s important to set the stage for effective learning. This involves gathering the right tools, understanding basic principles, and establishing a conducive practice environment.
2. 1 Essential Tools and Materials
To begin your cursive writing journey, you will need a few essential tools:
- Pens: Use pens that allow for smooth and consistent ink flow. Fountain pens, gel pens, or fine-tip ballpoint pens are excellent choices.
- Paper: Lined paper is ideal for practicing cursive, as it provides guidelines for letter height and spacing.
- Cursive Alphabet Charts: Having a reference chart with both lowercase and uppercase cursive letters can be incredibly helpful.
- Workbooks: Cursive writing workbooks offer structured exercises and practice pages to guide your learning.
2. 2 Understanding Basic Cursive Principles
Cursive writing is based on the principle of connecting letters in a fluid, continuous motion. Each letter flows into the next, creating a seamless word. Key elements include:
- Slant: Cursive letters typically slant slightly to the right.
- Loops: Many cursive letters feature loops, both ascending and descending.
- Baseline: Maintaining a consistent baseline is crucial for legibility.
- Connections: Smooth and consistent connections between letters are what define cursive writing.
2. 3 Creating a Practice Environment
A conducive practice environment can significantly impact your learning progress. Find a quiet space where you can focus without distractions. Ensure you have good lighting and a comfortable seating arrangement. Regular practice, even in short sessions, is more effective than sporadic, long sessions.
3. Mastering the Lowercase Cursive Alphabet
Starting with lowercase letters is often recommended, as they form the foundation of cursive writing. Many lowercase letters share similar strokes, making them easier to learn initially.
3. 1 Grouping Letters by Stroke Type
One effective approach is to group lowercase letters based on their initial strokes. This simplifies the learning process by focusing on common movements.
- “C” Family: Start with letters like “a,” “c,” “d,” “g,” “q,” and “o.” These letters begin with a similar curved stroke, making them easier to learn together.
- “L” Family: Letters like “b,” “e,” “f,” “h,” “k,” and “l” share a common looping stroke.
- “I” Family: Letters such as “i,” “j,” “p,” “r,” “s,” “t,” “u,” “w,” “x,” “y,” and “z” have unique characteristics but share some basic strokes.
3. 2 Step-by-Step Guide to Forming Lowercase Letters
Let’s explore how to form some of the most common lowercase cursive letters:
- a: Start with a small upward stroke, form a circle, and then bring the stroke down and out.
- b: Begin with a tall loop, bring the line down, and then curve it back up to form a small tail.
- c: Simply form a curved stroke, similar to a printed lowercase “c,” but with a slight upward extension.
- d: Start like “a,” with a small upward stroke, form a circle, bring the line straight up, and then down with a tail.
- e: Begin with a small loop at the baseline and extend it into a curved line.
3. 3 Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Inconsistent Slant: Keep a consistent slant by using guidelines or practicing with lined paper.
- Uneven Letter Size: Pay attention to letter height and maintain uniformity.
- Jerky Movements: Focus on fluid, continuous strokes rather than lifting the pen frequently.
- Incorrect Connections: Ensure letters connect smoothly without awkward gaps or overlaps.
4. Conquering the Uppercase Cursive Alphabet
Uppercase cursive letters often require more intricate strokes than their lowercase counterparts. Mastering them involves patience and consistent practice.
4. 1 Grouping Letters by Similarities
Like lowercase letters, uppercase letters can be grouped based on shared characteristics:
- “C” Family: Includes C, G, O, Q. These letters have a rounded, flowing shape.
- “L” Family: Includes L, E. These involve loops and elegant curves.
- “J” Family: Includes J, I. These have descenders and graceful strokes.
4. 2 Detailed Instructions for Forming Uppercase Letters
Here’s a step-by-step guide to forming some challenging uppercase cursive letters:
- A: Start with a large upward loop, bring the line down and to the right, and then add a curved stroke in the middle.
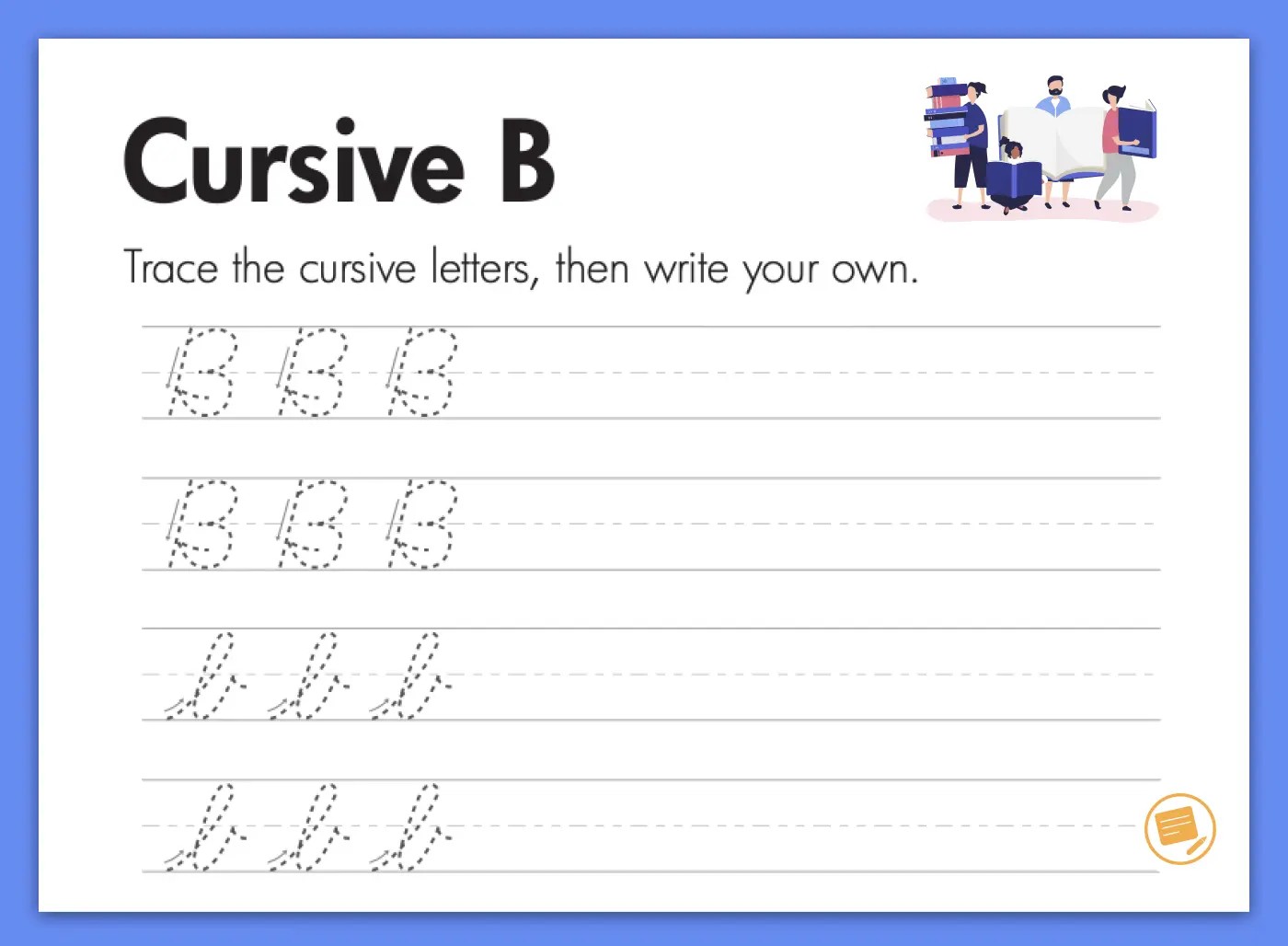
- B: Begin with a tall loop, bring the line down, and then create two rounded sections, connecting them smoothly.
- C: Form a large, sweeping curve, starting from the top and extending to the baseline.
- D: Start with a tall, curved stroke, bring the line down, and then create a large loop that connects back to the top.
- E: Begin with a curved stroke at the top, form a loop, bring the line down, and then add a small horizontal stroke.
4. 3 Tips for Maintaining Consistency and Legibility
- Practice Size Consistency: Keep uppercase letters proportionally larger than lowercase letters.
- Maintain Proper Spacing: Ensure enough space between uppercase and lowercase letters to avoid crowding.
- Focus on Distinct Shapes: Make each uppercase letter easily distinguishable from others to enhance legibility.
5. Connecting Letters and Forming Words
Once you’re comfortable with individual letters, the next step is to connect them to form words. This is where the true fluidity of cursive writing comes to life.
5. 1 Understanding Connection Strokes
Each letter has a specific ending stroke that connects it to the next letter. These connection strokes vary depending on the letters involved. For example, the connection between “a” and “t” is different from the connection between “e” and “t.”
5. 2 Practicing Common Letter Combinations
Focus on practicing common letter combinations to improve your connection skills. Some examples include:
- “th”
- “er”
- “in”
- “an”
- “ou”
5. 3 Exercises for Improving Word Formation
- Tracing Words: Start by tracing words to get a feel for the connections between letters.
- Copying Sentences: Copy sentences from a cursive writing workbook or a handwritten sample.
- Writing from Memory: Practice writing words and sentences from memory to reinforce your learning.
6. Selecting a Cursive Font and Style
While the basic principles of cursive remain consistent, there is room for personalization through font and style selection.
6. 1 Exploring Different Cursive Fonts
Various cursive fonts offer different aesthetic qualities. Some popular fonts include:
- Palmer Method: A traditional, formal style.
- D’Nealian Script: A simplified, more modern style.
- Zaner-Bloser: Another traditional style with distinct letter formations.
6. 2 Personalizing Your Cursive Style
Once you’re comfortable with a particular font, you can begin to personalize your cursive style. This might involve:
- Adjusting Letter Slant: Experiment with different degrees of slant.
- Modifying Loop Size: Vary the size and shape of loops in letters like “l,” “b,” and “e.”
- Adding Flourishes: Incorporate decorative strokes or embellishments.
6. 3 Maintaining Legibility While Adding Flair
While personalization is encouraged, it’s important to maintain legibility. Ensure that your modifications don’t make your handwriting difficult to read.
7. Effective Practice Techniques and Resources
Consistent and focused practice is key to mastering cursive writing. Incorporate these techniques and resources into your learning routine.
7. 1 Setting Realistic Goals
Set achievable goals to maintain motivation. Start with short practice sessions and gradually increase the duration as you improve.
7. 2 Utilizing Worksheets and Practice Drills
Cursive writing worksheets provide structured exercises for practicing letter formation and connections. Practice drills can help reinforce specific skills, such as maintaining consistent slant or forming loops.
7. 3 Incorporating Cursive into Daily Writing
Make cursive writing a part of your daily routine. Write notes, journal entries, or even grocery lists in cursive to reinforce your skills.
7. 4 Online Resources and Tutorials
Numerous online resources offer guidance and instruction on cursive writing. Websites like LEARNS.EDU.VN provide articles, tutorials, and practice materials to support your learning journey.
7. 5 Seeking Feedback and Guidance
Consider seeking feedback from a handwriting expert or joining a cursive writing community. Constructive criticism can help you identify areas for improvement and refine your technique.
8. Troubleshooting Common Cursive Writing Challenges
Even with diligent practice, you may encounter challenges along the way. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
8. 1 Difficulty Maintaining Consistent Slant
Use lined paper or create your own slant guidelines. Practice writing letters and words with a consistent angle.
8. 2 Problems with Letter Spacing
Pay attention to the space between letters and words. Avoid crowding or excessive gaps.
8. 3 Inconsistent Letter Size
Focus on maintaining uniform letter height and width. Use guidelines to ensure consistency.
8. 4 Fatigue and Hand Cramps
Take frequent breaks to rest your hand. Practice proper posture and grip to reduce strain.
8. 5 Losing Motivation
Set small, achievable goals to maintain momentum. Celebrate your progress and reward yourself for reaching milestones.
9. The Role of Cursive Writing in the Digital Age
While digital communication dominates modern life, cursive writing still holds relevance and value.
9. 1 Cursive as a Form of Personal Expression
Cursive writing allows for personal expression and creativity. It adds a unique touch to handwritten notes, letters, and cards.
9. 2 Cursive in Historical Documents and Calligraphy
Understanding cursive is essential for reading historical documents and appreciating the art of calligraphy. Many historical texts are written in cursive, and calligraphy relies heavily on cursive techniques.
9. 3 Blending Cursive with Digital Communication
Consider incorporating cursive elements into your digital communication. For example, you can use cursive fonts in digital documents or create handwritten signatures for emails.
10. The Future of Cursive Writing
Despite the rise of digital technology, cursive writing is experiencing a resurgence in popularity.
10. 1 Renewed Interest in Handwriting
Many educators and parents recognize the cognitive and educational benefits of handwriting, leading to a renewed emphasis on cursive instruction.
10. 2 Integrating Cursive into Modern Education
Some schools are reintroducing cursive writing into their curriculum, recognizing its value in developing fine motor skills, improving memory, and fostering creativity.
10. 3 The Enduring Appeal of Cursive Writing
Cursive writing remains a timeless skill that connects us to the past and enhances our cognitive abilities. Whether for personal expression, historical appreciation, or cognitive development, cursive writing continues to hold a special place in our lives.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Learning Cursive
- Is cursive writing still relevant in the digital age?
Yes, cursive writing offers cognitive and educational benefits, enhances personal expression, and aids in reading historical documents. - What are the cognitive benefits of learning cursive?
Learning cursive can improve memory, focus, fine motor skills, and reading comprehension. - How long does it take to learn cursive?
The time it takes varies, but with consistent practice, you can become proficient in a few months. - What tools do I need to start learning cursive?
You’ll need pens, lined paper, cursive alphabet charts, and workbooks. - Is it better to start with lowercase or uppercase letters?
Starting with lowercase letters is often recommended as they are generally simpler. - How can I maintain a consistent slant in my cursive writing?
Use lined paper or create slant guidelines and practice regularly. - What are some common mistakes to avoid when learning cursive?
Avoid inconsistent slant, uneven letter size, jerky movements, and incorrect connections. - How can I personalize my cursive style?
Experiment with letter slant, loop size, and add decorative strokes. - Where can I find online resources for learning cursive?
Websites like LEARNS.EDU.VN offer articles, tutorials, and practice materials. - What should I do if I encounter challenges while learning cursive?
Identify the specific issue, seek feedback, and practice targeted exercises.
Learning how to write in cursive is an enriching experience that offers numerous benefits. By following the steps outlined in this guide and dedicating time to practice, you can master this valuable skill and enhance your writing abilities. Remember to set realistic goals, utilize available resources, and seek feedback to refine your technique.
Are you eager to dive deeper into the art of cursive writing and explore more advanced techniques? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover a wealth of resources, including in-depth tutorials, personalized coaching, and a vibrant community of fellow learners. Unlock your full potential and transform your handwriting with LEARNS.EDU.VN. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212, or visit our website learns.edu.vn to get started.