Learning how to write in cursive opens doors to enhanced writing skills, improved memory, and can even be therapeutic. At learns.edu.vn, we believe mastering cursive writing is a valuable skill that can boost your cognitive abilities and offer a unique personal touch to your communications. Discover techniques for mastering cursive handwriting, unlock its potential for personal expression, and learn practical tips to refine your cursive writing style. Whether you’re a student seeking academic enrichment, a professional aiming to enhance your skillset, or simply someone with a passion for beautiful penmanship, this guide provides the tools you need.
1. Understanding the Importance of Cursive Writing
While digital communication dominates our modern world, cursive writing remains a valuable skill with numerous cognitive and personal benefits. Far from being obsolete, learning cursive enhances fine motor skills, improves memory, and offers a unique personal touch that typed text simply cannot replicate. Let’s explore the multifaceted reasons why cursive writing continues to be important.
1.1. Cognitive Development
Cursive writing engages different parts of the brain compared to printing or typing. The continuous strokes involved in cursive help improve:
- Fine Motor Skills: The precise hand movements required to form cursive letters enhance dexterity and coordination.
- Brain Connectivity: Studies have shown that cursive writing can improve brain connectivity, particularly between the left and right hemispheres. According to a study published in “Psychology Today”, cursive writing stimulates brain regions involved in thinking, language, and working memory.
- Memory: The act of writing information by hand, especially in cursive, helps encode the information more effectively, leading to better recall.
1.2. Educational Advantages
Learning cursive can provide students with significant academic advantages.
- Improved Reading Skills: Recognizing cursive letters helps students better understand the written word in various forms, including historical documents.
- Enhanced Writing Fluency: Cursive encourages a smoother, more connected flow of writing, which can improve overall writing speed and fluency.
- Dyslexia Therapy: Writing in cursive is often used as a therapeutic tool for individuals with dyslexia, as the connected letters can reduce letter reversals and improve reading accuracy. A study in the “Annals of Dyslexia” found that cursive writing can positively impact dyslexic students by improving their letter recognition and reducing confusion.
1.3. Personal and Professional Benefits
Beyond academics, cursive writing offers several personal and professional advantages.
- Personal Expression: Cursive allows for a unique and personal form of expression. Your handwriting becomes a recognizable signature, adding a personal touch to notes, letters, and documents.
- Professionalism: In certain professions, such as law or historical research, the ability to read and write cursive is invaluable. It demonstrates attention to detail and respect for tradition.
- Historical Connection: Cursive provides a direct link to the past, allowing you to read and understand historical documents, letters, and journals written in cursive. This connection enriches your understanding of history and culture.
1.4. The Enduring Appeal of Handwriting
In an increasingly digital world, the act of writing by hand has become a special and valued skill.
- Personal Connection: Handwritten notes and letters convey a sense of care and thoughtfulness that typed messages often lack. This personal touch can strengthen relationships and make communications more meaningful.
- Mindfulness: The act of writing by hand can be a form of mindfulness, allowing you to slow down, focus, and engage more deeply with your thoughts.
- Creativity: Cursive writing encourages creativity and self-expression. Experimenting with different styles and flourishes can be a fun and rewarding way to personalize your handwriting.
To sum up, the following information is displayed in the table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Fine Motor Skills | Enhances dexterity and coordination through precise hand movements. |
| Brain Connectivity | Improves communication between brain hemispheres, boosting cognitive functions. |
| Memory Enhancement | Facilitates better information encoding and recall. |
| Reading Improvement | Aids in recognizing various written forms, including historical documents. |
| Writing Fluency | Promotes smoother, faster writing. |
| Dyslexia Therapy | Reduces letter reversals and improves reading accuracy for dyslexic individuals. |
| Personal Expression | Offers a unique, recognizable signature, adding personality to communications. |
| Professional Advantage | Valuable in professions like law and historical research, demonstrating attention to detail. |
| Historical Connection | Enables understanding of historical documents, enriching cultural and historical knowledge. |
| Personal Connection | Conveys care and thoughtfulness, strengthening relationships. |
| Mindfulness Practice | Promotes focus and deeper engagement with thoughts. |
| Creativity Booster | Encourages experimentation and self-expression through different writing styles. |


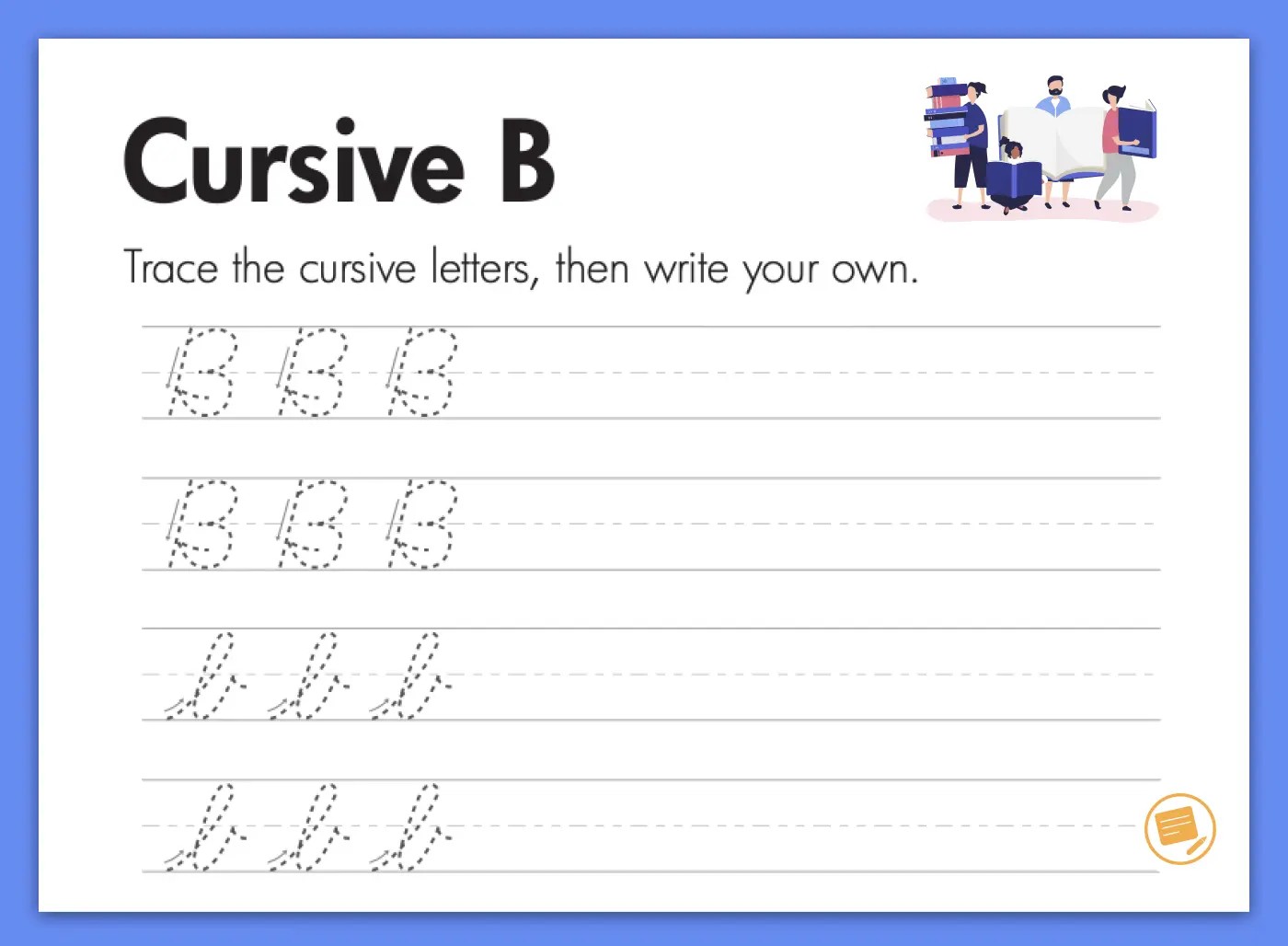
2. Getting Started with Cursive: Essential Steps
Embarking on the journey to learn cursive writing requires patience, practice, and a structured approach. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, these essential steps will guide you toward mastering this elegant form of handwriting.
2.1. Understanding the Basics
Before you pick up a pen, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental elements of cursive writing.
- Letter Formation: Each cursive letter has a specific shape and stroke order. Familiarize yourself with these forms using alphabet charts and instructional materials.
- Connections: Cursive writing involves connecting letters seamlessly. Pay attention to how each letter flows into the next.
- Slant: Maintaining a consistent slant is essential for creating legible and aesthetically pleasing cursive. Most cursive styles use a slight rightward slant.
2.2. Gathering the Right Materials
Having the right tools can significantly enhance your learning experience.
- Pens: Choose a pen that feels comfortable in your hand and provides smooth ink flow. Ballpoint pens, gel pens, and fountain pens are all suitable options.
- Paper: Lined paper is ideal for beginners, as it helps maintain consistent letter size and alignment. As you progress, you can transition to unlined paper.
- Workbooks and Guides: Invest in cursive writing workbooks or online resources that provide letter-by-letter instructions and practice exercises.
2.3. Mastering Lowercase Letters
Start with lowercase letters, as they form the foundation of cursive writing.
- Simple Letters: Begin with letters that are easy to form, such as “i,” “l,” “t,” “u,” and “e.” Focus on consistent stroke direction and letter height.
- Curved Letters: Practice letters with curves, such as “o,” “a,” “c,” and “d.” Pay attention to the shape and angle of the curves.
- Letters with Ascenders and Descenders: These letters extend above or below the baseline, such as “b,” “f,” “g,” “h,” “j,” “k,” “p,” “q,” and “y.” Maintain consistent loop sizes and extensions.
2.4. Tackling Uppercase Letters
Once you’re comfortable with lowercase letters, move on to uppercase letters.
- Basic Strokes: Practice the basic strokes used in uppercase letters, such as curves, loops, and straight lines.
- Letter Combinations: Some uppercase letters share similar strokes. Group these letters together for practice, such as “C,” “G,” “O,” and “Q.”
- Complex Letters: Some uppercase letters are more intricate, such as “R,” “Z,” and “K.” Break these letters down into smaller steps and practice each component individually.
2.5. Connecting Letters and Forming Words
The essence of cursive writing lies in connecting letters to form words.
- Simple Connections: Start by connecting simple letter combinations, such as “at,” “in,” “on,” and “up.”
- Consistent Spacing: Maintain consistent spacing between letters and words. Avoid overcrowding or spreading letters too far apart.
- Practice Words and Sentences: Practice writing common words and sentences to develop fluency and consistency.
2.6. Utilizing Online Resources
The internet offers a wealth of resources to support your cursive writing journey.
- Online Tutorials: Numerous websites and video platforms offer step-by-step tutorials on cursive letter formation and connections.
- Printable Worksheets: Download and print cursive writing worksheets to practice letter formation, word connections, and sentence writing.
- Interactive Apps: Explore interactive apps that provide real-time feedback on your handwriting and offer personalized practice exercises.
Here’s an easy-to-read table outlining the steps to learn cursive writing:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Basics | Learn letter shapes, connections, and slant. |
| 2. Materials | Use comfortable pens, lined paper, and cursive workbooks. |
| 3. Lowercase | Begin with simple letters like “i,” “l,” and “u,” then move to curved and ascender/descender letters. |
| 4. Uppercase | Practice basic strokes, group letters with similar strokes, and tackle complex letters. |
| 5. Connections | Connect letters, maintain consistent spacing, and practice writing words and sentences. |
| 6. Online Resources | Use tutorials, worksheets, and interactive apps. |
3. Mastering Advanced Techniques in Cursive Writing
Once you’ve grasped the basics of cursive writing, you can elevate your skills by exploring advanced techniques. These techniques will help you refine your handwriting, develop your personal style, and create elegant, legible cursive.
3.1. Refining Letter Consistency
Achieving consistent letter formation is crucial for creating clear and attractive cursive.
- Letter Height: Maintain uniform height for lowercase letters that don’t have ascenders or descenders (e.g., a, c, e, i, m, n, o, r, s, u, v, w, x, z).
- Ascenders and Descenders: Ensure that ascenders (b, d, f, h, k, l, t) and descenders (g, j, p, q, y) are consistently sized and extend appropriately above and below the baseline.
- Letter Width: Keep the width of your letters consistent. Avoid compressing or stretching letters disproportionately.
3.2. Perfecting Slant and Spacing
Slant and spacing contribute significantly to the overall appearance and readability of your cursive.
- Consistent Slant: Maintain a consistent slant angle throughout your writing. Most cursive styles use a slight rightward slant of about 45 degrees.
- Letter Spacing: Ensure adequate space between letters within words. Letters should be close enough to appear connected but not so close that they overlap.
- Word Spacing: Maintain consistent spacing between words. Words should be clearly separated but not too far apart.
3.3. Exploring Different Cursive Styles
There are various cursive styles, each with its unique characteristics. Experimenting with different styles can help you find one that suits your personal preferences and writing habits.
- Palmer Method: Known for its simplicity and efficiency, the Palmer Method emphasizes smooth, rhythmic strokes and minimal ornamentation.
- D’Nealian Cursive: D’Nealian is a simplified cursive style that closely resembles manuscript printing, making it easier for children to transition from print to cursive.
- Spencerian Script: Considered one of the most elegant cursive styles, Spencerian script features elaborate flourishes, delicate lines, and a high degree of ornamentation.
3.4. Developing Your Personal Style
While it’s important to master the fundamentals of cursive, don’t be afraid to develop your personal style.
- Letter Variations: Experiment with variations in letter forms, such as adding loops, changing the slant, or modifying the connections between letters.
- Flourishes: Incorporate flourishes to add decorative elements to your handwriting. Use flourishes sparingly to avoid overwhelming the text.
- Signature: Develop a unique signature that reflects your personality and style. Practice your signature regularly to maintain consistency.
3.5. Practicing with Different Writing Tools
Experimenting with different writing tools can enhance your cursive writing experience and help you discover new techniques.
- Fountain Pens: Fountain pens offer smooth ink flow and allow for variations in line width, making them ideal for creating expressive cursive.
- Calligraphy Pens: Calligraphy pens with broad nibs can be used to create thick and thin strokes, adding visual interest to your handwriting.
- Brush Pens: Brush pens are versatile tools that can be used to create a range of effects, from delicate hairlines to bold strokes.
3.6. Analyzing Exemplars
Studying examples of excellent cursive handwriting can provide inspiration and guidance for improving your skills.
- Historical Documents: Examine historical documents written in cursive to observe the techniques and styles used by master penmen.
- Calligraphy Manuals: Consult calligraphy manuals and books for detailed instructions and examples of various cursive styles.
- Online Galleries: Explore online galleries and forums dedicated to handwriting and calligraphy to see examples of contemporary cursive writing.
The following is a brief summary of how to master advanced cursive writing techniques:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Letter Consistency | Maintain uniform height, size, and width for consistent letter formation. |
| Slant and Spacing | Ensure a consistent slant angle, adequate letter spacing within words, and clear word spacing. |
| Style Exploration | Experiment with Palmer, D’Nealian, and Spencerian styles to find a personal fit. |
| Personal Style | Vary letter forms, add flourishes sparingly, and develop a unique signature. |
| Tool Experimentation | Use fountain, calligraphy, and brush pens for varied effects. |
| Exemplar Analysis | Study historical documents, calligraphy manuals, and online galleries. |
4. Integrating Cursive Writing Into Your Daily Life
Learning cursive is not just about mastering the technique; it’s about integrating it into your daily routines to enhance your personal and professional life. By finding practical applications for your cursive skills, you can reinforce your learning, develop your unique style, and enjoy the numerous benefits of handwriting.
4.1. Note-Taking and Journaling
One of the most effective ways to practice cursive is by using it for note-taking and journaling.
- Class Notes: Take notes in cursive during lectures or meetings. This will help you improve your writing speed and fluency while also reinforcing the information you’re learning.
- Personal Journal: Keep a personal journal and write entries in cursive. This will allow you to express your thoughts and feelings in a more personal and meaningful way.
- Gratitude Journal: Maintain a gratitude journal and write down things you’re thankful for each day. This can be a powerful way to cultivate positivity and improve your overall well-being.
4.2. Correspondence and Card Writing
In an age of digital communication, handwritten letters and cards stand out as special and personal gestures.
- Thank-You Notes: Write thank-you notes in cursive to express your appreciation for gifts, acts of kindness, or hospitality.
- Birthday Cards: Send handwritten birthday cards to friends and family members. A personalized card will mean more than a generic store-bought one.
- Letters to Loved Ones: Write letters to loved ones who live far away. A handwritten letter can be a tangible reminder of your connection.
4.3. Creative Writing and Calligraphy
Cursive writing can be a powerful tool for creative expression.
- Poetry: Write poems in cursive to explore the rhythm and flow of language. The act of writing by hand can enhance your connection to the words.
- Short Stories: Draft short stories in cursive to tap into your imagination and develop your narrative skills.
- Calligraphy Projects: Experiment with calligraphy techniques to create decorative lettering for invitations, announcements, or art projects.
4.4. Professional Applications
While digital communication is prevalent in the workplace, there are still opportunities to use cursive writing in professional settings.
- Signatures: Use your cursive signature on official documents, contracts, and correspondence.
- Personalized Notes: Add handwritten notes to client communications, such as thank-you notes or congratulatory messages.
- Brainstorming: Use cursive writing during brainstorming sessions to capture ideas quickly and creatively.
4.5. Mindfulness and Relaxation
The act of writing in cursive can be a form of mindfulness, allowing you to slow down, focus, and engage more deeply with your thoughts.
- Meditation: Use cursive writing as a form of meditation. Focus on the strokes and movements of your hand as you write, and let go of distractions.
- Stress Relief: Write in cursive to relieve stress and anxiety. The rhythmic act of writing can be calming and therapeutic.
- Creative Exploration: Engage in creative writing or calligraphy as a way to explore your emotions and express yourself.
4.6. Educational Reinforcement
If you’re learning a new language or subject, using cursive writing can help reinforce your understanding.
- Vocabulary Practice: Write out vocabulary words in cursive to help you memorize their spelling and meaning.
- Grammar Exercises: Complete grammar exercises in cursive to reinforce your understanding of sentence structure and syntax.
- Summaries: Write summaries of lectures or readings in cursive to consolidate your knowledge.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Note-Taking | Enhance learning by taking class notes in cursive to improve speed and fluency. |
| Journaling | Express thoughts personally through cursive in a personal journal. |
| Correspondence | Send handwritten thank-you notes and birthday cards for a personal touch. |
| Creative Writing | Write poems and short stories in cursive to connect deeply with the words. |
| Professional Use | Use cursive for signatures, personalized client notes, and brainstorming sessions. |
| Mindfulness | Meditate and relieve stress through the rhythmic act of cursive writing. |
| Educational Practice | Reinforce vocabulary and grammar by practicing cursive writing. |
5. The Benefits of Cursive Writing for Different Age Groups
Cursive writing offers distinct advantages for learners of all ages. From children developing fine motor skills to adults seeking cognitive enhancement, the benefits of cursive extend across various life stages.
5.1. Children and Adolescents (Ages 5-18)
For children and adolescents, learning cursive can significantly impact their cognitive and academic development.
- Fine Motor Skill Development: Cursive writing helps refine fine motor skills, which are essential for various tasks, including drawing, playing musical instruments, and using technology.
- Improved Brain Connectivity: Studies have shown that cursive writing can enhance brain connectivity, particularly between the left and right hemispheres. This can lead to improved cognitive function and academic performance.
- Enhanced Memory: The act of writing information by hand, especially in cursive, helps encode the information more effectively, leading to better recall.
- Dyslexia Therapy: Cursive writing is often used as a therapeutic tool for individuals with dyslexia, as the connected letters can reduce letter reversals and improve reading accuracy.
5.2. Young Adults (Ages 19-25)
Young adults can benefit from cursive writing in their academic and professional pursuits.
- Note-Taking Efficiency: Cursive writing can be faster than printing, making it an efficient method for taking notes during lectures or meetings.
- Personal Expression: Cursive allows for a unique and personal form of expression, which can be valuable for creative writing, journaling, and personal correspondence.
- Historical Literacy: The ability to read and write cursive can enhance historical literacy, allowing young adults to engage with historical documents and literature.
5.3. Adults (Ages 26-64)
Adults can use cursive writing to enhance their cognitive skills, express their creativity, and maintain a connection to the past.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Cursive writing engages different parts of the brain compared to typing, providing cognitive stimulation and helping to maintain mental agility.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: The act of writing in cursive can be a form of mindfulness, allowing adults to slow down, focus, and engage more deeply with their thoughts.
- Personal Correspondence: In an age of digital communication, handwritten letters and cards stand out as special and personal gestures, allowing adults to maintain meaningful connections with loved ones.
- Professional Advantage: In certain professions, such as law or historical research, the ability to read and write cursive is invaluable.
5.4. Seniors (Ages 65+)
Seniors can benefit from cursive writing as a way to maintain cognitive function, express their creativity, and connect with their personal history.
- Cognitive Exercise: Cursive writing provides a form of cognitive exercise that can help maintain mental sharpness and prevent cognitive decline.
- Reminiscence Therapy: Writing in cursive can trigger memories and emotions associated with past experiences, making it a valuable tool for reminiscence therapy.
- Creative Expression: Seniors can use cursive writing to express their creativity through journaling, calligraphy, or letter writing.
- Legacy Preservation: Writing letters, memoirs, or family histories in cursive can be a way for seniors to preserve their personal legacy and pass on their stories to future generations.
Here’s a concise table summarizing the benefits of cursive writing across different age groups:
| Age Group | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Children/Adolescents | Enhances fine motor skills, improves brain connectivity, boosts memory, supports dyslexia therapy. |
| Young Adults | Increases note-taking efficiency, enables personal expression, improves historical literacy. |
| Adults | Provides cognitive stimulation, promotes mindfulness and relaxation, enhances personal correspondence, offers professional advantages. |
| Seniors | Exercises cognitive functions, provides reminiscence therapy, encourages creative expression, preserves personal legacy. |
6. Common Challenges and Solutions in Learning Cursive
Learning cursive writing can be a rewarding experience, but it’s not without its challenges. Many learners encounter similar obstacles along the way. Recognizing these common challenges and implementing effective solutions can help you overcome them and progress toward mastering cursive.
6.1. Difficulty Forming Letters Correctly
One of the most common challenges in learning cursive is difficulty forming letters correctly. This can be due to unfamiliarity with the letter shapes, inconsistent stroke direction, or lack of fine motor control.
- Solution: Practice letter formation regularly using alphabet charts and instructional materials. Break down each letter into smaller steps and focus on consistent stroke direction and letter height. Use tracing exercises to reinforce muscle memory.
6.2. Trouble Connecting Letters Smoothly
Cursive writing involves connecting letters seamlessly, which can be challenging for beginners. Issues may arise from incorrect starting or ending points, inconsistent slant, or lack of flow between letters.
- Solution: Practice connecting simple letter combinations, such as “at,” “in,” “on,” and “up.” Pay attention to the starting and ending points of each letter and maintain a consistent slant. Use connecting stroke exercises to develop a smooth, fluid writing style.
6.3. Maintaining Consistent Slant
Maintaining a consistent slant is essential for creating legible and aesthetically pleasing cursive. Many learners struggle to maintain a uniform slant angle throughout their writing.
- Solution: Use slant guidelines or lined paper with a pre-printed slant angle. Practice writing letters and words while focusing on maintaining a consistent slant. Use a protractor or angle measurement tool to check the slant of your writing.
6.4. Keeping Consistent Spacing
Consistent spacing between letters and words is crucial for readability. Overcrowding or spreading letters too far apart can make cursive difficult to read.
- Solution: Practice writing letters and words while paying attention to spacing. Use a ruler or spacing guide to ensure consistent spacing between letters and words. Experiment with different spacing techniques to find a style that works for you.
6.5. Overcoming the Habit of Printing
If you’re accustomed to printing, it can be challenging to break the habit and transition to cursive. The urge to print individual letters can disrupt the flow and rhythm of cursive writing.
- Solution: Consciously focus on connecting letters and maintaining a continuous flow. Avoid lifting your pen between letters unless necessary. Practice writing words and sentences without pausing or reverting to printing.
6.6. Dealing with Frustration
Learning cursive can be frustrating at times, especially when you encounter difficulties or make mistakes. It’s important to stay positive and persistent, even when you feel discouraged.
- Solution: Set realistic goals and celebrate small victories. Focus on progress rather than perfection. Take breaks when you feel frustrated and return to your practice with a fresh perspective. Seek support from friends, family members, or online communities.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Letter Formation | Regularly practice using alphabet charts, break down letters into steps, and trace letters to build muscle memory. |
| Poor Letter Connections | Practice simple letter combinations, focus on starting and ending points, maintain slant, and use connecting stroke exercises for fluidity. |
| Inconsistent Slant | Use slant guidelines, practice consistently, and check slant angles with measuring tools. |
| Inconsistent Spacing | Focus on consistent letter and word spacing, use rulers or spacing guides, and experiment to find a comfortable style. |
| Habit of Printing | Consciously connect letters, avoid lifting the pen unnecessarily, and practice continuous writing. |
| Dealing with Frustration | Set realistic goals, celebrate progress, take breaks, and seek support from friends or online communities. |
7. Resources for Continued Learning and Practice
Mastering cursive writing is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning and practice. Fortunately, numerous resources are available to support your journey and help you refine your skills.
7.1. Online Tutorials and Courses
The internet offers a wealth of online tutorials and courses that provide step-by-step instructions, demonstrations, and practice exercises for learning cursive.
- Websites: Websites like “The Spruce Crafts” and “Wikihow” offer free tutorials and guides on cursive writing.
- Video Platforms: Platforms like YouTube and Vimeo host numerous video tutorials that demonstrate cursive letter formation, connections, and techniques.
- Online Courses: Websites like Udemy and Coursera offer comprehensive cursive writing courses taught by experienced instructors.
7.2. Printable Worksheets and Guides
Printable worksheets and guides are valuable resources for practicing letter formation, word connections, and sentence writing.
- Free Worksheets: Websites like “Education.com” and “K12Reader” offer free printable cursive writing worksheets for various skill levels.
- Cursive Guides: Purchase or download cursive writing guides that provide detailed instructions, examples, and exercises.
7.3. Interactive Apps and Software
Interactive apps and software provide a dynamic and engaging way to learn and practice cursive writing.
- Handwriting Apps: Apps like “Cursive Writing Wizard” and “Writing Academy” offer interactive exercises, real-time feedback, and personalized practice routines.
- Calligraphy Software: Software programs like “Calligraphr” allow you to create custom cursive fonts and practice writing with different styles and tools.
7.4. Books and Manuals
Books and manuals offer in-depth instruction, historical context, and examples of various cursive styles.
- Cursive Writing Manuals: Look for cursive writing manuals that provide detailed instructions, diagrams, and exercises.
- Calligraphy Books: Explore calligraphy books to learn about different cursive styles, lettering techniques, and decorative elements.
- Historical Documents: Study historical documents written in cursive to observe the techniques and styles used by master penmen.
7.5. Handwriting Communities and Forums
Connecting with other handwriting enthusiasts can provide support, inspiration, and feedback.
- Online Forums: Join online forums and communities dedicated to handwriting and calligraphy, such as “The Fountain Pen Network” and “Reddit’s r/handwriting”
- Social Media Groups: Follow handwriting and calligraphy groups on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest.
- Workshops and Classes: Attend local handwriting workshops or calligraphy classes to learn from experienced instructors and connect with fellow learners.
Here’s a table summarizing resources for learning cursive writing:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Online Tutorials/Courses | Use websites like “The Spruce Crafts,” video platforms like YouTube, and online courses on Udemy for instructions and demonstrations. |
| Printable Worksheets/Guides | Access free worksheets from sites like “Education.com” and purchase or download cursive guides. |
| Interactive Apps/Software | Use apps like “Cursive Writing Wizard” and software like “Calligraphr” for interactive exercises and custom font creation. |
| Books/Manuals | Consult cursive writing and calligraphy books, and study historical documents for diverse styles. |
| Handwriting Communities | Join online forums like “The Fountain Pen Network,” social media groups on Facebook and Instagram, and attend local workshops for support and inspiration. |
8. The Future of Cursive Writing in a Digital Age
While digital communication continues to dominate our modern world, cursive writing retains a unique value and relevance. Understanding the future of cursive writing in a digital age requires examining its potential role in education, personal expression, and cultural preservation.
8.1. Cursive in Education
The debate over whether to teach cursive in schools continues, with arguments both for and against its inclusion in the curriculum.
- Arguments for Cursive: Proponents argue that cursive writing enhances fine motor skills, improves brain connectivity, and provides a connection to historical documents.
- Arguments Against Cursive: Critics argue that cursive is no longer necessary in a digital age and that instructional time could be better spent on other skills.
- Balanced Approach: A balanced approach may involve teaching cursive as an elective or enrichment activity, rather than a mandatory subject.
8.2. Cursive as Personal Expression
In an increasingly digital world, cursive writing offers a unique and personal form of expression.
- Handwritten Notes: Handwritten notes and letters convey a sense of care and thoughtfulness that typed messages often lack.
- Creative Writing: Cursive writing can be a powerful tool for creative expression, allowing individuals to explore their thoughts and emotions in a more personal and meaningful way.
- Calligraphy: Calligraphy, a decorative form of cursive writing, can be used to create beautiful and expressive lettering for invitations, announcements, and art projects.
8.3. Cursive as Cultural Preservation
Cursive writing provides a direct link to the past, allowing individuals to read and understand historical documents, letters, and journals written in cursive.
- Historical Literacy: The ability to read cursive is essential for accessing and interpreting historical records, literature, and personal accounts.
- Family History: Cursive writing can be used to preserve family histories, write memoirs, and pass on personal stories to future generations.
- Cultural Heritage: By preserving cursive writing, we maintain a connection to our cultural heritage and ensure that future generations can access and appreciate the written works of the past.
8.4. Technology and Cursive
Technology can play a role in preserving and promoting cursive writing.
- Digital Fonts: Digital cursive fonts can be used to create documents and designs that incorporate the look and feel of cursive handwriting.
- Handwriting Recognition: Handwriting recognition software can convert handwritten cursive into digital text, making it easier to preserve and share handwritten documents.
- Interactive Learning Tools: Interactive apps and software can be used to teach and practice cursive writing in a fun and engaging way.
8.5. The Enduring Appeal of Handwriting
Despite the rise of digital communication, the act of writing by hand retains a special appeal.
- Personal Connection: Handwritten notes and letters convey a sense of care and thoughtfulness that typed messages often lack.
- Mindfulness: The act of writing by hand can be a form of mindfulness, allowing individuals to slow down, focus, and engage more deeply with their thoughts.
- Creativity: Cursive writing encourages creativity and self-expression, allowing individuals to develop their unique handwriting style.
Here’s a summary table of the future of cursive writing:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Education | Teaching cursive may become an elective rather than a mandatory subject. |
| Personal Expression | Cursive allows for unique self-expression through handwritten notes and calligraphy. |
| Cultural Preservation | Preserves historical literacy and family histories, maintaining a connection to cultural heritage. |
| Technology Integration | Digital fonts, handwriting recognition software, and interactive learning tools can preserve and promote cursive writing. |
| Enduring Appeal | Handwriting retains a personal connection, enhances mindfulness, and encourages creativity. |
9. Cursive Writing Styles to Explore
Exploring different cursive writing styles can significantly enhance your skills and add a personal touch to your handwriting. Each style offers unique characteristics and aesthetic qualities that cater to various preferences and purposes.
9.1. Palmer Method
The Palmer Method, developed by Austin Palmer in the late 19th century, emphasizes efficiency and legibility. It focuses on smooth, rhythmic strokes and minimal ornamentation. This style is perfect for beginners due to its simplicity and practicality.
- Characteristics:
- Simple, unadorned letterforms
- Emphasis on smooth, continuous strokes
- Rhythmic, consistent movements
- Minimal shading or variation in line weight
- Benefits:
- Easy to learn
- Promotes speed and efficiency
- Highly legible
9.2. Spencerian Script
Spencerian Script, created by Platt Rogers Spencer, is known for its elegance and fluidity. It features ornate flourishes, delicate lines, and a high degree of ornamentation. This style is often used for formal occasions and artistic purposes.
- Characteristics:
- Elaborate flourishes and swashes
- Delicate, fine lines
- Emphasis on graceful curves
- High degree of ornamentation
- Benefits:
- Visually stunning and elegant
- Ideal for formal occasions
- Allows for artistic expression
9.3. D’Nealian Cursive
D’Nealian Cursive, developed by Donald Neal Thurber, is a simplified cursive style designed to ease the transition from manuscript printing to cursive writing. It closely resembles print letterforms, making it easier for children to learn.
- Characteristics: