Micro learning is a powerful learning strategy that delivers content in focused, bite-sized segments. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by LEARNS.EDU.VN, explores the definition, benefits, and practical implementation of micro learning to enhance knowledge retention and engagement. Discover how to optimize your learning experience with this innovative approach and unlock its potential for continuous professional and personal development.
1. Defining How to Micro Learn: The Essence of Bite-Sized Knowledge
Micro learning is an educational approach that delivers content to learners in small, very specific bursts. Instead of long, comprehensive training sessions, micro learning provides focused, bite-sized pieces of information designed to be easily digestible and immediately applicable. This method, which typically involves learning modules lasting from two to five minutes, targets specific learning outcomes and enhances knowledge retention by breaking down complex topics into manageable parts. As defined by researchers at the University of Greenwich, micro learning leverages short-term memory effectively, making it an ideal strategy for busy professionals and lifelong learners.
1.1. Core Principles of Micro Learning
Several core principles underpin the effectiveness of micro learning:
- Bite-Sized Content: Information is presented in small, easily digestible units, focusing on a single learning objective.
- Specificity: Each module addresses a specific skill, concept, or piece of knowledge.
- Accessibility: Content is readily available and can be accessed anytime, anywhere, often via mobile devices.
- Engagement: Micro learning modules are designed to be interactive and engaging, using formats like videos, quizzes, and gamified elements.
- Relevance: The content is directly relevant to the learner’s needs and goals, ensuring immediate applicability.
1.2. Micro Learning vs. Traditional Learning: A Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Micro Learning | Traditional Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Content Delivery | Bite-sized, focused segments | Comprehensive, lengthy sessions |
| Duration | 2-5 minutes per module | Hours or days per course |
| Focus | Specific skills or knowledge | Broad understanding of a subject |
| Accessibility | Available anytime, anywhere | Scheduled classes or fixed online courses |
| Engagement | Interactive, uses diverse media | Often lecture-based, less interactive |
| Retention | Higher retention due to focused delivery and repetition | Lower retention due to information overload |
| Pace | Self-paced | Often fixed pace |
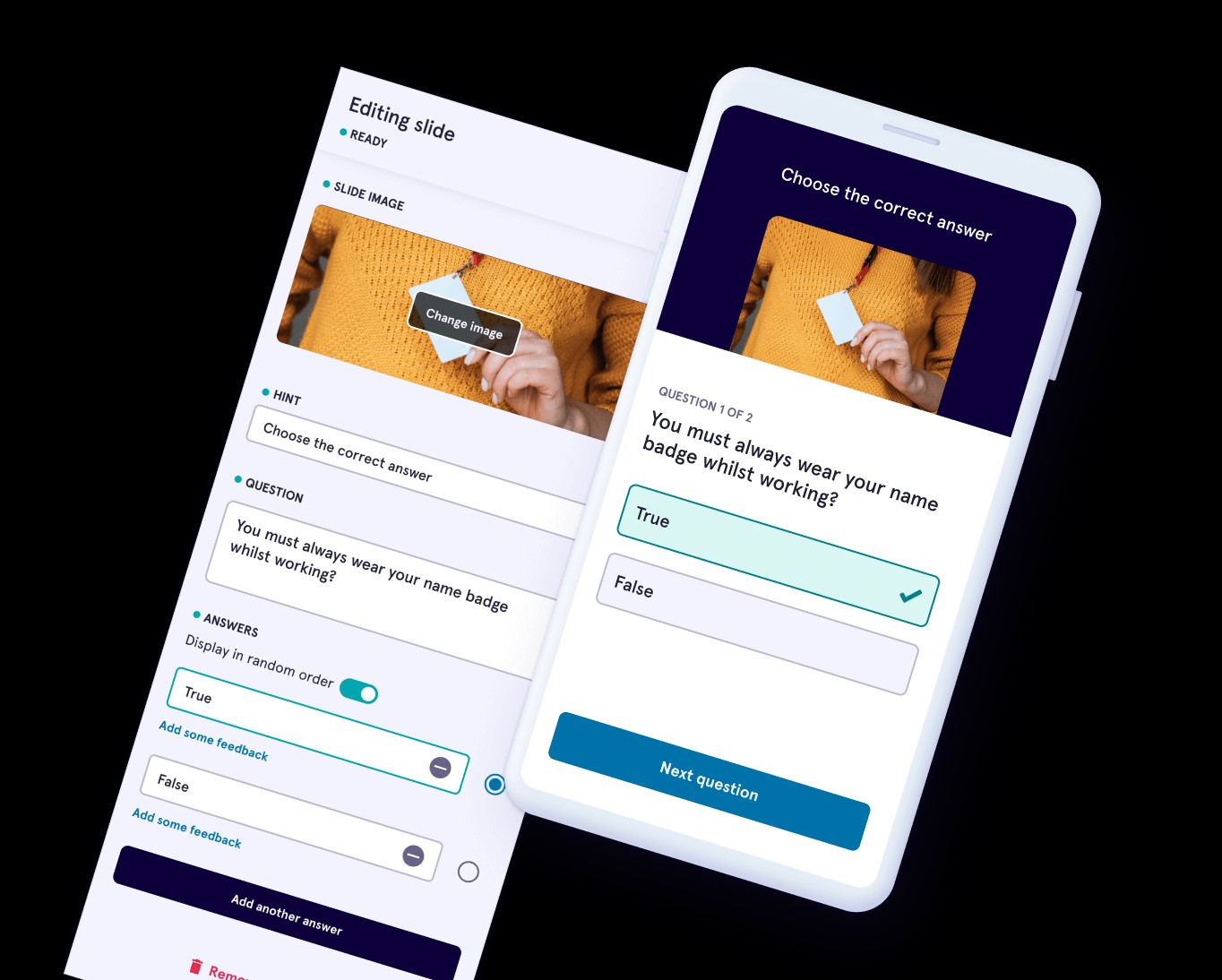
1.3. Why Micro Learning Resonates with Modern Learners
Micro learning aligns perfectly with the preferences and habits of modern learners:
- Attention Spans: Shorter attention spans necessitate learning methods that deliver information quickly and efficiently.
- Mobile-First World: The ubiquity of smartphones makes mobile-friendly micro learning modules easily accessible.
- Busy Schedules: Professionals with demanding schedules appreciate the flexibility and convenience of micro learning.
- Immediate Application: Learners value content that can be immediately applied to their work or personal lives.
2. The Benefits of How to Micro Learn: Unleashing Enhanced Learning Outcomes
Micro learning offers a multitude of benefits that make it a superior learning strategy in many contexts. From enhanced knowledge retention to improved engagement and cost-effectiveness, the advantages of micro learning are compelling.
2.1. Enhanced Knowledge Retention and Comprehension
Research consistently demonstrates that micro learning significantly improves knowledge retention:
- Focused Content: By concentrating on specific learning objectives, learners are more likely to grasp and remember key concepts.
- Repetition and Reinforcement: Short modules can be easily revisited, reinforcing learning and improving long-term retention.
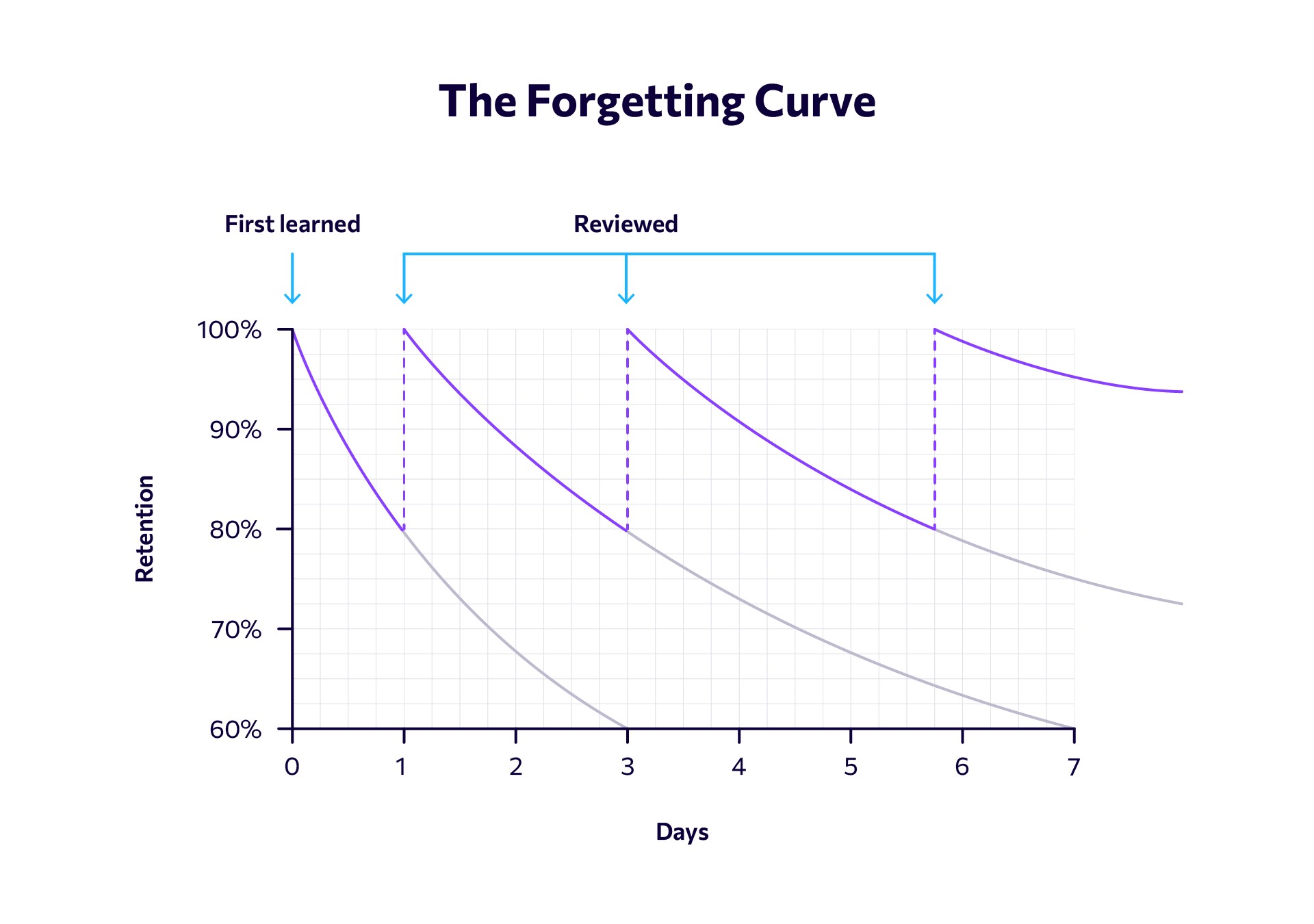
- Spaced Repetition: Micro learning facilitates spaced repetition, a technique where information is reviewed at increasing intervals, further solidifying memory.
- Reduced Cognitive Overload: Breaking down complex topics into smaller units prevents cognitive overload, allowing learners to process information more effectively.
2.2. Increased Engagement and Motivation
The interactive and engaging nature of micro learning modules boosts learner motivation and participation:
- Variety of Media: Micro learning uses a variety of media formats, such as videos, infographics, and quizzes, to keep learners interested.
- Gamification: Incorporating game-like elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, makes learning fun and competitive.
- Immediate Feedback: Quizzes and assessments provide immediate feedback, allowing learners to track their progress and stay motivated.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Completing short modules provides a sense of accomplishment, encouraging learners to continue their learning journey.
2.3. Time Efficiency and Flexibility
Micro learning fits seamlessly into busy schedules, offering unparalleled flexibility and time efficiency:
- Quick Completion: Modules can be completed in just a few minutes, making it easy to fit learning into short breaks or commutes.
- Self-Paced Learning: Learners can progress at their own pace, revisiting content as needed.
- Anytime, Anywhere Access: Mobile-friendly micro learning modules can be accessed anytime, anywhere, allowing learners to learn on the go.
- Reduced Disruption: Micro learning minimizes disruption to workflow, as it doesn’t require extended periods away from work.
2.4. Cost-Effectiveness and ROI
Implementing micro learning can lead to significant cost savings and a higher return on investment (ROI):
- Reduced Training Time: Shorter training sessions translate to less time away from work, reducing labor costs.
- Lower Development Costs: Micro learning modules are typically less expensive to develop than traditional training courses.
- Improved Retention: Higher retention rates mean less need for retraining, saving time and money.
- Increased Productivity: Employees can quickly acquire new skills and knowledge, leading to improved productivity and performance.
2.5. Improved Knowledge Transfer and Application
Micro learning enhances the transfer of knowledge from the training environment to real-world application:
- Contextual Learning: Modules are often designed to address specific, real-world scenarios, making it easier for learners to apply what they’ve learned.
- Just-in-Time Learning: Micro learning provides access to information exactly when it’s needed, ensuring that learners have the knowledge to tackle immediate challenges.
- Performance Support: Micro learning modules can serve as performance support tools, providing quick access to information and guidance when needed.
3. How to Implement Micro Learn: A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Implementation
Implementing micro learning effectively requires careful planning, design, and execution. Follow these steps to create a successful micro learning program:
3.1. Define Learning Objectives and Target Audience
Start by clearly defining the learning objectives and identifying the target audience:
- Learning Objectives: What specific skills or knowledge do you want learners to acquire? Ensure that objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Target Audience: Who are your learners? What are their needs, preferences, and learning styles? Understanding your audience will help you tailor the content and delivery methods.
- Gap Analysis: Identify the gap between the current knowledge and skills of your learners and the desired outcomes. This will help you focus your micro learning modules on the most critical areas.
3.2. Select Appropriate Content Formats and Tools
Choose content formats and tools that are engaging, accessible, and aligned with your learning objectives:
- Videos: Short, explainer videos are highly effective for demonstrating concepts and processes.
- Infographics: Visual representations of data and information can be easily digested and remembered.
- Quizzes: Interactive quizzes provide immediate feedback and reinforce learning.
- Games: Gamified elements can make learning fun and competitive.
- Podcasts: Audio snippets can be listened to on the go, making them ideal for busy learners.
- Micro learning Platforms: Invest in a robust micro learning platform like LEARNS.EDU.VN that supports various content formats, provides analytics, and allows for easy content creation and delivery.
3.3. Design Engaging and Interactive Modules
Create micro learning modules that are engaging, interactive, and focused on specific learning objectives:
- Keep it Short and Sweet: Aim for modules that are 2-5 minutes in length.
- Focus on One Key Concept: Each module should address a single, specific learning objective.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate images, videos, and infographics to enhance engagement and comprehension.
- Add Interactivity: Include quizzes, polls, and interactive exercises to keep learners involved.
- Provide Immediate Feedback: Give learners immediate feedback on their performance to reinforce learning.
3.4. Ensure Mobile Accessibility and Seamless Integration
Make sure your micro learning modules are accessible on mobile devices and seamlessly integrated into the learner’s workflow:
- Mobile-First Design: Design your modules with mobile devices in mind, ensuring that they are responsive and easy to navigate on smartphones and tablets.
- Seamless Access: Provide easy access to modules through a mobile app or a web-based platform.
- Integration with Existing Tools: Integrate micro learning modules into the tools and platforms that learners already use, such as email, messaging apps, and learning management systems (LMS).
- Push Notifications: Use push notifications to remind learners about new modules or to encourage them to revisit existing content.
3.5. Evaluate and Iterate
Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your micro learning program and make adjustments as needed:
- Track Completion Rates: Monitor the completion rates of your modules to identify areas where learners may be struggling.
- Assess Knowledge Retention: Use quizzes and assessments to measure knowledge retention and identify areas where reinforcement is needed.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from learners to identify what’s working well and what could be improved.
- Iterate and Improve: Use the data and feedback you gather to make adjustments to your modules and improve the overall effectiveness of your micro learning program.
4. Micro Learning in Practice: Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Micro learning can be applied in a wide range of contexts, from corporate training to academic education. Here are some real-world examples and use cases:
4.1. Onboarding New Employees
Micro learning can be used to efficiently onboard new employees:
- Company Culture: Short videos can introduce new hires to the company culture, values, and mission.
- Compliance Training: Micro modules can cover essential compliance topics, such as workplace safety, data security, and ethics.
- Job-Specific Skills: Bite-sized tutorials can teach new employees the specific skills they need to perform their jobs effectively.
- Policy and Procedure Updates: Short updates can keep employees informed about the latest policy and procedure changes.
4.2. Sales Training
Micro learning can enhance sales training by providing just-in-time information and reinforcement:
- Product Knowledge: Short modules can teach sales reps about new products and features.
- Sales Techniques: Bite-sized tutorials can cover effective sales techniques and strategies.
- Customer Service Skills: Micro learning can improve customer service skills by teaching reps how to handle common customer inquiries and complaints.
- Competitive Analysis: Short updates can keep sales reps informed about the latest competitive developments.
4.3. Leadership Development
Micro learning can be used to develop leadership skills in a flexible and efficient way:
- Communication Skills: Short modules can teach leaders how to communicate effectively with their teams.
- Conflict Resolution: Bite-sized tutorials can cover strategies for resolving conflicts in the workplace.
- Decision-Making: Micro learning can improve decision-making skills by teaching leaders how to analyze data and make informed choices.
- Team Building: Short activities and exercises can help leaders build stronger teams.
4.4. Compliance Training
Micro learning is an effective way to deliver compliance training:
- Data Security: Short videos can educate employees about data security risks and best practices.
- Workplace Safety: Bite-sized tutorials can cover essential workplace safety procedures.
- Ethics Training: Micro modules can teach employees about ethical behavior in the workplace.
- Harassment Prevention: Short videos can educate employees about harassment prevention and reporting procedures.
4.5. Academic Education
Micro learning can be used to supplement traditional academic education:
- Review and Reinforcement: Short modules can be used to review and reinforce key concepts.
- Test Preparation: Bite-sized quizzes can help students prepare for exams.
- Supplemental Materials: Micro learning can provide access to supplemental materials, such as videos and infographics.
- Personalized Learning: Micro learning can be used to personalize learning, providing students with content that is tailored to their individual needs and learning styles.
5. Advanced Strategies for How to Micro Learn: Optimizing Your Approach
To maximize the effectiveness of your micro learning program, consider these advanced strategies:
5.1. Personalized Learning Paths
Create personalized learning paths that are tailored to the individual needs and goals of your learners:
- Assessment: Start by assessing the knowledge and skills of your learners.
- Recommendations: Use the assessment data to recommend specific micro learning modules that are relevant to their needs.
- Adaptive Learning: Use adaptive learning algorithms to adjust the difficulty and content of the modules based on the learner’s performance.
- Progress Tracking: Allow learners to track their progress and see how far they’ve come.
5.2. Gamification and Rewards
Incorporate gamification and rewards to increase engagement and motivation:
- Points: Award points for completing modules and achieving learning objectives.
- Badges: Give learners badges for mastering specific skills or topics.
- Leaderboards: Create leaderboards to foster competition and encourage learners to strive for excellence.
- Rewards: Offer tangible rewards, such as gift cards or extra vacation days, for top performers.
5.3. Social Learning and Collaboration
Encourage social learning and collaboration by incorporating social features into your micro learning platform:
- Forums: Create forums where learners can ask questions, share ideas, and collaborate with one another.
- Peer-to-Peer Learning: Encourage learners to share their knowledge and expertise with one another.
- Group Projects: Assign group projects that require learners to collaborate and apply what they’ve learned.
- Social Recognition: Recognize and celebrate the achievements of learners in a social setting.
5.4. Data Analytics and Insights
Use data analytics to gain insights into the effectiveness of your micro learning program:
- Completion Rates: Track the completion rates of your modules to identify areas where learners may be struggling.
- Assessment Scores: Analyze assessment scores to measure knowledge retention and identify areas where reinforcement is needed.
- Engagement Metrics: Monitor engagement metrics, such as the number of comments and shares, to gauge the level of interest in your modules.
- Feedback Analysis: Analyze feedback from learners to identify what’s working well and what could be improved.
5.5. Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Continuously improve and adapt your micro learning program based on data, feedback, and best practices:
- Stay Up-to-Date: Keep abreast of the latest trends and best practices in micro learning.
- Experiment: Experiment with new content formats, delivery methods, and gamification techniques.
- Gather Feedback: Continuously solicit feedback from learners and stakeholders.
- Iterate: Use the data and feedback you gather to make adjustments to your program and improve its overall effectiveness.
6. The Future of How to Micro Learn: Trends and Innovations
Micro learning is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. Here are some of the key trends to watch:
6.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to personalize learning paths, automate content creation, and provide intelligent feedback:
- Personalized Recommendations: AI algorithms can analyze learner data to recommend specific micro learning modules that are relevant to their needs and interests.
- Automated Content Creation: AI can be used to generate micro learning content automatically, saving time and resources.
- Intelligent Feedback: AI-powered chatbots can provide learners with instant feedback and support.
6.2. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR are being used to create immersive and engaging micro learning experiences:
- Virtual Simulations: VR can be used to create virtual simulations that allow learners to practice skills in a safe and realistic environment.
- Augmented Reality Overlays: AR can be used to overlay digital information onto the real world, providing learners with just-in-time support and guidance.
- Interactive 3D Models: AR can be used to create interactive 3D models that allow learners to explore complex concepts in a visual and engaging way.
6.3. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is being used to create secure and transparent learning records:
- Digital Credentials: Blockchain can be used to issue digital credentials that are tamper-proof and easily verifiable.
- Learning Portfolios: Learners can use blockchain to create secure and portable learning portfolios that showcase their skills and achievements.
- Data Privacy: Blockchain can be used to protect learner data and ensure privacy.
6.4. Data-Driven Learning
Data is being used to personalize learning paths, optimize content, and measure the effectiveness of micro learning programs:
- Learning Analytics: Learning analytics platforms can track learner progress, identify areas where learners may be struggling, and measure the effectiveness of micro learning interventions.
- Personalized Learning Paths: Data can be used to create personalized learning paths that are tailored to the individual needs and goals of each learner.
- Adaptive Learning: Adaptive learning algorithms can adjust the difficulty and content of micro learning modules based on the learner’s performance.
6.5. Mobile Learning
Mobile learning continues to be a key trend in micro learning, with learners increasingly accessing content on their smartphones and tablets:
- Mobile-First Design: Micro learning modules are being designed with mobile devices in mind, ensuring that they are responsive and easy to navigate on smartphones and tablets.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps are being used to deliver micro learning content and provide learners with access to support and resources.
- Push Notifications: Push notifications are being used to remind learners about new modules and encourage them to revisit existing content.
7. Overcoming Challenges in How to Micro Learn: Strategies for Success
While micro learning offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges. Here’s how to overcome them:
7.1. Content Overload and Information Fragmentation
- Curate Content: Focus on high-quality, relevant content that aligns with specific learning objectives.
- Structured Learning Paths: Create structured learning paths that guide learners through a logical sequence of modules.
- Contextualization: Provide context and connect micro learning modules to larger learning goals.
7.2. Lack of Engagement and Motivation
- Gamification: Incorporate gamification elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, to increase engagement.
- Interactive Content: Use interactive quizzes, polls, and simulations to keep learners involved.
- Personalized Learning: Tailor content to the individual needs and interests of learners.
7.3. Difficulty in Measuring ROI
- Define Clear Metrics: Define clear metrics for measuring the ROI of your micro learning program, such as completion rates, assessment scores, and performance improvements.
- Track Data: Track data on these metrics and analyze the results.
- Compare Results: Compare the results of your micro learning program to the results of traditional training methods.
7.4. Resistance to Change
- Communicate Benefits: Clearly communicate the benefits of micro learning to learners and stakeholders.
- Provide Support: Provide learners with the support and resources they need to succeed.
- Pilot Programs: Start with pilot programs to demonstrate the effectiveness of micro learning.
7.5. Ensuring Quality and Accuracy
- Subject Matter Experts: Involve subject matter experts in the creation and review of micro learning content.
- Quality Control: Implement a quality control process to ensure that content is accurate, up-to-date, and free of errors.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms that allow learners to provide feedback on the quality and accuracy of content.
8. Tools and Resources for How to Micro Learn: Enhancing Your Learning Ecosystem
To create an effective micro learning program, you’ll need the right tools and resources:
8.1. Micro Learning Platforms
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: A comprehensive micro learning platform that offers a wide range of features, including content creation, delivery, and analytics.
- Other Platforms: Explore other platforms like TalentCards, OttoLearn, and Axonify, each offering unique features and benefits.
8.2. Content Creation Tools
- Video Editors: Use video editors like Camtasia or Adobe Premiere Rush to create engaging video content.
- Graphic Design Tools: Use graphic design tools like Canva or Adobe Photoshop to create visually appealing infographics and images.
- Interactive Content Tools: Use interactive content tools like Articulate Storyline or Adobe Captivate to create quizzes, simulations, and other interactive modules.
8.3. Learning Management Systems (LMS)
- Integration: Choose an LMS that integrates seamlessly with your micro learning platform.
- Features: Look for features like content management, learner tracking, and reporting.
8.4. Mobile Learning Apps
- Mobile Accessibility: Ensure that your micro learning content is accessible on mobile devices.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: Design your content with mobile devices in mind, ensuring that it is responsive and easy to navigate on smartphones and tablets.
8.5. Learning Resources
- Online Courses: Supplement your micro learning program with online courses from platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy.
- E-books and Articles: Provide learners with access to e-books and articles on relevant topics.
- Webinars and Podcasts: Offer webinars and podcasts to provide learners with additional insights and information.
9. How to Micro Learn for Different Learning Styles: Tailoring Your Approach
To maximize the effectiveness of micro learning, it’s essential to tailor your approach to different learning styles:
9.1. Visual Learners
- Use Visuals: Incorporate images, videos, infographics, and other visual aids into your micro learning modules.
- Color Coding: Use color coding to highlight key concepts and information.
- Mind Maps: Create mind maps to visually organize information.
9.2. Auditory Learners
- Podcasts and Audio Snippets: Include podcasts and audio snippets in your micro learning modules.
- Lectures and Presentations: Offer access to recorded lectures and presentations.
- Discussions: Encourage discussions and collaborative learning activities.
9.3. Kinesthetic Learners
- Interactive Exercises: Incorporate interactive exercises and simulations into your micro learning modules.
- Hands-On Activities: Provide opportunities for hands-on practice and experimentation.
- Role-Playing: Use role-playing scenarios to simulate real-world situations.
9.4. Reading/Writing Learners
- Written Summaries: Provide written summaries of key concepts and information.
- Articles and E-books: Offer access to articles and e-books on relevant topics.
- Note-Taking: Encourage learners to take notes and write summaries of what they’ve learned.
9.5. Multimodal Learners
- Variety of Content: Use a variety of content formats, including visuals, audio, and interactive exercises.
- Flexibility: Allow learners to choose the content formats and learning activities that work best for them.
- Personalization: Tailor the learning experience to the individual needs and preferences of each learner.
10. FAQs About How to Micro Learn
1. What is the ideal length of a micro learning module?
The ideal length is typically 2-5 minutes, focusing on a single learning objective.
2. Is micro learning suitable for complex topics?
While it’s best for specific skills or knowledge, complex topics can be broken down into smaller, manageable micro learning modules.
3. How can I measure the effectiveness of micro learning?
Track completion rates, assessment scores, and gather learner feedback.
4. What are some examples of content formats for micro learning?
Videos, infographics, quizzes, games, and podcasts.
5. How can I make micro learning more engaging?
Use gamification, interactive elements, and personalized content.
6. Is micro learning only for corporate training?
No, it can be used in various settings, including academic education and personal development.
7. What role does mobile learning play in micro learning?
Mobile learning makes micro learning more accessible, allowing learners to access content anytime, anywhere.
8. How can I ensure that micro learning content is accurate and up-to-date?
Involve subject matter experts in content creation and review, and implement a quality control process.
9. What are some common challenges of implementing micro learning?
Content overload, lack of engagement, and difficulty in measuring ROI.
10. How can I personalize micro learning for different learning styles?
Use a variety of content formats and learning activities to cater to visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and reading/writing learners.
Micro learning, when implemented effectively, offers a powerful approach to learning that enhances knowledge retention, boosts engagement, and improves efficiency. By following the strategies outlined in this guide and leveraging the resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can create a successful micro learning program that empowers learners to achieve their goals.
Ready to transform your learning experience with micro learning? Explore the resources and courses available at LEARNS.EDU.VN to discover how this innovative approach can help you achieve your personal and professional development goals. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Visit our website at learns.edu.vn to learn more.