Website analytics is foundational to understanding and improving your Search Engine Optimization (SEO) efforts. In the dynamic world of online visibility, the adage “What gets measured gets improved” rings especially true. To truly Learn About Seo, you must leverage the right tools to monitor and analyze your website’s performance. This data provides critical answers to vital SEO questions, empowering you to refine your strategies and achieve sustainable growth.
By effectively using analytics, you can discover:
- Which keywords are driving your website’s rankings on Google.
- The click-through rate (CTR) of your pages in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- The geographic distribution of your website visitors.
- The most effective traffic channels for your site.
- How users interact with your website content.
- Your most popular and engaging pages.
This guide will introduce you to three essential analytics tools every website owner and aspiring SEO professional should master to learn about SEO practically: Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and rank tracking tools. These tools will transform your approach to SEO from guesswork to data-driven strategy.
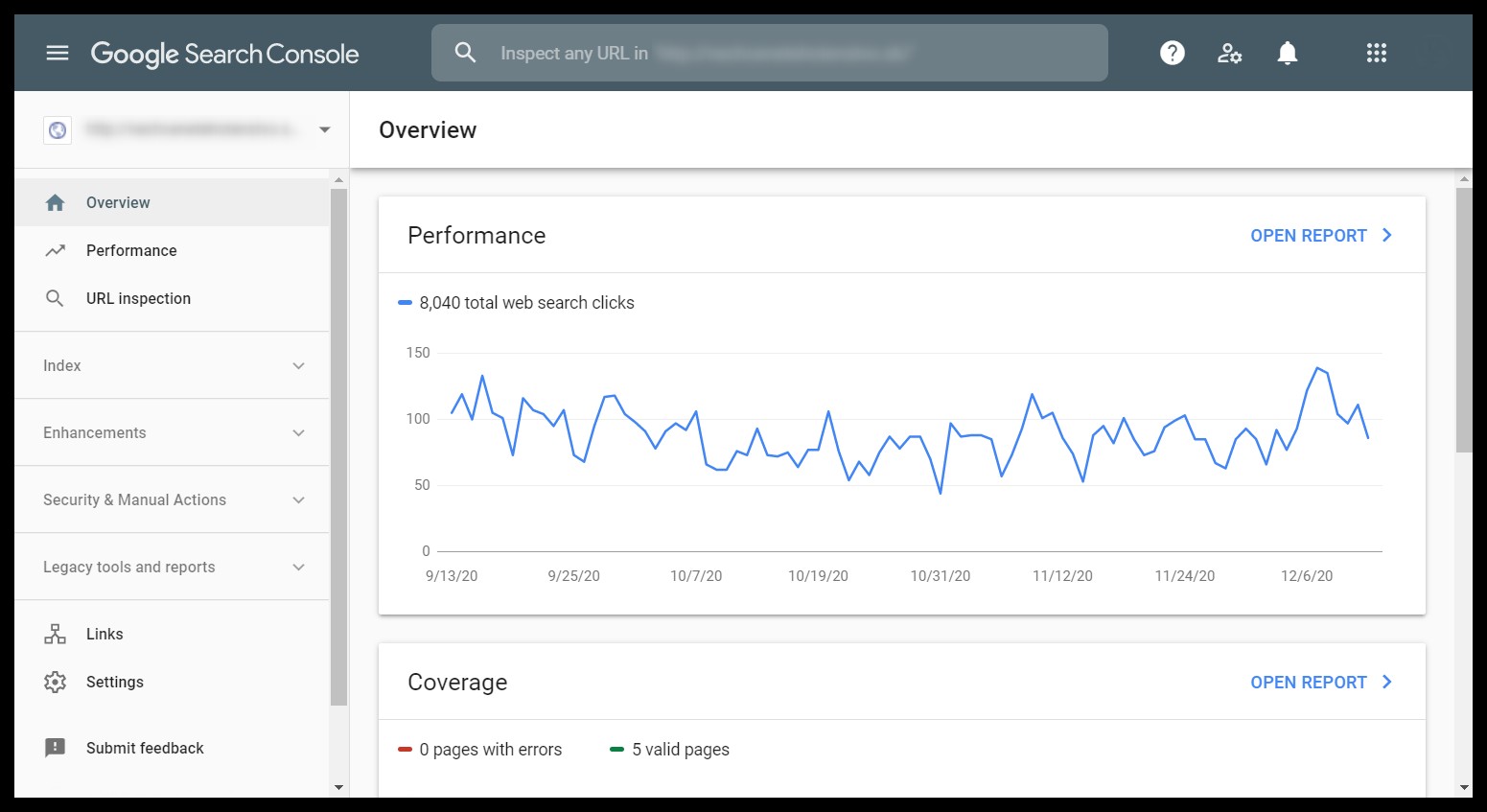
Google Search Console: Your Free SEO Performance Dashboard
Google Search Console (GSC) is an indispensable, free service provided by Google. It acts as a direct line of communication between Google and website owners, offering invaluable insights into how Google perceives your site and its performance in search results. For anyone serious about learn about SEO, mastering GSC is non-negotiable.
GSC is not just a tool; it’s your direct feedback loop from the world’s leading search engine. It’s difficult to overstate its importance in SEO; every website owner who wants to learn about SEO and improve their online presence should be using it.
Note: Before you can access the wealth of data in Google Search Console, you need to verify website ownership. For a detailed walkthrough, refer to resources like “our simple guide to Google Search Console” which will guide you through the verification process.
Once set up, Google Search Console presents a series of dashboards, ranging from high-level performance summaries to detailed reports on critical website issues that require immediate attention. These dashboards are crucial for anyone seeking to learn about SEO in a practical, hands-on manner.
Key reports within Google Search Console include:
- Performance: Provides crucial data on how your website performs in Google Search. This is where you learn about SEO through keyword rankings, impressions, clicks, and average position.
- URL Inspection: Allows you to examine how Google has indexed specific pages on your site, aiding in technical SEO and helping you learn about SEO issues on a page-by-page basis.
- Coverage: Reveals which pages are indexed by Google and highlights any indexation problems. Understanding coverage is fundamental to learn about SEO technical aspects.
- Sitemaps: Enables you to submit sitemaps to Google and monitor their status, ensuring Google can efficiently crawl and index your site. Sitemaps are a core concept to learn about SEO.
- Removals: Offers a tool to temporarily remove pages from Google search results, useful in content management and learn about SEO crisis control.
- Enhancements: Reports on enhancements like AMP and sitelinks and flags user experience or usability issues. Enhancements are important for advanced SEO learning.
- Manual actions: Informs you if Google has applied a manual penalty to your site, a critical area to understand when you learn about SEO best practices and potential pitfalls.
- Security issues: Alerts you to any security threats detected on your website, highlighting the importance of security in SEO, a crucial aspect to learn about SEO holistically.
- Links: Provides a basic overview of your website’s link profile, both internal and external links, essential for understanding off-page SEO and learn about SEO link building strategies.
For those looking to learn about SEO, the Performance report is often the most frequently used and insightful. Let’s delve deeper into this report and explore how it can enhance your SEO knowledge.
Performance Report: Unlocking SEO Insights
The Performance report is a treasure trove of data for anyone wanting to learn about SEO. It offers a detailed view of your website’s search performance in Google. Understanding this report is key to data-driven SEO.
The report is structured into three main interactive sections:
- Top Filter: Allows you to refine the data by search type (web, image, video), date range, and dimensions like query, page, country, device, or search appearance. Filtering is essential to learn about SEO nuances.
- Metrics Chart: Visually displays trends for four key metrics: clicks, impressions, average CTR, and average position. You can customize the chart by selecting any combination of these metrics. Visualizing data is a powerful way to learn about SEO patterns.
- Dimension Tabs & Data Table: Allows you to select a dimension (like Queries, Pages, Countries, Devices, Search Appearance) and view the corresponding data in a table format. Analyzing data tables is fundamental to learn about SEO details.
For a quick visual introduction to the Performance report, Google Search Central offers educational videos that can be incredibly helpful for visual learners who learn about SEO best through video tutorials.
Beyond basic metrics like top queries and pages, the Performance report is a goldmine for uncovering deeper SEO insights. Let’s explore some practical applications to learn about SEO using this report:
Diagnose Performance Drops to Learn About SEO Issues
When you observe any decline in website performance, such as a sudden decrease in clicks, the Performance report is your first stop to learn about SEO troubleshooting. Always aim to identify the root cause of performance changes.
By examining different dimensions, you can pinpoint the source of the issue. For instance, a drop in overall performance might be traced back to a decline in traffic from a specific country, a ranking drop for a crucial keyword, or a performance problem on a particular device type. This detailed analysis is vital to learn about SEO diagnosis.
Tip: Utilize the Comparison feature (Top filter – Date – Compare) to compare performance across two date ranges. This highlights the most significant changes compared to a previous period, helping you quickly learn about SEO performance shifts.
Optimize CTR to Learn About SEO Copywriting
Identify high-performing queries with low click-through rates by focusing on the Average CTR metric or comparing Impressions and Clicks. This is a practical way to learn about SEO optimization techniques.
Low CTR for high-impression keywords indicates an opportunity to improve your title tags and meta descriptions. Crafting compelling metadata is a key skill to learn about SEO content optimization. Improving these elements can significantly boost your CTR and drive more organic traffic.
Compare Desktop vs. Mobile Performance to Learn About Mobile SEO
Use the device dimension in the top filter and select Compare instead of Filter to analyze performance differences between desktop and mobile devices. This is crucial to learn about SEO in a mobile-first world.
This comparison allows you to understand how your website performs across different devices and make informed decisions regarding mobile optimization. Mobile SEO is a critical component to learn about SEO comprehensively. Take action based on these insights to improve user experience on mobile.
Find Low-Hanging Keywords to Learn About Keyword Opportunities
Filter the dimensions table to show queries ranking in positions 20 or lower (SERP 3 and beyond). This is a smart strategy to learn about SEO keyword targeting.
These keywords represent “low-hanging fruit” – terms for which you already have some ranking presence. Switch to the Pages tab to identify the pages ranking for these keywords. Often, minor optimizations to these pages can lead to significant ranking improvements. Keyword research and opportunity identification are core skills to learn about SEO.
Consider enhancing the existing page targeting the keyword or creating new, dedicated content to focus more intently on these valuable terms. This targeted approach is a key lesson when you learn about SEO content strategy.
Analyze Branded vs. Non-Branded Searches to Learn About Brand SEO
Use the top filter to show queries “containing” your brand name. This helps you learn about SEO branding and brand awareness.
This filter reveals the proportion of your search traffic originating from branded keywords and their performance. Understanding branded search is important to learn about SEO brand building and reputation management. Analyzing branded vs. non-branded search terms gives insights into brand recognition and customer search behavior.
Further reading: Google Search Console: A simple guide for SEO beginners
Google Analytics: Deep Dive into User Behavior for SEO Strategy
Google Analytics (GA) is another free and powerful website analytics tool that tracks and reports website traffic and user behavior in detail. While Google Search Console focuses on search performance, Google Analytics provides a broader view of website activity, crucial for anyone aiming to learn about SEO and its wider impact.
However, many beginners find Google Analytics overwhelming due to its vast array of reports, metrics, and complex navigation. It’s normal to feel lost initially, but mastering GA is a significant step in your journey to learn about SEO comprehensively.
Note: Setting up Google Analytics involves adding a tracking code to your website. Guides like “this detailed guide” provide step-by-step instructions.
To effectively learn about SEO with Google Analytics, take it one step at a time. Focus on understanding key reports and metrics relevant to SEO.
Data Categories in Google Analytics for SEO Learners
Google Analytics reports are categorized into five main sections, accessible from the left-hand menu. Each category provides different perspectives on your website data, all valuable for learn about SEO data analysis.
- Real-time: Shows user activity as it happens live on your site. While interesting, its direct SEO value is limited compared to other reports but can be useful to learn about SEO campaign impact in real-time.
- Audience: Provides demographic, interest, technology, and mobile data about your website visitors. Understanding your audience is crucial for targeted SEO strategies and to learn about SEO audience personas.
- Acquisition: Details where your website traffic originates, including traffic channels, sources, and mediums. Analyzing acquisition data is vital to learn about SEO channel effectiveness and traffic sources.
- Behavior: Reveals how users interact with your website, including pages visited, landing pages, exit pages, and site speed. Understanding user behavior is essential for optimizing content and user experience for SEO and to learn about SEO user engagement metrics.
- Conversions: Tracks how users complete defined goals, like purchases, form submissions, or newsletter sign-ups. Conversion tracking allows you to measure the ROI of your SEO efforts and to learn about SEO conversion optimization.
Data Segmentation in Google Analytics for Deeper SEO Insights
Within each Google Analytics report, you can segment and filter data to gain deeper insights tailored to your specific SEO questions. Segmentation is a powerful technique to learn about SEO through focused data analysis.
Segmentation and filtering are essential to isolate and analyze specific data sets relevant to your SEO learning objectives.
Date Range: Setting the Timeframe for SEO Analysis
Selecting the appropriate date range is the first step in any Google Analytics analysis. The date range selector, located at the top right of every report, allows you to view data over different periods and compare date ranges. Time-based analysis is crucial to learn about SEO trends and seasonal effects.
Segments: Isolating Specific Traffic for SEO Focus
Segments are subsets of your Google Analytics data. You can use default segments (e.g., Organic Traffic, Mobile Traffic) or create custom segments to focus on specific traffic types. Segmentation helps you learn about SEO for specific traffic groups.
Example: Create a custom segment to analyze organic blog traffic separately. This allows you to assess the organic reach of your blog content, a key metric for content SEO and to learn about SEO content performance.
Here’s an example of setting up an organic blog traffic segment:
Secondary Dimension: Adding Context to SEO Reports
A secondary dimension adds another layer of detail to the primary dimension in a report. This provides richer context for your SEO analysis and helps you learn about SEO data relationships.
Example: In the All Pages report (primary dimension: Pages), adding User Type (secondary dimension) shows the proportion of new vs. returning visitors for each page. This helps understand page engagement with different user segments and is valuable to learn about SEO user behavior.
Search Function: Refining Data Tables for SEO Queries
A simple search bar above each data table lets you quickly filter results. This is useful for finding specific pages, keywords, or other data points within reports, streamlining your SEO data exploration and helping you quickly learn about SEO relevant data.
Essential Google Analytics Reports for SEO Learners
While Google Analytics offers a vast number of reports, beginners can focus on a few key reports to gain valuable SEO insights. These reports provide a solid foundation to learn about SEO using Google Analytics.
1. All Pages Report: Understanding Content Popularity for SEO
Behavior – Site Content – All Pages
The All Pages report is fundamental for understanding content performance. It shows pageviews, average time on page, bounce rate, and other engagement metrics for each page on your site. This report helps you learn about SEO content performance and identify popular pages.
It reveals which pages attract the most traffic and user engagement, guiding content strategy and highlighting pages needing improvement. Analyzing popular pages is essential to learn about SEO content strategy.
2. Landing Pages Report: Analyzing Entry Points for SEO Traffic
Behavior – Site Content – Landing Pages
Similar to the All Pages report, the Landing Pages report focuses specifically on the first pages users visit on your site. This is particularly valuable for SEO, as organic search traffic typically lands on specific pages. Landing page analysis is crucial to learn about SEO traffic entry points.
It’s especially useful for analyzing organic traffic from Google, as search engine visits always start on landing pages. Optimizing landing pages is a key aspect of SEO and to learn about SEO user journey.
3. All Traffic Report: Identifying Traffic Sources for SEO
Acquisition – All Traffic
Understanding traffic sources is crucial for evaluating SEO effectiveness and broader marketing strategies. The All Traffic report breaks down traffic by channel, source, and medium, providing valuable data to learn about SEO traffic attribution.
The All Traffic report contains several sub-reports:
- Channels: Shows traffic distribution across major channels like Organic Search, Direct, Referral, Social, and Paid Search. Channel analysis is fundamental to learn about SEO channel performance.
- Source/Medium: Provides detailed traffic origins, such as google/organic, bing/organic, facebook/referral. Source/medium analysis offers granular insights to learn about SEO traffic sources.
- Referrals: Lists websites referring traffic to your site. Referral analysis helps identify valuable backlinks and partnerships and to learn about SEO referral traffic.
Example: If you notice a sudden traffic spike, use the Source/Medium report to compare time periods and identify the source/medium combination responsible for the increase. Further, add secondary dimensions like Landing Page or Country/City to understand which pages or regions are driving the traffic surge. This detailed investigation is a practical application of learn about SEO data analysis for traffic fluctuations.
4. Audience Demographics and Location: Understanding Your SEO Audience
Audience – Demographics; Audience – Geo – Location
Google Analytics provides insights into your audience’s demographics (age, gender) and geographic location (countries, cities). This data is invaluable for tailoring SEO strategies to your target audience and to learn about SEO audience targeting.
The Demographics and Location reports help you understand who your visitors are and where they are from, informing content localization and targeted SEO efforts. Audience understanding is crucial for effective SEO and to learn about SEO user demographics.
Here’s an example of the audience demographics Gender report:
Key Metrics in Google Analytics for SEO Analysis
Google Analytics metrics fall into three main categories, each providing different perspectives on website performance relevant to SEO and to learn about SEO metrics:
- Traffic acquisition metrics: Measure traffic volume.
- Behavior metrics: Measure user engagement.
- Conversion metrics: Measure goal achievement.
Traffic Acquisition Metrics: Measuring SEO Traffic Volume
Understanding the difference between key traffic metrics is essential for accurate SEO analysis. These metrics help you quantify the traffic driven by your SEO efforts and to learn about SEO traffic measurement.
- Users: Counts unique visitors. Multiple visits from the same user within the date range are counted as one user. User metrics are fundamental to learn about SEO audience reach.
- Sessions: Represents a period of user activity on your website. A session ends after 30 minutes of inactivity. One user can have multiple sessions. Session metrics show website engagement frequency and are important to learn about SEO user sessions.
- Pageviews: Counts each page loaded, including repeated views of the same page by the same user. Pageview metrics indicate content consumption volume and are useful to learn about SEO page traffic.
Tip: The percentage of returning visitors (found in the Audience Overview report) is a valuable engagement metric, indicating user loyalty and content resonance. Returning visitor rate is an engagement signal relevant to SEO and to learn about SEO user loyalty.
Bounce Rate: Assessing SEO Content Relevance
Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page. While a high bounce rate isn’t always negative, generally, a lower bounce rate is better, suggesting higher user engagement and content relevance for SEO and to learn about SEO bounce rate interpretation.
Tip: Always compare bounce rates for similar page types (e.g., blog posts vs. landing pages) for meaningful insights. Contextual bounce rate analysis is key to learn about SEO content engagement. Refer to resources like “bounce rate” for a deeper understanding.
Pages per Session: Measuring SEO Engagement Depth
Pages per session indicates the average number of pages a user views during a session. This metric reflects user engagement depth and site navigation effectiveness, both important for SEO and to learn about SEO user engagement metrics.
Higher pages per session suggest users are exploring more content on your site, a positive signal for engagement. Improving internal linking, related content suggestions, and site navigation can increase pages per session. Internal linking and site structure are SEO elements that impact pages per session and are important to learn about SEO site architecture.
Average Time on Page / Session Duration: Gauging Content Engagement Time
These time-based metrics aim to measure user engagement duration. However, they have accuracy limitations. Average time on page is generally a more reliable indicator of how long users actively spend on a specific page, but caution is advised when interpreting these metrics for SEO analysis and to learn about SEO time-based metrics.
If you must choose one, average time on page is a slightly better indicator of page-level engagement. Understand their limitations and use them cautiously when you learn about SEO metrics accuracy. Resources like “here’s an explanation why” explain the nuances of time-based metrics.
Rank Tracking: Monitoring Your SEO Progress
Rank tracking is the process of monitoring your website’s search engine rankings for your target keywords. Unlike Google Search Console and Google Analytics, rank trackers are specialized tools focused solely on keyword ranking data, providing a direct measure of SEO performance and progress and are essential tools to learn about SEO ranking analysis.
Rank trackers are typically simpler to use but highly effective for monitoring SEO performance.
Here’s an example of a rank tracking dashboard from “SERPWatcher”:
Key advantages of using a rank tracker for SEO learning include:
- Daily Ranking Updates: Track daily changes in your keyword positions, providing timely insights into SEO effectiveness and helping you quickly learn about SEO ranking fluctuations.
- Ranking Drop/Spike Alerts: Receive automatic notifications about significant ranking changes, enabling rapid response to SEO issues or successes and allowing you to proactively learn about SEO changes.
- Location-Specific Tracking: Monitor rankings in specific geographic locations (country or city), crucial for local SEO and to learn about SEO local targeting.
- Search Volume Metrics: View search volumes for tracked keywords, understanding the potential traffic impact of ranking changes and helping you prioritize keywords as you learn about SEO keyword prioritization.
- Competitor Tracking: Compare your rankings against competitors, benchmarking your SEO performance and identifying competitive opportunities and enabling you to learn about SEO competitive analysis.
Tip: Interpret ranking data realistically. Moving from position 90 to 45 is progress, but significant organic traffic typically comes from first-page rankings. Focus on top SERP rankings when you learn about SEO ranking impact.
Analytics Tips and Best Practices for SEO Learning
Let’s conclude with practical tips for effective website analytics to maximize your SEO learning and improve your strategies.
Monitor Overall Progress and Investigate Details for SEO Insights
Website performance fluctuates daily. Focus on long-term trends rather than daily micro-changes. However, when unexpected changes occur, delve into the details to identify the root cause. Balance high-level overview with granular analysis when you learn about SEO data interpretation.
The fundamental rule of analytics is to investigate anomalies deeply to uncover the underlying reasons. Detailed investigation is key to learn about SEO troubleshooting.
Understand Your Metrics for Data-Driven SEO
You don’t need to analyze every metric constantly, but a basic understanding of key metrics prevents misinterpretations. Metric literacy is essential for data-driven SEO decisions and to learn about SEO metric definitions.
Contextualize Your Data for Actionable SEO Insights
Don’t treat data in isolation. Seek to understand why certain trends or changes occur. Contextual understanding is crucial for actionable SEO insights and to learn about SEO data context.
Example: When troubleshooting ranking drops, consider various internal and external factors:
- Recent website changes: Analyze website updates for potential SEO impact.
- Google algorithm updates: Check for recent algorithm updates that might affect rankings.
- Technical issues or website outages: Verify website accessibility and technical health.
- Google manual actions: Check Google Search Console for manual penalties.
- Rank tracking tool errors: Occasionally, verify data accuracy with your rank tracker.
A thorough analysis using Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and your rank tracker provides a comprehensive understanding of the issue, enabling informed decisions for your next SEO steps. Combining data from multiple tools is crucial for comprehensive SEO analysis and to learn about SEO holistic analysis.
Use Annotations to Add Context to SEO Data
Google Analytics and most rank trackers allow annotations to add context to your data dashboards. Annotations help you correlate website changes or external events with performance fluctuations and are valuable for learn about SEO cause-and-effect.
Annotate your actions and significant events to assess their impact on website performance. Examples include:
- Google algorithm updates: Record algorithm updates to correlate with ranking changes.
- Website changes: Annotate significant website modifications.
- Article updates: Mark content update dates for performance tracking.
- Marketing campaign launches: Track campaign start dates to measure SEO impact.
- Website issues and outages: Note technical problems for performance dips.
- Seasonal events (e.g., Black Friday): Annotate seasonal events impacting traffic.
Set Up Alerts for Proactive SEO Monitoring
Most analytics tools offer email alerts for predefined conditions. Alerts proactively notify you of significant changes, enabling timely responses without constant manual data monitoring. Proactive monitoring is essential for responsive SEO management and to learn about SEO proactive strategies.
Set up alerts to be notified of dramatic performance changes, allowing you to stay informed without constant data table monitoring and to learn about SEO efficient monitoring techniques.