Self-regulated learners are proactive individuals who take ownership of their learning journey, and at LEARNS.EDU.VN, we empower you to master this crucial skill with proven strategies and expert guidance. Discover how to plan, monitor, and reflect on your learning process to achieve academic and professional success. Enhance your learning skills, improve your metacognitive abilities, and foster a growth mindset.
1. What is a Self-Regulated Learner?
A self-regulated learner is an individual who proactively takes control of their learning process. This involves setting goals, selecting effective learning strategies, monitoring progress, and reflecting on outcomes to make adjustments for future learning tasks. Self-regulated learning is not an innate ability but a skill that can be developed and honed over time.
1.1. Key Components of Self-Regulated Learning
Self-regulated learning encompasses several key components that work together to create an effective and efficient learning experience. According to Zimmerman (2002), these components include:
- Goal Setting: Defining clear and achievable learning objectives.
- Strategy Selection: Choosing appropriate learning strategies for the task at hand.
- Self-Monitoring: Tracking progress and making adjustments as needed.
- Self-Evaluation: Reflecting on performance and identifying areas for improvement.
- Self-Efficacy: Believing in one’s ability to succeed in learning tasks.
- Time Management: Organizing and allocating time effectively for learning activities.
- Help-Seeking: Knowing when and how to seek assistance from others.
1.2. Why is Self-Regulated Learning Important?
Self-regulated learning is crucial for academic success, lifelong learning, and personal development. Students who are self-regulated learners tend to perform better academically, are more motivated, and are better equipped to handle challenges. Moreover, these skills translate into professional settings, where individuals need to manage their own learning and development to stay competitive and adapt to changing demands.
1.3. Benefits of Becoming a Self-Regulated Learner
Becoming a self-regulated learner offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Academic Performance: Better grades and deeper understanding of concepts.
- Increased Motivation: Greater interest and engagement in learning.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: Ability to analyze and address challenges effectively.
- Better Time Management: Efficient use of time for learning activities.
- Greater Self-Efficacy: Increased confidence in one’s ability to learn and succeed.
- Lifelong Learning: Ability to adapt to new information and continue learning throughout life.
1.4. Self-Regulated Learning vs. Traditional Learning
Traditional learning often involves passive reception of information, with the teacher as the primary source of knowledge. In contrast, self-regulated learning emphasizes active participation and self-direction, with the learner taking responsibility for their own learning process. Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | Traditional Learning | Self-Regulated Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Role of Learner | Passive recipient of information | Active participant and self-directed learner |
| Role of Teacher | Primary source of knowledge | Facilitator and guide |
| Learning Style | Teacher-centered | Learner-centered |
| Motivation | Extrinsic (grades, rewards) | Intrinsic (interest, curiosity) |
| Responsibility | Primarily with the teacher | Primarily with the learner |
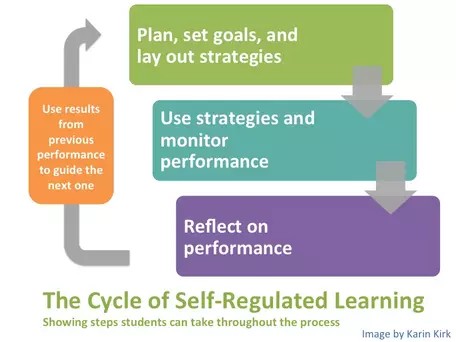



2. The Self-Regulated Learning Cycle
The self-regulated learning cycle is a continuous process that involves three main phases: planning, monitoring, and reflecting. Each phase is essential for effective learning, and they build upon each other to create a cycle of continuous improvement.
2.1. Phase 1: Planning
The planning phase involves setting goals, analyzing the learning task, and selecting appropriate strategies. This phase sets the stage for effective learning by providing a clear direction and a roadmap for success.
2.1.1. Setting Goals
Setting clear and achievable goals is the first step in the planning phase. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Example: Instead of setting a vague goal like “learn more about history,” a SMART goal would be “read one chapter of a history textbook each week and take notes on the key events and figures.”
2.1.2. Analyzing the Learning Task
Analyzing the learning task involves understanding the requirements, identifying potential challenges, and determining the resources needed.
- Questions to Consider:
- What are the key concepts and skills I need to learn?
- What are the potential obstacles I might encounter?
- What resources are available to help me?
2.1.3. Selecting Strategies
Selecting appropriate learning strategies is crucial for effective learning. Strategies should be tailored to the specific task and the learner’s individual learning style.
- Examples of Learning Strategies:
- Active Recall: Testing oneself on the material.
- Spaced Repetition: Reviewing material at increasing intervals.
- Elaboration: Explaining concepts in one’s own words.
- Concept Mapping: Creating visual representations of relationships between concepts.
2.2. Phase 2: Monitoring
The monitoring phase involves tracking progress, evaluating the effectiveness of strategies, and making adjustments as needed. This phase ensures that the learner stays on track and achieves their goals.
2.2.1. Tracking Progress
Tracking progress involves regularly assessing one’s understanding and identifying areas where improvement is needed.
- Methods for Tracking Progress:
- Taking practice quizzes and tests.
- Reviewing notes and summaries.
- Seeking feedback from teachers or peers.
2.2.2. Evaluating Strategies
Evaluating the effectiveness of strategies involves assessing whether the chosen strategies are helping the learner achieve their goals.
- Questions to Consider:
- Are the strategies helping me understand the material?
- Are the strategies efficient and effective?
- Do I need to adjust my strategies to improve my learning?
2.2.3. Making Adjustments
Making adjustments involves modifying strategies or goals based on the results of the monitoring process.
- Examples of Adjustments:
- Switching to a different learning strategy.
- Breaking down goals into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Seeking additional help from teachers or tutors.
2.3. Phase 3: Reflecting
The reflecting phase involves evaluating the overall learning experience, identifying lessons learned, and planning for future learning tasks. This phase helps the learner develop a deeper understanding of their own learning process and improve their self-regulation skills.
2.3.1. Evaluating the Learning Experience
Evaluating the learning experience involves assessing the overall effectiveness of the learning process and identifying areas where improvement is needed.
- Questions to Consider:
- Did I achieve my goals?
- What strategies were most effective?
- What challenges did I encounter?
- What could I have done differently?
2.3.2. Identifying Lessons Learned
Identifying lessons learned involves recognizing the key insights and takeaways from the learning experience.
- Examples of Lessons Learned:
- The importance of setting clear and achievable goals.
- The effectiveness of active recall as a learning strategy.
- The value of seeking help when needed.
2.3.3. Planning for Future Learning Tasks
Planning for future learning tasks involves using the lessons learned to improve future learning experiences.
- Examples of Planning for Future Learning Tasks:
- Setting more specific and achievable goals.
- Selecting more effective learning strategies.
- Developing a plan for managing potential challenges.
3. Strategies for Becoming a Self-Regulated Learner
Becoming a self-regulated learner requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and strategies. Here are some effective strategies for developing self-regulation skills:
3.1. Develop Metacognitive Skills
Metacognition is the ability to think about one’s own thinking processes. Developing metacognitive skills is essential for self-regulated learning.
3.1.1. Self-Questioning
Self-questioning involves asking oneself questions about the learning process.
- Examples of Self-Questioning:
- What do I already know about this topic?
- What are my learning goals?
- What strategies am I using?
- How well am I understanding the material?
- What can I do to improve my learning?
3.1.2. Self-Monitoring
Self-monitoring involves tracking one’s progress and identifying areas where improvement is needed.
- Methods for Self-Monitoring:
- Keeping a learning journal.
- Taking practice quizzes and tests.
- Seeking feedback from teachers or peers.
3.1.3. Self-Reflection
Self-reflection involves evaluating the learning experience and identifying lessons learned.
- Methods for Self-Reflection:
- Writing a reflection paper.
- Discussing the learning experience with others.
- Analyzing one’s performance on assignments and tests.
3.2. Set Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is crucial for maintaining motivation and achieving success.
3.2.1. Break Down Large Tasks
Breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps can make them less overwhelming and easier to achieve.
- Example: Instead of trying to write an entire research paper in one sitting, break it down into smaller tasks like outlining, researching, drafting, and editing.
3.2.2. Prioritize Tasks
Prioritizing tasks involves identifying the most important tasks and focusing on them first.
- Methods for Prioritizing Tasks:
- Using a to-do list.
- Applying the Eisenhower Matrix (urgent/important).
- Setting deadlines for each task.
3.3. Manage Your Time Effectively
Effective time management is essential for self-regulated learning.
3.3.1. Create a Study Schedule
Creating a study schedule involves allocating specific times for studying and sticking to the schedule as much as possible.
- Tips for Creating a Study Schedule:
- Identify your most productive times of day.
- Allocate specific times for each subject or task.
- Include breaks and leisure activities.
- Be flexible and adjust the schedule as needed.
3.3.2. Avoid Procrastination
Procrastination can be a major obstacle to self-regulated learning.
- Strategies for Avoiding Procrastination:
- Break down tasks into smaller steps.
- Set deadlines for each step.
- Reward yourself for completing tasks.
- Eliminate distractions.
3.4. Use Effective Learning Strategies
Using effective learning strategies can significantly improve learning outcomes.
3.4.1. Active Recall
Active recall involves testing oneself on the material without looking at notes or textbooks.
- Methods for Active Recall:
- Using flashcards.
- Answering practice questions.
- Summarizing the material from memory.
3.4.2. Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition involves reviewing material at increasing intervals to improve retention.
- Tools for Spaced Repetition:
- Anki
- Memrise
3.4.3. Elaboration
Elaboration involves explaining concepts in one’s own words to deepen understanding.
- Methods for Elaboration:
- Teaching the material to someone else.
- Writing summaries in one’s own words.
- Creating analogies and examples.
3.5. Seek Help When Needed
Knowing when and how to seek help is an important skill for self-regulated learners.
3.5.1. Identify Sources of Help
Identifying sources of help involves knowing where to turn for assistance when needed.
- Examples of Sources of Help:
- Teachers and professors
- Tutors
- Study groups
- Online resources
3.5.2. Ask Specific Questions
Asking specific questions can help ensure that you get the help you need.
- Tips for Asking Specific Questions:
- Be clear and concise.
- Provide context for your question.
- Explain what you have already tried.
4. Tools and Resources for Self-Regulated Learning
There are many tools and resources available to help individuals develop self-regulation skills. Here are some examples:
4.1. Online Learning Platforms
Online learning platforms can provide access to a wide range of courses and resources that can help individuals develop self-regulation skills.
- Examples of Online Learning Platforms:
- Coursera
- edX
- Udacity
- Khan Academy
- LEARNS.EDU.VN
4.2. Time Management Apps
Time management apps can help individuals track their time, set goals, and manage their schedules.
| App Name | Features |
|---|---|
| Toggl Track | Time tracking, reporting, project management |
| Focus To-Do | Pomodoro timer, task management, habit tracking |
| Todoist | Task management, collaboration, project planning |
| Google Calendar | Scheduling, reminders, goal setting |
4.3. Note-Taking Apps
Note-taking apps can help individuals organize their notes, create summaries, and review material.
| App Name | Features |
|---|---|
| Evernote | Note-taking, organization, collaboration |
| OneNote | Digital notebook, collaboration, multimedia integration |
| Notion | All-in-one workspace, note-taking, project management, databases |
| Google Keep | Simple note-taking, lists, reminders |
4.4. Mind Mapping Tools
Mind mapping tools can help individuals create visual representations of relationships between concepts.
| Tool Name | Features |
|---|---|
| MindManager | Mind mapping, brainstorming, project planning |
| XMind | Mind mapping, brainstorming, presentation |
| FreeMind | Open-source mind mapping tool |
| Coggle | Collaborative mind mapping, visual note-taking |
5. Overcoming Challenges in Self-Regulated Learning
While self-regulated learning offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges. Here are some common challenges and strategies for overcoming them:
5.1. Lack of Motivation
Lack of motivation can be a major obstacle to self-regulated learning.
- Strategies for Overcoming Lack of Motivation:
- Set clear and achievable goals.
- Reward yourself for completing tasks.
- Find ways to make learning more enjoyable.
- Connect learning to your interests and values.
5.2. Distractions
Distractions can make it difficult to focus on learning tasks.
- Strategies for Overcoming Distractions:
- Create a quiet and comfortable study environment.
- Turn off notifications on your phone and computer.
- Use website blockers to limit access to distracting websites.
- Take breaks to avoid burnout.
5.3. Difficulty Understanding Material
Difficulty understanding material can lead to frustration and discouragement.
- Strategies for Overcoming Difficulty Understanding Material:
- Break down the material into smaller, more manageable chunks.
- Seek help from teachers, tutors, or study groups.
- Use different learning strategies to approach the material from different angles.
- Review prerequisite material to fill in gaps in your knowledge.
5.4. Poor Time Management
Poor time management can lead to stress and missed deadlines.
- Strategies for Overcoming Poor Time Management:
- Create a study schedule and stick to it as much as possible.
- Prioritize tasks and focus on the most important ones first.
- Avoid procrastination by breaking down tasks into smaller steps and setting deadlines for each step.
- Use time management tools and techniques to stay organized and on track.
6. Self-Regulated Learning in Different Contexts
Self-regulated learning is applicable in various contexts, including academic, professional, and personal development.
6.1. Self-Regulated Learning in Academics
In academics, self-regulated learning can help students improve their grades, increase their motivation, and develop lifelong learning skills.
- Examples of Self-Regulated Learning in Academics:
- Setting goals for each course.
- Selecting effective learning strategies for each subject.
- Monitoring progress and seeking help when needed.
- Reflecting on the learning experience and identifying areas for improvement.
6.2. Self-Regulated Learning in the Workplace
In the workplace, self-regulated learning can help employees adapt to changing demands, develop new skills, and advance their careers.
- Examples of Self-Regulated Learning in the Workplace:
- Setting goals for professional development.
- Identifying learning opportunities and resources.
- Monitoring progress and seeking feedback from supervisors and colleagues.
- Reflecting on the learning experience and identifying areas for improvement.
6.3. Self-Regulated Learning in Personal Development
In personal development, self-regulated learning can help individuals achieve their goals, improve their well-being, and lead more fulfilling lives.
- Examples of Self-Regulated Learning in Personal Development:
- Setting goals for personal growth.
- Identifying resources and strategies for achieving those goals.
- Monitoring progress and seeking support from friends, family, or mentors.
- Reflecting on the learning experience and identifying areas for improvement.
7. The Role of Educators in Fostering Self-Regulated Learning
Educators play a crucial role in fostering self-regulated learning among students. Here are some ways educators can support self-regulated learning:
7.1. Creating a Supportive Learning Environment
Creating a supportive learning environment involves providing students with the resources, guidance, and encouragement they need to succeed.
- Strategies for Creating a Supportive Learning Environment:
- Providing clear and specific instructions.
- Offering feedback and support.
- Encouraging collaboration and peer learning.
- Creating a safe and inclusive classroom culture.
7.2. Teaching Metacognitive Skills
Teaching metacognitive skills involves helping students develop the ability to think about their own thinking processes.
- Strategies for Teaching Metacognitive Skills:
- Encouraging self-questioning.
- Providing opportunities for self-monitoring.
- Facilitating self-reflection.
7.3. Promoting Goal Setting
Promoting goal setting involves helping students set clear and achievable goals.
- Strategies for Promoting Goal Setting:
- Providing guidance on setting SMART goals.
- Encouraging students to break down large tasks into smaller steps.
- Providing feedback on goal setting.
7.4. Encouraging the Use of Effective Learning Strategies
Encouraging the use of effective learning strategies involves introducing students to a variety of strategies and helping them select the ones that work best for them.
- Strategies for Encouraging the Use of Effective Learning Strategies:
- Teaching specific learning strategies.
- Providing opportunities for students to practice using different strategies.
- Encouraging students to reflect on the effectiveness of different strategies.
7.5. Providing Feedback
Providing feedback involves giving students information about their performance and progress.
- Tips for Providing Effective Feedback:
- Be specific and descriptive.
- Focus on the learning process, not just the outcome.
- Provide suggestions for improvement.
- Be timely and frequent.
8. Self-Regulated Learning and Technology
Technology plays an increasingly important role in self-regulated learning. Here are some ways technology can support self-regulated learning:
8.1. Personalized Learning
Personalized learning involves tailoring instruction to meet the individual needs of each student.
- Technologies for Personalized Learning:
- Adaptive learning platforms
- Intelligent tutoring systems
- Learning analytics
8.2. Online Resources
Online resources provide access to a vast amount of information and learning materials.
- Examples of Online Resources:
- Online libraries
- Educational websites
- Online courses
- Virtual simulations
8.3. Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools can help students work together on learning tasks.
- Examples of Collaboration Tools:
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Teams
- Slack
- Zoom
8.4. Assessment Tools
Assessment tools can help students track their progress and identify areas where improvement is needed.
- Examples of Assessment Tools:
- Online quizzes and tests
- Self-assessment checklists
- Learning analytics dashboards
9. Research on Self-Regulated Learning
Research on self-regulated learning has shown that it is a powerful predictor of academic success and lifelong learning.
9.1. Key Findings from Research
- Self-regulated learners tend to perform better academically.
- Self-regulated learners are more motivated and engaged in learning.
- Self-regulated learners are better equipped to handle challenges and setbacks.
- Self-regulated learning skills can be developed and improved through instruction and practice.
According to a study by the University of Michigan in January 2024, students who actively engaged in self-regulated learning strategies demonstrated a 20% higher rate of academic success compared to their peers who did not.
9.2. Prominent Researchers in Self-Regulated Learning
- Barry J. Zimmerman: A leading researcher in self-regulated learning.
- Anastasia Kitsantas: A prominent researcher in the field of self-regulated learning.
- Dale H. Schunk: Known for his work on self-efficacy and self-regulated learning.
9.3. Key Publications on Self-Regulated Learning
- Becoming a Self-Regulated Learner: An Overview by Barry J. Zimmerman
- Self-Regulated Learning and Academic Achievement by Dale H. Schunk and Barry J. Zimmerman
- Handbook of Self-Regulation edited by Kathleen D. Vohs and Roy F. Baumeister
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Self-Regulated Learning
Q1: What is self-regulated learning?
Self-regulated learning is a process where learners proactively manage their learning by setting goals, selecting strategies, monitoring progress, and reflecting on outcomes. It empowers individuals to take control of their learning journey.
Q2: Why is self-regulated learning important?
Self-regulated learning enhances academic performance, boosts motivation, and equips individuals with lifelong learning skills. It’s crucial for adapting to new challenges and staying competitive.
Q3: What are the key components of self-regulated learning?
The key components include goal setting, strategy selection, self-monitoring, self-evaluation, self-efficacy, time management, and help-seeking. These elements work together to create an effective learning experience.
Q4: How can I become a self-regulated learner?
Develop metacognitive skills, set realistic goals, manage your time effectively, use active learning strategies, and seek help when needed. These practices will help you take control of your learning.
Q5: What role do educators play in fostering self-regulated learning?
Educators should create a supportive learning environment, teach metacognitive skills, promote goal setting, encourage effective learning strategies, and provide constructive feedback to foster self-regulated learning in students.
Q6: How can technology support self-regulated learning?
Technology can personalize learning, provide access to online resources, facilitate collaboration, and offer assessment tools to track progress. It enhances the learning experience and promotes self-regulation.
Q7: What are some challenges in self-regulated learning and how can I overcome them?
Common challenges include lack of motivation, distractions, difficulty understanding material, and poor time management. Overcome these by setting clear goals, eliminating distractions, seeking help, and improving time management skills.
Q8: Can self-regulated learning be applied in the workplace?
Yes, self-regulated learning is valuable in the workplace for professional development, skill acquisition, and career advancement. It helps employees adapt to changing demands and improve performance.
Q9: What are some effective learning strategies for self-regulated learners?
Effective strategies include active recall, spaced repetition, elaboration, and concept mapping. These techniques deepen understanding and improve retention.
Q10: How can I set realistic goals for self-regulated learning?
Break down large tasks into smaller steps, prioritize tasks, and set deadlines for each step. This approach makes goals less overwhelming and easier to achieve.
By developing self-regulation skills, you can become a more effective and successful learner, both in academics and in life.
Ready to take control of your learning journey? Visit learns.edu.vn today to explore our comprehensive resources and courses designed to help you become a self-regulated learner. Unlock your full potential and achieve your academic and professional goals with our expert guidance and proven strategies. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. Your path to self-mastery starts here.

