Asynchronous learning provides flexible education by allowing students to access materials at their own pace. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we empower learners with resources tailored for effective self-paced study, offering flexibility and personalized learning experiences that fit individual schedules. Discover resources and expert guidance to master self-directed education.
1. What is Asynchronous Learning?
Asynchronous learning is a method of education where students learn at different times and locations. It doesn’t require real-time interaction. According to a study by Davidson-Shivers et al. (2001), this approach gives students more time to explore and engage with the material.
1.1. Key Features of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning is defined by several key features that distinguish it from traditional, real-time learning environments. These characteristics cater to the needs of diverse learners and promote a flexible educational experience.
- Flexibility: Students can access learning materials anytime, anywhere, fitting education into their personal schedules.
- Self-Paced Progress: Learners advance through the course content at their own speed, revisiting topics as needed.
- Wide Accessibility: Asynchronous learning eliminates geographical barriers, enabling learners from all over the world to participate.
- Diverse Materials: A range of materials such as pre-recorded videos, readings, and discussion boards are available.
- Extended Interaction: Learners have time to thoughtfully respond to peers and instructors through forums and email.
1.2. Benefits of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning offers numerous benefits that cater to different learning styles and life circumstances. These advantages make education more accessible and effective for a wide range of students.
- Improved Time Management: Students learn to manage their time effectively as they balance studies with other commitments.
- Personalized Learning: Students can focus on areas where they need more help, enhancing their understanding.
- Accessibility: Overcomes geographical and time zone barriers, opening education to a global audience.
- Development of Self-Discipline: Students become more self-disciplined and responsible for their learning outcomes.
- Reduced Stress: Flexible deadlines and self-paced learning reduce the pressure associated with traditional education.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: Students have more time to reflect on the materials and formulate thoughtful responses.
1.3. Examples of Asynchronous Learning Activities
Various asynchronous activities can be incorporated into online courses to enhance the learning experience. These activities allow students to engage with the material in a flexible and self-directed manner.
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-recorded Video Lectures | Students watch lectures at their convenience, pausing and rewatching as needed. |
| Online Discussion Forums | Students post responses to prompts and engage with peers over an extended period. |
| Assigned Readings | Students read articles, book chapters, or other materials and reflect on the content. |
| Email Communication | Students and instructors communicate through email, allowing for detailed questions and answers. |
| Self-Paced Quizzes | Students complete quizzes at their own pace, reinforcing their understanding of the material. |
| Project-Based Assignments | Students work on projects independently, applying what they have learned to solve real-world problems. |
| Online Simulations | Students engage in simulations that allow them to apply concepts in a risk-free environment. |
| Writing Assignments | Students complete essays or reports that require research, analysis, and synthesis of information. |
| Multimedia Presentations | Students create presentations using various media to demonstrate their understanding of course content. |
| Peer Review | Students review and provide feedback on each other’s work asynchronously. |
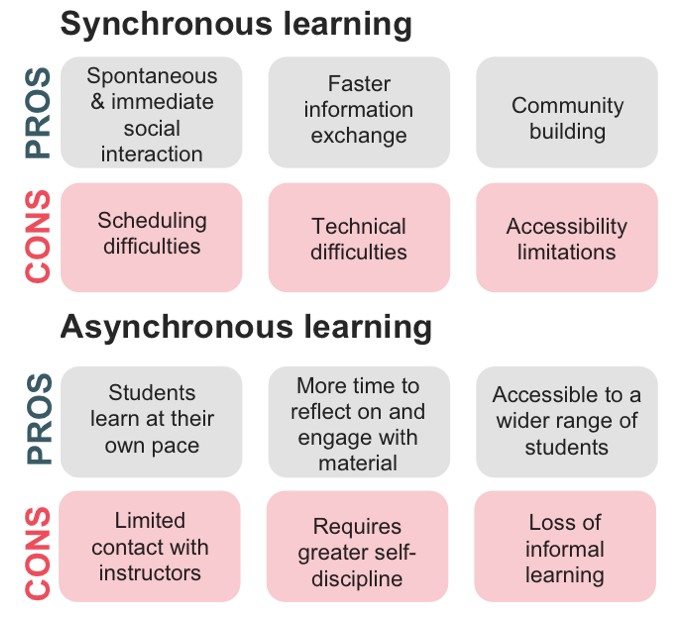
1.4. Asynchronous Learning vs. Synchronous Learning
Asynchronous and synchronous learning represent two distinct approaches to education, each with its unique set of characteristics, advantages, and challenges. Understanding the differences between these methods can help educators design more effective learning experiences.
| Feature | Asynchronous Learning | Synchronous Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Flexible; students access materials at different times. | Real-time; students and instructors interact simultaneously. |
| Interaction | Delayed; communication via forums, email, or recorded feedback. | Immediate; live discussions, instant feedback. |
| Pace | Self-paced; students progress at their own speed. | Fixed; students must keep up with the course schedule. |
| Location | Independent; students can learn from anywhere with internet access. | Specific; often requires being in a designated place at a set time. |
| Materials | Pre-recorded videos, readings, online modules. | Live lectures, real-time discussions, interactive presentations. |
| Community Building | Can be slower; requires deliberate efforts to foster interaction and engagement. | Immediate; fosters a sense of community through shared experiences and real-time interaction. |
| Accessibility | Highly accessible; accommodates different time zones and schedules. | Can be challenging; requires everyone to be available at the same time. |
| Technology Needs | Reliable internet access. | Requires robust internet connectivity and potentially more advanced tools for live interaction. |
1.5. The Role of Technology in Asynchronous Learning
Technology plays a pivotal role in facilitating asynchronous learning, providing the tools and platforms necessary to deliver content and support student interaction. Here are key technological components that enable effective asynchronous learning environments:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms like Moodle, Canvas, and Blackboard provide a centralized hub for course materials, assignments, and communication tools.
- Video Conferencing Software: While primarily used for synchronous sessions, tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams can host recorded lectures and presentations for asynchronous viewing.
- Discussion Boards: Online forums where students can post questions, share insights, and engage in discussions at their own pace.
- Email Communication: A reliable means for students to communicate with instructors and peers, ask questions, and receive feedback.
- Multimedia Tools: Software that allows for the creation and distribution of engaging content, such as video editors, animation software, and interactive presentation tools.
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive and Dropbox enable easy sharing and access to course materials from anywhere.
- Mobile Learning Apps: Applications that allow students to access course content and participate in activities on their smartphones or tablets.
1.6. Optimizing Asynchronous Learning Outcomes
To maximize the effectiveness of asynchronous learning, several strategies can be implemented to enhance engagement, support student success, and foster a sense of community.
- Clear Communication: Establish clear expectations and provide regular updates to keep students informed.
- Engaging Content: Use a variety of multimedia formats to keep students interested and cater to different learning styles.
- Interactive Activities: Incorporate discussion boards, quizzes, and peer review activities to promote active learning.
- Timely Feedback: Provide prompt and constructive feedback on assignments to help students improve.
- Community Building: Create opportunities for students to connect and collaborate, such as group projects or virtual meetups.
- Accessibility: Ensure that all materials are accessible to students with disabilities, following accessibility guidelines.
- Technical Support: Offer readily available technical support to help students troubleshoot any issues they may encounter.
- Regular Check-Ins: Conduct regular check-ins to gauge student progress and address any concerns.
2. What are the 5 Intended Searches of Asynchronous Learning?
The term “asynchronous learning” can prompt various search intentions among users. Understanding these intentions helps educators and content creators tailor their resources to meet specific needs. Here are five common search intentions:
2.1. Definition and Explanation
Users often search for a clear definition of asynchronous learning to understand what it entails. They want to know the basic concept and how it differs from other learning methods.
2.2. Advantages and Disadvantages
Many users want to know the pros and cons of asynchronous learning to evaluate whether it suits their learning style or educational goals.
2.3. Examples and Applications
Users look for practical examples of asynchronous learning to understand how it is applied in real-world scenarios, such as online courses or training programs.
2.4. Tools and Platforms
Some users are interested in the specific tools and platforms that facilitate asynchronous learning, such as LMS (Learning Management Systems) or video conferencing software.
2.5. Strategies for Effective Implementation
Educators and instructional designers search for strategies to effectively implement asynchronous learning, including tips on creating engaging content and fostering student interaction.
3. How Does Asynchronous Learning Work?
Asynchronous learning operates on a flexible schedule, allowing students to engage with course materials and activities at different times. This method relies on self-directed learning and delayed interaction.
3.1. Course Structure and Design
The design of an asynchronous course is crucial for its success. It should be structured to guide students through the material logically and intuitively.
- Modular Content: Break down the course into smaller, manageable modules or units.
- Clear Objectives: Define clear learning objectives for each module to help students focus.
- Varied Materials: Use a mix of video lectures, readings, and interactive exercises.
- Assessment Strategy: Incorporate quizzes, assignments, and projects to assess understanding.
- Navigation: Ensure easy navigation through the course content with clear instructions.
3.2. Student Engagement Techniques
Keeping students engaged in an asynchronous environment requires deliberate effort. Employing various engagement techniques can enhance their learning experience.
- Discussion Forums: Encourage students to participate in online discussion forums.
- Interactive Quizzes: Use interactive quizzes to test understanding and provide immediate feedback.
- Peer Review: Implement peer review activities to foster collaboration and critical thinking.
- Multimedia Content: Use videos, animations, and infographics to make the content more engaging.
- Gamification: Incorporate game elements, such as points and badges, to motivate students.
3.3. Instructor’s Role in Asynchronous Learning
While students learn at their own pace, the instructor plays a crucial role in guiding and supporting them. This involves creating a well-structured course and actively engaging with students.
- Course Design: The instructor designs the course, selects materials, and creates activities.
- Facilitation: The instructor facilitates discussions, answers questions, and provides feedback.
- Availability: The instructor is available to students via email, forums, or virtual office hours.
- Feedback: The instructor provides timely and constructive feedback on assignments.
- Monitoring: The instructor monitors student progress and intervenes when necessary.
3.4. Tools and Technologies Used
Asynchronous learning relies on various tools and technologies to deliver content and facilitate interaction. These include Learning Management Systems (LMS), video platforms, and communication tools.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms like Moodle, Canvas, and Blackboard are used to host course materials and activities.
- Video Platforms: YouTube, Vimeo, and other video platforms are used to host pre-recorded lectures.
- Discussion Forums: Online forums, such as those in LMS platforms, are used for student discussions.
- Email: Email is used for communication between students and instructors.
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive and Dropbox are used for sharing files and resources.
3.5. Assessment Methods in Asynchronous Learning
Assessment in asynchronous learning involves various methods to evaluate student understanding and progress. These include quizzes, assignments, and projects.
- Quizzes: Online quizzes are used to test knowledge and understanding of the material.
- Assignments: Written assignments, such as essays and reports, are used to assess critical thinking and writing skills.
- Projects: Projects are used to assess the application of knowledge and skills to real-world problems.
- Peer Review: Peer review is used to assess students’ ability to evaluate and provide feedback on their peers’ work.
- Self-Assessment: Self-assessment tools help students reflect on their learning and identify areas for improvement.
3.6. Best Practices for Asynchronous Learning
To maximize the effectiveness of asynchronous learning, several best practices should be followed. These include clear communication, engaging content, and timely feedback.
- Clear Communication: Communicate expectations clearly and provide regular updates.
- Engaging Content: Use a variety of multimedia formats to keep students interested.
- Timely Feedback: Provide prompt and constructive feedback on assignments.
- Community Building: Create opportunities for students to connect and collaborate.
- Accessibility: Ensure that all materials are accessible to students with disabilities.
- Technical Support: Offer readily available technical support to help students troubleshoot issues.
- Regular Check-Ins: Conduct regular check-ins to gauge student progress and address concerns.
 Asynchronous learning
Asynchronous learning
4. What Are The Advantages of Asynchronous Learning Environments?
Asynchronous learning environments offer numerous advantages that cater to diverse student needs and promote effective learning. These benefits include flexibility, accessibility, personalized learning, and enhanced critical thinking.
4.1. Flexibility and Convenience
One of the primary advantages of asynchronous learning is its flexibility. Students can access course materials and complete assignments at their convenience, fitting education into their personal schedules.
- Self-Paced Learning: Students learn at their own pace, revisiting topics as needed.
- Time Management: Students develop effective time management skills.
- Work-Life Balance: Asynchronous learning allows students to balance studies with work and other commitments.
- Reduced Commuting: Students save time and money by eliminating the need to commute to a physical classroom.
4.2. Increased Accessibility
Asynchronous learning removes geographical barriers, making education accessible to a global audience. This is particularly beneficial for students in remote areas or with mobility issues.
- Global Reach: Students from anywhere in the world can participate in courses.
- Remote Learning: Ideal for students in remote or underserved areas.
- Disability Access: Accommodates students with disabilities through flexible learning options.
- Diverse Perspectives: Students benefit from interacting with peers from diverse backgrounds.
4.3. Personalized Learning Experience
Asynchronous learning allows students to personalize their learning experience by focusing on areas where they need more help. This leads to a deeper understanding and better retention of information.
- Customized Learning: Students can focus on topics they find challenging.
- Adaptive Learning: Courses can be tailored to individual learning styles.
- Targeted Feedback: Instructors can provide personalized feedback to each student.
- Self-Reflection: Students have time to reflect on their learning and identify areas for improvement.
4.4. Enhanced Critical Thinking Skills
Asynchronous learning promotes critical thinking by giving students time to reflect on the material and formulate thoughtful responses.
- In-Depth Analysis: Students can analyze materials in greater detail.
- Thoughtful Responses: Students have time to formulate thoughtful responses to discussion prompts.
- Research Opportunities: Students can conduct independent research to deepen their understanding.
- Problem-Solving: Students can work on complex problems at their own pace.
4.5. Cost-Effectiveness
Asynchronous learning can be more cost-effective than traditional education, as it reduces the need for physical infrastructure and commuting.
- Lower Tuition Costs: Online courses often have lower tuition fees.
- Reduced Travel Costs: Students save money on commuting and accommodation.
- Affordable Materials: Digital materials are often more affordable than textbooks.
- Flexible Payment Options: Many online programs offer flexible payment plans.
4.6. Development of Self-Discipline
Asynchronous learning requires students to be self-disciplined and responsible for their learning outcomes. This helps them develop important skills that are valuable in both academic and professional settings.
- Self-Motivation: Students learn to motivate themselves to complete assignments.
- Responsibility: Students take responsibility for their learning.
- Time Management: Students develop effective time management skills.
- Organizational Skills: Students learn to organize their learning materials and schedules.
5. What Are The Disadvantages of Asynchronous Learning?
While asynchronous learning offers numerous advantages, it also has some drawbacks that need to be considered. These include potential for isolation, lack of immediate feedback, technical issues, and the need for self-discipline.
5.1. Potential for Social Isolation
One of the main disadvantages of asynchronous learning is the potential for social isolation. Students may feel disconnected from their peers and instructors, which can impact their motivation and engagement.
- Lack of Face-to-Face Interaction: Students miss out on the social interaction of a traditional classroom.
- Reduced Community Building: It can be challenging to build a sense of community in an asynchronous environment.
- Loneliness: Students may feel lonely and isolated, especially if they are new to online learning.
- Decreased Motivation: Lack of social interaction can lead to decreased motivation.
5.2. Delayed Feedback
Asynchronous learning often involves delayed feedback, which can hinder students’ ability to correct mistakes and improve their understanding in real-time.
- Delayed Responses: Students may have to wait longer for responses to questions.
- Slower Clarification: It can take longer to clarify misunderstandings.
- Missed Opportunities: Students may miss opportunities for immediate feedback.
- Confusion: Lack of immediate feedback can lead to confusion and frustration.
5.3. Technical Issues and Requirements
Technical issues can be a significant barrier to asynchronous learning. Students need reliable internet access and the necessary hardware and software to participate in online courses.
- Internet Access: Students need reliable internet access to access course materials.
- Hardware and Software: Students need the necessary hardware and software to participate in online courses.
- Technical Skills: Students need basic technical skills to navigate online platforms.
- Troubleshooting: Technical issues can disrupt learning and cause frustration.
5.4. Requires Strong Self-Discipline
Asynchronous learning requires a high degree of self-discipline and motivation. Students need to be able to manage their time effectively and stay on track without the structure of a traditional classroom.
- Time Management: Students need to manage their time effectively.
- Self-Motivation: Students need to be self-motivated to complete assignments.
- Procrastination: Students may struggle with procrastination.
- Distractions: Students need to minimize distractions to stay focused.
5.5. Limited Spontaneity and Impromptu Discussions
Asynchronous learning lacks the spontaneity and impromptu discussions that often occur in a traditional classroom setting.
- Planned Interactions: Interactions are typically planned and structured.
- Lack of Spontaneity: Students miss out on spontaneous discussions and brainstorming sessions.
- Limited Networking: It can be challenging to network with peers and instructors in an asynchronous environment.
- Reduced Collaboration: Collaboration may be less dynamic and interactive.
5.6. Increased Preparation Time for Instructors
Creating and managing an asynchronous course can require more preparation time for instructors compared to teaching a traditional course.
- Content Creation: Instructors need to create engaging and informative content.
- Course Design: Instructors need to design a well-structured and intuitive course.
- Technical Support: Instructors may need to provide technical support to students.
- Facilitation: Instructors need to actively facilitate discussions and provide feedback.
6. What Skills Can You Develop Through Asynchronous Learning?
Asynchronous learning helps develop a range of valuable skills that are beneficial in both academic and professional settings. These include time management, self-discipline, critical thinking, and technical proficiency.
6.1. Time Management Skills
Asynchronous learning requires students to manage their time effectively, balancing studies with other commitments.
- Scheduling: Students learn to create and follow schedules.
- Prioritization: Students learn to prioritize tasks and assignments.
- Deadline Management: Students learn to meet deadlines consistently.
- Efficiency: Students develop efficient study habits.
6.2. Self-Discipline and Motivation
Asynchronous learning fosters self-discipline and motivation, as students need to stay on track without the structure of a traditional classroom.
- Self-Motivation: Students learn to motivate themselves to complete assignments.
- Responsibility: Students take responsibility for their learning outcomes.
- Goal Setting: Students learn to set and achieve learning goals.
- Persistence: Students develop persistence in overcoming challenges.
6.3. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Asynchronous learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as students have time to reflect on the material and formulate thoughtful responses.
- Analytical Skills: Students develop analytical skills by examining complex materials.
- Evaluation: Students learn to evaluate information and arguments.
- Inference: Students learn to draw inferences and make connections.
- Decision Making: Students develop decision-making skills through problem-solving activities.
6.4. Communication Skills
Asynchronous learning enhances communication skills, particularly written communication, as students interact with peers and instructors through forums and email.
- Written Communication: Students improve their written communication skills.
- Clarity: Students learn to communicate clearly and concisely.
- Feedback: Students learn to provide and receive constructive feedback.
- Collaboration: Students develop collaboration skills through group projects.
6.5. Technical Proficiency
Asynchronous learning increases technical proficiency, as students need to navigate online platforms and use various digital tools.
- Software Skills: Students learn to use various software applications.
- Online Navigation: Students develop skills in navigating online platforms.
- Troubleshooting: Students learn to troubleshoot technical issues.
- Digital Literacy: Students improve their digital literacy skills.
6.6. Research Skills
Asynchronous learning often involves independent research, which helps students develop valuable research skills.
- Information Gathering: Students learn to gather information from various sources.
- Source Evaluation: Students learn to evaluate the credibility of sources.
- Synthesis: Students learn to synthesize information from multiple sources.
- Citation: Students learn to cite sources correctly.
7. How Can Asynchronous Learning Be Integrated With Synchronous Learning?
Integrating asynchronous and synchronous learning can create a blended learning environment that combines the best of both worlds. This approach leverages the flexibility of asynchronous learning with the real-time interaction of synchronous learning.
7.1. Blended Learning Models
Blended learning models combine asynchronous and synchronous learning to create a dynamic and engaging educational experience.
- Flipped Classroom: Students review materials asynchronously before attending synchronous sessions for discussions and activities.
- HyFlex Model: Students choose whether to attend synchronous sessions in person, participate online, or complete the course asynchronously.
- Online Labs: Students complete hands-on labs asynchronously, followed by synchronous sessions for Q&A and feedback.
- Project-Based Learning: Students work on projects asynchronously, with synchronous check-ins and presentations.
7.2. Strategies for Effective Integration
To effectively integrate asynchronous and synchronous learning, it is important to plan carefully and use appropriate strategies.
- Clear Objectives: Define clear learning objectives for both asynchronous and synchronous activities.
- Varied Activities: Use a mix of asynchronous and synchronous activities to cater to different learning styles.
- Meaningful Interaction: Encourage meaningful interaction during both asynchronous and synchronous sessions.
- Timely Feedback: Provide prompt and constructive feedback on assignments.
- Community Building: Create opportunities for students to connect and collaborate.
7.3. Examples of Integrated Activities
Various activities can be integrated into a blended learning environment to enhance student engagement and learning outcomes.
| Activity | Asynchronous Component | Synchronous Component |
|---|---|---|
| Lecture and Discussion | Students watch pre-recorded lectures. | Live discussions to clarify concepts and answer questions. |
| Reading and Group Work | Students read assigned materials. | Online group work to discuss and apply the readings. |
| Project and Presentation | Students work on projects independently. | Live presentations of project findings. |
| Lab and Q&A | Students complete lab activities. | Q&A sessions to address questions and provide feedback. |
| Assessment and Review | Students take online quizzes. | Review sessions to discuss quiz results and address misconceptions. |
| Peer Review and Feedback | Students review each other’s work. | Synchronous feedback sessions to discuss peer reviews. |
| Simulations and Debrief | Students engage in simulations. | Debrief sessions to discuss simulation outcomes and lessons learned. |
| Case Studies and Analysis | Students analyze case studies. | Synchronous discussions to analyze case studies and draw conclusions. |
| Guest Speakers and Q&A | Students prepare questions for guest speakers. | Live Q&A sessions with guest speakers. |
| Field Trips and Reflection | Students go on virtual field trips. | Reflection sessions to discuss field trip experiences and insights. |
7.4. Benefits of a Blended Approach
A blended approach offers numerous benefits, combining the flexibility of asynchronous learning with the interactivity of synchronous learning.
- Increased Flexibility: Students have more flexibility in their learning schedule.
- Enhanced Engagement: Students are more engaged through a variety of learning activities.
- Personalized Learning: Students can personalize their learning experience to meet their needs.
- Improved Learning Outcomes: Students achieve better learning outcomes through a combination of learning methods.
7.5. Tools and Technologies for Integration
Various tools and technologies can be used to integrate asynchronous and synchronous learning effectively.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms like Moodle, Canvas, and Blackboard support both asynchronous and synchronous activities.
- Video Conferencing Software: Tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams facilitate live sessions.
- Discussion Forums: Online forums provide a space for asynchronous discussions.
- Collaboration Tools: Tools like Google Docs and Microsoft Office 365 support collaborative work.
- Interactive Whiteboards: Tools like Miro and Mural facilitate real-time collaboration.
8. How Can LEARNS.EDU.VN Help You With Asynchronous Learning?
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wide range of resources and support to help you succeed in asynchronous learning environments. Whether you are a student, educator, or instructional designer, LEARNS.EDU.VN can provide the tools and guidance you need.
8.1. Resources for Students
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides students with access to high-quality learning materials and resources to support their asynchronous learning journey.
- Comprehensive Course Library: Access a vast library of courses covering various subjects and topics.
- Multimedia Content: Engage with videos, animations, and interactive simulations to enhance your understanding.
- Self-Paced Modules: Learn at your own pace with self-paced modules and assessments.
- Expert Instructors: Learn from experienced instructors who provide guidance and support.
8.2. Resources for Educators
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers educators the resources they need to design and deliver effective asynchronous courses.
- Course Design Templates: Use course design templates to create well-structured and engaging courses.
- Instructional Design Support: Get support from instructional designers to optimize your course content.
- Assessment Tools: Utilize assessment tools to evaluate student learning and provide feedback.
- Professional Development: Access professional development opportunities to enhance your teaching skills.
8.3. Instructional Design Services
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides instructional design services to help organizations create high-quality asynchronous learning programs.
- Custom Course Development: Develop custom courses tailored to your specific needs and objectives.
- Content Creation: Create engaging and informative content for your courses.
- Technology Integration: Integrate the latest technologies to enhance the learning experience.
- Program Evaluation: Evaluate the effectiveness of your asynchronous learning programs.
8.4. Community Support
LEARNS.EDU.VN fosters a community of learners and educators who can connect, collaborate, and share ideas.
- Discussion Forums: Participate in discussion forums to ask questions and share insights.
- Networking Opportunities: Connect with peers and experts in your field.
- Webinars and Workshops: Attend webinars and workshops to learn new skills and strategies.
- Resource Sharing: Share your resources and experiences with the community.
8.5. Latest Trends and Innovations
Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and innovations in asynchronous learning through LEARNS.EDU.VN.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Microlearning | Breaking down content into small, easily digestible units for just-in-time learning. |
| Personalized Learning Paths | Tailoring learning experiences to individual student needs and preferences using adaptive technologies. |
| Gamification | Incorporating game elements such as points, badges, and leaderboards to increase engagement and motivation. |
| Mobile Learning | Optimizing course content for mobile devices to allow students to learn on the go. |
| AI-Powered Tools | Using AI-powered tools to provide personalized feedback, automate administrative tasks, and enhance the learning experience. |
| Virtual and Augmented Reality | Integrating VR and AR technologies to create immersive and interactive learning experiences. |
| Blockchain Technology | Using blockchain to verify and secure academic credentials, providing learners with a portable and verifiable record of their achievements. |
| Analytics and Data-Driven Insights | Using data analytics to track student progress, identify areas for improvement, and optimize course design. |
| Open Educational Resources (OER) | Utilizing freely available educational materials to reduce costs and increase access to high-quality learning content. |
| Accessibility Enhancements | Improving accessibility for students with disabilities through features such as closed captions, screen readers, and alternative formats. |
8.6. Success Stories
Read success stories from learners and educators who have benefited from using LEARNS.EDU.VN for asynchronous learning.
- Learner Testimonials: Hear from students who have achieved their learning goals through asynchronous courses.
- Educator Spotlights: Learn from educators who have successfully implemented asynchronous learning strategies.
- Case Studies: Review case studies that demonstrate the impact of LEARNS.EDU.VN on asynchronous learning outcomes.
- Success Metrics: See data on student achievement, engagement, and satisfaction.
9. FAQ about Asynchronous Learning
Here are some frequently asked questions about asynchronous learning, along with detailed answers to help you understand this educational approach.
9.1. What is the primary difference between synchronous and asynchronous learning?
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction, while asynchronous learning allows students to learn at their own pace without requiring simultaneous participation.
9.2. How does asynchronous learning benefit students with different learning styles?
Asynchronous learning allows students to personalize their learning experience, focusing on areas where they need more help and using materials that suit their learning preferences.
9.3. What role does the instructor play in asynchronous learning environments?
The instructor designs the course, facilitates discussions, provides feedback, and supports students throughout their learning journey.
9.4. What types of activities are common in asynchronous courses?
Common activities include watching pre-recorded lectures, participating in discussion forums, completing self-paced quizzes, and working on projects independently.
9.5. How can I stay motivated in an asynchronous learning environment?
Set clear goals, create a study schedule, minimize distractions, and connect with peers to stay motivated.
9.6. What are the key technologies used in asynchronous learning?
Key technologies include Learning Management Systems (LMS), video platforms, discussion forums, and email communication.
9.7. How can I ensure that asynchronous learning is accessible to all students?
Ensure that all materials are accessible to students with disabilities, following accessibility guidelines and providing technical support.
9.8. What strategies can I use to foster a sense of community in an asynchronous course?
Encourage participation in discussion forums, create group projects, and offer virtual meetups to foster a sense of community.
9.9. How can I provide effective feedback in an asynchronous learning environment?
Provide prompt and constructive feedback on assignments, using a variety of feedback methods such as written comments, audio recordings, and video reviews.
9.10. What are some potential challenges of asynchronous learning, and how can they be addressed?
Potential challenges include social isolation, delayed feedback, and technical issues. These can be addressed by fostering community, providing timely feedback, and offering technical support.
Asynchronous learning offers a flexible and accessible approach to education, providing numerous benefits for students and educators alike. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing the resources and support you need to succeed in asynchronous learning environments.
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our courses and resources. For further assistance, contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212 or visit our website at learns.edu.vn. Enhance your educational journey with our expertly crafted materials. Explore opportunities in remote education, self-paced courses, and virtual classrooms.
