Want to learn how to play the keyboard but prefer to learn at your own pace? Learning How Can I Learn Keyboard By Myself is entirely possible with the right approach and resources. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and tools you need to succeed, offering structured guidance and resources to help you master the keyboard independently.
Discover effective self-teaching methods, practice tips, and essential resources to start your musical journey today. Explore our comprehensive lessons, skill-building exercises, and expert advice on LEARNS.EDU.VN, complemented by advanced music theory, ear training techniques, and performance tips.
1. Getting Started: Setting the Stage for Self-Taught Keyboard Mastery
Before diving into scales and chords, setting up your learning environment and understanding the basics are essential. This initial step ensures you have the necessary foundation for effective self-study.
1.1. Acquiring the Right Instrument
Choosing the right keyboard is crucial. While acoustic pianos offer an authentic experience, digital pianos provide versatility and affordability.
- Try Before You Buy: Always test a keyboard to assess key action and feel.
- Digital vs. Acoustic: Digital pianos offer features like headphone jacks and various instrument sounds.
- Key Count: Opt for 88 weighted keys for a full range and proper technique development.
Consider entry-level models if unsure about long-term commitment, and remember, renting is a viable option.
1.2. Establishing Proper Posture and Ergonomics
Correct posture prevents strain and improves playing efficiency.
- Upright Posture: Avoid hunching; align your spine naturally.
- Warm-Up: Stretch your wrists, arms, neck, and shoulders before each session.
- Keyboard Height: Adjust keyboard height for comfortable arm and wrist positioning.
These simple adjustments enhance comfort and prevent injuries during practice.
1.3. Understanding Basic Music Theory
Grasping basic music theory provides a framework for understanding music.
- Musical Alphabet: Learn the notes A-G.
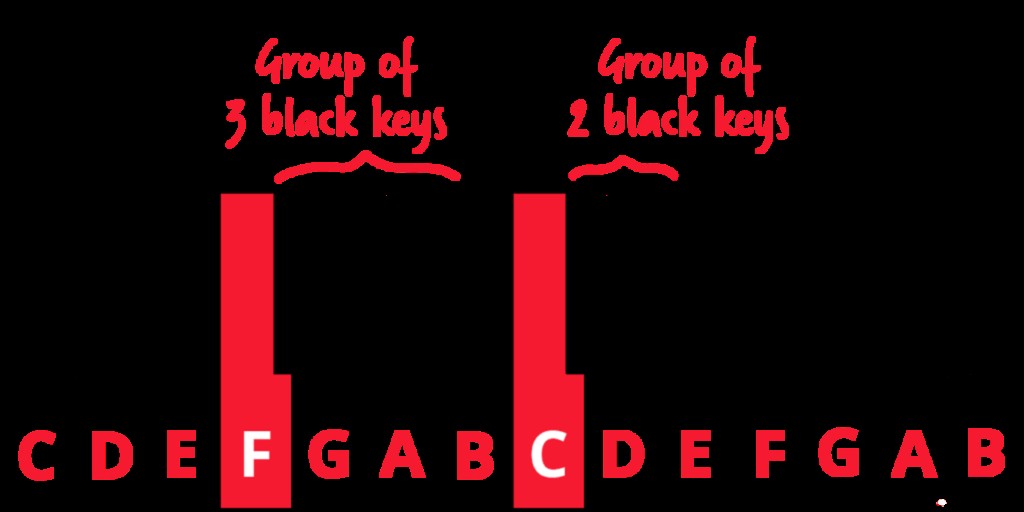
- Key Identification: Locate C (left of two black keys) and F (left of three black keys).
- Middle C: Identify the central C note as a reference point.
These fundamentals are the building blocks for more complex concepts.
1.4. Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations
Realistic goals keep you motivated and track progress.
- Start Small: Begin with simple exercises and gradually increase difficulty.
- Consistent Practice: Schedule regular practice sessions.
- Patience: Understand that progress takes time.
Regular, focused practice yields the best results.
2. Choosing Your Learning Path: Methods and Styles for Keyboard Mastery
Different learning methods cater to various preferences and goals. Selecting the right one is crucial for effective self-instruction.
2.1. The Classical Method: Building a Solid Foundation
The classical method emphasizes technique, music literacy, and studying works by renowned composers.
- Emphasis on Technique: Focuses on proper hand positioning and finger dexterity.
- Sheet Music Literacy: Develops skills in reading and interpreting musical notation.
- Classical Repertoire: Involves learning and performing classical pieces.
While comprehensive, it may not cover contemporary genres extensively.
2.2. The Modern Method: Chords and Contemporary Music
This approach focuses on chords, ear training, and improvisation, making it ideal for contemporary music.
- Chord-Based Learning: Emphasizes understanding and playing chords.
- Ear Training: Develops the ability to recognize and play music by ear.
- Improvisation: Encourages creative expression through improvisation.
Suitable for those interested in playing popular music quickly, though it may lack in-depth technique training.
2.3. Gamified Methods: Engaging and Interactive Learning
Gamified methods use software to make learning fun and interactive, ideal for beginners and children.
- Interactive Software: Provides real-time feedback and guidance.
- Game-Like Environment: Makes learning engaging and enjoyable.
- Immediate Gratification: Offers quick progress and rewards.
Effective for beginners, but may not provide a deep understanding of music theory.
2.4. Hybrid Approaches: Combining Methods for Comprehensive Learning
Combining elements from different methods provides a well-rounded learning experience.
- Classical Foundation: Develops solid technique and music reading skills.
- Modern Application: Applies knowledge to contemporary music.
- Personalized Learning: Tailors the approach to individual goals.
This approach offers a balanced and adaptable learning path.
3. Mastering Essential Techniques: Building Blocks for Keyboard Proficiency
Developing essential techniques is critical for keyboard proficiency. These foundational skills enable you to play with accuracy and expression.
3.1. Scale Patterns: Five-Finger Scales and Octave Scales
Scales are fundamental building blocks found in various musical genres.
-
Five-Finger Scale:
- Position thumb on middle C.
- Align fingers on subsequent keys.
- Play each note sequentially.
-
Octave Scales:
- Learn thumb tuck and crossover techniques.
- Practice with both hands.
- Master major and minor scales.
Consistent scale practice enhances finger dexterity and musical understanding.
3.2. Chord Progressions: Major, Minor, and Inversions
Chords are the foundation of Western music, essential for playing songs.
-
Basic Chords:
- Learn the “Big Four” (C, G, Am, F).
- Understand major and minor triads.
- Explore chord inversions.
-
Chord Progressions:
- Practice common chord progressions.
- Experiment with different voicings.
- Apply progressions to songs.
Mastering chords unlocks the ability to play a wide range of songs.
3.3. Rhythm and Timing: Developing a Steady Beat
Rhythm and timing are crucial for musicality.
-
Metronome Practice:
- Use a metronome to develop a steady beat.
- Start at slow tempos and gradually increase speed.
- Practice scales, chords, and songs with a metronome.
-
Rhythmic Exercises:
- Practice clapping and tapping rhythms.
- Use different time signatures.
- Incorporate rhythmic variations into practice.
Consistent rhythm practice enhances musical precision and expression.
3.4. Hand Independence: Coordinating Both Hands
Playing with both hands requires coordination and practice.
-
Separate Hand Practice:
- Practice each hand separately before combining.
- Focus on accuracy and fluency.
- Use scales, chords, and exercises for each hand.
-
Combined Hand Practice:
- Start slowly and gradually increase tempo.
- Focus on rhythm and timing.
- Use exercises specifically designed for hand independence.
Patience and persistence are key to mastering hand independence.
4. Essential Resources for Self-Taught Keyboard Players
Accessing quality resources is essential for self-taught keyboard players. These tools provide structured learning, feedback, and inspiration.
4.1. Online Courses and Tutorials: Structured Learning at Your Fingertips
Online platforms offer comprehensive courses and tutorials.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Offers structured courses, skill-building exercises, and expert advice.
- YouTube Channels: Provides free lessons and tutorials from various instructors.
- Subscription Services: Offers in-depth courses and personalized feedback.
Choose resources that align with your learning style and goals.
4.2. Sheet Music and Songbooks: Expanding Your Repertoire
Sheet music and songbooks provide material for practice and performance.
- Classical Collections: Offers works by renowned composers.
- Pop Songbooks: Features arrangements of popular songs.
- Online Sheet Music Stores: Provides a vast selection of digital sheet music.
Start with easy pieces and gradually increase difficulty.
4.3. Apps and Software: Enhancing Practice and Learning
Apps and software enhance practice with interactive features.
- Piano Learning Apps: Provides real-time feedback and progress tracking.
- Metronome Apps: Helps develop a steady beat.
- Music Notation Software: Aids in composing and arranging music.
These tools make practice more engaging and efficient.
4.4. Online Communities and Forums: Connecting with Fellow Musicians
Connecting with fellow musicians provides support and inspiration.
- Online Forums: Share experiences and ask questions.
- Social Media Groups: Connect with keyboard players worldwide.
- Local Music Groups: Participate in jam sessions and performances.
Engaging with a community enhances motivation and learning.
5. Overcoming Challenges: Strategies for Self-Taught Keyboard Success
Learning keyboard by yourself presents unique challenges. Addressing these obstacles effectively is crucial for progress.
5.1. Maintaining Motivation: Staying Focused and Inspired
Motivation is essential for consistent practice.
- Set Achievable Goals: Break down large goals into smaller steps.
- Track Progress: Monitor your progress and celebrate milestones.
- Find Enjoyable Music: Play music that you love.
These strategies help maintain enthusiasm and commitment.
5.2. Avoiding Bad Habits: Ensuring Proper Technique
Self-taught learners may develop poor technique.
- Record Yourself: Identify areas for improvement.
- Seek Feedback: Share recordings with experienced players.
- Focus on Fundamentals: Ensure proper posture and hand positioning.
Addressing bad habits early prevents long-term problems.
5.3. Structuring Practice: Creating a Routine for Progress
Structured practice is more effective than unstructured sessions.
- Warm-Up: Start with scales and exercises.
- Focused Practice: Dedicate time to specific techniques.
- Repertoire Work: Practice songs and pieces.
A well-structured routine maximizes learning and retention.
5.4. Dealing with Plateaus: Breaking Through Sticking Points
Plateaus are a normal part of the learning process.
- Change Routine: Try new exercises or pieces.
- Seek New Resources: Explore different learning methods.
- Rest and Recover: Take breaks to avoid burnout.
These strategies help overcome plateaus and continue progress.
6. Advanced Techniques and Concepts: Elevating Your Keyboard Skills
Once you’ve mastered the basics, exploring advanced techniques and concepts elevates your keyboard skills.
6.1. Advanced Chord Voicings and Progressions: Creating Rich Harmonies
Explore advanced chord voicings and progressions to create richer harmonies.
- Extended Chords: Learn 9th, 11th, and 13th chords.
- Altered Chords: Experiment with altered dominant chords.
- Complex Progressions: Study jazz and contemporary progressions.
These techniques add depth and sophistication to your playing.
6.2. Improvisation Techniques: Creating Your Own Music
Improvisation is a powerful tool for creative expression.
- Scale and Mode Practice: Improvise using scales and modes.
- Chord Tone Soloing: Create solos based on chord tones.
- Motifs and Phrases: Develop and vary musical ideas.
Consistent improvisation practice enhances creativity and musicality.
6.3. Sight-Reading Skills: Mastering Musical Notation
Advanced sight-reading skills enable you to learn new music quickly.
- Regular Practice: Sight-read daily.
- Rhythmic Accuracy: Focus on precise rhythm and timing.
- Pattern Recognition: Identify common patterns and phrases.
Improved sight-reading opens up a vast repertoire of music.
6.4. Performance Techniques: Engaging Your Audience
Effective performance techniques enhance your stage presence.
- Practice Performing: Simulate performance conditions.
- Connect with Audience: Engage with your listeners.
- Stage Presence: Develop confident body language.
These techniques transform your playing into a captivating performance.
7. Integrating Keyboard Skills into Your Life: Practical Applications and Opportunities
Integrating keyboard skills into your life enriches your experiences and opens new opportunities.
7.1. Playing in a Band or Ensemble: Collaborating with Other Musicians
Playing with others enhances your musicality and teamwork.
- Join a Band: Participate in local music groups.
- Ensemble Playing: Collaborate with other instrumentalists.
- Rehearsal Techniques: Develop effective rehearsal strategies.
Collaborating with others broadens your musical horizons.
7.2. Composing and Arranging Music: Expressing Your Creativity
Composing and arranging music allows you to express your unique voice.
- Music Theory Knowledge: Apply theoretical concepts to composition.
- Arranging Techniques: Adapt existing songs for keyboard.
- Software Tools: Use music notation software for composition.
Creative expression through composition is a rewarding endeavor.
7.3. Teaching Keyboard to Others: Sharing Your Passion
Teaching keyboard to others reinforces your knowledge and shares your passion.
- Lesson Planning: Develop structured lesson plans.
- Teaching Techniques: Use effective teaching methods.
- Student Assessment: Evaluate student progress and provide feedback.
Sharing your knowledge benefits both you and your students.
7.4. Performing at Events: Showcasing Your Talent
Performing at events showcases your talent and builds confidence.
- Practice Regularly: Ensure polished performances.
- Choose Appropriate Music: Select songs that suit the event.
- Promote Your Performances: Attract an audience.
Public performance is a fulfilling culmination of your learning journey.
8. Case Studies: Success Stories of Self-Taught Keyboard Players
Inspirational stories can motivate and provide practical insights for self-taught learners.
8.1. Case Study 1: Emily’s Journey from Beginner to Band Member
Emily started learning keyboard at 25 with no prior musical experience. By using online resources and practicing consistently, she joined a local band within two years.
- Challenges: Overcoming initial frustration with hand independence.
- Strategies: Breaking down complex passages into smaller parts, using a metronome.
- Key Takeaway: Consistent practice and targeted problem-solving yield significant results.
8.2. Case Study 2: David’s Transition to Music Composition
David, a software engineer, started learning keyboard as a hobby. He utilized online courses to learn music theory and composition, eventually creating his own pieces.
- Challenges: Balancing learning with a demanding full-time job.
- Strategies: Setting specific practice times each day, focusing on short, productive sessions.
- Key Takeaway: Efficient time management and clear goals facilitate progress.
8.3. Case Study 3: Sarah’s Path to Teaching Keyboard
Sarah, a retired teacher, started learning keyboard to stay active. She mastered advanced techniques through self-study and now teaches keyboard to children in her community.
- Challenges: Adapting to new technologies and online teaching methods.
- Strategies: Participating in online forums, taking short courses on digital teaching tools.
- Key Takeaway: Continuous learning and adapting to new tools are essential for growth.
8.4. Analysis of Common Success Factors
Several common factors contribute to the success of self-taught keyboard players.
| Factor | Description | Implementation Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Learning | Following a clear curriculum or course to ensure comprehensive skill development. | Use online courses, textbooks, or create a personal learning plan. |
| Consistent Practice | Regular practice to reinforce learned skills and develop muscle memory. | Schedule daily practice sessions, even if only for 30 minutes. |
| Targeted Problem-Solving | Identifying and addressing specific weaknesses or challenges in technique or understanding. | Record practice sessions, seek feedback, focus on areas needing improvement. |
| Community Engagement | Connecting with other musicians for support, inspiration, and feedback. | Join online forums, attend local music events, collaborate with other musicians. |
| Adaptability | Being willing to adjust learning methods and incorporate new resources or technologies. | Stay updated with new learning tools, be open to different teaching styles, adapt practice routines as needed. |





These success stories and factors highlight the potential for self-taught learners to achieve their musical goals.
9. The Role of AI in Keyboard Learning: Enhancing Self-Study
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the landscape of music education, providing self-taught keyboard players with innovative tools to enhance their learning experience.
9.1. AI-Powered Learning Apps
AI-driven apps offer personalized feedback, adaptive learning paths, and real-time performance analysis.
- Personalized Feedback: AI analyzes playing technique and provides specific recommendations.
- Adaptive Learning: Adjusts difficulty levels based on progress and skill level.
- Real-Time Analysis: Offers instant feedback on rhythm, timing, and accuracy.
Examples include apps that listen to your playing and offer suggestions for improvement.
9.2. Virtual Tutors and Mentors
AI can simulate virtual tutors, providing guidance, answering questions, and offering encouragement.
- Interactive Q&A: AI answers questions about music theory, technique, and repertoire.
- Personalized Guidance: Provides tailored advice based on learning style and goals.
- Motivational Support: Offers encouragement and tracks progress.
These virtual tutors can supplement traditional learning resources.
9.3. AI-Generated Music and Accompaniment
AI can generate custom music and accompaniment tracks for practice and performance.
- Custom Compositions: AI creates original pieces tailored to skill level and preferences.
- Accompaniment Tracks: Generates backing tracks for solo practice and performance.
- Style Imitation: AI can compose music in the style of famous composers or genres.
This technology offers endless possibilities for creative exploration.
9.4. Ethical Considerations and Limitations
While AI offers numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of its limitations and potential ethical concerns.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy and security of user data collected by AI systems.
- Algorithmic Bias: Addressing potential biases in AI algorithms that could affect learning outcomes.
- Over-Reliance: Avoiding over-dependence on AI and maintaining a balance with traditional learning methods.
Responsible use of AI enhances learning while preserving the human element of music education.
10. Future Trends in Keyboard Learning: Emerging Technologies and Methodologies
The future of keyboard learning is shaped by emerging technologies and innovative methodologies that promise to make education more accessible, personalized, and effective.
10.1. Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR)
VR and AR technologies offer immersive learning experiences that simulate real-world environments.
- Virtual Concerts: Attend virtual concerts and interact with musicians in real-time.
- Interactive Lessons: Engage in lessons with virtual instructors.
- Enhanced Practice: Visualize musical concepts in augmented reality.
These technologies offer unique opportunities for engagement and immersion.
10.2. Blockchain Technology for Music Education
Blockchain technology can revolutionize music education by providing secure, transparent, and decentralized learning platforms.
- Secure Credentials: Blockchain-based credentials verify skills and accomplishments.
- Decentralized Learning: Connects learners with educators directly, bypassing traditional institutions.
- Transparent Payments: Ensures fair compensation for educators and artists.
Blockchain can foster a more equitable and efficient music education ecosystem.
10.3. Personalized Learning Paths
AI and data analytics enable the creation of highly personalized learning paths tailored to individual needs and goals.
- Adaptive Assessments: AI evaluates skills and recommends appropriate learning materials.
- Customized Content: Tailored content based on learning preferences and pace.
- Progress Tracking: AI monitors progress and provides personalized feedback.
Personalized learning paths optimize learning outcomes and engagement.
10.4. Integration with Neurosciences
Integrating insights from neurosciences can enhance learning methodologies and optimize practice techniques.
- Brain Training: Using exercises to improve cognitive functions related to music learning.
- Memory Optimization: Applying memory techniques to enhance retention.
- Stress Reduction: Incorporating mindfulness practices to reduce anxiety and improve focus.
By understanding how the brain learns, educators can create more effective teaching strategies.
By embracing these emerging trends and technologies, self-taught keyboard players can unlock new possibilities for growth and creativity.
Ready to take your keyboard skills to the next level? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive courses, resources, and expert advice. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, we have everything you need to succeed. Join our community of passionate learners and start your musical journey with us.
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Is it possible to learn keyboard entirely by myself?
Yes, it is possible with the right resources, discipline, and structured approach.
-
What is the best keyboard for a beginner?
A digital keyboard with 88 weighted keys is ideal for beginners.
-
How much time should I practice each day?
Aim for at least 30 minutes to an hour of practice each day for consistent progress.
-
Do I need to learn music theory to play the keyboard?
While not essential, learning basic music theory enhances your understanding and skills.
-
What are some good online resources for learning keyboard?
learns.edu.vn, YouTube channels, and subscription services offer valuable lessons and tutorials.
-
How can I improve my hand independence?
Practice each hand separately before combining, focus on rhythm, and use specific exercises for hand independence.
-
How can I stay motivated while learning keyboard by myself?
Set achievable goals, track your progress, find enjoyable music, and join a community.
-
What should I do if I hit a plateau in my learning?
Change your routine, seek new resources, rest and recover, and focus on your weaknesses.
-
How can AI help me learn keyboard?
AI-powered apps provide personalized feedback, adaptive learning paths, and real-time performance analysis.
-
What are some future trends in keyboard learning?
Virtual and augmented reality, blockchain technology, personalized learning paths, and integration with neurosciences are emerging trends shaping the future of keyboard learning.
