Are you a teacher looking for effective strategies to support students with learning disabilities? At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide practical guidance and resources to help educators like you create inclusive and supportive learning environments that empower every student to succeed, regardless of their learning challenges. This comprehensive guide explores actionable strategies and accommodations, ensuring you can effectively support students with learning disabilities.
1. Understanding Learning Disabilities
What exactly are learning disabilities, and how do they impact students’ learning experiences? Learning disabilities are neurological conditions that affect a person’s ability to receive, process, store, and respond to information. These disabilities can manifest in various ways, impacting reading, writing, math, and other academic skills. Understanding these challenges is the first step in providing effective support.
1.1. Types of Learning Disabilities
What are the different types of learning disabilities that educators should be aware of? Here’s a list:
- Dyslexia: A reading disability that affects decoding, fluency, and comprehension.
- Dysgraphia: A writing disability that impacts handwriting, spelling, and composition.
- Dyscalculia: A math disability that affects number sense, calculation, and problem-solving.
- Auditory Processing Disorder: A disability that affects the ability to understand and process auditory information.
- Visual Processing Disorder: A disability that affects the ability to interpret and process visual information.
1.2. Impact on Learning
How do learning disabilities affect a student’s ability to succeed in school? Learning disabilities can significantly impact academic performance, self-esteem, and social interactions. Students may struggle with specific tasks, experience frustration and anxiety, and require tailored support to reach their full potential.
According to the National Center for Learning Disabilities, early identification and intervention are crucial for improving outcomes for students with learning disabilities.
2. Creating an Inclusive Classroom Environment
How can teachers create a classroom environment that supports students with learning disabilities? Creating an inclusive classroom involves adapting teaching methods, providing necessary accommodations, and fostering a culture of acceptance and understanding.
2.1. Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
What is Universal Design for Learning (UDL) and how can it benefit students with learning disabilities? UDL is an educational framework that guides the development of flexible learning environments that can accommodate individual learning differences. UDL focuses on three main principles:
- Multiple Means of Representation: Presenting information in various formats to cater to different learning styles.
- Multiple Means of Action and Expression: Allowing students to demonstrate their knowledge in different ways.
- Multiple Means of Engagement: Providing choices and activities that motivate and engage students.
2.2. Accessible Materials
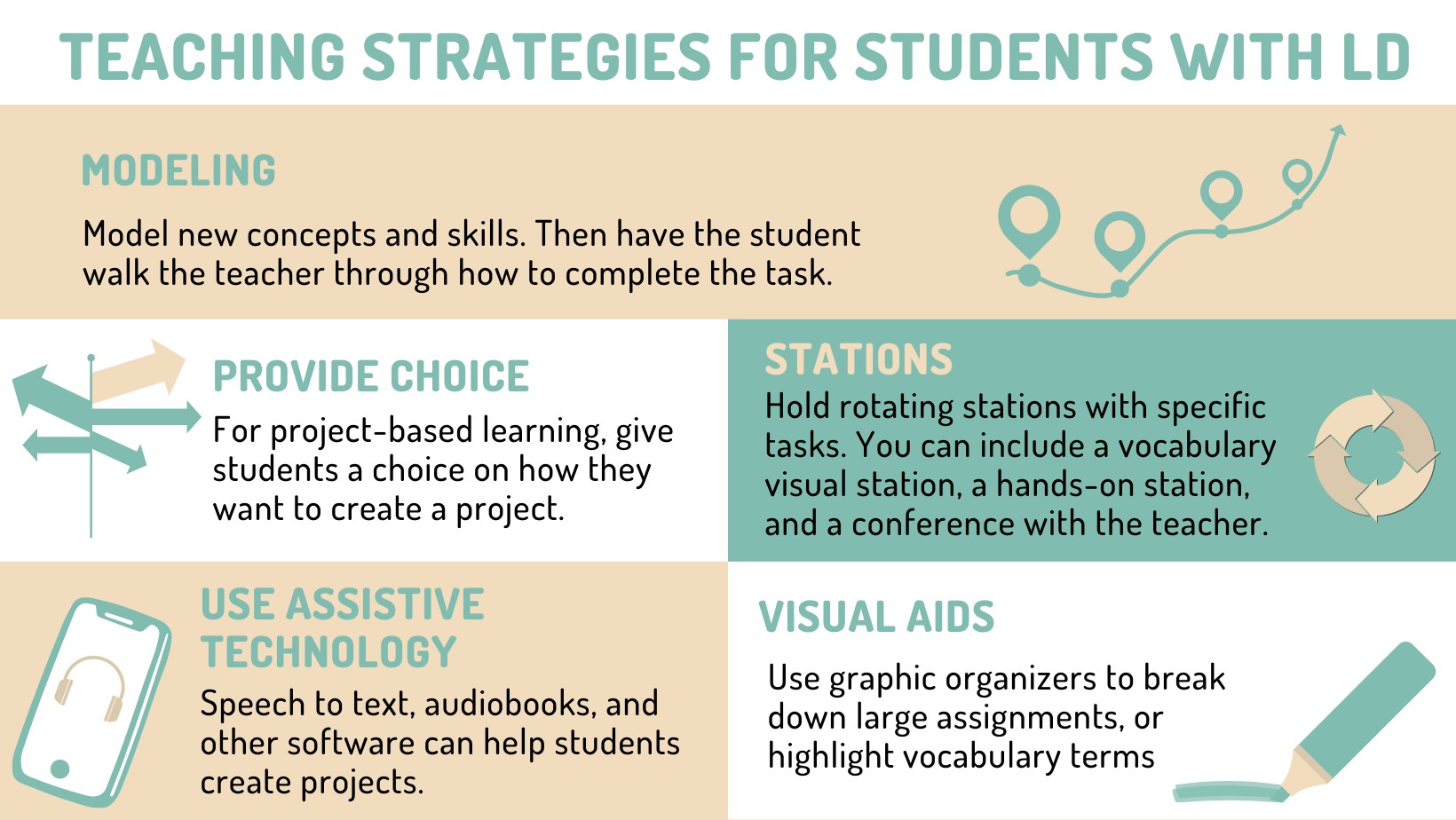
How can teachers ensure that learning materials are accessible to all students, including those with learning disabilities? Making materials accessible involves providing alternative formats, such as audiobooks, large print, and digital text, as well as using assistive technology to support reading and writing.
3. Effective Teaching Strategies
What are some effective teaching strategies that can help students with learning disabilities succeed in the classroom? Implementing evidence-based strategies is essential for supporting students with learning disabilities.
3.1. Differentiated Instruction
What is differentiated instruction, and how can it be used to meet the diverse needs of students with learning disabilities? Differentiated instruction involves tailoring instruction to meet the individual needs of students. This can include modifying content, process, product, and learning environment to match students’ readiness, interests, and learning profiles.
For example, consider the following table:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Content | Modifying what is taught, such as simplifying complex texts or providing background knowledge. |
| Process | Adjusting how students learn, such as using visual aids, hands-on activities, or cooperative learning. |
| Product | Allowing students to demonstrate their learning in different ways, such as through presentations, projects, or written reports. |
| Learning Environment | Creating a supportive and flexible classroom that accommodates different learning styles and needs. |
3.2. Explicit Instruction
What is explicit instruction, and why is it effective for students with learning disabilities? Explicit instruction is a structured and systematic approach to teaching that involves clearly explaining concepts, modeling strategies, and providing guided practice. This approach is particularly effective for students with learning disabilities who benefit from clear and direct instruction.
3.3. Multi-Sensory Teaching
How can multi-sensory teaching methods benefit students with learning disabilities? Multi-sensory teaching involves engaging multiple senses—visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and tactile—to enhance learning and memory. This approach can be particularly helpful for students who struggle with traditional teaching methods.
 Multi-sensory teaching: Engage multiple senses, provide hands-on activities, use visual aids, incorporate movement, and allow students to explore concepts in a variety of ways.
Multi-sensory teaching: Engage multiple senses, provide hands-on activities, use visual aids, incorporate movement, and allow students to explore concepts in a variety of ways.
3.4. Assistive Technology
What types of assistive technology can support students with learning disabilities? Assistive technology includes a wide range of tools and devices that can help students overcome learning barriers. These tools can include:
- Text-to-Speech Software: Converts written text into spoken words, helping students with reading difficulties.
- Speech-to-Text Software: Converts spoken words into written text, assisting students with writing difficulties.
- Graphic Organizers: Visual tools that help students organize information and ideas.
- Calculators: Tools that support students with math calculations.
3.5. Scaffolding
What is scaffolding, and how can teachers use it to support students with learning disabilities? Scaffolding involves providing temporary support to students as they learn new skills and concepts. This support can include breaking down tasks into smaller steps, providing prompts and cues, and offering feedback and encouragement. As students become more proficient, the scaffolding is gradually removed.
4. Accommodations and Modifications
What are some common accommodations and modifications that can be implemented in the classroom to support students with learning disabilities? Accommodations and modifications are changes made to the learning environment or curriculum to help students with learning disabilities access and demonstrate their knowledge.
4.1. Common Accommodations
What are some examples of accommodations that teachers can provide to students with learning disabilities? Common accommodations include:
- Extended Time: Allowing students more time to complete assignments and tests.
- Preferential Seating: Placing students in a location that minimizes distractions and maximizes focus.
- Reduced Workload: Adjusting the amount of work assigned to match students’ abilities.
- Alternative Assessments: Providing alternative ways for students to demonstrate their knowledge, such as oral presentations or projects.
- Use of Technology: Allowing students to use assistive technology, such as text-to-speech software or graphic organizers.
4.2. Modifications to Curriculum
When should modifications be made to the curriculum for students with learning disabilities? Modifications involve changing the content or expectations of the curriculum to better meet the needs of students with learning disabilities. Modifications should be made when accommodations are not sufficient to support a student’s learning.
4.3. Examples of Modifications
What are some examples of modifications that teachers can make to the curriculum? Examples of modifications include:
- Simplified Texts: Providing texts that are written at a lower reading level.
- Reduced Complexity: Breaking down complex concepts into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Alternative Assignments: Providing alternative assignments that focus on essential skills and concepts.
- Modified Grading: Adjusting grading criteria to reflect students’ abilities and progress.
5. Collaboration and Communication
How important is collaboration and communication between teachers, parents, and specialists in supporting students with learning disabilities? Collaboration and communication are essential for creating a comprehensive support system for students with learning disabilities.
5.1. Working with Special Education Teachers
How can general education teachers collaborate with special education teachers to support students with learning disabilities? General education teachers can collaborate with special education teachers to:
- Co-Plan Lessons: Develop lessons that incorporate accommodations and modifications to meet students’ needs.
- Co-Teach: Work together to deliver instruction, with one teacher providing direct instruction and the other providing support and assistance.
- Co-Assess: Evaluate students’ progress and adjust instruction as needed.
- Share Expertise: Exchange knowledge and strategies to enhance teaching practices.
According to a study by the Council for Exceptional Children, collaborative teaching models can significantly improve outcomes for students with learning disabilities.
5.2. Engaging Parents
How can teachers engage parents in supporting their child with learning disabilities? Engaging parents involves:
- Regular Communication: Providing regular updates on students’ progress and challenges.
- Parent-Teacher Conferences: Holding meetings to discuss students’ needs and develop strategies for support.
- Home-School Collaboration: Working together to reinforce skills and strategies at home and at school.
- Providing Resources: Sharing information about learning disabilities and available resources.
5.3. Seeking Support from Specialists
When should teachers seek support from specialists, such as school psychologists or educational diagnosticians? Teachers should seek support from specialists when they have concerns about a student’s learning or behavior, or when they need assistance with assessment, diagnosis, or intervention.
6. Creating a Positive and Supportive Classroom Climate
How can teachers create a positive and supportive classroom climate for students with learning disabilities? Creating a positive classroom climate involves fostering a culture of acceptance, understanding, and respect.
6.1. Building Self-Esteem
How Can Teachers Help Students With Learning Disabilities build self-esteem and confidence? Teachers can help students build self-esteem by:
- Focusing on Strengths: Highlighting students’ abilities and accomplishments.
- Providing Positive Feedback: Offering specific and genuine praise for effort and progress.
- Setting Achievable Goals: Helping students set realistic goals and celebrate their successes.
- Promoting Self-Advocacy: Encouraging students to speak up and ask for help when they need it.
6.2. Addressing Stigma
How can teachers address the stigma associated with learning disabilities? Teachers can address stigma by:
- Educating Students: Providing accurate information about learning disabilities and dispelling myths and misconceptions.
- Promoting Understanding: Encouraging empathy and acceptance among students.
- Celebrating Diversity: Recognizing and valuing the unique strengths and talents of all students.
- Modeling Respect: Treating all students with dignity and respect, regardless of their learning differences.
6.3. Promoting Independence
Why is it important to promote independence in students with learning disabilities? Promoting independence is essential for helping students develop the skills and confidence they need to succeed in school and in life.
6.4. Strategies for Promoting Independence
What are some strategies for promoting independence in students with learning disabilities? Strategies for promoting independence include:
- Teaching Self-Advocacy Skills: Helping students learn how to identify their needs and ask for help.
- Encouraging Problem-Solving: Providing opportunities for students to solve problems and make decisions independently.
- Fading Support: Gradually reducing the amount of support provided as students become more proficient.
- Providing Opportunities for Success: Creating opportunities for students to experience success and build confidence.
7. Specific Strategies for Reading Disabilities (Dyslexia)
What specific strategies can teachers use to support students with reading disabilities, such as dyslexia? Dyslexia is a common learning disability that affects reading fluency, decoding, and comprehension.
7.1. Phonological Awareness Training
What is phonological awareness, and why is it important for students with dyslexia? Phonological awareness is the ability to recognize and manipulate the sounds in spoken language. It is a foundational skill for reading and spelling.
7.2. Systematic Phonics Instruction
What is systematic phonics instruction, and how can it benefit students with dyslexia? Systematic phonics instruction involves teaching the relationships between letters and sounds in a structured and sequential manner. This approach helps students develop the decoding skills they need to read words accurately and fluently.
7.3. Fluency-Building Activities
What types of fluency-building activities can teachers use to support students with dyslexia? Fluency-building activities include:
- Repeated Reading: Having students read the same passage multiple times to improve speed and accuracy.
- Choral Reading: Having students read aloud together as a group.
- Partner Reading: Having students take turns reading aloud to each other.
- Reader’s Theater: Having students perform scripts to practice reading with expression and fluency.
7.4. Comprehension Strategies
What comprehension strategies can teachers teach to students with dyslexia to improve their reading comprehension? Comprehension strategies include:
- Activating Prior Knowledge: Helping students connect what they are reading to what they already know.
- Making Predictions: Encouraging students to predict what will happen next in the text.
- Asking Questions: Teaching students to ask questions about the text to monitor their understanding.
- Summarizing: Helping students identify the main ideas and key details in the text.
- Visualizing: Encouraging students to create mental images of what they are reading.
8. Strategies for Writing Disabilities (Dysgraphia)
What specific strategies can teachers use to support students with writing disabilities, such as dysgraphia? Dysgraphia is a learning disability that affects handwriting, spelling, and written expression.
8.1. Fine Motor Skills Activities
What types of fine motor skills activities can teachers use to support students with dysgraphia? Fine motor skills activities include:
- Handwriting Practice: Providing structured practice in letter formation and handwriting.
- Pencil Grip Training: Teaching students how to hold a pencil correctly.
- Typing Skills: Encouraging students to learn how to type as an alternative to handwriting.
- Activities that Strengthen Hand Muscles: Using activities such as playing with clay, building with blocks, or using scissors to strengthen hand muscles.
8.2. Organization and Planning Strategies
How can teachers help students with dysgraphia improve their organization and planning skills for writing? Teachers can help students by:
- Using Graphic Organizers: Providing visual tools to help students organize their ideas and plan their writing.
- Breaking Down Tasks: Breaking down writing assignments into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Providing Templates: Providing templates for different types of writing, such as essays or reports.
- Teaching Outlining: Helping students learn how to create outlines to organize their thoughts and ideas.
8.3. Spelling Strategies
What spelling strategies can teachers teach to students with dysgraphia to improve their spelling skills? Spelling strategies include:
- Multi-Sensory Spelling: Using visual, auditory, and kinesthetic cues to help students learn to spell words.
- Phonetic Spelling: Encouraging students to spell words based on their sounds.
- Memorization Strategies: Teaching students strategies for memorizing spelling words, such as using flashcards or mnemonic devices.
- Use of Technology: Allowing students to use spell-checkers and other technology tools to support their spelling.
8.4. Assistive Technology for Writing
What types of assistive technology can support students with dysgraphia in their writing? Assistive technology tools for writing include:
- Speech-to-Text Software: Converting spoken words into written text.
- Word Prediction Software: Suggesting words as students type to improve speed and accuracy.
- Grammar Checkers: Identifying and correcting grammatical errors in writing.
- Voice Recorders: Allowing students to record their thoughts and ideas and then transcribe them later.
9. Strategies for Math Disabilities (Dyscalculia)
What specific strategies can teachers use to support students with math disabilities, such as dyscalculia? Dyscalculia is a learning disability that affects math skills, such as number sense, calculation, and problem-solving.
9.1. Concrete Manipulatives
What are concrete manipulatives, and how can they benefit students with dyscalculia? Concrete manipulatives are physical objects that students can use to represent math concepts. These can include:
- Base Ten Blocks: Helping students understand place value.
- Counters: Helping students learn to count and perform basic operations.
- Number Lines: Helping students visualize numbers and their relationships.
- Fraction Bars: Helping students understand fractions and their operations.
9.2. Visual Aids
How can visual aids support students with dyscalculia in learning math concepts? Visual aids can help students visualize math concepts and make them more concrete. Visual aids include:
- Charts and Graphs: Helping students organize and interpret data.
- Diagrams: Helping students understand geometric concepts.
- Color-Coding: Using different colors to represent different numbers or operations.
- Pictures and Illustrations: Helping students understand word problems and their solutions.
9.3. Explicit Instruction in Math Facts
Why is explicit instruction in math facts important for students with dyscalculia? Explicit instruction in math facts helps students develop automaticity, which is the ability to recall math facts quickly and accurately. This is essential for success in higher-level math.
9.4. Real-Life Applications
How can teachers connect math concepts to real-life applications to help students with dyscalculia understand their relevance? Connecting math concepts to real-life applications helps students see the relevance and importance of math in their daily lives. For example:
- Using Money: Teaching students how to count money, make change, and budget.
- Measuring: Teaching students how to measure length, weight, and volume.
- Cooking: Teaching students how to use fractions and ratios in recipes.
- Telling Time: Teaching students how to read a clock and understand time intervals.
10. Resources and Support
What resources and support are available for teachers who are working with students with learning disabilities? There are many resources and support available for teachers, including:
10.1. Professional Development
What types of professional development opportunities are available for teachers to learn more about supporting students with learning disabilities? Professional development opportunities include:
- Workshops and Seminars: Providing training on specific strategies and interventions.
- Online Courses: Offering flexible learning opportunities on various topics related to learning disabilities.
- Conferences: Providing opportunities to network with other educators and learn about the latest research and best practices.
- Mentoring Programs: Pairing experienced teachers with new teachers to provide support and guidance.
10.2. Educational Organizations
What educational organizations provide resources and support for teachers of students with learning disabilities? Educational organizations include:
- Learning Disabilities Association of America (LDA): Providing information, resources, and advocacy for individuals with learning disabilities.
- National Center for Learning Disabilities (NCLD): Providing research-based information and resources on learning disabilities.
- Council for Exceptional Children (CEC): Advocating for the rights and needs of students with disabilities.
- International Dyslexia Association (IDA): Providing resources and training on dyslexia and reading instruction.
10.3. Online Resources
What online resources are available for teachers to learn more about supporting students with learning disabilities? Online resources include:
- Websites: Providing information, articles, and resources on various topics related to learning disabilities.
- Blogs: Sharing insights, tips, and strategies from educators and experts in the field.
- Webinars: Offering live and recorded presentations on various topics related to learning disabilities.
- Online Communities: Providing forums for educators to connect, share ideas, and ask questions.
10.4. Legal and Ethical Considerations
What are the legal and ethical considerations that teachers should be aware of when working with students with learning disabilities? Teachers should be aware of:
- Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA): Ensuring that students with disabilities receive a free and appropriate public education.
- Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act: Prohibiting discrimination against individuals with disabilities in programs and activities that receive federal funding.
- Confidentiality: Protecting the privacy of students’ educational records.
- Due Process: Ensuring that students and parents have the right to challenge decisions made by the school.
By understanding and addressing these legal and ethical considerations, teachers can ensure that they are providing a fair and equitable education for all students with learning disabilities.
FAQ: Supporting Students with Learning Disabilities
Q1: What are the first signs of a learning disability in a child?
A: Early signs can include difficulty with reading, writing, math, or understanding instructions. Watch for persistent struggles in these areas despite typical classroom support.
Q2: How can I differentiate instruction for a student with dyslexia?
A: Use multi-sensory techniques, provide audiobooks, offer extra time for reading tasks, and focus on phonological awareness.
Q3: What is the role of assistive technology in supporting students with learning disabilities?
A: Assistive technology can provide tools like text-to-speech software, speech-to-text software, and graphic organizers to help students overcome learning barriers.
Q4: How can I create a supportive classroom environment for students with learning disabilities?
A: Foster a culture of acceptance and understanding, focus on strengths, provide positive feedback, and encourage self-advocacy.
Q5: What strategies can I use to help a student with dysgraphia improve their writing skills?
A: Provide fine motor skills activities, teach organization and planning strategies, offer spelling support, and use assistive technology like speech-to-text software.
Q6: How can I collaborate effectively with special education teachers?
A: Co-plan lessons, co-teach, co-assess, and share expertise to provide comprehensive support for students with learning disabilities.
Q7: What are some effective math strategies for students with dyscalculia?
A: Use concrete manipulatives, visual aids, provide explicit instruction in math facts, and connect math concepts to real-life applications.
Q8: How can I engage parents in supporting their child with learning disabilities?
A: Maintain regular communication, hold parent-teacher conferences, collaborate on home-school activities, and provide resources about learning disabilities.
Q9: Where can I find professional development opportunities to enhance my skills in supporting students with learning disabilities?
A: Look for workshops, online courses, conferences, and mentoring programs offered by educational organizations and online platforms.
Q10: What legal considerations should I keep in mind when working with students with learning disabilities?
A: Be aware of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, ensure confidentiality, and provide due process.
Conclusion
Supporting students with learning disabilities requires a multifaceted approach that includes understanding their specific challenges, creating an inclusive classroom environment, implementing effective teaching strategies, and fostering collaboration between teachers, parents, and specialists. By providing tailored support and accommodations, teachers can empower students with learning disabilities to overcome their challenges and achieve their full potential.
Ready to take your support for students with learning disabilities to the next level? Explore LEARNS.EDU.VN for in-depth articles, practical resources, and expert-led courses designed to empower educators like you. Unlock the strategies and tools you need to create an inclusive and effective learning environment for every student. Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and transform your teaching!
Contact us:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: learns.edu.vn
By understanding the challenges of students with learning disabilities, implementing effective strategies, and collaborating with parents and specialists, teachers can make a significant difference in the lives of these students.