Learning how a switch learns MAC addresses is crucial for understanding network functionality. This comprehensive guide from LEARNS.EDU.VN simplifies the process, explaining address learning, forwarding decisions, and loop avoidance with clear examples and actionable insights, making network concepts accessible to everyone. Dive in to master MAC address learning and enhance your networking skills, unlocking advanced knowledge.
1. Understanding the Basics: What is a MAC Address?
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier assigned to each network interface card (NIC). Think of it as a device’s physical address on a network, essential for communication within a local area network (LAN). These addresses are crucial for switches to accurately forward data packets to their intended destinations.
- Uniqueness: Each MAC address is globally unique, ensuring no two devices share the same identifier.
- Structure: A MAC address consists of 12 hexadecimal digits, often represented in pairs separated by colons (e.g., 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E).
- Function: It facilitates communication between devices on the same network segment by providing a direct addressing mechanism.
2. The Role of a Switch in a Network
A switch operates as a central connection point for devices in a network, improving efficiency and reducing collisions compared to older technologies like hubs. Switches perform three primary functions:
- Address Learning: Identifying and recording MAC addresses of connected devices.
- Forward/Filter Decisions: Determining whether to forward or block network traffic based on destination MAC addresses.
- Loop Avoidance: Preventing network loops using protocols like Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
2.1. Address Learning
Address learning is how a switch discovers which devices are connected to its ports. This process allows the switch to build a MAC address table, also known as a CAM (Content Addressable Memory) table.
2.2. Forward/Filtering Decisions
Based on the MAC address table, the switch makes informed decisions about where to send network traffic. It forwards traffic only to the port connected to the destination MAC address, reducing unnecessary traffic on other network segments.
2.3. Loop Avoidance
Network loops can cause broadcast storms, crippling network performance. Switches use STP to detect and block redundant paths, ensuring a loop-free topology.
3. How a Switch Learns MAC Addresses: A Step-by-Step Guide
When a switch receives a frame, it examines the frame’s source MAC address and records this information in its MAC address table. This table maps MAC addresses to the corresponding switch ports. Let’s break down the process step-by-step.
- Frame Reception: A device sends a frame to the switch.
- Source MAC Address Examination: The switch reads the source MAC address from the incoming frame.
- MAC Address Table Update: The switch adds the source MAC address and the port it was received on to the MAC address table.
- Destination MAC Address Lookup: The switch checks the destination MAC address against its MAC address table.
- Frame Forwarding: If the destination MAC address is in the table, the switch forwards the frame only to the corresponding port. If not, it floods the frame to all ports except the incoming port.
3.1. Detailed Example of MAC Address Learning
Consider a scenario where Host A (MAC address AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA) connects to Port 1 of a switch, and Host B (MAC address BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB) connects to Port 2.
- Host A sends a frame to Host B.
- The switch receives this frame on Port 1.
- The switch examines the source MAC address (AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA) and notes that this MAC address is associated with Port 1, adding this information to its MAC address table.
- The switch then looks up the destination MAC address (BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB) in its MAC address table.
- If the destination MAC address is known (associated with Port 2), the switch forwards the frame only to Port 2.
- If the destination MAC address is unknown, the switch floods the frame to all ports except Port 1.
- When Host B responds, the switch learns that MAC address BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB is associated with Port 2.
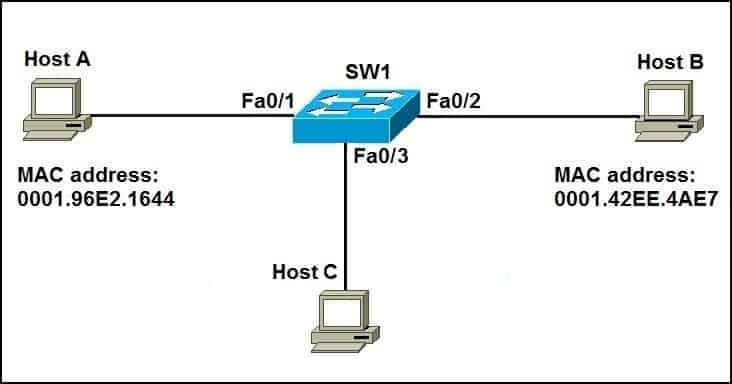
3.2. Visual Representation
This image illustrates how a switch forwards data between hosts by learning and utilizing MAC addresses.
3.3. The Aging Process
MAC address entries in the switch’s table are not permanent. To ensure the table remains current and accurate, entries have an aging time (typically 5 minutes). If a MAC address is not seen within this time, it is removed from the table.
3.4. Displaying the MAC Address Table
Most switches provide a command to view the current MAC address table. For example, on a Cisco switch, you can use the command show mac address-table. The output will list the VLAN, MAC address, type (dynamic or static), and the associated port.
Switch#show mac address-table
Mac Address Table
-------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports
---- ----------- -------- -----
1 000a.111b.222c DYNAMIC Fa0/1
1 000d.333e.444f DYNAMIC Fa0/2- VLAN: The Virtual LAN the MAC address belongs to.
- MAC Address: The MAC address of the device.
- Type: Indicates whether the address was learned dynamically or configured statically.
- Ports: The switch port associated with the MAC address.
4. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) and MAC Address Learning
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) plays a crucial role in the MAC address learning process. ARP is used to discover the MAC address associated with a known IP address.
4.1. The ARP Process
- A host needs to find the MAC address of another host on the same network.
- The sending host broadcasts an ARP request containing the target IP address.
- The host with the matching IP address responds with its MAC address.
- Both hosts store this MAC address in their ARP cache for future communication.
4.2. ARP and Switch Learning
When the switch forwards the ARP request, it learns the MAC address of the sending host. When the target host responds, the switch learns its MAC address as well. This bidirectional learning is essential for establishing communication.
5. Practical Applications and Benefits of Understanding MAC Address Learning
Understanding how switches learn MAC addresses provides numerous practical benefits for network administrators and anyone studying networking.
- Troubleshooting: Quickly identify connectivity issues by examining the MAC address table.
- Network Design: Design efficient networks that minimize unnecessary traffic.
- Security: Implement MAC address filtering to enhance network security.
- Optimization: Optimize network performance by understanding traffic flow patterns.
5.1. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Connectivity Problems: Verify that the MAC address table contains the correct entries for devices experiencing connectivity issues.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Identify devices flooding the network by examining traffic patterns associated with specific MAC addresses.
- Security Breaches: Detect unauthorized devices by monitoring the MAC address table for unknown entries.
5.2. Enhancing Network Security
MAC address filtering allows administrators to restrict network access to only known devices. This can prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to the network.
5.3. Optimizing Network Performance
By understanding how switches forward traffic based on MAC addresses, administrators can segment networks to reduce broadcast traffic and improve overall performance.
6. Advanced Concepts Related to MAC Address Learning
Delving deeper into MAC address learning involves understanding more complex concepts.
6.1. VLANs (Virtual LANs)
VLANs allow you to segment a physical network into multiple logical networks. Each VLAN maintains its own MAC address table, isolating traffic between VLANs.
6.2. Trunking
Trunking allows multiple VLANs to be carried over a single physical link. Switches use trunking protocols like 802.1Q to tag frames with VLAN identifiers, ensuring traffic is properly segregated.
6.3. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
STP prevents network loops by blocking redundant paths. Switches exchange Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) to determine the best path and block redundant links.
6.4. MAC Flooding Attacks
A MAC flooding attack occurs when an attacker floods the switch with numerous frames containing different source MAC addresses, overwhelming the MAC address table. This can cause the switch to forward traffic to all ports, similar to a hub, potentially exposing sensitive data.
7. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Consider some real-world examples to illustrate the importance of understanding MAC address learning.
7.1. Enterprise Network Scenario
In a large enterprise network, understanding MAC address learning is critical for maintaining network stability and performance. Network administrators must ensure that switches correctly learn and forward traffic to thousands of devices.
7.2. Data Center Environment
In a data center, switches handle massive amounts of traffic between servers. Efficient MAC address learning and forwarding are essential for minimizing latency and maximizing throughput.
7.3. Small Business Network
Even in a small business network, understanding MAC address learning can help troubleshoot connectivity issues and improve network performance.
8. Tools and Technologies for Monitoring MAC Address Learning
Several tools and technologies can help monitor MAC address learning and network performance.
- Switch Management Interfaces: Most switches provide a web-based or command-line interface for monitoring the MAC address table and other network statistics.
- Network Monitoring Software: Tools like SolarWinds, PRTG, and Wireshark can provide detailed insights into network traffic and MAC address activity.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): SNMP allows network administrators to remotely monitor and manage network devices, including switches.
8.1. Wireshark
Wireshark is a powerful network protocol analyzer that can capture and analyze network traffic. It can be used to examine ARP requests and responses, providing insights into MAC address learning.
8.2. SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds NPM provides comprehensive network monitoring capabilities, including the ability to track MAC address activity and identify potential issues.
9. Common Misconceptions About MAC Address Learning
Several misconceptions exist regarding MAC address learning. Let’s clarify some of them.
- MAC Addresses are Permanent: MAC addresses can be changed through software, though this is typically done for testing or security purposes.
- Switches Only Learn MAC Addresses from Data Frames: Switches learn MAC addresses from any frame they receive, including control frames like ARP requests.
- MAC Address Learning is Unnecessary: Without MAC address learning, switches would function like hubs, forwarding all traffic to all ports, leading to significant performance issues.
10. Best Practices for Managing MAC Address Tables
Effective management of MAC address tables is crucial for maintaining network performance and security.
- Regularly Monitor the MAC Address Table: Use the
show mac address-tablecommand to monitor the MAC address table for unexpected entries. - Implement MAC Address Filtering: Use MAC address filtering to restrict network access to known devices.
- Configure Port Security: Configure port security to limit the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a port.
- Use VLANs to Segment the Network: Segment the network using VLANs to reduce broadcast traffic and improve performance.
11. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Master Networking
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing comprehensive and accessible educational resources. Understanding how switches learn MAC addresses is just one aspect of networking that we cover in detail.
11.1. Comprehensive Courses
Our courses offer in-depth coverage of networking fundamentals, including MAC addressing, switching, routing, and network security. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, you will find valuable information to enhance your skills.
11.2. Expert Instructors
Our instructors are industry experts with years of experience in networking. They provide clear explanations and practical examples to help you understand complex concepts.
11.3. Hands-On Labs
Our courses include hands-on labs that allow you to practice configuring and troubleshooting network devices. This practical experience is essential for developing real-world skills.
11.4. Community Support
Join our community of learners to connect with other students and experts. Share your knowledge, ask questions, and get support from your peers.
12. The Future of MAC Address Learning
As networks continue to evolve, MAC address learning will remain a critical component of network infrastructure. New technologies and protocols are emerging that build upon the fundamentals of MAC addressing.
12.1. Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN centralizes network control, allowing administrators to programmatically manage network devices. SDN controllers can use MAC address information to make intelligent forwarding decisions.
12.2. Network Virtualization
Network virtualization allows you to create virtual networks on top of a physical infrastructure. MAC addresses play a crucial role in identifying and routing traffic within these virtual networks.
12.3. The Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of IoT devices is driving the need for more efficient MAC address management. As more devices connect to the network, switches must be able to handle a growing number of MAC addresses.
13. Case Study: Improving Network Performance with Optimized MAC Address Learning
A large university experienced significant network performance issues due to broadcast storms and inefficient traffic forwarding. By implementing the following strategies, they were able to improve network performance significantly.
- VLAN Segmentation: Segmented the network into VLANs based on department and function.
- MAC Address Filtering: Implemented MAC address filtering to restrict access to sensitive network resources.
- Port Security: Configured port security to limit the number of MAC addresses learned on each port.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitored the MAC address table regularly to identify and resolve issues.
13.1. Results
- Reduced broadcast traffic by 50%.
- Improved network response time by 30%.
- Enhanced network security by preventing unauthorized access.
14. How to Stay Updated on the Latest Networking Trends
Staying updated on the latest networking trends is essential for keeping your skills current.
- Read Industry Blogs and Publications: Follow leading networking blogs and publications to stay informed about new technologies and best practices.
- Attend Conferences and Webinars: Attend industry conferences and webinars to learn from experts and network with your peers.
- Join Online Communities: Join online communities and forums to share your knowledge and learn from others.
- Get Certified: Pursue industry certifications to demonstrate your knowledge and skills.
14.1. Recommended Resources
- Cisco Learning Network
- Network World
- TechTarget
- LEARNS.EDU.VN
15. The Importance of Practical Experience
While theoretical knowledge is important, practical experience is essential for mastering networking concepts. Hands-on labs and real-world projects can help you develop the skills you need to succeed.
15.1. Setting Up a Home Lab
Setting up a home lab is a great way to gain practical experience with networking devices. You can use virtual machines or physical devices to simulate a network environment.
15.2. Contributing to Open Source Projects
Contributing to open source networking projects can provide valuable experience and help you learn from other developers.
15.3. Internships and Entry-Level Positions
Internships and entry-level positions in networking can provide valuable on-the-job training and help you develop your skills.
16. Ethical Considerations in MAC Address Learning
As with any technology, MAC address learning raises ethical considerations. It is important to use this knowledge responsibly and ethically.
16.1. Privacy Concerns
MAC addresses can be used to track devices and users. It is important to respect user privacy and avoid using MAC addresses for unauthorized tracking.
16.2. Security Risks
MAC address spoofing can be used to bypass security measures. It is important to implement security measures to prevent MAC address spoofing.
16.3. Responsible Use
Use your knowledge of MAC address learning to improve network performance and security, not to harm or exploit others.
17. The Impact of Cloud Computing on MAC Address Learning
Cloud computing has a significant impact on MAC address learning. In cloud environments, virtual machines (VMs) are assigned MAC addresses, and switches must learn these addresses to forward traffic correctly.
17.1. Virtual Switches
Virtual switches are used to connect VMs within a cloud environment. These switches learn the MAC addresses of the VMs and forward traffic accordingly.
17.2. Overlay Networks
Overlay networks are used to create virtual networks on top of a physical infrastructure. MAC addresses are used to identify and route traffic within these overlay networks.
17.3. Scalability Challenges
Cloud environments can scale to thousands of VMs, creating scalability challenges for MAC address learning. Switches must be able to handle a large number of MAC addresses efficiently.
18. The Role of Automation in MAC Address Management
Automation can play a key role in simplifying MAC address management and improving network efficiency.
18.1. Automated MAC Address Learning
Automated MAC address learning tools can automatically discover and map MAC addresses to network devices.
18.2. Automated MAC Address Filtering
Automated MAC address filtering tools can automatically configure MAC address filters to restrict network access.
18.3. Network Configuration Management (NCM)
NCM tools can automate the configuration and management of network devices, including MAC address settings.
19. Future Trends in Networking Technology
Several future trends in networking technology are likely to impact MAC address learning.
19.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI can be used to analyze network traffic and identify patterns related to MAC address activity.
19.2. Machine Learning (ML)
ML can be used to predict future MAC address activity and optimize network performance.
19.3. Blockchain
Blockchain can be used to create a secure and decentralized record of MAC address assignments.
20. Why Continuous Learning is Essential in Networking
Networking technology is constantly evolving. Continuous learning is essential for staying current and maintaining your skills.
20.1. Industry Certifications
Pursuing industry certifications can help you demonstrate your knowledge and skills.
20.2. Online Courses and Resources
Online courses and resources can provide valuable learning opportunities.
20.3. Networking Communities
Networking communities can provide a supportive environment for learning and sharing knowledge.
By understanding how switches learn MAC addresses and staying updated on the latest networking trends, you can build a successful career in networking. LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to support you on your learning journey.
21. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About How Switches Learn MAC Addresses
Here are some frequently asked questions about how switches learn MAC addresses.
21.1. What is a MAC address?
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface card (NIC) for communication within a network.
21.2. How does a switch learn MAC addresses?
A switch learns MAC addresses by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames and recording the MAC address and corresponding port in its MAC address table.
21.3. What is a MAC address table?
A MAC address table (or CAM table) is a table maintained by a switch that maps MAC addresses to the corresponding switch ports.
21.4. Why is MAC address learning important?
MAC address learning enables switches to forward traffic only to the intended destination port, improving network efficiency and reducing collisions.
21.5. What is ARP and how does it relate to MAC address learning?
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used to discover the MAC address associated with a known IP address. Switches learn MAC addresses when forwarding ARP requests and responses.
21.6. How long do MAC address entries stay in the switch’s table?
MAC address entries typically stay in the switch’s table for about 5 minutes (the aging time), after which they are removed if no traffic is seen from that MAC address.
21.7. What is MAC address flooding?
MAC address flooding is an attack where an attacker floods the switch with numerous frames containing different source MAC addresses, overwhelming the MAC address table.
21.8. How can I view the MAC address table on a switch?
You can view the MAC address table on a Cisco switch using the command show mac address-table.
21.9. What is MAC address filtering?
MAC address filtering is a security technique used to restrict network access to only known devices by filtering traffic based on MAC addresses.
21.10. How do VLANs affect MAC address learning?
Each VLAN maintains its own MAC address table, isolating traffic between VLANs and improving network segmentation.
22. Summary: Key Takeaways on How Switches Learn MAC Addresses
Understanding how switches learn MAC addresses is crucial for effective network management and troubleshooting. This process enables efficient traffic forwarding, enhances network security, and optimizes performance. Key takeaways include:
- Switches learn MAC addresses by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames.
- The MAC address table maps MAC addresses to corresponding switch ports.
- ARP plays a crucial role in discovering MAC addresses.
- MAC address filtering enhances network security.
- VLANs provide network segmentation and isolation.
23. Additional Resources for Further Learning
To deepen your understanding of MAC address learning and networking, consider exploring these additional resources:
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification materials
- Online networking courses at LEARNS.EDU.VN
- Networking books and publications
- Industry conferences and webinars
24. Call to Action: Start Your Networking Journey with LEARNS.EDU.VN
Ready to take your networking skills to the next level? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive courses, hands-on labs, and expert instructors. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance your career, we have the resources you need to succeed.
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN to learn more and enroll in our networking courses.
Contact Information:
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
This image shows how a switch forwards unicast frames based on the learned MAC addresses.
Understanding how switches learn MAC addresses is fundamental to mastering network technology. With the right resources and guidance, you can develop the skills you need to succeed in this dynamic field. Start your journey today with learns.edu.vn and unlock your full potential.