Stress significantly impacts learning, affecting memory, focus, and overall academic performance. Discover effective strategies to mitigate stress and enhance your learning potential with LEARNS.EDU.VN. Learn how to manage stress hormones and improve knowledge retention and comprehension.
1. What is the Impact of Stress on Learning?
Stress profoundly affects learning by impairing cognitive functions essential for effective knowledge acquisition. Chronic stress disrupts memory, focus, and overall academic performance, making it difficult to concentrate and retain information. According to a study by the American Psychological Association, high stress levels can lead to decreased cognitive performance and increased difficulty in learning new concepts. Understanding how stress affects learning is crucial for implementing effective stress-management techniques to improve educational outcomes.
1.1. How Stress Affects Memory and Recall
Stress can significantly impair memory and recall abilities, making it harder to remember previously learned information. The impact of stress on memory recall is a common issue for students, especially during exams or high-pressure situations. Research from Stanford University indicates that chronic stress disrupts the hippocampus, a brain region crucial for memory formation and retrieval. This disruption can lead to difficulty recalling information, impacting academic performance and overall learning success. Implementing stress-reduction techniques can help mitigate these effects and improve memory recall.
1.2. The Role of Stress Hormones in Learning
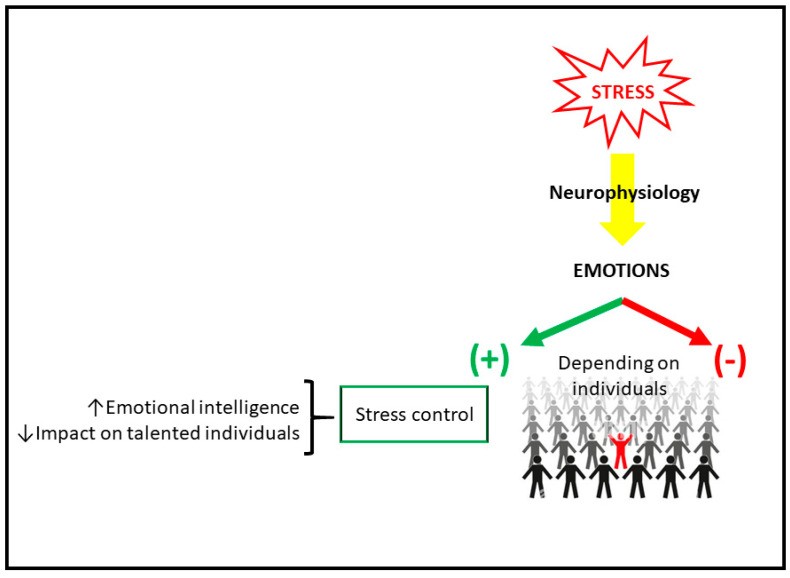
Stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, play a significant role in influencing learning processes. While short-term stress can enhance alertness and focus, chronic exposure to stress hormones can have detrimental effects on cognitive functions. Research published in “Nature Neuroscience” shows that prolonged cortisol exposure can shrink the hippocampus, affecting memory consolidation and retrieval. Adrenaline, while initially boosting attention, can lead to anxiety and impaired decision-making when levels remain high. Managing stress hormones is crucial for maintaining optimal learning conditions and cognitive health.
1.3. Stress and its Influence on Cognitive Function
Stress significantly influences cognitive function, impacting attention, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities. High stress levels can impair the prefrontal cortex, the brain region responsible for executive functions. A study in the “Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience” found that chronic stress reduces cognitive flexibility and increases impulsive decision-making. Managing stress is essential for maintaining optimal cognitive function and enhancing learning outcomes.
2. Understanding the Different Types of Stress
Different types of stress, including acute, chronic, and academic stress, can affect learning in unique ways. Identifying the specific stressors impacting students can help tailor effective stress-management strategies. The American Institute of Stress highlights the importance of recognizing these different stress types to implement appropriate interventions for improved learning outcomes.
2.1. Acute Stress and Its Immediate Effects on Learning
Acute stress refers to short-term stress resulting from specific events or situations, such as exams or presentations. While it can initially enhance focus, excessive acute stress can impair cognitive functions. Research from Harvard Medical School shows that acute stress triggers the release of cortisol, which can interfere with working memory and attention. Managing acute stress through techniques like deep breathing and mindfulness can help mitigate its negative effects on immediate learning tasks.
2.2. Chronic Stress and Long-Term Learning Impairments
Chronic stress, resulting from prolonged exposure to stressors such as financial difficulties or ongoing academic pressure, can lead to long-term learning impairments. This type of stress can cause persistent changes in brain structure and function. Studies at Yale University have demonstrated that chronic stress reduces neuroplasticity, impairing the brain’s ability to form new connections and retain information. Addressing chronic stress through lifestyle changes, counseling, and stress-reduction techniques is essential for long-term cognitive health and improved learning outcomes.
2.3. Academic Stress: Specific Challenges for Students
Academic stress presents unique challenges for students, stemming from coursework, exams, and competition. High academic stress levels can lead to burnout, anxiety, and decreased motivation. A survey by the National Education Association found that a significant percentage of students report feeling overwhelmed by academic demands. Implementing effective time-management strategies, seeking support from academic advisors, and practicing self-care can help students manage academic stress and enhance their learning experience.
3. Strategies for Managing Stress and Enhancing Learning
Effective strategies for managing stress and enhancing learning include time management, mindfulness, physical activity, and seeking social support. These techniques can help students reduce stress levels, improve focus, and enhance overall academic performance. The Mayo Clinic emphasizes the importance of incorporating these strategies into daily routines for optimal stress management and cognitive health.
3.1. Time Management Techniques for Reducing Academic Stress
Effective time management is crucial for reducing academic stress and improving learning outcomes. Strategies such as creating a study schedule, prioritizing tasks, and breaking down large assignments into smaller, manageable parts can significantly reduce feelings of overwhelm. Research from the University of California, Berkeley, shows that students who effectively manage their time experience lower stress levels and achieve higher academic success. Utilizing tools like calendars, to-do lists, and time-management apps can further enhance these benefits.
3.2. Mindfulness and Meditation for Improved Focus
Mindfulness and meditation are powerful tools for improving focus and reducing stress, which can significantly enhance learning. Regular mindfulness practices can help students become more aware of their thoughts and emotions, allowing them to better manage stress and improve concentration. Studies published in the “Journal of Educational Psychology” have shown that mindfulness meditation can improve attention span and cognitive performance in students. Incorporating mindfulness exercises into daily routines can lead to improved academic outcomes and overall well-being.
3.3. The Role of Physical Activity in Stress Reduction
Physical activity plays a vital role in reducing stress and improving cognitive function, thereby enhancing learning. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain and releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting and stress-reducing effects. Research from the University of British Columbia indicates that regular physical activity can improve memory and cognitive performance in students. Engaging in activities such as jogging, swimming, or yoga can help students manage stress and optimize their learning potential.
3.4. Social Support Networks for Stress Management
Social support networks are essential for managing stress and promoting overall well-being among students. Connecting with friends, family, and support groups can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation. A study in the “Journal of College Student Development” found that students with strong social support networks experience lower stress levels and higher academic success. Building and maintaining these networks can offer a buffer against stress and enhance the learning environment.
4. Creating a Stress-Free Learning Environment
Creating a stress-free learning environment involves implementing strategies at home, school, and in study habits to foster a positive and supportive atmosphere. These measures can significantly reduce stress levels and improve learning outcomes for students. The National Association of School Psychologists emphasizes the importance of holistic approaches to creating such environments.
4.1. Strategies for Parents to Reduce Student Stress
Parents can play a crucial role in reducing student stress by creating a supportive and encouraging home environment. Strategies include open communication, helping with time management, and promoting a healthy lifestyle. Research from the University of Michigan shows that parental support can significantly reduce academic stress in students. Establishing realistic expectations, providing emotional support, and encouraging self-care are essential components of a stress-free home environment.
4.2. School Policies and Programs to Support Student Well-being
School policies and programs are vital for supporting student well-being and reducing academic stress. Implementing stress-reduction workshops, providing access to counseling services, and promoting a positive school climate can significantly improve student mental health. A report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights the effectiveness of comprehensive school-based mental health programs in reducing stress and improving academic performance. Creating a supportive and inclusive school environment is essential for fostering student well-being.
4.3. Optimizing Study Habits for Reduced Stress
Optimizing study habits can significantly reduce stress and enhance learning efficiency. Techniques such as breaking study sessions into shorter intervals, taking regular breaks, and using active learning strategies can improve focus and retention. A study in the “Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition” found that spaced repetition and interleaving can enhance learning and reduce stress during study sessions. Creating a structured and effective study routine can lead to improved academic outcomes and reduced stress levels.
5. The Impact of Stress on Different Learning Styles
Stress can affect different learning styles in unique ways, impacting how students process and retain information. Understanding these differences can help tailor stress-management strategies to optimize learning for each individual. Research from the VARK model suggests that adapting learning strategies to specific learning styles can reduce stress and improve academic performance.
5.1. Stress and Visual Learners: Strategies for Success
Visual learners may experience increased stress when learning materials are not visually engaging or are presented in a cluttered, overwhelming format. High stress levels can impair their ability to process visual information effectively. Strategies for success include using visual aids, creating mind maps, and organizing study materials with clear visuals. Research from the Association for Educational Communications and Technology (AECT) emphasizes the importance of visual design in reducing cognitive load and enhancing learning for visual learners.
5.2. Auditory Learners: Overcoming Stress-Related Challenges
Auditory learners may find it challenging to focus and retain information when stressed, particularly in noisy or distracting environments. Stress can interfere with their ability to process auditory information effectively. Overcoming these challenges involves creating a quiet study space, using audio recordings, and engaging in discussions to reinforce learning. Studies in the “Journal of Applied Cognitive Psychology” have shown that auditory learners benefit from verbal repetition and active listening techniques.
5.3. Kinesthetic Learners: Staying Engaged Under Pressure
Kinesthetic learners thrive on hands-on activities and movement, but stress can limit their ability to engage in these activities effectively. High stress levels can lead to restlessness and difficulty concentrating during traditional study sessions. Strategies for staying engaged under pressure include incorporating movement breaks, using tactile learning tools, and participating in role-playing or simulations. Research from the National Center for Learning Disabilities highlights the effectiveness of kinesthetic learning strategies in promoting engagement and reducing stress.
5.4. Read/Write Learners: Managing Stress Through Organization
Read/write learners excel in processing information through reading and writing, but stress can disrupt their ability to organize and articulate their thoughts effectively. High stress levels can lead to writer’s block and difficulty comprehending written materials. Managing stress through organization techniques such as note-taking, summarizing, and creating outlines can help these learners maintain focus and improve their learning outcomes. Studies in the “Journal of Academic Writing” emphasize the importance of structured writing practices in reducing stress and enhancing academic performance for read/write learners.
6. Identifying and Addressing Stress in Education
Identifying and addressing stress in education requires proactive measures from educators, students, and parents to create a supportive and stress-free learning environment. Early intervention can prevent long-term negative effects on academic performance and mental health. The American School Counselor Association highlights the importance of comprehensive approaches to addressing stress in schools.
6.1. Recognizing Signs of Stress in Students
Recognizing the signs of stress in students is the first step toward providing effective support. Common indicators include changes in behavior, academic performance, and physical health. A report by the American Psychological Association indicates that early identification of stress symptoms can lead to timely intervention and improved outcomes. Educators and parents should be vigilant in observing students for signs of stress, such as increased anxiety, withdrawal, or difficulty concentrating.
6.2. Effective Communication Strategies for Discussing Stress
Effective communication strategies are essential for discussing stress with students and providing them with support. Creating a safe and non-judgmental environment can encourage students to share their concerns openly. Techniques such as active listening, empathy, and validation can help students feel heard and understood. Research from the National Education Association emphasizes the importance of open communication in addressing student stress and promoting mental well-being.
6.3. Counseling and Mental Health Resources for Students
Counseling and mental health resources are crucial for providing students with the support they need to manage stress and promote their overall well-being. Schools should offer access to counseling services, mental health professionals, and support groups to address student needs. A study by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) found that access to mental health resources can significantly reduce stress and improve academic outcomes for students.
6.4. Creating a Supportive School Culture
Creating a supportive school culture is essential for reducing stress and promoting student well-being. This involves fostering a sense of belonging, respect, and inclusivity among students and staff. Strategies include implementing anti-bullying programs, promoting positive relationships, and celebrating diversity. Research from the Gay, Lesbian & Straight Education Network (GLSEN) highlights the importance of creating a safe and inclusive school environment for all students.
7. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Supports Stress-Free Learning
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources and support to help students manage stress and enhance their learning experience. Our comprehensive approach includes stress-management techniques, study tips, and access to educational experts.
7.1. Stress-Management Techniques Available on LEARNS.EDU.VN
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides a variety of stress-management techniques designed to help students cope with academic pressures. These resources include guided meditation exercises, time-management tips, and relaxation techniques. By incorporating these tools into their daily routines, students can reduce stress levels and improve their focus. LEARNS.EDU.VN is committed to supporting student well-being and academic success.
7.2. Study Tips and Resources for Efficient Learning
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers study tips and resources to help students learn more efficiently and reduce academic stress. Our platform provides access to study guides, practice tests, and expert advice on effective study strategies. By utilizing these resources, students can optimize their learning process and achieve better academic outcomes. LEARNS.EDU.VN is dedicated to empowering students with the tools they need to succeed.
7.3. Access to Educational Experts and Support
LEARNS.EDU.VN connects students with educational experts who can provide personalized support and guidance. Our platform offers access to tutors, academic advisors, and mental health professionals who can help students manage stress and achieve their academic goals. By fostering a supportive community, LEARNS.EDU.VN ensures that students have the resources they need to thrive.
7.4. Success Stories and Testimonials from Students
LEARNS.EDU.VN features success stories and testimonials from students who have benefited from our resources and support. These stories highlight the positive impact of our platform on reducing stress and improving academic outcomes. By sharing these experiences, we aim to inspire and motivate other students to take control of their learning and achieve their full potential.
8. Future Trends in Stress Management for Education
Future trends in stress management for education include integrating technology, personalized interventions, and holistic approaches to promote student well-being. These innovations aim to create more effective and accessible support systems for students facing academic stress. The World Health Organization (WHO) highlights the importance of addressing mental health in education to foster healthy and productive learning environments.
8.1. The Role of Technology in Stress Reduction
Technology is playing an increasingly significant role in stress reduction for education. Mobile apps, online platforms, and virtual reality tools offer innovative ways to manage stress and promote well-being. These technologies provide access to guided meditation, stress-tracking tools, and virtual support groups. Research from the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) indicates that technology-based interventions can be effective in reducing stress and improving mental health outcomes for students.
8.2. Personalized Interventions for Individual Student Needs
Personalized interventions tailored to individual student needs are becoming more prevalent in stress management for education. These interventions involve assessing student stress levels, identifying their specific stressors, and developing customized support plans. By addressing the unique challenges faced by each student, personalized interventions can be more effective in reducing stress and improving learning outcomes. A report by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) emphasizes the importance of individualized approaches to supporting student well-being.
8.3. Holistic Approaches to Student Well-being
Holistic approaches to student well-being are gaining traction in education, focusing on addressing the physical, emotional, and social needs of students. These approaches involve integrating mindfulness practices, physical activity, and social support into the school curriculum. By promoting overall well-being, holistic approaches aim to reduce stress and enhance learning outcomes for all students. The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) highlights the benefits of holistic approaches in creating a supportive and thriving school environment.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
9.1. How does stress affect learning in children?
Stress can impair cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving, which are essential for learning in children. High stress levels can lead to decreased academic performance and increased behavioral issues.
9.2. What are the main causes of stress among students?
The main causes of stress among students include academic pressure, exams, competition, social issues, financial concerns, and family expectations.
9.3. Can stress ever be beneficial for learning?
Short-term stress can enhance alertness and focus, which can be beneficial for learning in some situations. However, chronic or excessive stress is detrimental to cognitive functions.
9.4. What are some quick stress-relief techniques for students?
Quick stress-relief techniques for students include deep breathing exercises, taking short breaks, practicing mindfulness, listening to music, and engaging in light physical activity.
9.5. How can parents support their children in managing stress?
Parents can support their children by providing a supportive home environment, encouraging open communication, helping with time management, and promoting a healthy lifestyle.
9.6. What resources are available for students struggling with stress?
Resources available for students struggling with stress include school counseling services, mental health professionals, support groups, online resources, and stress-management workshops.
9.7. How does online learning impact stress levels in students?
Online learning can impact stress levels in students differently. While it offers flexibility, it can also lead to increased isolation, technical difficulties, and challenges in maintaining focus and motivation.
9.8. What are the long-term effects of chronic stress on learning?
The long-term effects of chronic stress on learning include impaired memory, decreased cognitive function, increased risk of mental health issues, and reduced academic performance.
9.9. How can schools create a stress-free learning environment?
Schools can create a stress-free learning environment by implementing supportive policies, providing access to mental health resources, promoting positive relationships, and fostering a sense of belonging.
9.10. What is emotional intelligence, and how does it help in managing stress?
Emotional intelligence (EI) involves recognizing, understanding, and managing one’s own emotions and the emotions of others. EI helps in managing stress by enabling individuals to regulate their emotional responses, build positive relationships, and cope effectively with challenging situations.
10. Conclusion
Stress significantly impacts learning, but with the right strategies, students can manage stress and enhance their academic performance. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a variety of resources to support students in their journey to stress-free learning. Remember to prioritize your well-being and seek support when needed.
To further explore stress-management techniques, efficient study habits, and personalized support, visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today. Unlock your full learning potential with our comprehensive resources and expert guidance.
Contact Information:
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: learns.edu.vn