Learning How Long Does It Take To Learn Each Language is a common question for aspiring polyglots. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide insights into language acquisition and effective learning strategies. Discover the time investment needed and unlock your linguistic potential with language learning resources.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Language Learning Difficulty
- Factors Influencing Language Learning Time
- FSI Language Difficulty Categories
- Category I Languages: Easiest for English Speakers
- Category II Languages: Slightly More Challenging
- Category III Languages: Linguistic and Cultural Differences
- Category IV Languages: Significant Differences
- Category V Languages: Exceptionally Difficult
- Strategies to Accelerate Language Learning
- Resources and Tools for Language Learners
- The Role of Motivation and Consistency
- Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations
- Debunking Myths About Language Learning
- The Benefits of Multilingualism
- Language Learning for Career Advancement
- Language Learning for Personal Enrichment
- The Future of Language Learning
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Language Acquisition
- Success Stories: Inspiring Language Learning Journeys
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Language Learning
1. Understanding Language Learning Difficulty
The question of how long it takes to learn a new language is complex, influenced by various factors. According to the Foreign Service Institute (FSI), language difficulty is categorized based on the time it takes for a native English speaker to achieve professional working proficiency. The FSI’s research provides a valuable framework for understanding the relative difficulty of different languages, helping learners set realistic expectations and plan their study schedules effectively. Remember, personalized learning paths and effective language programs can significantly impact your language acquisition journey.
2. Factors Influencing Language Learning Time
Several key factors influence how quickly someone can learn a new language. These include:
-
Native Language: The similarity between your native language and the target language plays a crucial role. For example, Spanish is generally easier for English speakers than Mandarin due to shared linguistic roots and grammatical structures.
-
Learning Experience: Prior language learning experience can significantly reduce the time required to learn a new language. Familiarity with grammatical concepts and learning strategies can be transferred to the new language.
-
Time Commitment: The amount of time dedicated to studying and practicing a language directly impacts the learning speed. Consistent, focused effort yields faster results.
-
Learning Methods: Effective learning methods, such as immersion, spaced repetition, and interactive practice, can accelerate language acquisition.
-
Motivation: A strong intrinsic motivation to learn a language can drive persistence and enhance learning outcomes.
-
Resources and Tools: Access to quality learning resources, such as language courses, textbooks, language exchange partners, and online tools, can greatly facilitate the learning process.
-
Cultural Exposure: Immersing oneself in the culture of the target language through travel, media, and interactions with native speakers can deepen understanding and improve fluency.
3. FSI Language Difficulty Categories
The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) categorizes languages into five groups based on the approximate time required for a native English speaker to achieve professional working proficiency. Here’s a breakdown:
| Category | Estimated Time (Hours) | Example Languages |
|---|---|---|
| I | 575-600 | Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese |
| II | 750 | German |
| III | 900 | Indonesian, Swahili |
| IV | 1100 | Russian, Czech, Vietnamese |
| V | 2200 | Arabic, Chinese, Japanese, Korean |
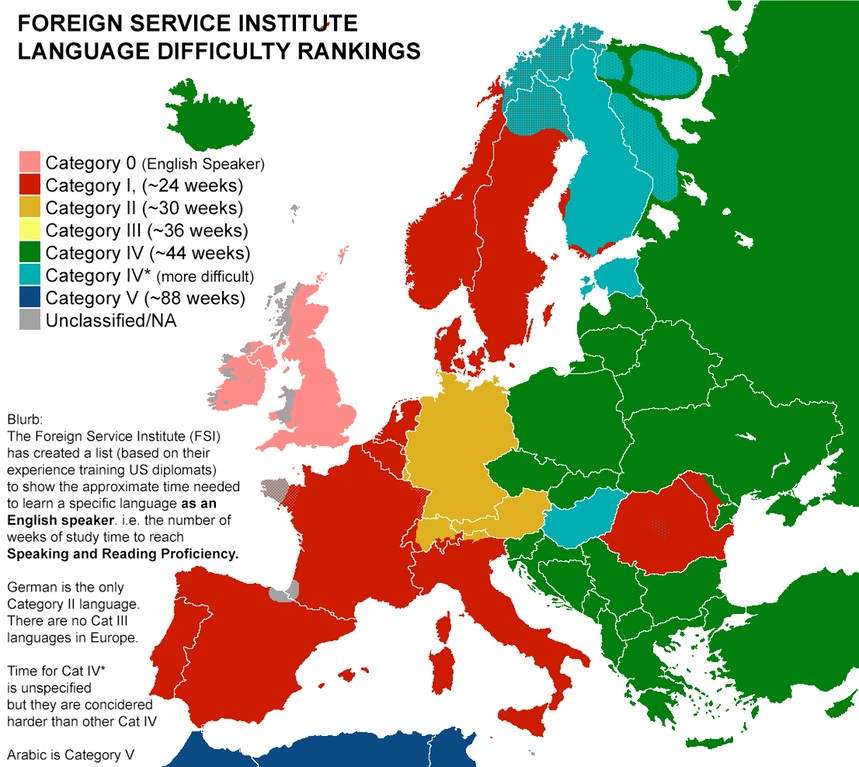

These categories provide a general guideline, but individual learning times may vary.
4. Category I Languages: Easiest for English Speakers
Category I languages are the easiest for native English speakers to learn, typically requiring around 575-600 hours of study. These languages share many similarities with English in terms of vocabulary, grammar, and syntax.
- Spanish: With a large number of cognates and relatively straightforward grammar, Spanish is a popular choice for English speakers.
- French: Despite some pronunciation challenges, French shares many words with English and has a logical grammatical structure.
- Italian: Italian is known for its beautiful sound and relatively simple grammar, making it accessible for beginners.
- Portuguese: Similar to Spanish, Portuguese offers a wealth of cognates and a grammar that is not overly complex for English speakers.
These languages are often taught in high schools and colleges, providing ample resources for learners.
5. Category II Languages: Slightly More Challenging
Category II languages, like German, present a slightly higher level of difficulty, requiring approximately 750 hours of study. While still sharing some similarities with English, these languages often have more complex grammar rules and sentence structures.
- German: German grammar can be challenging due to its case system and word order rules. However, many English words are derived from German, aiding vocabulary acquisition.
German requires dedication and a willingness to tackle its grammatical complexities, but it’s a rewarding language to learn.
6. Category III Languages: Linguistic and Cultural Differences
Category III languages, such as Indonesian and Swahili, require around 900 hours of study. These languages present linguistic and cultural differences that can pose additional challenges for English speakers.
- Indonesian: Indonesian is known for its relatively simple grammar, but it has a different sentence structure and cultural nuances that learners need to grasp.
- Swahili: As a widely spoken language in East Africa, Swahili has a unique grammar and vocabulary that reflect its cultural context.
These languages offer a fascinating glimpse into different cultures and ways of thinking.
7. Category IV Languages: Significant Differences
Category IV languages require approximately 1100 hours of study due to their significant linguistic and cultural differences from English. This category includes a diverse range of languages from around the world.
- Russian: Russian grammar is complex, with a case system, verb conjugations, and aspects that can be challenging for English speakers.
- Czech: Czech is known for its complex grammar, including seven cases and verb conjugations that require significant effort to master.
- Vietnamese: Vietnamese presents challenges due to its tonal nature and different sentence structure compared to English.
These languages require a considerable investment of time and effort, but they offer access to rich cultures and perspectives.
8. Category V Languages: Exceptionally Difficult
Category V languages are considered exceptionally difficult for native English speakers, requiring approximately 2200 hours of study. These languages have significant linguistic and cultural differences, including unfamiliar writing systems, complex grammar, and tonal systems.
- Arabic: Arabic grammar is highly complex, with verb conjugations, gender agreement, and a writing system that is read from right to left.
- Chinese (Mandarin and Cantonese): Chinese languages are tonal, meaning that the meaning of a word can change depending on the tone used. The writing system also requires memorization of thousands of characters.
- Japanese: Japanese combines three writing systems (hiragana, katakana, and kanji) and has a grammar that is very different from English.
- Korean: Korean grammar is unique, with a subject-object-verb sentence structure and honorifics that must be used appropriately.
These languages are a significant undertaking, but they offer unparalleled opportunities for cultural immersion and intellectual growth.
9. Strategies to Accelerate Language Learning
While the FSI provides estimates, several strategies can help accelerate your language learning journey:
- Immersion: Immerse yourself in the language as much as possible by listening to music, watching movies, and interacting with native speakers.
- Spaced Repetition: Use spaced repetition systems (SRS) like Anki to review vocabulary and grammar at increasing intervals.
- Active Recall: Practice active recall by testing yourself regularly on what you have learned.
- Language Exchange: Find a language exchange partner to practice speaking and receive feedback.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set achievable goals and track your progress to stay motivated.
By implementing these strategies, you can optimize your learning process and achieve fluency faster.
10. Resources and Tools for Language Learners
Numerous resources and tools are available to support language learners:
- Language Learning Apps: Duolingo, Babbel, Memrise
- Online Courses: Coursera, edX, Udemy
- Language Exchange Platforms: HelloTalk, Tandem
- Dictionaries and Translators: Google Translate, WordReference
- Language Learning Websites: LEARNS.EDU.VN, BBC Languages, Open Culture
These resources provide structured lessons, interactive exercises, and opportunities to practice with native speakers.
11. The Role of Motivation and Consistency
Motivation and consistency are key to successful language learning. Maintain a strong intrinsic motivation by focusing on your personal goals and interests.
- Set Clear Goals: Define why you want to learn the language and what you hope to achieve.
- Find Enjoyable Activities: Incorporate activities you enjoy, such as reading, watching movies, or listening to music, into your learning routine.
- Track Your Progress: Monitor your progress and celebrate your achievements to stay motivated.
- Establish a Routine: Set aside dedicated time each day or week for language learning.
- Be Patient: Language learning takes time and effort, so be patient with yourself and celebrate small victories.
12. Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations
Setting realistic goals and expectations is crucial for maintaining motivation and avoiding frustration. Understand that language learning is a gradual process, and progress may not always be linear.
- Start Small: Begin with basic vocabulary and grammar, and gradually increase the complexity of your studies.
- Focus on Communication: Prioritize developing your ability to communicate effectively, rather than striving for perfect grammar from the outset.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress along the way, no matter how small.
- Adjust Your Goals: Be prepared to adjust your goals and expectations as you gain experience and understanding of the language.
13. Debunking Myths About Language Learning
Several myths surround language learning, which can discourage potential learners. Let’s debunk some common misconceptions:
- Myth: You need to be young to learn a language.
- Reality: Adults can learn languages effectively, often bringing greater focus and experience to the process.
- Myth: Some people are naturally good at languages.
- Reality: Language learning is a skill that can be developed through consistent effort and effective strategies.
- Myth: You need to be fluent to start speaking.
- Reality: Speaking from the beginning is essential for developing fluency and confidence.
- Myth: You need to live in a country where the language is spoken to become fluent.
- Reality: While immersion can be helpful, it is possible to achieve fluency through dedicated study and practice.
14. The Benefits of Multilingualism
Learning multiple languages offers numerous cognitive, social, and economic benefits:
- Cognitive Benefits: Improved memory, problem-solving skills, and multitasking abilities.
- Social Benefits: Enhanced cultural awareness, empathy, and communication skills.
- Economic Benefits: Increased job opportunities, higher earning potential, and greater career flexibility.
Multilingualism opens doors to new cultures, experiences, and opportunities.
15. Language Learning for Career Advancement
In today’s globalized world, language skills are highly valued by employers. Learning a new language can enhance your career prospects and open doors to international opportunities.
- Increased Job Opportunities: Many companies seek employees with language skills to expand into new markets and serve international clients.
- Higher Earning Potential: Multilingual employees often command higher salaries than their monolingual counterparts.
- Career Flexibility: Language skills can provide greater flexibility in terms of job roles and locations.
Consider learning a language that is relevant to your industry or career goals.
16. Language Learning for Personal Enrichment
Beyond career benefits, language learning can enrich your life in countless ways:
- Cultural Appreciation: Deeper understanding and appreciation of different cultures and perspectives.
- Travel Experiences: Enhanced travel experiences and the ability to connect with locals on a deeper level.
- Personal Growth: Increased self-confidence, cognitive flexibility, and personal satisfaction.
- New Friendships: Opportunities to connect with people from different backgrounds and build meaningful relationships.
Language learning is a journey of discovery that can transform your life.
17. The Future of Language Learning
The future of language learning is being shaped by technology and globalization. Online learning platforms, AI-powered tools, and virtual reality are making language learning more accessible and engaging than ever before.
- AI-Powered Language Learning: AI-powered apps and platforms offer personalized learning experiences and real-time feedback.
- Virtual Reality Immersion: VR technology can simulate immersive language environments, allowing learners to practice in realistic scenarios.
- Global Online Communities: Online communities connect language learners from around the world, providing opportunities for practice and cultural exchange.
Embrace these innovations to enhance your language learning journey.
18. LEARNS.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Language Acquisition
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing high-quality language learning resources and support to learners of all levels. Our website offers:
- Comprehensive Language Guides: Detailed guides on various languages, including grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
- Effective Learning Strategies: Proven strategies and techniques to accelerate language acquisition.
- Resource Recommendations: Curated lists of the best language learning apps, websites, and tools.
- Community Forum: A supportive community where learners can connect, share tips, and practice with each other.
We believe that anyone can learn a new language with the right resources and support.
19. Success Stories: Inspiring Language Learning Journeys
Reading about the success stories of other language learners can be incredibly motivating. Here are a few examples:
- Benny Lewis: A renowned polyglot who advocates for speaking from day one and embracing mistakes.
- Lydia Machova: A language mentor who emphasizes the importance of finding joy in the learning process.
- Steve Kaufmann: A polyglot who uses a combination of reading, listening, and speaking to learn new languages.
These individuals demonstrate that language learning is achievable with dedication, passion, and the right approach.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Language Learning
Q1: How long does it take to become fluent in a new language?
The time it takes to achieve fluency varies depending on the language, your learning style, and the amount of time you dedicate to studying. Generally, it can take anywhere from 600 hours for easier languages to 2200 hours for more difficult ones.
Q2: What is the best way to learn a new language?
The best approach is to combine structured learning with immersive practice. Use a variety of resources, such as language learning apps, online courses, and language exchange partners.
Q3: Can I learn a language on my own?
Yes, it is possible to learn a language on your own with the help of online resources and self-study materials. However, interacting with native speakers can greatly enhance your learning experience.
Q4: What are the most effective language learning apps?
Popular and effective language learning apps include Duolingo, Babbel, Memrise, and Rosetta Stone.
Q5: How can I stay motivated while learning a language?
Set clear goals, find enjoyable activities, track your progress, and connect with other language learners to stay motivated.
Q6: Is it necessary to study grammar to learn a language?
While grammar is important, it’s not the only focus. Aim for a balance between grammar study and practical communication.
Q7: How can I improve my pronunciation in a new language?
Listen to native speakers, practice shadowing (repeating what you hear), and use pronunciation tools to improve your accent.
Q8: What should I do if I feel stuck in my language learning journey?
Try changing your learning routine, seeking feedback from native speakers, or focusing on a new aspect of the language to overcome plateaus.
Q9: How important is cultural immersion in language learning?
Cultural immersion can greatly enhance your understanding of the language and its context. Try to incorporate cultural activities, such as watching movies, listening to music, and attending cultural events.
Q10: Where can I find language exchange partners?
Language exchange platforms like HelloTalk and Tandem connect you with native speakers who are interested in learning your language.
Ready to embark on your language learning journey? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover a wealth of resources, strategies, and support to help you achieve your language goals. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212, or visit our website at learns.edu.vn to get started.