Learning guitar can be a rewarding journey, and understanding the average time it takes to become proficient is a common curiosity; How Long Does It Take To Learn Guitar On Average? At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide a comprehensive guide to help you navigate this musical endeavor, offering insights into realistic timelines, effective practice methods, and personalized learning paths. By exploring different phases of learning and focusing on consistent effort, you can achieve your guitar-playing goals. Discover tailored resources, expert tips, and a supportive community to accelerate your progress. Begin your musical journey today with LEARNS.EDU.VN and transform your ambition into achievement. Explore guitar learning stages, musical instrument proficiency, and skill development.
1. Understanding the Timeline: How Long Does It Really Take to Learn Guitar?
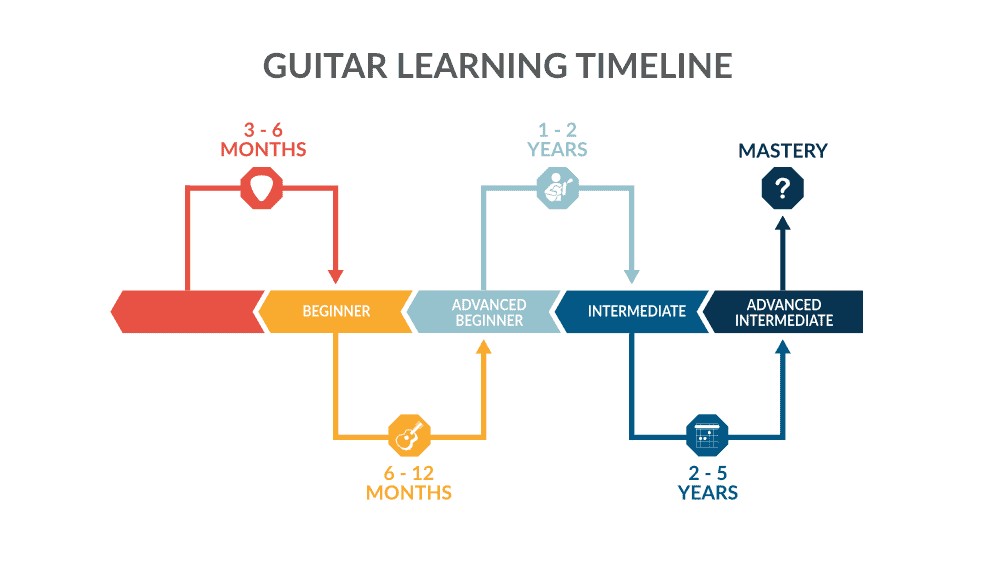
The journey of learning guitar is a unique experience for everyone, influenced by various factors such as practice consistency, learning style, and personal goals. Understanding a realistic timeline can help you set achievable expectations and stay motivated.
1.1 Initial Stages: Building the Foundation (0-6 Months)
The first six months are crucial for building a solid foundation. This period involves developing essential skills and habits that will shape your future progress.
1.1.1 Developing Finger Strength and Calluses
One of the initial challenges for beginners is developing finger strength and calluses. According to a study by the American Academy of Dermatology, calluses form as a protective response to repeated pressure and friction.
- Challenge: Sore fingers and discomfort.
- Solution: Consistent practice in short intervals. Start with 15-20 minutes per day and gradually increase the duration as your fingers get stronger.
- Expected Timeline: Calluses typically start forming within 2-4 weeks of regular practice.
1.1.2 Learning Basic Chords and Strumming Patterns
Mastering basic chords like G, C, D, and Em, along with simple strumming patterns, is fundamental. A research by the Guitar Alliance suggests that learning these chords allows beginners to play a wide range of songs.
- Goals: Learn 5-7 basic chords and 2-3 strumming patterns.
- Practice Tip: Use online resources and video tutorials to visualize proper finger placement and strumming techniques.
- Expected Timeline: Most beginners can learn these chords within 1-2 months with consistent practice.
1.1.3 Understanding Basic Music Theory
Grasping basic music theory concepts such as rhythm, notes, and chord progressions can significantly enhance your learning experience. The Berklee College of Music emphasizes the importance of understanding music theory for effective guitar playing.
- Key Concepts: Learn about time signatures, notes on the fretboard, and how chords are constructed.
- Learning Method: Supplement your practice with online courses or books on music theory.
- Expected Timeline: Dedicate 30 minutes per week to music theory studies. Aim to understand the basics within 2-3 months.
1.2 Intermediate Stages: Refining Skills (6-18 Months)
After the initial phase, you’ll move into refining your skills and expanding your repertoire. This stage focuses on improving technique and musicality.
1.2.1 Mastering Barre Chords
Barre chords are a significant step up from open chords and require more finger strength and dexterity. Guitar World highlights the importance of mastering barre chords for playing a wider variety of songs.
- Challenge: Barre chords can be difficult to play cleanly at first.
- Practice Tip: Focus on proper finger placement and apply even pressure across the strings.
- Expected Timeline: It may take 2-4 months of consistent practice to play barre chords comfortably.
1.2.2 Learning Scales and Basic Lead Guitar Techniques
Learning scales such as the pentatonic and major scales opens up opportunities for improvisation and lead guitar playing. Fender Play emphasizes the role of scales in developing soloing skills.
- Goals: Learn the major and minor pentatonic scales, and practice simple licks and solos.
- Practice Method: Use backing tracks to practice improvising over different chord progressions.
- Expected Timeline: Dedicate 1-2 hours per week to scale practice. Aim to develop basic soloing skills within 3-6 months.
1.2.3 Developing a Practice Routine
Creating a structured practice routine is essential for consistent progress. A study by the Journal of Research in Music Education underscores the importance of structured practice for skill development.
- Elements of a Good Routine: Include warm-ups, chord practice, scale exercises, and learning new songs.
- Consistency: Aim for at least 30-60 minutes of practice per day.
- Expected Timeline: Stick to your routine for at least 3-6 months to see significant improvements.
1.3 Advanced Stages: Mastery and Specialization (18+ Months)
The advanced stage involves mastering advanced techniques, developing your unique style, and potentially specializing in a specific genre.
1.3.1 Advanced Guitar Techniques
Explore advanced techniques such as sweep picking, tapping, and complex chord voicings. Premier Guitar offers resources and tutorials on these techniques.
- Techniques to Learn: Sweep picking, tapping, hybrid picking, and advanced chord voicings.
- Practice Method: Break down complex techniques into smaller, manageable steps.
- Expected Timeline: Each technique may take several months to master.
1.3.2 Developing Your Own Style
As you progress, you’ll start to develop your unique style and musical voice. This involves incorporating your influences and experimenting with different sounds and techniques.
- Exploration: Listen to a wide range of guitarists and musical genres to find inspiration.
- Experimentation: Try combining different techniques and sounds to create your own unique style.
- Expected Timeline: Developing a unique style is an ongoing process that evolves over years of playing.
1.3.3 Specializing in a Specific Genre
Many guitarists choose to specialize in a particular genre such as blues, jazz, rock, or classical. This allows you to focus your efforts and develop deep expertise.
- Genre Selection: Choose a genre that resonates with your musical interests.
- Immersion: Immerse yourself in the genre by listening to its key artists, learning its signature techniques, and studying its history.
- Expected Timeline: Becoming proficient in a specific genre can take several years of dedicated study and practice.
2. Key Factors Influencing Learning Speed
Several factors can significantly impact how quickly you progress in your guitar-learning journey. Understanding these factors can help you optimize your approach and accelerate your progress.
2.1 Practice Consistency and Quality
The frequency and quality of your practice sessions are crucial. Consistent, focused practice yields better results than sporadic, unfocused sessions.
2.1.1 Setting Realistic Practice Goals
Set achievable goals for each practice session to maintain focus and motivation. The National Association for Music Education emphasizes the importance of goal-setting in music learning.
- Specific Goals: Identify specific skills or songs to work on during each session.
- Measurable Goals: Track your progress to see how you’re improving over time.
- Achievable Goals: Set goals that are challenging but attainable within the given timeframe.
- Relevant Goals: Ensure your goals align with your overall musical aspirations.
- Time-Bound Goals: Set deadlines for achieving your goals to stay on track.
2.1.2 Structuring Your Practice Sessions
A well-structured practice session should include warm-ups, technique exercises, learning new material, and reviewing old material.
- Warm-Ups: Start with simple exercises to get your fingers and hands ready.
- Technique Exercises: Focus on specific skills such as chord changes, scales, or strumming patterns.
- New Material: Spend time learning new songs or techniques.
- Review: Review previously learned material to reinforce your knowledge and skills.
2.1.3 Avoiding Common Practice Pitfalls
Be aware of common practice pitfalls such as practicing without a plan, neglecting fundamentals, and not taking breaks.
- Plan Your Practice: Always have a clear idea of what you want to accomplish during each session.
- Focus on Fundamentals: Don’t neglect basic skills, as they are the foundation of your playing.
- Take Breaks: Regular breaks can help prevent fatigue and improve focus.
2.2 Natural Aptitude and Musical Background
Some individuals may have a natural aptitude for music, while others may have prior musical experience that gives them a head start.
2.2.1 Leveraging Prior Musical Experience
If you have experience playing other instruments or singing, you may find it easier to learn guitar. The University of Southern California’s Thornton School of Music highlights the transferability of musical skills.
- Rhythm: Prior experience with rhythm can help you develop a strong sense of timing.
- Ear Training: Familiarity with music theory and ear training can make it easier to learn chords and melodies.
- Coordination: Experience with other instruments can improve your hand-eye coordination.
2.2.2 Overcoming Perceived Lack of Talent
Even if you don’t believe you have a natural aptitude for music, you can still learn to play guitar with dedication and hard work.
- Focus on Effort: Emphasize effort and persistence rather than innate talent.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress, no matter how small.
- Seek Support: Connect with other learners and experienced guitarists for encouragement and guidance.
2.2.3 The Role of Ear Training
Developing your ear training skills can significantly accelerate your progress. Berklee College of Music emphasizes the importance of ear training for all musicians.
- Interval Recognition: Learn to recognize different musical intervals.
- Chord Recognition: Practice identifying different chord types and progressions.
- Melodic Dictation: Try to transcribe simple melodies by ear.
2.3 Learning Resources and Guidance
The quality of your learning resources and the guidance you receive can greatly impact your progress.
2.3.1 Choosing the Right Learning Method
There are various ways to learn guitar, including private lessons, online courses, books, and self-teaching.
- Private Lessons: Offer personalized instruction and feedback.
- Online Courses: Provide structured lessons and learning materials.
- Books: Offer in-depth explanations and exercises.
- Self-Teaching: Allows you to learn at your own pace using free resources.
2.3.2 Seeking Feedback and Mentorship
Getting feedback from experienced guitarists can help you identify areas for improvement and stay motivated.
- Join a Guitar Community: Connect with other guitarists online or in person.
- Take Workshops or Masterclasses: Attend workshops or masterclasses to learn from experienced players.
- Record Yourself: Record your playing and listen back to identify areas for improvement.
2.3.3 Utilizing Online Resources Effectively
The internet offers a wealth of resources for learning guitar, including video tutorials, tablature, and backing tracks.
- YouTube: Search for tutorials on specific techniques or songs.
- Guitar Tabs: Use online tablature to learn to play your favorite songs.
- Backing Tracks: Practice improvising over backing tracks in different keys and styles.
3. Optimizing Your Guitar Learning Journey
To make the most of your guitar learning journey, consider these strategies for optimizing your progress and maintaining motivation.
3.1 Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations
Having realistic goals and expectations can prevent frustration and keep you motivated.
3.1.1 Defining Your Objectives
Clearly define what you want to achieve with your guitar playing.
- Play for Fun: If your goal is simply to enjoy playing guitar, focus on learning songs you love.
- Join a Band: If you want to join a band, focus on developing skills that are relevant to playing in a group.
- Become a Professional Musician: If you aspire to become a professional musician, set ambitious goals and be prepared for a long and challenging journey.
3.1.2 Breaking Down Long-Term Goals into Smaller Steps
Break down your long-term goals into smaller, manageable steps.
- Monthly Goals: Set monthly goals for learning new songs or techniques.
- Weekly Goals: Plan your practice sessions for each week.
- Daily Goals: Focus on specific tasks during each practice session.
3.1.3 Celebrating Milestones
Acknowledge and celebrate your accomplishments along the way.
- Reward Yourself: Treat yourself when you reach a significant milestone.
- Share Your Progress: Share your progress with friends, family, or online communities.
- Reflect on Your Journey: Take time to reflect on how far you’ve come and what you’ve learned.
3.2 Maintaining Motivation and Overcoming Plateaus
It’s normal to experience periods of frustration or plateaus in your learning. Here are some strategies for staying motivated and overcoming these challenges.
3.2.1 Finding Inspiration
Seek out sources of inspiration to keep your passion for guitar alive.
- Listen to Music: Listen to your favorite guitarists and bands.
- Attend Concerts: Go to live concerts to see your favorite musicians perform.
- Watch Guitar Tutorials: Watch video tutorials to learn new techniques and songs.
3.2.2 Varying Your Practice Routine
Keep your practice routine fresh and engaging by trying new exercises and songs.
- Learn New Genres: Explore different musical genres to expand your skills and knowledge.
- Try Different Techniques: Experiment with new techniques to challenge yourself.
- Play with Others: Jam with other musicians to improve your timing and improvisation skills.
3.2.3 Seeking Support from a Community
Connect with other guitarists for support and encouragement.
- Join a Guitar Forum: Participate in online guitar forums to ask questions and share your experiences.
- Take Group Lessons: Attend group lessons to learn alongside other students.
- Find a Practice Partner: Practice with a friend or fellow guitarist to stay motivated and accountable.
3.3 Leveraging Technology and Tools
Take advantage of technology and tools to enhance your learning experience.
3.3.1 Guitar Learning Apps
Use guitar learning apps to track your progress, access lessons, and practice exercises.
- Yousician: Offers interactive lessons and real-time feedback.
- Fender Play: Provides structured courses and personalized learning paths.
- Ultimate Guitar: Offers access to a vast library of tablature and chords.
3.3.2 Metronomes and Drum Machines
Use a metronome or drum machine to improve your timing and rhythm.
- Metronome: Helps you develop a steady beat.
- Drum Machine: Provides a more engaging rhythm accompaniment.
3.3.3 Recording Software
Use recording software to record your playing and analyze your performance.
- Audacity: A free and open-source recording and editing software.
- GarageBand: A user-friendly recording software available for Mac users.
- Pro Tools: An industry-standard recording software used by professional musicians.
4. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
To provide a more concrete understanding of the guitar learning timeline, let’s look at some real-life examples and case studies.
4.1 Case Study 1: The Hobbyist Guitarist
Background: John, a 35-year-old professional, wanted to learn guitar as a hobby. He dedicated 30 minutes to practice each day.
- First 6 Months: John learned basic chords and strumming patterns. He could play a few simple songs.
- 6-18 Months: John mastered barre chords and learned basic scales. He could play more complex songs and started experimenting with improvisation.
- 18+ Months: John developed his own style and joined a local band. He specialized in blues and rock music.
4.2 Case Study 2: The Aspiring Professional
Background: Emily, a 20-year-old student, wanted to become a professional guitarist. She dedicated 2-3 hours to practice each day.
- First 6 Months: Emily quickly learned basic chords and scales. She started taking private lessons.
- 6-18 Months: Emily mastered advanced techniques and studied music theory extensively. She started performing at local venues.
- 18+ Months: Emily enrolled in a music college and continued to hone her skills. She aimed to become a session musician or a solo artist.
4.3 Expert Opinions and Advice
Here are some expert opinions and advice from renowned guitarists and music educators.
- Steve Vai: “The key to learning guitar is to practice consistently and to have fun. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results right away. Just keep practicing and you’ll eventually get there.”
- Joe Satriani: “Focus on the fundamentals and build a strong foundation. Don’t try to learn too much too quickly. Take your time and master each skill before moving on to the next.”
- Berklee College of Music: “A well-rounded music education includes both practical skills and theoretical knowledge. Study music theory and ear training to enhance your playing.”
5. Common Questions About Learning Guitar
Here are some frequently asked questions about learning guitar, along with detailed answers.
5.1 Is it Hard to Learn Guitar?
Learning guitar can be challenging, but with consistent practice and the right approach, it is achievable for most people.
- Initial Challenges: Sore fingers, developing coordination, and learning basic chords.
- Overcoming Challenges: Consistent practice, proper technique, and setting realistic goals.
5.2 How Often Should I Practice Guitar?
Ideally, you should practice guitar every day for at least 30 minutes. However, even short, focused sessions can be effective.
- Daily Practice: 30-60 minutes per day for optimal results.
- Consistent Practice: Even 15-20 minutes per day is better than sporadic, longer sessions.
5.3 Can I Teach Myself Guitar?
Yes, it is possible to teach yourself guitar using online resources, books, and other learning materials. However, private lessons or structured courses can provide more personalized guidance and feedback.
- Self-Teaching Resources: YouTube tutorials, online tablature, and guitar learning apps.
- Benefits of Instruction: Personalized feedback, structured learning, and expert guidance.
5.4 What is the Best Age to Start Learning Guitar?
There is no best age to start learning guitar. Children as young as 6 or 7 can start learning, while adults can also learn guitar at any age.
- Children: May learn more quickly due to greater neuroplasticity.
- Adults: May have greater focus and discipline.
5.5 How Long Does It Take to Learn a Specific Song?
The time it takes to learn a specific song depends on its complexity and your skill level. Simple songs with basic chords can be learned in a few days or weeks, while more complex songs may take several months.
- Simple Songs: A few days to a few weeks.
- Complex Songs: Several months.
5.6 What are the Most Important Skills to Learn First?
The most important skills to learn first include basic chords, strumming patterns, and basic music theory.
- Basic Chords: G, C, D, Em, Am.
- Strumming Patterns: Simple down-up strumming patterns.
- Music Theory: Understanding rhythm, notes, and chord progressions.
5.7 How Do I Choose the Right Guitar?
Choosing the right guitar depends on your budget, playing style, and personal preferences.
- Acoustic vs. Electric: Acoustic guitars are good for beginners, while electric guitars offer more versatility.
- Budget: Set a budget and look for guitars within that price range.
- Comfort: Choose a guitar that feels comfortable to play.
5.8 How Can I Improve My Finger Dexterity?
Improving finger dexterity involves practicing exercises such as scales, arpeggios, and finger independence exercises.
- Scales and Arpeggios: Practice scales and arpeggios to improve finger coordination.
- Finger Independence Exercises: Use exercises that require each finger to move independently.
5.9 What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid?
Common mistakes to avoid include practicing without a plan, neglecting fundamentals, and not taking breaks.
- Plan Your Practice: Always have a clear idea of what you want to accomplish during each session.
- Focus on Fundamentals: Don’t neglect basic skills, as they are the foundation of your playing.
- Take Breaks: Regular breaks can help prevent fatigue and improve focus.
5.10 How Can I Stay Motivated to Learn Guitar?
Staying motivated involves setting realistic goals, finding inspiration, and connecting with other guitarists.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your long-term goals into smaller, manageable steps.
- Find Inspiration: Listen to your favorite guitarists and bands.
- Connect with Others: Join a guitar community or find a practice partner.
6. Further Resources and Support at LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to succeed in your guitar learning journey.
6.1 Comprehensive Learning Materials
Access our extensive library of articles, tutorials, and courses covering all aspects of guitar playing.
- Beginner’s Guides: Step-by-step guides for learning basic chords, strumming patterns, and music theory.
- Advanced Techniques: Tutorials on advanced techniques such as sweep picking, tapping, and complex chord voicings.
- Song Lessons: Learn to play your favorite songs with our detailed song lessons.
6.2 Expert Instructors and Personalized Guidance
Connect with our team of experienced guitar instructors for personalized guidance and feedback.
- Private Lessons: One-on-one instruction tailored to your individual needs and goals.
- Group Classes: Learn alongside other students in a supportive and engaging environment.
- Online Consultations: Get expert advice and feedback through online consultations.
6.3 Supportive Community
Join our vibrant community of guitar learners and enthusiasts.
- Forums: Participate in discussions, ask questions, and share your experiences.
- Groups: Connect with other learners who share your interests and goals.
- Events: Attend online and in-person events to network with other guitarists.
6.4 Latest Trends and Updates in Guitar Education
Stay informed about the latest trends and updates in guitar education.
| Topic | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Learning | Integration of AI in guitar learning apps for personalized feedback and adaptive lessons. | Apps like Yousician and Fender Play are incorporating AI to analyze playing and offer tailored exercises. |
| Virtual Reality (VR) | VR applications for immersive guitar practice and learning experiences. | VR platforms are being developed to simulate live performance environments and interactive lessons. |
| Gamification | Use of game-like elements to make learning more engaging and motivating. | Apps are using points, badges, and leaderboards to encourage consistent practice. |
| Online Communities | Growth of online guitar communities and forums for peer support and knowledge sharing. | Platforms like Reddit’s r/guitarlessons and dedicated guitar forums are becoming increasingly popular for learners. |
| Hybrid Learning | Combining online and in-person instruction for a balanced learning experience. | Many instructors are offering hybrid models that include both online lessons and occasional in-person workshops. |
| Mobile Learning | Increased accessibility of guitar learning resources on mobile devices. | Mobile apps and websites are optimized for on-the-go learning, allowing users to practice anytime, anywhere. |
| Personalized Learning | Tailoring learning paths to individual needs and goals through adaptive assessments and customized content. | Learning platforms are using data analytics to identify individual strengths and weaknesses and adjust the curriculum accordingly. |
| Focus on Mental Health | Emphasis on the mental and emotional aspects of learning guitar, including stress management and self-compassion. | Instructors are incorporating mindfulness techniques and positive psychology principles to help learners manage frustration and build confidence. |
| Integration of Music Theory | Enhanced integration of music theory concepts into practical guitar lessons for a deeper understanding. | Lessons are now incorporating more music theory explanations to help learners understand the “why” behind what they are playing. |
| Accessibility for All | Efforts to make guitar learning accessible to individuals with disabilities through adapted instruments and methods. | Companies are developing adapted guitars and teaching methods for individuals with physical limitations. |


6.5 Call to Action
Ready to start your guitar learning journey? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our resources, connect with our instructors, and join our community. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
Embark on a fulfilling musical journey with LEARNS.EDU.VN, where learning is not just about acquiring skills but also about nurturing passion and achieving personal growth. Whether you aspire to play for leisure, join a band, or become a professional musician, learns.edu.vn is your ultimate destination for comprehensive guitar education. Explore our courses, engage with our community, and unlock your musical potential today. Discover guitar playing techniques, musical skill enhancement, and music education resources.
