Learning SQL for beginners can be achieved relatively quickly. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe acquiring fundamental SQL skills, which are essential for manipulating and managing data, typically takes only a few weeks with consistent effort. This article will guide you through the journey of learning SQL, optimizing your learning process, and highlighting the benefits of mastering this crucial language. Discover effective strategies and resources to accelerate your SQL learning journey.
1. How Long Does It Take to Learn SQL? A Detailed Breakdown
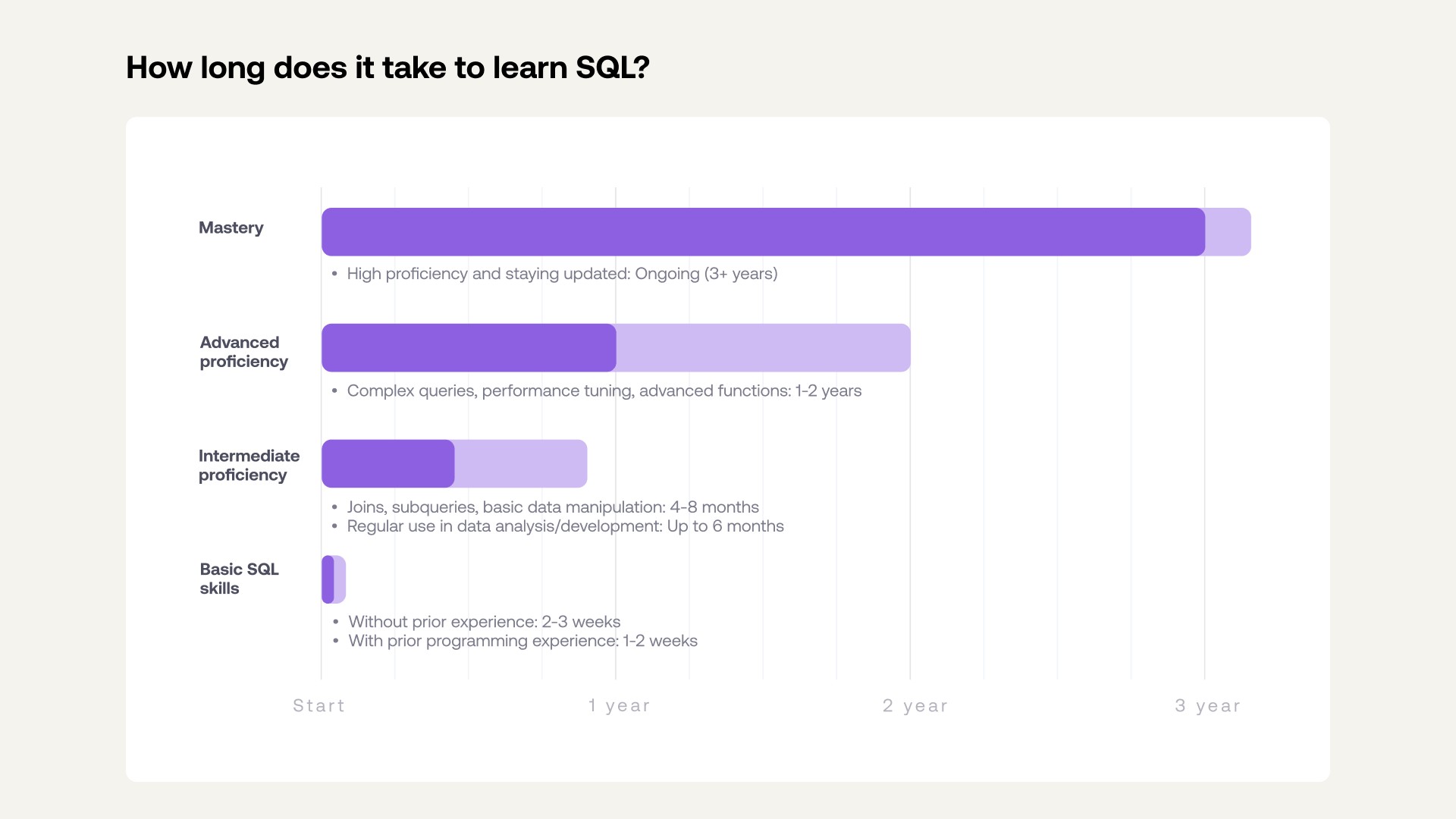
The timeframe to learn SQL (Structured Query Language) varies significantly based on individual goals, learning methods, and the depth of knowledge pursued. Grasping the basics can be swift, but achieving mastery requires dedicated practice and continuous learning.
1.1. Basic SQL Skills: Weeks to a Month
- Timeline: 2-4 weeks
- Focus: Core SQL commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. Understanding WHERE clauses for filtering data.
- Objective: Perform simple data retrieval and manipulation tasks.
For individuals with prior programming experience, this phase can be completed in as little as 1-2 weeks. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources to help beginners quickly grasp these fundamental concepts, laying a solid foundation for more advanced topics.
1.2. Intermediate Proficiency: Several Months
- Timeline: 3-6 months
- Focus: Joins, subqueries, and basic data manipulation techniques.
- Objective: Competently use SQL in data analysis and development tasks.
During this phase, learners gain the ability to combine data from multiple tables, write more complex queries, and perform data transformations. Regular practice and real-world application are crucial for accelerating progress.
1.3. Advanced Proficiency: One to Two Years
- Timeline: 1-2 years
- Focus: Complex queries, performance tuning, and advanced SQL functions.
- Objective: Optimize database performance and write efficient SQL code.
Mastering advanced SQL involves understanding database internals and employing techniques to improve query speed and resource utilization. This stage requires significant hands-on experience and a deep understanding of database management principles.
1.4. Mastery: Ongoing Learning
- Timeline: 3+ years and continuous learning
- Focus: Staying updated with new SQL developments, advanced optimization techniques, and emerging database technologies.
- Objective: Maintain expertise in SQL and apply it to solve complex data challenges.
SQL is a dynamic field, and continuous learning is essential to stay proficient. This includes keeping up with new features, best practices, and industry trends.
1.5. Factors Influencing Learning Time
Several factors influence how quickly one can learn SQL:
- Prior Coding Experience: Experience with other programming languages or data manipulation tools can significantly accelerate the learning process.
- Learning Goals: Whether you need SQL for basic tasks or aspire to become a database expert impacts the depth of knowledge required.
- Frequency of Use: Regular practice and applying SQL in real-world projects are essential for reinforcing learning.
- Learning Style: Structured learning programs, such as online courses and tutorials available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, can provide a more efficient learning path.
2. Why Learn SQL in 2025?
Learning SQL in 2025 remains highly relevant due to its widespread use in data management and analysis. According to a 2023 Stack Overflow survey, SQL is one of the most popular languages among professional developers. Its demand spans across various industries, making it a valuable skill for numerous professions.
2.1. Key Areas Where SQL is Valuable
- Data Analysis and Data Science: SQL is crucial for extracting and analyzing data from relational databases. Data analysts and scientists use SQL to retrieve, filter, and aggregate data for analysis and reporting.
- Business Intelligence: SQL facilitates the generation of reports and insights from large datasets. Business intelligence professionals rely on SQL to create dashboards, visualizations, and reports that drive decision-making.
- Software Development: SQL is necessary for backend development and database management. Software developers use SQL to interact with databases, store and retrieve data, and ensure data integrity.
- Database Administration: SQL is used to maintain and optimize database systems. Database administrators use SQL to manage user access, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues.
- Finance, Banking, Healthcare, E-commerce: SQL is essential for managing financial data, patient records, product inventories, and more. These industries rely on SQL to ensure data accuracy, security, and compliance.
2.2. Career Opportunities with SQL Skills
Mastering SQL opens doors to various career opportunities, including:
| Career Path | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Analyst | Analyzes data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. |
| Database Developer | Designs, develops, and maintains databases. |
| Business Intelligence Analyst | Uses data to create reports and dashboards that support business decisions. |
| Data Scientist | Applies statistical and machine learning techniques to analyze data and build predictive models. |
| Database Administrator | Manages and maintains database systems to ensure optimal performance and security. |
3. Essential SQL Skills to Master
The path to SQL mastery involves acquiring a range of skills, from basic syntax to advanced techniques. The specific skills needed depend on your role and the projects you undertake.
3.1. Foundational SQL Skills
- SELECT Statements: Retrieving data from one or more tables.
- WHERE Clauses: Filtering data based on specific conditions.
- JOIN Operations: Combining data from multiple tables.
- GROUP BY and Aggregate Functions: Summarizing and aggregating data.
- Data Manipulation Language (DML): Adding (INSERT), updating (UPDATE), and deleting (DELETE) data.
- Data Definition Language (DDL): Creating (CREATE), altering (ALTER), and dropping (DROP) tables and other database objects.
- Data Control Language (DCL): Managing data access with commands like GRANT and REVOKE.
3.2. Intermediate SQL Skills
- Subqueries: Embedding queries within other queries.
- Common Table Expressions (CTEs): Creating temporary named result sets for use in a single query.
- Window Functions: Performing calculations across a set of table rows related to the current row.
- Transactions: Ensuring data integrity by grouping a set of operations into a single unit of work.
3.3. Advanced SQL Skills
- Performance Tuning: Optimizing queries for faster execution.
- Indexing: Improving query performance by creating indexes on frequently accessed columns.
- Stored Procedures: Writing and using stored procedures to encapsulate and reuse SQL code.
- Triggers: Automatically executing SQL code in response to certain events.
- SQL Syntax Variations: Familiarizing yourself with the specific SQL syntax used by different database systems, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server.
4. Learning SQL as a Beginner: What to Expect
Beginners can quickly grasp the fundamental concepts of SQL with focused effort. Acquiring basic SQL skills typically takes only 2-3 weeks of dedicated study. Prior coding experience can further reduce this timeframe to 1-2 weeks.
4.1. Effective Learning Resources
- Online Tutorials: LEARNS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive tutorials that cover the basics of SQL.
- Interactive Courses: Platforms like Codecademy and DataCamp provide interactive SQL courses.
- Books: “SQL for Dummies” and “SQL Cookbook” are excellent resources for beginners.
- Practice Exercises: Solving practice exercises is crucial for reinforcing learning.
4.2. Integrating Practice
Consistent practice is essential for mastering SQL. Spending a few hours each day writing and running SQL queries will accelerate your learning and make it more efficient.
The LEARNS.EDU.VN community provides a supportive environment where learners can ask questions, share their experiences, and collaborate on projects.
5. Mastering Advanced SQL: A Long-Term Commitment
Achieving proficiency in advanced SQL requires a more significant investment of time and effort. Getting comfortable with subqueries, CTEs, and window functions typically takes 2-3 months of regular practice. Mastering performance tuning, complex queries, and advanced functions can take six months to a year.
5.1. Strategies for Mastering Advanced SQL
- Focus on Performance Tuning: Learn how to optimize queries for faster execution.
- Practice with Real-World Projects: Gain hands-on experience by working on real-world projects.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest SQL developments and best practices.
- Seek Mentorship: Find a mentor who can provide guidance and feedback.
- Join Advanced Courses: Enroll in advanced SQL courses to deepen your knowledge.
5.2. Continuous Learning
SQL is an evolving language, and continuous learning is essential for staying proficient. Stay updated with new features, best practices, and industry trends by reading blogs, attending conferences, and participating in online communities.
6. Is SQL Easy to Learn? Weighing the Challenges
SQL is often considered an easy language to learn, especially for those with some programming experience. Its relatively simple syntax, which resembles natural language, makes it more intuitive than many other programming languages. However, mastering advanced SQL concepts requires significant practice and logical thinking.
6.1. Factors Contributing to SQL’s Ease of Learning
- Simple Syntax: SQL’s syntax is relatively straightforward and easy to understand.
- Abundant Resources: Numerous online tutorials, courses, and books are available for learning SQL.
- Community Support: A large and active community of SQL developers provides ample support and guidance.
- Practical Application: SQL is widely used in various industries, providing numerous opportunities for practical application.
6.2. Challenges in Mastering SQL
- Complex Queries: Writing complex queries that involve multiple tables and conditions can be challenging.
- Performance Tuning: Optimizing queries for faster execution requires a deep understanding of database internals.
- SQL Syntax Variations: Different database systems use slightly different SQL syntax, which can be confusing.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated with the latest SQL developments requires continuous learning.
7. How to Learn SQL: Tips for Accelerated Learning
Learning SQL effectively requires a structured approach and the right learning resources. Here are some tips for accelerating your SQL learning journey:
7.1. Start with the Basics
Creating a solid foundation is crucial for learning SQL. Begin by understanding core concepts such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers various resources to help beginners quickly grasp these fundamental concepts.
7.2. Practice Regularly
Consistency is key when mastering SQL. Set aside time each day or week to write SQL queries and solve SQL challenges. Online resources like HackerRank and LeetCode offer numerous SQL challenges to practice your skills.
7.3. Work with Real Data
Applying your skills to real-world settings makes learning easier and more engaging. Experiment with real-world datasets to understand how to use SQL in practice. Websites like Kaggle and data.gov offer free datasets you can use.
7.4. Engage with the SQL Community
SQL communities are a great source of learning and support. Join forums and discussion groups where you can ask questions, stay up-to-date with trends, and learn new things. Reddit’s r/SQL and Stack Overflow are excellent platforms for engaging with the SQL community.
7.5. Build a Portfolio
Building a strong portfolio is essential for showcasing your skills and documenting your progress. Add projects that demonstrate your ability to solve real-life SQL problems to potential employers. Use GitHub to host your SQL projects and document each project thoroughly, explaining the problem, approach, and SQL code used.
7.6. Seek Relevant Projects or Jobs
Start looking for entry-level positions that require SQL skills, such as data analyst, business analyst, or database administrator roles. Tailor your resume to highlight your SQL skills and relevant projects, and be prepared to answer technical questions during interviews.
8. FAQ: Common Questions About Learning SQL
Q1: How long does it take to learn SQL if I have no prior programming experience?
A1: If you have no prior programming experience, expect to spend 3-4 weeks mastering the basics and several months to achieve intermediate proficiency.
Q2: What are the best resources for learning SQL online?
A2: LEARNS.EDU.VN, Codecademy, DataCamp, and Udemy offer excellent online courses and tutorials.
Q3: Is SQL certification worth it?
A3: Yes, SQL certification can enhance your resume and demonstrate your skills to potential employers.
Q4: What are the most common SQL interview questions?
A4: Common interview questions include explaining joins, subqueries, indexing, and performance tuning.
Q5: How can I practice SQL for free?
A5: Online platforms like HackerRank and LeetCode offer free SQL challenges to practice your skills.
Q6: What are the best datasets to practice SQL with?
A6: Websites like Kaggle and data.gov offer free datasets you can use for practicing SQL.
Q7: How important is performance tuning in SQL?
A7: Performance tuning is crucial for optimizing query execution and ensuring efficient database performance.
Q8: What are the differences between SQL and NoSQL databases?
A8: SQL databases are relational databases that use structured data, while NoSQL databases are non-relational databases that use unstructured or semi-structured data.
Q9: How can I stay updated with the latest SQL developments?
A9: Read blogs, attend conferences, and participate in online communities to stay updated with the latest SQL developments.
Q10: What are the key skills I need to become a proficient SQL developer?
A10: Key skills include understanding SQL syntax, writing complex queries, performance tuning, and database design.
Conclusion: Your Journey to SQL Proficiency
Learning SQL is a rewarding journey that can open doors to numerous career opportunities. The time it takes to learn SQL depends on various factors, including your goals, previous experience, and learning methods. Whether you’re aiming to master basic queries or become an expert in database administration, consistent practice and continuous learning are essential.
Begin your SQL learning journey with confidence, knowing that the skills you acquire will be valuable assets in today’s data-driven world. Remember to practice consistently, engage with the community, and stay updated with new developments.
Ready to dive in? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive resources and unlock your potential in SQL!
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: learns.edu.vn
Take the first step towards mastering SQL and transforming your career!