How Long Does It Take To Learn The Handstand? Achieving a handstand is a rewarding journey that combines strength, balance, and perseverance. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand that everyone’s journey is unique, and we’re here to provide you with a comprehensive guide to help you achieve your handstand goals. This detailed guide offers insights into the factors influencing your progress and practical tips to enhance your training.
1. Understanding the Handstand Learning Timeline
The timeline for learning a handstand varies significantly from person to person. Several factors influence how quickly you can achieve a freestanding handstand, including your current fitness level, dedication to practice, and learning approach.
1.1. Initial Assessment and Goal Setting
Before embarking on your handstand journey, it’s crucial to assess your current physical condition and set realistic goals. This involves evaluating your strength, flexibility, and balance to identify areas that need improvement.
1.2. Average Timeframes
While individual experiences differ, here’s a general timeline of what you can expect:
- Beginner (0-3 months): Focus on building foundational strength and flexibility. Expect to hold a handstand against a wall for 30-60 seconds.
- Intermediate (3-6 months): Develop balance and control. Aim for a freestanding handstand of 5-10 seconds.
- Advanced (6+ months): Refine technique and increase endurance. Work towards holding a handstand for 30 seconds or more and exploring advanced variations.
1.3 Factors Influencing the Learning Timeline:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Fitness Level | Your current strength, flexibility, and balance significantly impact your initial progress. | Higher fitness levels generally lead to faster progress. |
| Practice Consistency | Regular and consistent practice is crucial. Short, frequent sessions are more effective than infrequent, long sessions. | Consistent practice accelerates learning. |
| Training Methodology | Using a structured and progressive training plan, like the one provided by LEARNS.EDU.VN, ensures you build the necessary skills in a logical order. | A well-structured plan optimizes training and reduces the risk of plateaus. |
| Body Awareness | Developing a strong sense of body awareness helps you make subtle adjustments to maintain balance. | Increased body awareness improves balance and control. |
| Mindset | A positive and persistent mindset is essential. Learning a handstand can be challenging, and setbacks are normal. | Perseverance and a growth mindset help overcome obstacles. |
| Prior Experience | Previous experience in gymnastics, yoga, or other balancing activities can provide a head start. | Prior experience accelerates initial learning. |
| Age | While age isn’t a limiting factor, younger individuals may adapt more quickly due to greater neuroplasticity. | Younger learners may progress faster in the early stages. |
| Injury History | Previous injuries, especially to the wrists, shoulders, or back, can hinder progress. | Injuries may require modifications to training and potentially slow down progress. |
| Nutrition and Recovery | Proper nutrition and adequate rest are essential for muscle recovery and overall progress. | Adequate nutrition and recovery support consistent training and reduce the risk of injury. |
| Coaching and Feedback | Receiving guidance from an experienced coach can provide valuable feedback and help you correct technique issues. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers expert guidance to support your learning journey. | Coaching and feedback improve technique and prevent the development of bad habits. |
| Genetics | Genetic factors can influence strength, flexibility, and balance, which can impact learning speed. | Genetic predispositions can influence potential, but consistent effort can overcome limitations. |
| Environment | A safe and supportive training environment is essential for building confidence. | A supportive environment encourages consistent practice and reduces anxiety. |
| Sleep Quality | Adequate sleep is crucial for muscle recovery, cognitive function, and overall well-being, all of which impact your ability to learn and progress in handstand training. | Consistent and quality sleep supports efficient learning and physical recovery. |
| Stress Levels | High stress levels can negatively impact focus, motivation, and physical performance, potentially slowing down progress in handstand training. | Managing stress is important for maintaining consistency and focus in training. |
| Equipment | Having access to the right equipment, such as mats, blocks, and resistance bands, can enhance your training and help you progress more efficiently. | Proper equipment can improve safety, effectiveness, and enjoyment of training. |
| Social Support | Having friends or training partners who are also working towards handstand goals can provide motivation, encouragement, and accountability, which can help you stay consistent and progress faster. | A supportive social network can increase motivation and adherence to training. |
| Cultural Factors | Cultural attitudes towards physical activity, body image, and risk-taking can influence your willingness to try handstands and your level of support from family and friends. | Cultural factors can impact your motivation and access to resources for training. |
| Access to Resources | Having access to quality training programs, experienced instructors, and reliable information can significantly impact your learning curve. LEARNS.EDU.VN provides a wealth of resources to support your handstand journey. | Access to quality resources and guidance accelerates learning and prevents misinformation. |
| Technological Factors | The availability of online tutorials, apps, and wearable devices can provide valuable feedback, track your progress, and enhance your understanding of handstand technique and training principles. | Technology can enhance your training by providing real-time feedback and personalized guidance. |
| Economic Factors | Financial constraints can limit access to training facilities, coaching, and equipment, potentially impacting your progress. | Financial resources can influence the quality and consistency of your training. |
| Political Factors | Government policies that promote physical activity and provide access to public spaces for training can indirectly influence your ability to learn handstands. | Supportive government policies can create a more favorable environment for physical training. |
| Educational Background | Your educational background can influence your understanding of biomechanics, physiology, and training principles, which can help you design a more effective and personalized handstand training program. | A solid educational foundation enhances your ability to learn and apply training principles effectively. |


2. Essential Handstand Concepts: The 5P Framework
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we emphasize a structured approach to learning handstands. Our “5P Framework” ensures a well-rounded and effective training regimen.
2.1. Prepare
Warming up is crucial to prevent injuries and optimize performance. Targeted exercises prepare your body for the specific demands of handstands.
- Wrist Stretches: Improve wrist flexibility and strength.
- Shoulder Mobility Drills: Enhance shoulder range of motion and stability.
- Leg Squeezes: Activate core muscles and improve body awareness.
- Handstand Bails: Practice safe exits to build confidence.
2.2. Practice
Consistent practice is key to mastering handstand skills. Break down the handstand into smaller components and focus on refining each aspect.
- Elevated A-Frame: Build shoulder strength and stability.
- Frogger: Develop core engagement and balance.
- Wall Entries: Practice controlled entries into a handstand against a wall.
- Wall Float: Improve balance and body alignment.
- Split Leg Kick Up: Develop control and precision in your handstand entry.
2.3. Play
Playful exploration enhances your understanding and mastery of handstand skills. Experiment with variations and find what works best for you.
- Head Movements: Explore how head position affects balance.
- Breathing Techniques: Experiment with different breathing patterns to improve stability.
- Palm Pressure: Play with pressure distribution through your palms to fine-tune balance.
2.4. Push
Conditioning exercises strengthen your body and improve your ability to hold a handstand for longer.
- Band Drills: Strengthen shoulder and back muscles.
- A-Frame Shrugs: Improve shoulder stability.
- Hollow Body Holds: Engage core muscles for better body alignment.
- High Frogger: Build strength and endurance in the core and shoulders.
2.5. Ponder
Mindful reflection is essential for continuous improvement. Analyze your performance, identify areas for improvement, and adjust your training accordingly.
- Session Review: Reflect on what you learned during each session.
- Struggle Analysis: Identify challenges and develop strategies to overcome them.
- Progress Tracking: Monitor your progress and celebrate your achievements.
3. Handstand Assessment: Identifying Your Weak Spots
A thorough assessment helps you understand your current capabilities and identify areas that need the most attention.
3.1. Wrist Strength & Flexibility Assessment
- Purpose: Determine your ability to extend your wrists.
- Procedure: Perform wrist extensions and assess your range of motion.
- Interpretation: Limited wrist extension indicates a need for more wrist preparation exercises.
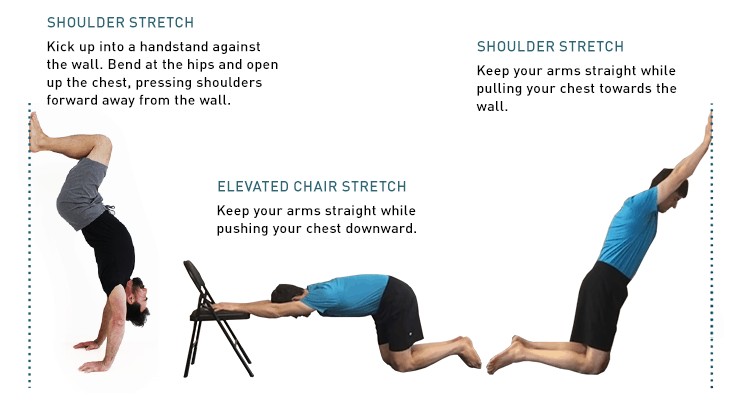
3.2. Shoulder Mobility Assessment
- Purpose: Evaluate your shoulder flexion before each session.
- Procedure: Perform shoulder flexion exercises and assess your range of motion.
- Interpretation: Tight shoulders indicate a need for more shoulder preparation exercises and potentially a lower-level practice.
3.3. Wall Walk Assessment
- Purpose: Test your comfort level and control while upside down.
- Procedure: Slowly walk your feet up a wall while placing your hands on the ground.
- Interpretation: Difficulty with the wall walk indicates a need to focus on foundational strength and balance exercises.
4. Joint Preparation: Warming Up for Success
Proper joint preparation is essential to prevent injuries and optimize performance. Focus on exercises that improve wrist and shoulder mobility.
4.1. Wrist Exercises
| Exercise | Description | Benefits | Sets/Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wrist Circles | Rotate your wrists clockwise and counterclockwise. | Improves wrist flexibility and range of motion. | 2 sets of 10 reps |
| Wrist Extensions | Extend your hands forward, fingers pointing up, and gently stretch back. | Increases flexibility in the wrist extensors. | 2 sets of 10-15 seconds |
| Wrist Flexions | Extend your hands forward, fingers pointing down, and gently stretch back. | Increases flexibility in the wrist flexors. | 2 sets of 10-15 seconds |
| Finger Stretches | Spread your fingers wide and then make a fist, repeating the motion. | Improves finger dexterity and wrist mobility. | 2 sets of 10 reps |
4.2. Shoulder Exercises
| Exercise | Description | Benefits | Sets/Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arm Circles | Rotate your arms forward and backward in large circles. | Improves shoulder mobility and warms up the shoulder joint. | 2 sets of 10 reps |
| Shoulder Rolls | Roll your shoulders forward and backward, focusing on smooth, controlled movements. | Increases shoulder flexibility and reduces tension. | 2 sets of 10 reps |
| Cross-Body Shoulder Stretch | Bring one arm across your body and gently pull it closer with the opposite hand. | Stretches the shoulder muscles and improves flexibility. | 2 sets of 15-20 seconds |
| Overhead Tricep Stretch | Reach one arm overhead and bend it behind your head, gently pulling with the other hand. | Stretches the triceps and shoulder muscles. | 2 sets of 15-20 seconds |
5. Step-by-Step Handstand Drills & Progressions
Mastering the handstand requires a structured approach with progressive drills. Each drill builds upon the previous one, ensuring a solid foundation.
5.1. Beginner Progressions
- Elevated A-Frame: Start with your hands on the ground and feet on an elevated surface. This helps build shoulder strength and stability.
- Frogger: Place your knees on your elbows and lean forward, gradually shifting your weight onto your hands. This develops core engagement and balance.
- High Frogger: Similar to the Frogger, but with your hips higher. This increases the challenge and further develops balance.
- Elevated L-Stand: Place your feet on an elevated surface and walk your hands towards the wall, forming an L-shape. This builds shoulder strength and prepares you for vertical alignment.
5.2. Intermediate Progressions
- Wall Entries: Kick up against a wall and focus on maintaining a straight line from your hands to your heels. This improves body alignment and balance.
- Wall Float: Kick up against a wall and then slowly float one foot away from the wall, maintaining your balance. This develops control and precision.
- Wall Line Work: Practice shifting your weight from hand to hand while maintaining a straight line against the wall. This enhances balance and coordination.
5.3. Advanced Progressions
- Split Leg Kick Up: Practice kicking up into a handstand with one leg forward and one leg back. This develops control and precision in your entry.
- Straddle Handstand: Kick up into a handstand with your legs straddled wide. This improves balance and body awareness.
- Full Handstand Entries: Practice kicking up into a full handstand without relying on a wall for support. This requires significant strength, balance, and control.
6. Handstand Exploration: Playing with Your Skills
Playful exploration is crucial for mastering the handstand. Experiment with different variations and challenge yourself in new ways.
6.1. Head Movements
Explore how tilting your head in different directions affects your balance. This helps you develop a better understanding of your body’s center of gravity.
6.2. Breathing Techniques
Experiment with different breathing patterns to improve stability. Try inhaling deeply and exhaling slowly to maintain control.
6.3. Palm Pressure
Play with shifting your weight from your fingers to the heels of your hands. This helps you fine-tune your balance and make subtle adjustments.
7. Handstand Conditioning: Pushing Your Skills
Conditioning exercises strengthen your body and improve your ability to hold a handstand for longer. Focus on exercises that target your shoulders, core, and wrists.
7.1. Band Drill
Use resistance bands to perform exercises that strengthen your shoulder and back muscles. This improves stability and endurance.
7.2. A-Frame Shrugs
Perform shrugs in an A-frame position to improve shoulder stability. This helps you maintain proper alignment in your handstand.
7.3. Hollow Body Hold
Engage your core muscles and maintain a hollow body position. This improves core strength and body alignment.
7.4. High Frogger
Practice the High Frogger to build strength and endurance in your core and shoulders. This prepares you for more challenging handstand variations.
8. Reflecting on Your Practice: Learning from Mistakes
Mindful reflection is essential for continuous improvement. Analyze your performance, identify areas for improvement, and adjust your training accordingly.
8.1. Session Review
Take a few minutes after each session to reflect on what you learned. What went well? What could you improve?
8.2. Struggle Analysis
Identify any challenges you encountered during your practice. What caused these struggles? How can you overcome them in the future?
8.3. Progress Tracking
Keep track of your progress over time. Are you getting stronger? Is your balance improving? Celebrating your achievements can help you stay motivated.
9. Handstand Positioning and Breathing Tips
Proper positioning and breathing are crucial for maintaining balance and control in a handstand.
9.1. Body Alignment
- Stack the Blocks: Imagine stacking your joints like blocks, aiming for a straight line from your wrists to your ankles.
- Maintain Tension: Squeeze your muscles to create stability.
- Balance Through Your Hands: Shift your weight slightly to maintain balance by pressing through your fingers and the heels of your hands.
9.2. Breathing Techniques
- Say Your ABCs: Focus on maintaining a steady breathing pattern. Saying your ABCs can help you stay relaxed and focused.
- Cartwheel Bail: Practice your cartwheel so you can safely exit the handstand if you lose your balance.
10. Learn to Handstand: Your Training Plan
A structured training plan is essential for making consistent progress. Here’s a sample program for 4 days a week, 45 minutes per session.
| Monday/Thursday | Tuesday/Friday | |
|---|---|---|
| Prepare | 10 minutes total: • Wrist prep • Shoulder prep • A-Frame Shrugs | 15 minutes total: • Do the full prep routine |
| Practice | 20 minutes total: • Bailing Practice and Entries (either using wall or freestanding split leg kick-up) [5 minutes] • Single attempt handstand holds (either using wall or freestanding for attempts) [15 minutes] | 20 minutes total: • Bailing Practice and Entries (either using wall or freestanding split leg kick-up) [5 minutes] • Single attempt handstand holds (either using wall or freestanding for attempts) [15 minutes] |
| Play | 5 minutes total: Choose a movement at an appropriate level and explore. Some examples: • Kicking up to hold before you bail • High Frogger tying to pause at the top • Wall Floats | 5 minutes total: Choose a movement at an appropriate level and explore. Some examples: • Kicking up to hold before you bail • High Frogger tying to pause at the top • Wall Floats |
| Push | 5 minutes total: • 1-minute Stamina Hold x 3 (Using wall facing in or the band standing up) • 1-minute Hollow Body Hold x 2 | No push session today! Take it easy 🙂 |
| Ponder | 5 minutes total: Spend some time reflecting on the session and prepping for the next one. | 5 minutes total: Spend some time reflecting on the session and prepping for the next one. |
11. Advanced Handstand Variations
For those who have mastered the basic handstand, there are many advanced variations to explore.
- One-Arm Handstand: Requires significant strength and balance.
- Handstand Push-Ups: Challenge your upper body strength.
- Pinching Handstand: Focuses on balance.
- Press to Handstand: A strength-based move.
- Tigris Handstand: Relies on flexibility.
- Figure 8 Handstand: Combination of strength and flexibility
12. FAQs About Holding a Handstand
12.1. What if I can’t keep my balance?
Master the set-up, control the kick-up, and learn to bail.
12.2. Do handstands build muscle?
Not significantly, but they improve strength.
12.3. Do you need to be strong to do a handstand?
Not initially, but strength is necessary for advanced variations.
12.4. How do you get strong enough to do a handstand?
With practice and progressive training.
12.5. How do you do a handstand against a wall?
Facing the wall (walk up) or facing away (kick up).
12.6. What muscles does a handstand use?
The entire body, mainly fingers, wrists, shoulders, and core.
12.7. Are handstands good for you?
Yes, they improve circulation, spatial awareness, and strength.
12.8. How do you train to do a handstand?
Safety and strength, balance, and endurance.
12.9. How long should I do a handstand for?
As long as you can, gradually increasing the duration.
12.10. How do you hold a handstand for a minute?
Gradually work up to it with consistent practice.
12.11. How long does it take to learn handstands?
It varies, from a few months to several years, depending on individual factors.
12.12. Should you do handstands every day?
Build up to it gradually to avoid strain.
12.13. Are handstands bad for your back?
Not if done correctly with proper core stability and shoulder range of motion.
12.14. Can headstands be dangerous?
Any movement can be, so start slowly and progress gradually.
12.15. Are handstand push-ups dangerous?
Only if done improperly; focus on proper form.
12.16. Can you lose weight doing handstands?
Weight loss comes down to good nutritional habits.
12.17. Is the headstand or handstand harder?
Handstands are generally harder due to the increased balance required.
12.18. What is the longest someone has held a handstand?
Records vary, and the focus should be on personal progress.
12.19. Does doing handstands help hair growth?
No scientific evidence supports this claim.
13. Additional Tips for Handstand Success
- Consistency: Regular practice is key.
- Patience: Progress takes time and effort.
- Listen to Your Body: Rest when needed to avoid injuries.
- Seek Guidance: Consider working with a coach or trainer.
- Stay Positive: A positive mindset can make all the difference.
14. LEARNS.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Handstand Mastery
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the resources and support you need to achieve your handstand goals. Our comprehensive programs, expert guidance, and supportive community can help you unlock your full potential.
Learning a handstand is a challenging but rewarding journey. By understanding the factors that influence your progress, following a structured training plan, and staying committed to your goals, you can achieve your handstand dreams. Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover more resources and courses that can help you on your journey to handstand mastery.
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: learns.edu.vn
15. Free Cheatsheet: Learn How to Do a Handstand
Download this entire tutorial and our simple cheatsheet for easy reference.
👉 Tap or click here and it’s yours.
We’ll walk you through each step to getting your first handstand.
Working towards, and maintaining, a solid handstand is great training.
If you follow the instructions and guidelines I’ve shared here, I know you’ll find the practice both rewarding and fun 🙂
Keywords: handstand, handstand training, how to learn a handstand, hand balancing, handstand progression, gymnastics, bodyweight training, fitness, balance, strength training.
LSI Keywords: handstand for beginners, handstand exercises, handstand benefits, handstand tutorial, handstand workout, handstand tips, handstand drills, handstand conditioning.