Learning guitar proficiency varies, but you can make significant progress within a few months with focused effort, and LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources to accelerate your learning journey. Understanding realistic timelines, optimizing practice routines, and focusing on personal growth is key to mastering guitar. Explore effective guitar education and musical skill development with LEARNS.EDU.VN.
1. Understanding the Guitar Learning Timeline
Many aspiring guitarists wonder, How long will it take to learn guitar? There’s no definitive answer, as learning depends on many factors, including your individual aptitude, practice habits, and learning goals. However, understanding typical timelines can provide helpful expectations and motivation.
Just like Eddie Van Halen, Jimi Hendrix, and Stevie Ray Vaughn started where you are, everyone learns at their own pace. Let’s break down the learning process into different phases.
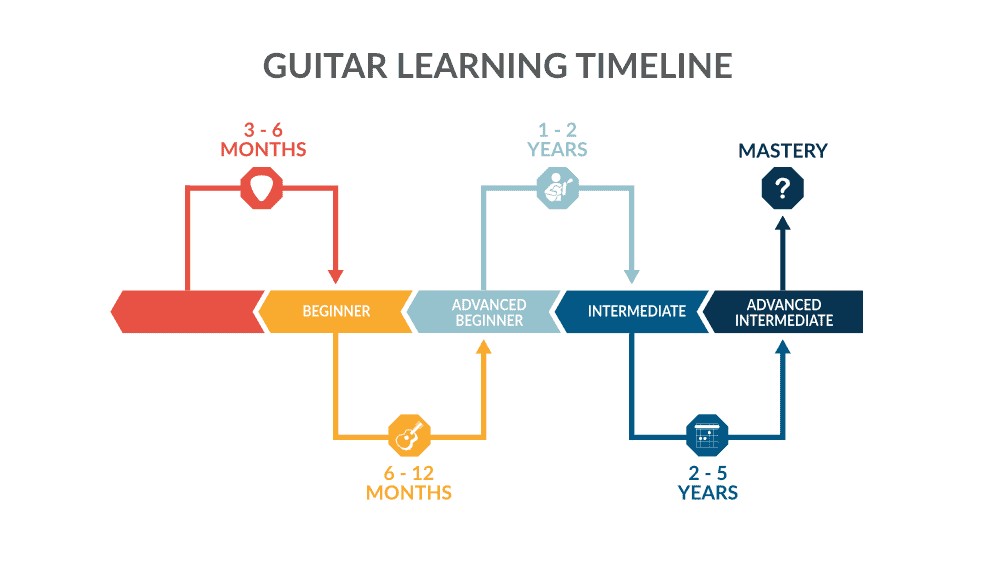
1.1 The Beginner Phase: 3-6 Months
In the initial 3-6 months, most students can play simple songs and chords. This is a crucial period for building foundational skills.
- Developing Calluses: Initially, your fingers will hurt as you build calluses.
- Hand Strength and Coordination: You’ll develop the necessary hand strength and coordination.
- Fundamental Techniques: Learning basic chords, strumming patterns, and fingerpicking.
Many beginners find this phase challenging and may lose interest. Those who persist develop a solid base for future progress.
1.2 The Advanced Beginner Phase: 6 Months to 1 Year
After the initial burst of progress, you might feel like your learning has plateaued. This can be disheartening but is a normal part of the learning curve.
- Increased Expectations: Your standards are higher, and you’re tackling more complex techniques.
- Smaller Increments of Progress: Progress may seem slower compared to the initial months.
- Maintaining Momentum: It’s essential to stay consistent with your practice routine.
This phase requires patience and dedication. Those who stick with it are often rewarded with another growth spurt.
1.3 The Intermediate Phase: 1-2 Years
This phase involves “buckling down” and refining your skills. The question of how long it will take to learn guitar becomes less relevant.
- Mastering Chords: Learning all open chords and barre chords.
- Smooth Transitions: Changing chords smoothly and comfortably.
- Basic Scales and Melodies: Playing basic scales and simple melodies.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement: Recognizing your strengths and weaknesses.
By this stage, playing guitar feels more natural, and you can play a variety of songs.
1.4 The Advanced Intermediate Phase: 2-5 Years
At this point, your foundational skills are solid, and you’re developing more advanced techniques.
- Confidence and Technique: Playing confidently with good technique.
- Expanding Chord Library: Continuously learning new and complex chords.
- Improvisation: Working on improvisation and lead guitar skills.
- Genre Specialization: Deciding to focus on a specific genre, such as Jazz or Classical.
A shift occurs as you focus on improving existing skills rather than constantly learning new ones. Practicing becomes more about refining your abilities.
2. Factors Influencing Learning Speed
Several factors can significantly affect how quickly you learn guitar. Understanding these can help you tailor your approach for more efficient learning.
- Natural Aptitude: Some people naturally pick up musical skills more quickly.
- Practice Habits: Consistent and focused practice is crucial.
- Learning Resources: Access to quality learning materials and instructors.
- Personal Goals: Clear, achievable goals can provide motivation and direction.
- Consistency: Regular practice, even for short periods, is more effective than sporadic long sessions. According to a study by the University of Texas at Austin, consistent practice leads to better retention and skill development.
- Quality of Practice: Focused, deliberate practice is more effective than mindless repetition.
- Feedback: Getting feedback from instructors or experienced players can help identify and correct mistakes.
3. Optimizing Your Practice Routine
A well-structured practice routine can significantly accelerate your learning.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your goals into smaller, achievable steps.
- Warm-Up Exercises: Start with warm-up exercises to prepare your fingers and hands.
- Focus on Fundamentals: Dedicate time to practicing basic chords, scales, and techniques.
- Learn Songs: Incorporate learning songs into your routine to apply your skills.
- Record Yourself: Recording your playing can help you identify areas for improvement.
- Vary Your Routine: Keep your practice routine interesting by incorporating different exercises and songs.
3.1 Example Practice Routine
Here’s an example of a 30-minute daily practice routine:
| Time (Minutes) | Activity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Warm-Up Exercises | Finger stretches, scales, and arpeggios to prepare your hands. |
| 10 | Chord Practice | Review and practice basic chords, focusing on smooth transitions. |
| 10 | Song Learning | Work on a song, breaking it down into manageable sections. |
| 5 | Improvisation/Technique | Experiment with improvisation or practice a specific technique (e.g., alternate picking). |

3.2 Utilizing Online Resources
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to help you structure your practice:
- Video Lessons: Access a variety of video lessons covering different techniques and styles.
- Downloadable Exercises: Download exercises and practice routines to supplement your learning.
- Community Forum: Connect with other guitarists and share tips and advice.
4. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Learning guitar can be challenging. Here are some common obstacles and how to address them:
- Finger Pain: Building calluses can be painful initially. Play in short bursts and use lighter gauge strings.
- Lack of Progress: Plateaus are normal. Focus on refining existing skills and exploring new techniques.
- Motivation: Set clear goals, find a practice buddy, or join a local guitar group.
- Time Constraints: Even 15-30 minutes of focused practice can be effective. Prioritize consistent, short sessions over sporadic long ones.
- Information Overload: Focus on a few key resources and techniques. Avoid trying to learn everything at once. LEARNS.EDU.VN can help you curate a focused learning path.
4.1 Seeking Guidance and Support
- Guitar Teachers: Consider taking lessons from a qualified guitar teacher for personalized guidance.
- Online Communities: Join online guitar communities to connect with other learners and share experiences.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Use the resources available on LEARNS.EDU.VN to supplement your learning.
5. Setting Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic expectations is crucial for staying motivated and avoiding discouragement. Remember that everyone progresses at their own pace.
5.1 Defining “Good” at Guitar
What does it mean to be good at guitar? The definition varies from person to person.
- Playing Favorite Songs: Being able to play songs you enjoy.
- Improvisation: Being able to improvise and create your own music.
- Technical Proficiency: Mastering advanced techniques and styles.
- Performance: Being able to perform confidently in front of others.
Focus on your personal goals and measure your progress against your own standards, not others.
5.2 Avoiding Comparisons
Comparing yourself to other guitarists can be discouraging. Focus on your own journey and celebrate your achievements.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress, no matter how small.
- Focus on Personal Growth: Concentrate on improving your own skills and knowledge.
- Use Comparisons as Motivation: If you find yourself comparing, use it as inspiration to push yourself further.
6. The Role of Deliberate Practice
Deliberate practice involves focusing on specific areas for improvement and actively working to enhance those skills.
- Identify Weaknesses: Pinpoint the areas where you struggle the most.
- Set Specific Goals: Create targeted goals for improving those weaknesses.
- Focused Attention: Practice with focused attention and avoid distractions.
- Seek Feedback: Get feedback from teachers or experienced players.
- Repeat and Refine: Continuously repeat and refine your practice based on feedback.
According to research from Florida State University, deliberate practice is a key factor in achieving expertise in any field.
6.1 Examples of Deliberate Practice Techniques
- Slow Practice: Practicing difficult passages at a slow tempo to ensure accuracy.
- Targeted Drills: Using specific drills to improve technique.
- Error Analysis: Identifying and correcting mistakes.
7. Different Learning Styles
Understanding your learning style can help you optimize your learning approach.
- Visual Learners: Learn best through visual aids such as videos, diagrams, and charts.
- Auditory Learners: Learn best through listening, such as lectures, recordings, and discussions.
- Kinesthetic Learners: Learn best through hands-on experience, such as playing and experimenting.
Identify your learning style and tailor your learning resources and methods accordingly.
7.1 Tailoring Your Learning Approach
- Visual Learners: Utilize video lessons and instructional diagrams available on LEARNS.EDU.VN.
- Auditory Learners: Listen to recordings of songs and practice along, and participate in online discussions.
- Kinesthetic Learners: Focus on hands-on practice and experimentation with different techniques.
8. The Importance of a Good Learning Environment
Creating a supportive and conducive learning environment is essential for success.
8.1 Physical Environment
- Dedicated Practice Space: Set up a dedicated practice space free from distractions.
- Comfortable Seating: Use a comfortable chair and ensure proper posture.
- Good Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting to reduce eye strain.
- Proper Equipment: Use a quality guitar and accessories.
8.2 Mental Environment
- Positive Mindset: Maintain a positive attitude and believe in your ability to learn.
- Patience: Be patient with yourself and understand that progress takes time.
- Persistence: Stay persistent and don’t give up when faced with challenges.
- Motivation: Find ways to stay motivated, such as setting goals, joining a community, or learning songs you enjoy.
9. Utilizing Technology to Enhance Learning
Technology offers numerous tools to enhance your guitar learning experience.
9.1 Guitar Learning Apps
- Interactive Lessons: Apps like Yousician and GuitarTricks offer interactive lessons and feedback.
- Chord Libraries: Apps like Ultimate Guitar provide access to vast chord libraries and tabs.
- Tuning Apps: Apps like GuitarTuna help you keep your guitar in tune.
9.2 Online Resources
- YouTube: Access a wealth of free guitar lessons and tutorials.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Explore a variety of guitar learning resources, including video lessons, downloadable exercises, and community forums.
- Online Communities: Join online guitar communities to connect with other learners and share experiences.
10. The Mental Game of Learning Guitar
Learning guitar is as much a mental challenge as it is a physical one. Developing a strong mental game can significantly enhance your progress.
10.1 Overcoming Self-Doubt
- Positive Self-Talk: Replace negative thoughts with positive affirmations.
- Focus on Progress: Concentrate on how far you’ve come, not how far you have to go.
- Celebrate Achievements: Acknowledge and celebrate your accomplishments, no matter how small.
10.2 Staying Motivated
- Set Clear Goals: Define your goals and break them down into smaller steps.
- Find a Practice Buddy: Practice with a friend to stay accountable and motivated.
- Learn Songs You Enjoy: Learning songs you love can make practice more enjoyable.
- Join a Community: Connect with other guitarists and share your experiences.
11. The Benefits of Learning Guitar
Learning guitar offers numerous benefits beyond just musical proficiency.
11.1 Cognitive Benefits
- Improved Memory: Learning guitar can improve memory and cognitive function.
- Enhanced Coordination: Playing guitar requires hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills.
- Increased Focus: Practicing guitar can improve focus and concentration.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Learning new techniques and songs requires problem-solving skills.
11.2 Emotional Benefits
- Stress Relief: Playing guitar can be a great way to relieve stress and relax.
- Self-Expression: Guitar allows you to express yourself creatively.
- Increased Confidence: Mastering new skills can boost your self-confidence.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Learning guitar provides a sense of accomplishment and pride.
12. Long-Term Development
Learning guitar is a lifelong journey. Embrace the process and continue to challenge yourself.
12.1 Setting New Goals
- Learn New Genres: Explore different genres of music to broaden your skills.
- Master Advanced Techniques: Focus on mastering advanced techniques such as sweep picking and tapping.
- Compose Your Own Music: Try composing your own songs to express your creativity.
- Perform Live: Challenge yourself by performing live in front of an audience.
12.2 Staying Engaged
- Join a Band: Playing in a band can be a great way to stay engaged and motivated.
- Take Lessons: Continue taking lessons to refine your skills and learn new techniques.
- Attend Workshops: Attend guitar workshops and seminars to learn from experienced players.
- Share Your Knowledge: Teach others what you’ve learned to reinforce your own understanding.
13. Expert Insights on Guitar Learning
To further illustrate the learning journey, let’s consider insights from expert guitarists and educators.
13.1 Quotes from Renowned Guitarists
- B.B. King: “The beautiful thing about learning is nobody can take it away from you.” This quote emphasizes the intrinsic value of continuous learning.
- Jimi Hendrix: “Music is my religion.” Hendrix’s passion underscores the importance of connecting with your instrument on a personal level.
- Tommy Emmanuel: “There’s always something to learn. If you’re not learning, you’re going backwards.” This highlights the necessity of constant improvement.
13.2 Advice from Guitar Educators
- Troy Stetina: “Practice doesn’t make perfect. Perfect practice makes perfect.” Stetina stresses the importance of focused and deliberate practice.
- Steve Vai: “Listen to your own music. Don’t listen to what anyone says.” Vai encourages individual expression and trusting your musical instincts.
- Jennifer Batten: “Be prepared to put in the time. There are no shortcuts.” Batten’s advice underscores the commitment required for mastering guitar.
These insights emphasize that learning guitar is a unique blend of passion, dedication, and continuous improvement. It’s not just about the hours you put in, but how you use those hours to refine your skills and express your musical voice.
14. Real-Life Examples of Guitar Learning Journeys
To provide a more relatable perspective, let’s look at some real-life examples of individuals learning guitar and their experiences.
14.1 Case Study 1: The Weekend Warrior
- Background: John is a 35-year-old professional who works full-time. He has always wanted to learn guitar but never had the time.
- Approach: John dedicates 30 minutes each day to practice. He uses online resources and a structured learning plan from LEARNS.EDU.VN.
- Challenges: Balancing work, family, and practice time.
- Results: Within six months, John can play several of his favorite songs. After a year, he joins a local amateur band.
14.2 Case Study 2: The Student
- Background: Maria is a 16-year-old student with a passion for music.
- Approach: Maria takes weekly guitar lessons and practices for an hour each day. She focuses on developing her technique and learning music theory.
- Challenges: Overcoming plateaus and staying motivated during busy school periods.
- Results: After two years, Maria excels in her guitar skills. She starts writing her own songs and performs at school events.
14.3 Case Study 3: The Retiree
- Background: Robert is a 65-year-old retiree looking for a new hobby.
- Approach: Robert takes online guitar courses and joins a local guitar club. He practices for about 45 minutes each day.
- Challenges: Dealing with physical limitations and lack of prior musical experience.
- Results: After three years, Robert can play a wide range of songs and enjoys performing for his family and friends.
These real-life examples illustrate that anyone can learn guitar with the right approach, resources, and dedication.
15. Staying Motivated Long-Term
Maintaining motivation over the long term is key to continuing progress and enjoyment in your guitar journey.
15.1 Setting Achievable Milestones
- Short-Term Goals: Set weekly or monthly goals, such as learning a new chord or song.
- Long-Term Goals: Define broader goals, such as mastering a specific genre or performing in public.
15.2 Joining a Community
- Local Guitar Clubs: Connect with fellow guitar enthusiasts in your area.
- Online Forums: Engage in online communities like the LEARNS.EDU.VN forums to share experiences and tips.
15.3 Rewarding Yourself
- New Gear: Treat yourself to new guitar accessories or equipment when you reach significant milestones.
- Concerts: Attend live music events to inspire and energize your playing.
15.4 Embracing the Journey
- Focus on Enjoyment: Remember why you started playing guitar and prioritize having fun.
- Accept Imperfection: Acknowledge that mistakes are part of the learning process and embrace them as opportunities for growth.
- Continuous Learning: Stay curious and always seek new challenges and opportunities to expand your musical horizons.
By setting achievable milestones, connecting with a community, rewarding your progress, and embracing the journey, you can maintain long-term motivation and continue to thrive in your guitar playing endeavors.
16. Integrating Music Theory
While it’s possible to learn guitar without delving deeply into music theory, understanding basic theoretical concepts can significantly enhance your playing and overall musical understanding.
16.1 Basic Music Theory Concepts
- Scales: Understanding scales (major, minor, pentatonic) helps you create melodies and improvise.
- Chords: Learning chord construction and progressions enables you to create harmonic structures.
- Rhythm: Grasping rhythmic patterns and time signatures is essential for playing in time and creating grooves.
- Key Signatures: Knowing key signatures helps you understand the relationships between chords and scales within a specific key.
16.2 Applying Music Theory to Guitar
- Chord Voicings: Experiment with different chord voicings to add color and depth to your playing.
- Improvisation: Use scales and modes to improvise over chord progressions.
- Songwriting: Apply music theory principles to write your own songs.
- Analyzing Music: Use music theory to analyze and understand the structure of your favorite songs.
16.3 Resources for Learning Music Theory
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer comprehensive music theory courses.
- Textbooks: “Music Theory for Dummies” and “The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Music Theory” are excellent resources for beginners.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Explore music theory tutorials and guides specifically tailored for guitarists.
By integrating music theory into your guitar learning journey, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of music and unlock new creative possibilities.
17. The Role of Ear Training
Ear training involves developing your ability to recognize and identify musical elements by ear. This skill is invaluable for guitarists, enhancing your ability to learn songs, improvise, and communicate with other musicians.
17.1 Basic Ear Training Exercises
- Interval Recognition: Learn to identify musical intervals (e.g., major third, perfect fifth) by ear.
- Chord Identification: Practice recognizing different chord types (e.g., major, minor, dominant) by ear.
- Melodic Dictation: Transcribe simple melodies by ear.
- Rhythmic Dictation: Notate rhythmic patterns that you hear.
17.2 Applying Ear Training to Guitar
- Learning Songs by Ear: Transcribe songs by ear, rather than relying solely on tabs or sheet music.
- Improvisation: Use your ear to guide your improvisations and respond to the music around you.
- Communication with Musicians: Develop the ability to communicate musical ideas effectively with other musicians.
- Identifying Chord Progressions: Learn to recognize chord progressions by ear, which can aid in songwriting and analysis.
17.3 Resources for Ear Training
- Online Tools: Websites like Teoria and musictheory.net offer interactive ear training exercises.
- Mobile Apps: Apps like Functional Ear Trainer and EarMaster provide structured ear training programs.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Utilize ear training exercises and tutorials specifically designed for guitarists.
Incorporating ear training into your guitar practice routine will sharpen your musical instincts and enhance your overall musicianship.
18. Exploring Different Guitar Styles and Genres
One of the most rewarding aspects of learning guitar is the opportunity to explore various musical styles and genres. This not only expands your musical palette but also challenges you to develop new techniques and approaches to playing.
18.1 Popular Guitar Styles and Genres
- Rock: Focuses on power chords, riffs, and solos.
- Blues: Emphasizes soulful melodies, improvisation, and expressive bending techniques.
- Jazz: Features complex chords, improvisation, and sophisticated harmonic concepts.
- Country: Involves fingerpicking patterns, pedal steel-inspired licks, and twangy tones.
- Classical: Centers on fingerstyle technique, arpeggios, and intricate melodic lines.
- Acoustic: Highlights fingerpicking patterns, strumming techniques, and songwriting.
18.2 Developing Genre-Specific Skills
- Rock: Practice playing power chords, pentatonic scales, and iconic rock riffs.
- Blues: Learn blues scales, bending techniques, and 12-bar blues progressions.
- Jazz: Study jazz chords, scales, and improvisation techniques.
- Country: Practice fingerpicking patterns, chicken pickin’ licks, and country chord progressions.
- Classical: Develop fingerstyle technique, arpeggios, and sight-reading skills.
- Acoustic: Master fingerpicking patterns, strumming techniques, and songwriting.
18.3 Resources for Exploring Different Styles
- YouTube: Search for tutorials and lessons on specific genres.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer courses on various guitar styles.
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Explore lessons and resources tailored to different guitar genres.
- Listen to Music: Immerse yourself in the music of different genres to absorb their unique characteristics.
By exploring different guitar styles and genres, you’ll not only broaden your musical horizons but also develop a more versatile and well-rounded approach to playing.
19. Performing Live
Performing live is a significant milestone for many guitarists. It provides an opportunity to share your music with others, gain valuable experience, and overcome stage fright.
19.1 Preparing for Live Performances
- Practice Your Set: Rehearse your songs thoroughly to ensure you can play them confidently and accurately.
- Memorize Your Music: Memorizing your songs allows you to connect with the audience and move freely on stage.
- Prepare Your Gear: Ensure that your guitar, amplifier, and other equipment are in good working order.
- Plan Your Stage Presence: Think about how you’ll move and interact with the audience during your performance.
19.2 Overcoming Stage Fright
- Practice Performing: Simulate live performances by playing for friends or family.
- Visualize Success: Imagine yourself playing well and enjoying the performance.
- Breathe Deeply: Take slow, deep breaths to calm your nerves before going on stage.
- Focus on the Music: Concentrate on playing the music and connecting with the audience, rather than worrying about mistakes.
19.3 Finding Performance Opportunities
- Open Mic Nights: Many bars and clubs host open mic nights, providing a low-pressure environment to perform.
- Local Venues: Contact local venues and offer to play a set.
- Online Platforms: Use online platforms like YouTube and SoundCloud to share your music with the world.
- Community Events: Volunteer to play at community events, such as festivals and charity fundraisers.
Performing live can be a rewarding and transformative experience for any guitarist. It challenges you to push your boundaries, connect with others through music, and grow as a musician.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about learning guitar, along with detailed answers to help guide you on your journey.
- How long does it take to learn basic guitar chords?
Most beginners can learn basic guitar chords within a few weeks to a couple of months, with consistent practice. - Is it harder to learn guitar as an adult?
Adults may face time constraints, but they often have more discipline and focus, making learning possible at any age. - How often should I practice guitar?
Practicing for at least 20-30 minutes daily is more effective than sporadic long sessions. - What is the best age to start learning guitar?
There’s no best age, but children around 6-8 years old can start with smaller-sized guitars. - Can I learn guitar without a teacher?
Yes, with online resources and dedication, you can learn guitar without a teacher, but a teacher can provide personalized guidance. - What are the most important things to learn as a beginner?
Basic chords, strumming patterns, and finger exercises are essential for beginners. - How do I build calluses on my fingers faster?
Play regularly in short bursts, and use lighter gauge strings initially to build calluses gradually. - What should I do if I feel stuck in my guitar playing?
Try learning new songs, techniques, or exploring different genres to break out of the rut. - Is it necessary to learn music theory to play guitar?
Not necessary, but music theory can enhance your understanding and creativity. - How can I stay motivated to keep learning guitar?
Set realistic goals, join a community, and learn songs you enjoy to stay motivated.
By addressing these common questions, we hope to provide you with the information and encouragement you need to embark on your guitar learning journey with confidence.
Learning guitar is a rewarding journey that combines dedication, practice, and the right resources. How Long On Average Does It Take To Learn Guitar? The answer varies, but with consistent effort and the support of LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can achieve your musical goals. Explore our comprehensive lessons, resources, and community to start your guitar adventure today. Visit us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212 or visit our website at learns.edu.vn for more information. Find the perfect course for you.