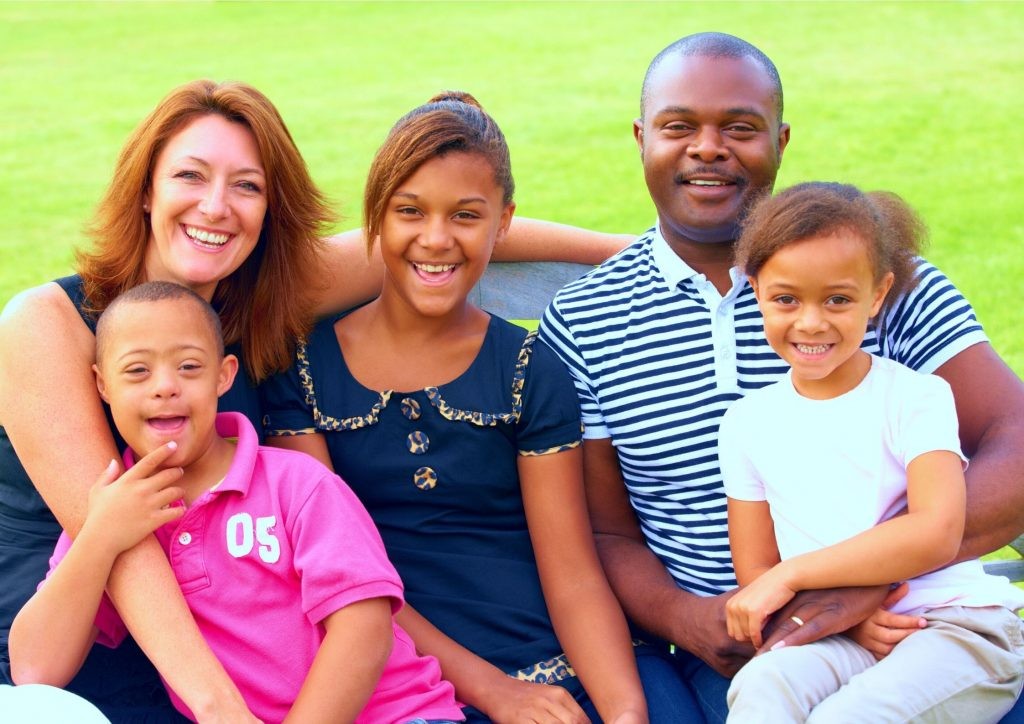
Navigating communication with individuals who have learning disabilities can be fulfilling. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we offer strategies that enhance understanding and foster inclusivity. By using patient, empathetic approaches, and adaptive techniques, you can build meaningful connections and empower effective communication with people of all abilities.
1. Understanding Learning Disabilities
What exactly are learning disabilities, and how do they impact communication?
Learning disabilities are neurological conditions that affect a person’s ability to understand, remember, or use information. They impact communication by affecting how individuals process and express thoughts, leading to challenges in reading, writing, speaking, and listening. According to the National Center for Learning Disabilities, approximately 1 in 5 children in the United States have a learning disability. These disabilities are intrinsic to the individual and presumed to be due to central nervous system dysfunction. Even though a learning disability may affect learning, it is important to know that does not reflect overall intelligence.
1.1 Intellectual Functions
How do intellectual functions influence communication skills in individuals with learning disabilities?
Intellectual functions encompass abilities like reasoning, problem-solving, and judgment, crucial for effective communication. When these functions are impacted by a learning disability, it affects how someone processes information, formulates responses, and understands complex concepts. For example, difficulties in problem-solving can lead to struggles in understanding the nuances of a conversation or responding appropriately to questions. A study by the American Psychological Association highlights that individuals with learning disabilities often require explicit instruction and support to develop these intellectual functions, directly improving their communication skills.
- Learning: Impacts the acquisition of new information, which can hinder vocabulary development and understanding of grammar rules.
- Problem-Solving: Affects the ability to navigate complex conversational topics or understand abstract concepts.
- Judgment: Can lead to difficulties in understanding social cues and responding appropriately in various social contexts.
1.2 Adaptive Functions
In what ways do adaptive functions influence daily communication for people with learning disabilities?
Adaptive functions are the skills needed to function independently in daily life, including communication, daily living activities, and independent living. For individuals with learning disabilities, impairments in these areas can present considerable barriers to expressing themselves and understanding others. For instance, challenges in daily living activities might make it difficult to follow instructions or participate in group discussions. Research from the Arc of the United States emphasizes the importance of tailored support to improve these adaptive functions, fostering greater independence and enhanced communication abilities.
- Communication: Impacts the ability to express thoughts and understand others, leading to difficulties in social interactions.
- Activities in Daily Living: Affects the capacity to follow instructions, understand schedules, and participate in routine tasks.
- Independent Living: Can limit the ability to manage personal affairs and communicate needs effectively in various settings.
2. Common Causes of Learning Disabilities
What are the primary factors that contribute to the development of learning disabilities?
Learning disabilities can arise from various factors, including genetic conditions, complications during pregnancy, issues during birth, and exposure to certain diseases or toxins. Understanding these causes is essential for early identification and intervention. According to the National Institutes of Health, genetic factors play a significant role in many learning disabilities. These causes influence brain development and function, leading to challenges in cognitive and adaptive skills.
2.1 Genetic Conditions
How do genetic conditions passed down through families influence the occurrence of learning disabilities?
Genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome and Fragile X syndrome, are significant contributors to learning disabilities. These conditions result from chromosomal or genetic mutations that affect brain development. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that genetic factors account for a substantial percentage of intellectual disabilities.
- Down Syndrome: Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to intellectual disability and physical abnormalities.
- Fragile X Syndrome: Results from a mutation in the FMR1 gene, causing a range of developmental and intellectual disabilities.
2.2 Complications During Pregnancy
What prenatal factors can lead to the development of learning disabilities in children?
Complications during pregnancy, such as infections, exposure to toxins, or malnutrition, can disrupt fetal brain development. Maternal alcohol consumption, for instance, can result in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs), leading to a range of physical, behavioral, and intellectual disabilities. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of prenatal care to mitigate these risks.
- Alcohol Exposure: Can cause Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, characterized by intellectual disabilities and physical abnormalities.
- Infections: Maternal infections, such as rubella or cytomegalovirus (CMV), can interfere with fetal brain development.
- Malnutrition: Insufficient nutrient intake during pregnancy can impair the development of the fetal nervous system.
2.3 Problems During Birth
How can complications during the birthing process impact a child’s cognitive development?
Problems during birth, such as oxygen deprivation (hypoxia) or premature delivery, can cause brain damage and lead to learning disabilities. Hypoxia, in particular, can result in severe neurological impairments. The American Academy of Pediatrics highlights the importance of monitoring and managing birth complications to minimize the risk of long-term disabilities.
- Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia): Insufficient oxygen to the brain can cause irreversible damage and intellectual disability.
- Premature Delivery: Premature infants are at higher risk for developmental delays and learning disabilities due to incomplete brain development.
- Birth Trauma: Physical injuries during birth can lead to brain damage and subsequent learning disabilities.
2.4 Diseases or Toxic Exposure
In what ways can diseases and environmental toxins affect cognitive abilities and lead to learning disabilities?
Exposure to certain diseases, such as measles or meningitis, and toxins like lead or mercury can impair brain function and cause learning disabilities. These factors can damage the central nervous system, leading to cognitive and developmental delays. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides guidelines for reducing exposure to environmental toxins to protect children’s health.
- Measles and Meningitis: Infections that can cause inflammation of the brain, leading to intellectual disabilities.
- Lead Exposure: Can damage the brain and nervous system, resulting in learning and behavioral problems.
- Mercury Exposure: Similar to lead, mercury can cause neurological damage and developmental delays.
3. Recognizing Common Types of Learning Disabilities
What are the common types of learning disabilities that educators and caregivers should be aware of?
Several types of learning disabilities affect communication and cognitive development. Recognizing these conditions helps in providing targeted support and interventions. The Learning Disabilities Association of America (LDA) identifies specific learning disabilities that impact reading, writing, math, and other essential academic skills.
3.1 Fragile X Syndrome
What are the key characteristics and communication challenges associated with Fragile X Syndrome?
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition that causes a range of developmental problems, including learning disabilities and cognitive impairment. Individuals with Fragile X syndrome often experience difficulties with communication, social interaction, and sensory processing. The National Fragile X Foundation offers resources and support for families and individuals affected by this condition.
- Developmental Delay: Slower development of speech, language, and motor skills.
- Communication Difficulties: Challenges in expressive and receptive language, affecting the ability to communicate effectively.
- Anxiety and ADHD: These conditions can further complicate communication and social interactions.
3.2 Down Syndrome
How does Down Syndrome affect learning and communication skills, and what strategies can support these areas?
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to intellectual disability and physical abnormalities. People with Down syndrome often have delays in speech and language development, making communication challenging. The National Down Syndrome Society (NDSS) provides information and support to improve the quality of life for individuals with Down syndrome.
- Intellectual Disability: Impacts cognitive functions, including learning and problem-solving.
- Speech and Language Delays: Slower development of language skills, requiring early intervention and support.
- Increased Risk of Respiratory and Heart Conditions: These health issues can indirectly affect communication and overall development.
3.3 Developmental Delay
What are the signs of developmental delay, and how can early intervention improve outcomes?
Developmental delay refers to a condition where a child develops slower than other children of the same age in one or more areas, such as motor skills, language, or social skills. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for children with developmental delays. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasizes the importance of early detection and intervention services.
- Motor Skills: Delays in walking, crawling, or other physical activities.
- Learning: Difficulties in acquiring new information and academic skills.
- Communication: Slower development of speech and language skills, impacting the ability to interact with others.
3.4 Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
How does prenatal alcohol exposure lead to Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, and what are the resulting challenges?
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is an intellectual disability caused by prenatal alcohol exposure. Children with FAS may experience a range of physical, behavioral, and intellectual disabilities. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) provides resources and information about FAS and its prevention.
- Poor Memory and Judgment: Affects the ability to learn from experiences and make sound decisions.
- Learning Disabilities: Challenges in academic performance and cognitive development.
- Behavioral Challenges: Difficulties with attention, impulse control, and social interactions.
4. Effective Communication Strategies
What are some effective communication strategies for interacting with people who have learning disabilities?
Communicating effectively with people who have learning disabilities requires patience, empathy, and understanding. Tailoring your communication style to meet their needs can foster meaningful interactions. The National Disability Rights Network (NDRN) advocates for the rights of people with disabilities, including the right to effective communication.
4.1 Person-First Language
Why is it important to use person-first language when referring to individuals with learning disabilities?
Using person-first language emphasizes the individual rather than the disability, promoting respect and dignity. This approach ensures that people are not defined solely by their disability. The American Psychological Association (APA) recommends using person-first language in all professional and academic contexts.
- Focus on the Individual: Emphasize that the person is more than their disability.
- Respect and Dignity: Promote a positive and inclusive attitude.
- Avoid Stereotypes: Challenge negative assumptions about people with disabilities.
4.2 Understanding Communication Styles
How can understanding different communication styles improve interactions with people who have learning disabilities?
People with learning disabilities may have varied communication styles, including non-verbal cues, sign language, or communication devices. Understanding these styles and adapting your approach accordingly can enhance communication. The Assistive Technology Industry Association (ATIA) provides resources on assistive communication devices and strategies.
- Sign Language: A visual language used by people who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- Written Text: Providing written information can help those who struggle with auditory processing.
- Visual Cues: Using pictures, diagrams, and other visual aids to support understanding.
- Communication Devices: Assistive technology devices that help individuals express themselves.
4.3 Active Listening Techniques
What active listening techniques can facilitate better communication and understanding?
Active listening involves fully concentrating on what the speaker is saying, showing that you are engaged and interested. This includes using open body language, making eye contact, and responding appropriately. The National Institute for Mental Health (NIMH) highlights the importance of active listening in building rapport and trust.
- Open Body Language: Demonstrating attentiveness through posture and gestures.
- Direct Eye Contact: Maintaining eye contact to show you are engaged.
- Non-Verbal Reactions: Nodding and other cues to indicate understanding.
- Deferring Judgments: Avoiding premature judgments and focusing on understanding the speaker’s perspective.
4.4 Emotional Intelligence
How can emotional intelligence enhance communication and create supportive interactions?
Emotional intelligence involves understanding and managing your own emotions, as well as recognizing and responding to the emotions of others. This skill is crucial for effective communication and building supportive relationships. The Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence provides resources and training on emotional intelligence.
- Encourage Elaboration: Prompting the speaker to provide more details.
- Seek Clarification: Asking questions to ensure understanding.
- Empathy: Showing understanding and compassion.
- Calmness: Maintaining a calm demeanor to foster a safe and supportive environment.
4.5 Inclusive Communication Practices
What inclusive communication practices can foster a sense of belonging and respect?
Inclusive communication involves creating an environment where everyone feels valued and respected. This includes setting clear expectations, being patient, and asking for their opinions. The United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities promotes inclusive practices in all areas of life.
- Setting Expectations: Clearly outlining the topic and purpose of the conversation.
- Patience: Giving the person time to express themselves.
- Seeking Opinions: Asking for their thoughts and feelings.
- Enthusiasm: Showing genuine interest and support.
5. Practical Tips for Enhancing Communication
What are some actionable tips to improve communication with individuals with learning disabilities?
Improving communication with people who have learning disabilities involves adapting your approach and being mindful of their needs. These practical tips can help foster better interactions and understanding.
5.1 Simplify Your Language
How can using simple language improve comprehension and reduce confusion?
Using clear and simple language helps in conveying your message effectively. Avoid jargon, complex sentences, and abstract terms. Instead, use straightforward vocabulary and break down information into manageable chunks.
- Use Common Words: Opt for everyday words that are easy to understand.
- Short Sentences: Keep sentences concise and to the point.
- Avoid Jargon: Refrain from using technical terms or industry-specific language.
- Be Concrete: Use concrete examples and avoid abstract concepts.
5.2 Use Visual Aids
How can visual aids support communication and make information more accessible?
Visual aids such as pictures, diagrams, and videos can enhance understanding and retention. These tools are particularly useful for individuals who struggle with auditory processing or abstract concepts.
- Pictures: Use images to illustrate concepts and ideas.
- Diagrams: Create visual representations of processes or relationships.
- Videos: Employ short videos to demonstrate tasks or explain complex topics.
- Flashcards: Utilize flashcards to reinforce learning and memory.
5.3 Provide Extra Time
Why is it important to provide extra time for individuals with learning disabilities to respond?
Allowing extra time for processing and responding is crucial, as individuals with learning disabilities may require more time to understand and formulate their thoughts. Rushing them can lead to frustration and miscommunication.
- Avoid Rushing: Be patient and allow them to respond at their own pace.
- Pause Frequently: Give them opportunities to process information.
- Repeat Information: Reinforce key points by repeating them as needed.
- Encourage Questions: Create a safe space for them to ask questions.
5.4 Break Down Tasks
How can breaking down complex tasks into smaller steps improve understanding and success?
Breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable steps can make them less overwhelming and easier to understand. This approach promotes a sense of accomplishment and encourages continued effort.
- Identify Sub-Tasks: Break down the overall task into smaller components.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Provide clear, sequential instructions for each step.
- Visual Schedules: Use visual schedules to illustrate the sequence of tasks.
- Positive Reinforcement: Offer praise and encouragement for each completed step.
5.5 Create a Quiet Environment
How does creating a quiet environment reduce distractions and improve focus during communication?
Minimizing distractions and creating a quiet environment can significantly improve focus and concentration. This is particularly important for individuals with sensory sensitivities or attention deficits.
- Reduce Noise: Minimize background noise and distractions.
- Private Space: Choose a quiet, private area for conversations.
- Limit Visual Stimuli: Remove unnecessary visual clutter.
- Comfortable Setting: Ensure the environment is comfortable and conducive to communication.
6. Benefits of Effective Communication
What are the overall benefits of enhancing communication with people with learning disabilities?
Effective communication fosters independence, improves relationships, and enhances overall well-being. It empowers individuals with learning disabilities to express themselves, participate fully in society, and achieve their potential.
6.1 Increased Independence
How does effective communication contribute to greater independence in daily life?
When individuals can communicate their needs and preferences effectively, they become more self-reliant and capable of managing their daily activities. This increased independence enhances their quality of life and reduces their reliance on others.
- Self-Advocacy: Ability to express their needs and rights.
- Decision-Making: Capacity to make informed choices.
- Problem-Solving: Skills to address challenges independently.
6.2 Improved Relationships
How does good communication strengthen relationships and foster social connections?
Effective communication builds trust, strengthens relationships, and fosters social connections. When individuals feel understood and valued, they are more likely to form meaningful relationships and participate in social activities.
- Building Trust: Creating a sense of safety and security.
- Reducing Isolation: Encouraging social interaction and participation.
- Enhancing Empathy: Promoting understanding and compassion.
6.3 Enhanced Well-Being
How does effective communication contribute to overall well-being and emotional health?
Being able to communicate effectively reduces frustration, promotes emotional well-being, and enhances overall quality of life. It empowers individuals to express their feelings, seek support, and participate fully in their communities.
- Reducing Frustration: Minimizing communication barriers and misunderstandings.
- Promoting Self-Esteem: Enhancing confidence and self-worth.
- Improving Mental Health: Reducing stress and anxiety.
7. Resources and Support
What resources and support systems are available for individuals with learning disabilities and their families?
Numerous organizations and resources offer support, information, and advocacy for individuals with learning disabilities and their families. These resources can provide valuable assistance in navigating the challenges associated with learning disabilities.
7.1 Educational Support
What educational resources and accommodations are available to support students with learning disabilities?
Educational support includes specialized instruction, accommodations, and assistive technology to help students with learning disabilities succeed academically. These resources ensure that students receive the individualized support they need to achieve their full potential.
- Individualized Education Programs (IEPs): Customized plans that outline specific learning goals and accommodations.
- Assistive Technology: Tools and devices that support learning and communication.
- Specialized Instruction: Tailored teaching methods and strategies.
7.2 Community Services
What community services provide support and resources for individuals with learning disabilities and their families?
Community services offer a range of support, including vocational training, counseling, and recreational activities. These services help individuals with learning disabilities participate fully in their communities and lead fulfilling lives.
- Vocational Training: Programs that provide job skills and employment support.
- Counseling Services: Mental health support to address emotional and behavioral challenges.
- Recreational Activities: Opportunities for social interaction and leisure.
7.3 Advocacy Organizations
What advocacy organizations work to protect the rights and promote the interests of individuals with learning disabilities?
Advocacy organizations work to ensure that the rights of people with learning disabilities are protected and their voices are heard. These organizations advocate for policy changes, raise awareness, and provide legal support.
- Learning Disabilities Association of America (LDA): Provides resources, support, and advocacy for individuals with learning disabilities.
- National Disability Rights Network (NDRN): Protects and advocates for the rights of people with disabilities.
- The Arc of the United States: Advocates for the rights and full participation of people with intellectual and developmental disabilities.
8. Assistive Technology in Communication
What role does assistive technology play in improving communication for individuals with learning disabilities?
Assistive technology (AT) includes devices and tools that help individuals with learning disabilities overcome communication barriers. AT can range from simple aids like pencil grips to sophisticated communication devices.
8.1 Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices
How do AAC devices assist individuals with limited verbal communication skills?
AAC devices help individuals who have difficulty with verbal communication express themselves. These devices can include speech-generating devices (SGDs) and communication boards.
- Speech-Generating Devices (SGDs): Electronic devices that produce synthesized speech.
- Communication Boards: Boards with pictures or symbols that individuals can point to in order to communicate.
8.2 Speech-to-Text Software
How does speech-to-text software facilitate written communication for individuals with learning disabilities?
Speech-to-text software converts spoken words into written text, making it easier for individuals with writing difficulties to communicate in written form.
- Real-Time Transcription: Converts speech into text in real-time.
- Accessibility: Provides an alternative method for written communication.
8.3 Text-to-Speech Software
How does text-to-speech software enhance comprehension and accessibility of written materials?
Text-to-speech software reads written text aloud, which can be beneficial for individuals with reading difficulties.
- Enhanced Comprehension: Helps individuals understand written material by hearing it read aloud.
- Accessibility: Makes written content accessible to those with visual impairments or reading disabilities.
9. Building Inclusive Environments
How can we create inclusive environments that support and celebrate diversity in communication?
Creating inclusive environments requires a commitment to understanding, acceptance, and support. By promoting inclusivity, we can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to communicate and participate fully in society.
9.1 Promoting Awareness
How does raising awareness about learning disabilities foster understanding and empathy?
Raising awareness helps to dispel myths and misconceptions about learning disabilities. It also promotes understanding and empathy, creating a more inclusive and accepting society.
- Education Campaigns: Initiatives to educate the public about learning disabilities.
- Community Events: Activities that promote awareness and inclusion.
9.2 Encouraging Acceptance
How can we encourage acceptance and respect for individuals with diverse communication styles?
Encouraging acceptance involves valuing diversity and respecting individual differences. It also means creating a culture where everyone feels welcome and supported.
- Inclusive Language: Using respectful and person-first language.
- Valuing Diversity: Recognizing and celebrating individual differences.
9.3 Providing Support
What support systems can be put in place to ensure that individuals with learning disabilities have the resources they need to communicate effectively?
Providing support involves creating accessible environments, offering assistive technology, and providing training and resources for families, educators, and caregivers.
- Accessible Environments: Ensuring that physical spaces are accessible and communication materials are available in multiple formats.
- Assistive Technology: Providing access to assistive technology devices and training on how to use them effectively.
- Training and Resources: Offering training for families, educators, and caregivers on how to support individuals with learning disabilities.
10. Overcoming Communication Barriers
What are some common communication barriers and how can they be overcome?
Communication barriers can prevent effective interaction between individuals with and without learning disabilities. Understanding these barriers and implementing strategies to overcome them is crucial for fostering inclusivity.
10.1 Language Barriers
How can language barriers be addressed to improve communication with individuals with learning disabilities?
Language barriers occur when the language used is too complex or unfamiliar. To address this, use simple language, visual aids, and repetition.
- Simple Language: Use clear and straightforward language.
- Visual Aids: Incorporate pictures and diagrams to illustrate concepts.
- Repetition: Repeat key information as needed.
10.2 Environmental Barriers
How do environmental factors such as noise and distractions impact communication, and how can these be minimized?
Environmental barriers include noise, distractions, and uncomfortable settings that can interfere with communication. Minimize these barriers by creating a quiet, comfortable environment.
- Reduce Noise: Minimize background noise and distractions.
- Comfortable Setting: Ensure the environment is comfortable and conducive to communication.
- Private Space: Choose a quiet, private area for conversations.
10.3 Attitudinal Barriers
How do attitudes and misconceptions create barriers to communication, and how can these be challenged?
Attitudinal barriers involve negative beliefs and stereotypes about learning disabilities. Challenge these barriers by promoting awareness, encouraging empathy, and fostering a culture of acceptance.
- Promote Awareness: Educate others about learning disabilities and their impact.
- Encourage Empathy: Help people understand the experiences of individuals with learning disabilities.
- Foster Acceptance: Create a culture of acceptance and respect for diversity.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of clear, effective communication with everyone, regardless of their abilities. By adopting these strategies, you can enhance your interactions and foster more inclusive and supportive relationships.
Ready to learn more and enhance your communication skills? Visit learns.edu.vn to discover a wealth of resources, including detailed guides, expert advice, and interactive courses designed to help you communicate effectively with individuals who have learning disabilities. Together, we can build a more understanding and inclusive world. For further assistance, contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 555-555-1212.
FAQ: Communicating with People with Learning Disabilities
Q1: What are learning disabilities?
Learning disabilities are neurological conditions that affect a person’s ability to understand, remember, or use information, impacting communication skills.
Q2: What causes learning disabilities?
Causes include genetic conditions, complications during pregnancy, issues during birth, and exposure to certain diseases or toxins.
Q3: What are some common types of learning disabilities?
Common types include Fragile X syndrome, Down syndrome, developmental delay, and Fetal Alcohol Syndrome.
Q4: How can I communicate more effectively with someone who has a learning disability?
Use person-first language, understand their communication style, practice active listening, and show emotional intelligence.
Q5: What are some practical tips for enhancing communication?
Simplify your language, use visual aids, provide extra time, break down tasks, and create a quiet environment.
Q6: What are the benefits of effective communication?
Increased independence, improved relationships, and enhanced overall well-being.
Q7: What resources and support are available for individuals with learning disabilities?
Educational support, community services, and advocacy organizations provide valuable assistance.
Q8: How can assistive technology help?
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) devices, speech-to-text, and text-to-speech software can improve communication.
Q9: How can we create more inclusive environments?
Promote awareness, encourage acceptance, and provide necessary support systems.
Q10: What are some common communication barriers and how can they be overcome?
Language, environmental, and attitudinal barriers can be overcome through simple language, quiet environments, and promoting empathy and understanding.