Learning How To Learn Constellations effectively involves a blend of techniques and resources, enhanced by educational platforms like LEARNS.EDU.VN, to transform the daunting task of celestial navigation into an accessible and enjoyable journey. This article will guide you through methods to master constellation identification, utilizing mnemonic devices, star-hopping strategies, and technological tools, ensuring you can confidently navigate the night sky.
1. What Are Constellations and Why Learn Them?
Constellations are patterns of stars visible from Earth that have been grouped together and given names, often after mythological figures, animals, or objects. Learning constellations opens up a deeper understanding of astronomy, enhances your appreciation of the night sky, and connects you to ancient cultures that used these patterns for navigation, storytelling, and timekeeping.
1.1 Historical Significance of Constellations
Throughout history, constellations have played a vital role in human civilization:
- Navigation: Ancient mariners relied on constellations to navigate the seas.
- Agriculture: Farmers used the positions of constellations to determine planting and harvesting seasons.
- Mythology: Many cultures have rich stories and myths associated with different constellations, reflecting their beliefs and worldview.
Understanding these historical contexts adds depth to your learning experience. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources that delve into the cultural and historical significance of constellations, providing a richer, more meaningful learning journey.
1.2 Benefits of Learning Constellations
There are several benefits to learning constellations:
- Enhanced Night Sky Observation: Knowing constellations allows you to locate other celestial objects like planets, nebulae, and galaxies.
- Improved Spatial Awareness: Identifying constellations improves your spatial orientation and understanding of the universe.
- Intellectual Stimulation: Learning about constellations can be a rewarding intellectual pursuit, expanding your knowledge of astronomy and related fields.
- Relaxation and Mindfulness: Observing the night sky can be a calming and meditative experience.
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides structured learning paths and expert guidance to help you achieve these benefits efficiently.
2. Where to Begin Learning Constellations?
Starting your journey to learn constellations requires a strategic approach. Begin by familiarizing yourself with essential tools and resources, selecting easy-to-identify constellations, and focusing on a specific region of the sky.
2.1 Essential Tools and Resources
To effectively learn constellations, gather the following tools and resources:
- Star Charts and Planispheres: These tools provide a visual representation of the night sky, helping you locate constellations at different times of the year.
- Astronomy Apps: Mobile apps like SkyView Lite, Star Walk 2, and Stellarium allow you to point your device at the sky and identify constellations in real-time.
- Binoculars: Binoculars enhance your viewing experience, revealing fainter stars and celestial objects.
- Red Flashlight: A red flashlight preserves your night vision, allowing you to see stars more clearly.
- Guidebooks: Books such as “National Audubon Society Field Guide to the Night Sky” and “Turn Left at Orion” provide detailed information and guidance.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers curated lists of recommended tools and resources, ensuring you have everything you need to start your astronomical adventure.
2.2 Start with Easy-to-Identify Constellations
Begin with prominent and easily recognizable constellations like:
- The Big Dipper (Ursa Major): This asterism is not a constellation, but a part of Ursa Major, and it is a great starting point due to its distinctive shape and visibility.
- Orion: Recognizable by its three bright belt stars and surrounding rectangle of stars.
- Cassiopeia: Shaped like a W or M, depending on its orientation.
- Leo: Features a distinctive sickle-shaped asterism.
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides detailed guides and interactive exercises to help you master these foundational constellations.
2.3 Focus on a Specific Region of the Sky
Instead of trying to learn the entire sky at once, concentrate on a specific region, such as the northern or southern sky. This focused approach allows you to become familiar with the constellations in that area before moving on.
3. How to Learn Constellations: Step-by-Step Guide
A structured approach can greatly enhance your learning experience and retention. This step-by-step guide provides a comprehensive strategy for mastering constellations:
3.1 Learn the Brightest Stars First
Start by identifying the brightest stars in the night sky. These stars serve as anchor points, making it easier to locate and identify surrounding constellations.
Table: Brightest Stars and Their Constellations
| Star Name | Constellation | Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| Sirius | Canis Major | -1.46 |
| Canopus | Carina | -0.72 |
| Alpha Centauri | Centaurus | -0.27 |
| Arcturus | Boötes | -0.04 |
| Vega | Lyra | 0.03 |
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers detailed profiles of each star, including their coordinates, spectral type, and distance from Earth.
3.2 Use Star-Hopping Techniques
Star-hopping involves using known stars to find other stars and constellations. This method is particularly useful for locating fainter constellations that are not immediately visible.
Example: To find Polaris (the North Star), start with the Big Dipper. Draw a line from Merak to Dubhe (the two stars forming the end of the Dipper’s bowl) and extend it about five times the distance between them. This line leads directly to Polaris.
3.3 Master Mnemonic Devices and Stories
Mnemonic devices and stories can help you remember the names and locations of constellations. Create your own or use existing ones.
Examples:
- Cassiopeia: Imagine a queen sitting on her throne, forming the W shape.
- Orion: Think of Orion as a hunter with a belt and sword.
- Leo: Picture a lion resting with its head outlined by the sickle asterism.
LEARNS.EDU.VN features a collection of mnemonic devices and cultural stories associated with each constellation, making learning more engaging and memorable.
3.4 Practice Regularly
Consistency is key. Spend time observing the night sky regularly. Even 15-30 minutes a few times a week can make a significant difference.
Tips for Regular Practice:
- Choose a Dark Location: Minimize light pollution for better visibility.
- Use a Star Chart or App: Guide your observations.
- Keep a Sky Journal: Record your observations and track your progress.
3.5 Join Astronomy Clubs and Communities
Joining an astronomy club or online community provides opportunities to learn from experienced observers, ask questions, and share your experiences.
Benefits of Joining a Community:
- Expert Guidance: Learn from seasoned astronomers.
- Shared Experiences: Connect with others who share your passion.
- Observing Events: Participate in group observing sessions.
LEARNS.EDU.VN hosts a forum where you can connect with fellow astronomy enthusiasts, ask questions, and share your discoveries.
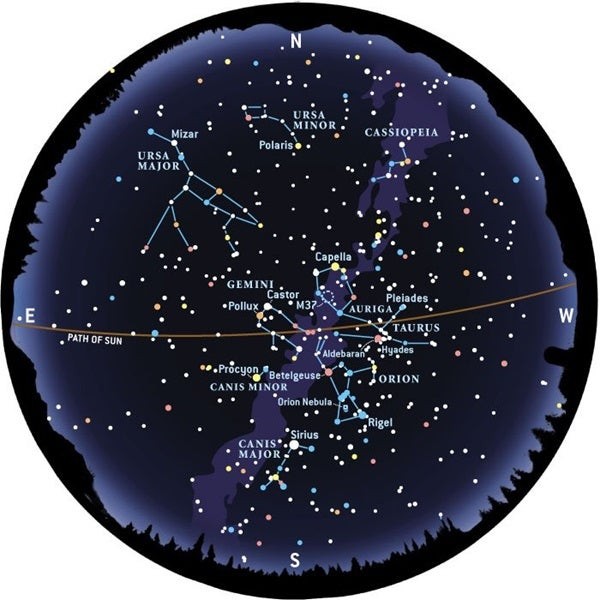
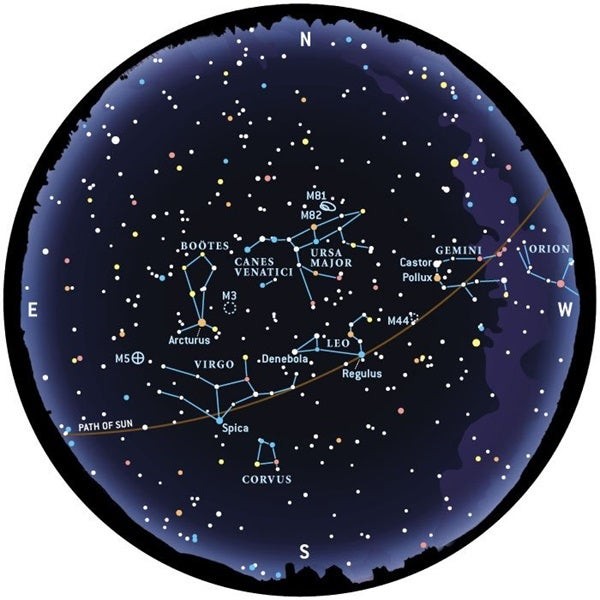
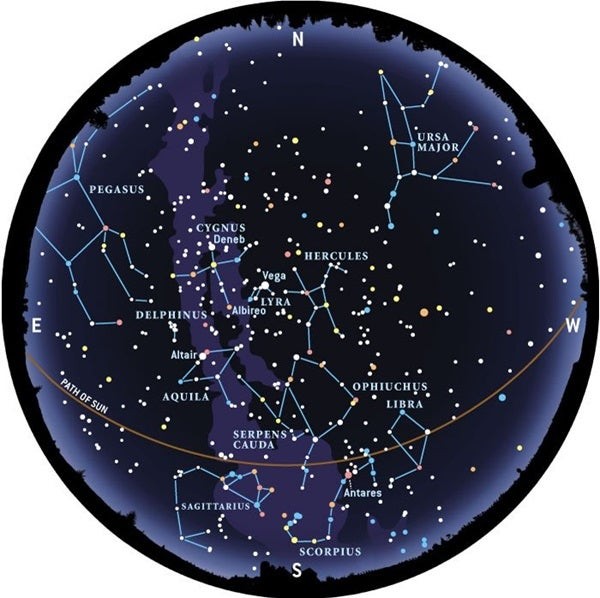
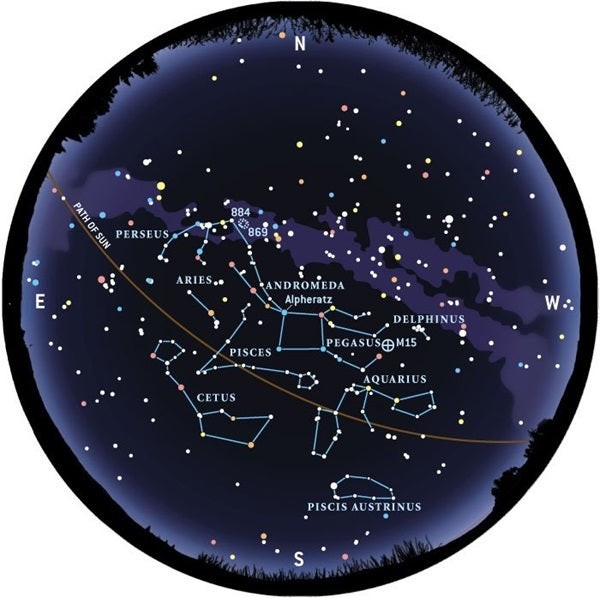
4. Constellations Through the Seasons
The constellations visible in the night sky change with the seasons due to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Understanding these seasonal changes is crucial for effective constellation identification.
4.1 Spring Constellations
Key Constellations:
- Leo: Prominent in the southern sky, featuring the sickle asterism.
- Boötes: Shaped like a kite, with the bright star Arcturus.
- Virgo: A large constellation containing the star Spica.
- Corvus: A small, distinctive constellation resembling a sail.
4.2 Summer Constellations
Key Constellations:
- Lyra: Home to the bright star Vega, forming part of the Summer Triangle.
- Cygnus: Also known as the Swan, contains the star Deneb and the Northern Cross asterism.
- Aquila: Features the star Altair, another component of the Summer Triangle.
- Sagittarius: Resembles a teapot and marks the location of the Milky Way’s center.
- Scorpius: Easily recognizable by its J-shape and the red giant star Antares.
4.3 Autumn Constellations
Key Constellations:
- Pegasus: Known for the Great Square asterism.
- Andromeda: Home to the Andromeda Galaxy, the closest major galaxy to the Milky Way.
- Delphinus: A small, dolphin-shaped constellation.
4.4 Winter Constellations
Key Constellations:
- Orion: Dominates the winter sky with its bright stars and the Orion Nebula.
- Canis Major: Contains Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky.
- Taurus: Features the Hyades star cluster and the star Aldebaran.
- Auriga: A pentagon-shaped constellation with the bright star Capella.
- Gemini: Home to the bright stars Castor and Pollux.
- Canis Minor: Contains the star Procyon.
Table: Seasonal Constellations
| Season | Key Constellations |
|---|---|
| Spring | Leo, Boötes, Virgo, Corvus |
| Summer | Lyra, Cygnus, Aquila, Sagittarius, Scorpius |
| Autumn | Pegasus, Andromeda, Delphinus |
| Winter | Orion, Canis Major, Taurus, Auriga, Gemini, Canis Minor |
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides seasonal star charts and observing guides, ensuring you can identify constellations year-round.
5. Advanced Techniques for Constellation Learning
Once you have a solid foundation, explore advanced techniques to deepen your knowledge and skills:
5.1 Deep-Sky Objects within Constellations
Many constellations contain fascinating deep-sky objects, such as nebulae, galaxies, and star clusters. Identifying these objects adds another layer of complexity and excitement to your observations.
Examples:
- Orion Nebula (M42): Located in the constellation Orion, easily visible through binoculars or a small telescope.
- Pleiades (M45): A beautiful open star cluster in the constellation Taurus.
- Andromeda Galaxy (M31): The closest major galaxy to the Milky Way, located in the constellation Andromeda.
5.2 Astrophotography
Astrophotography involves capturing images of the night sky. This hobby combines astronomy with photography, allowing you to create stunning images of constellations and deep-sky objects.
Tips for Astrophotography:
- Use a Telescope or Camera Lens: Capture detailed images.
- Use a Tracking Mount: Compensate for Earth’s rotation.
- Learn Image Processing Techniques: Enhance your images.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers courses on astrophotography, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced image processing.
5.3 Understanding Celestial Coordinates
Celestial coordinates, such as right ascension and declination, are used to pinpoint the exact location of celestial objects. Understanding these coordinates allows you to locate specific stars and constellations with precision.
Key Concepts:
- Right Ascension (RA): Similar to longitude on Earth, measured in hours, minutes, and seconds.
- Declination (Dec): Similar to latitude on Earth, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides interactive tools and tutorials to help you master celestial coordinates.
6. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Learning constellations can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can overcome these obstacles:
6.1 Light Pollution
Light pollution is a major obstacle for stargazers. Minimize its impact by:
- Observing from Dark Locations: Travel to areas with minimal light pollution.
- Using Light Pollution Filters: Enhance contrast and reduce glare.
- Observing During New Moon: The absence of moonlight improves visibility.
6.2 Difficulty Remembering Constellations
Improve retention by:
- Using Mnemonic Devices: Create memorable associations.
- Practicing Regularly: Reinforce your knowledge.
- Reviewing Star Charts: Refresh your memory.
6.3 Identifying Faint Constellations
Enhance your ability to see faint constellations by:
- Allowing Time for Dark Adaptation: Spend at least 20-30 minutes in darkness.
- Using Binoculars: Increase visibility.
- Observing on Clear Nights: Avoid hazy or cloudy conditions.
7. The Role of Technology in Learning Constellations
Technology has revolutionized the way we learn about the night sky. Astronomy apps, planetarium software, and online resources make it easier than ever to identify constellations and explore the universe.
7.1 Astronomy Apps
Astronomy apps provide real-time information about the night sky, allowing you to identify constellations, planets, and other celestial objects simply by pointing your device at the sky.
Popular Astronomy Apps:
- SkyView Lite: A free app that uses your device’s camera to overlay constellations and stars on the sky.
- Star Walk 2: A paid app with stunning graphics and detailed information about celestial objects.
- Stellarium: A free, open-source planetarium app that simulates the night sky from any location on Earth.
7.2 Planetarium Software
Planetarium software allows you to simulate the night sky on your computer, providing a virtual observatory that you can use to explore constellations and plan observing sessions.
Popular Planetarium Software:
- Stellarium: A free, open-source software that offers realistic simulations of the night sky.
- Cartes du Ciel: A free software with advanced features for experienced observers.
- Celestia: A 3D astronomy program that allows you to explore the universe in detail.
7.3 Online Resources
Online resources such as websites, videos, and interactive tutorials provide a wealth of information about constellations and astronomy.
Valuable Online Resources:
- LEARNS.EDU.VN: Offers structured learning paths, expert guidance, and a community forum.
- Astronomy.com: Provides articles, news, and observing tips for astronomy enthusiasts.
- Sky & Telescope: Features in-depth articles, star charts, and observing guides.
8. Tips for Educators: Teaching Constellations to Students
If you are an educator, teaching constellations can be an engaging and rewarding experience for your students. Here are some tips for making your lessons effective and fun:
8.1 Use Visual Aids
Visual aids such as star charts, planetarium software, and images of constellations can help students visualize the night sky and understand the patterns of stars.
8.2 Incorporate Hands-On Activities
Hands-on activities such as building constellation models, creating star finders, and conducting night sky observations can make learning more interactive and memorable.
8.3 Tell Stories and Myths
Sharing the stories and myths associated with constellations can capture students’ imaginations and help them remember the names and locations of the constellations.
8.4 Organize Observing Sessions
Organizing night sky observing sessions can provide students with real-world experience in identifying constellations and exploring the universe.
8.5 Leverage Technology
Using astronomy apps, planetarium software, and online resources can enhance your lessons and provide students with access to a wealth of information.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources specifically designed for educators, including lesson plans, activities, and multimedia materials.
9. The Importance of Dark Skies
Preserving dark skies is essential for astronomy and for our cultural heritage. Light pollution not only hinders our ability to see the stars but also has negative impacts on wildlife and human health.
9.1 Understanding Light Pollution
Light pollution is the excessive or misdirected use of artificial light. It can take many forms, including:
- Skyglow: The brightening of the night sky over urban areas.
- Glare: Excessive brightness that causes discomfort or impaired vision.
- Light Trespass: Light that shines where it is not needed or wanted.
9.2 Taking Action to Reduce Light Pollution
There are many things you can do to reduce light pollution in your community:
- Use Shielded Lighting: Direct light downwards, where it is needed.
- Use Energy-Efficient Bulbs: Reduce energy consumption and light output.
- Support Dark Sky Initiatives: Advocate for policies that protect dark skies.
9.3 Dark Sky Parks and Sanctuaries
Dark sky parks and sanctuaries are areas that have been designated for their exceptional dark skies. Visiting these places can provide a unique and awe-inspiring experience.
Examples of Dark Sky Parks:
- Death Valley National Park: Located in California and Nevada.
- Cherry Springs State Park: Located in Pennsylvania.
- Natural Bridges National Monument: Located in Utah.
LEARNS.EDU.VN supports dark sky initiatives and provides information about dark sky parks and sanctuaries around the world.
10. Resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN for Constellation Learning
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to support your constellation learning journey, including:
10.1 Structured Learning Paths
Our structured learning paths guide you step-by-step, from beginner to advanced levels. Each path includes a series of lessons, quizzes, and activities designed to help you master constellations effectively.
10.2 Expert Guidance
Our team of experienced astronomers and educators provides expert guidance and support, answering your questions and helping you overcome challenges.
10.3 Interactive Tools
We offer interactive tools such as star charts, planetarium software, and constellation simulators, making learning more engaging and fun.
10.4 Community Forum
Our community forum allows you to connect with fellow astronomy enthusiasts, share your experiences, and learn from others.
10.5 Multimedia Resources
We provide a variety of multimedia resources, including videos, images, and audio recordings, to enhance your learning experience.
Table: LEARNS.EDU.VN Resources for Constellation Learning
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Structured Learning Paths | Step-by-step guides for beginners to advanced learners, covering key constellations and observing techniques. |
| Expert Guidance | Access to experienced astronomers and educators for personalized support and answers to your questions. |
| Interactive Tools | Star charts, planetarium software simulations, and constellation finders for interactive learning. |
| Community Forum | A platform to connect with fellow astronomy enthusiasts, share experiences, and participate in discussions. |
| Multimedia Resources | Videos, images, and audio recordings that enhance understanding and engagement. |
| Seasonal Observing Guides | Up-to-date guides listing constellations and celestial events visible each season. |
| Quizzes and Assessments | Regular quizzes and assessments to help track progress and reinforce learning. |
| Mobile App | A mobile app for on-the-go learning and sky identification using augmented reality. |
| Dark Sky Maps | Maps identifying areas with minimal light pollution for optimal stargazing. |
| Astrophotography Courses | Tutorials on capturing and processing images of constellations and other celestial objects. |
Ready to start your constellation learning journey? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our resources and join our community.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Learning Constellations
1. How long does it take to learn all the constellations?
The time it takes to learn all 88 constellations varies depending on your dedication and learning style. However, you can become familiar with the most prominent constellations within a few months with regular practice.
2. What is the best way to memorize constellations?
Using mnemonic devices, practicing regularly, and associating constellations with stories and myths are effective ways to memorize constellations.
3. Do I need a telescope to learn constellations?
No, you do not need a telescope to learn constellations. A star chart, astronomy app, and binoculars can be helpful, but many constellations are visible with the naked eye.
4. How can I find constellations in a light-polluted area?
Focus on the brightest stars and constellations, use a light pollution filter, and observe during the new moon when the sky is darkest.
5. What are the best astronomy apps for learning constellations?
SkyView Lite, Star Walk 2, and Stellarium are popular astronomy apps for learning constellations.
6. How can I join an astronomy club?
Search online for astronomy clubs in your area or check with local science museums and planetariums.
7. What is the difference between a constellation and an asterism?
A constellation is a recognized pattern of stars, while an asterism is a prominent pattern of stars that is not officially recognized as a constellation. The Big Dipper is an example of an asterism within the constellation Ursa Major.
8. Can I see the same constellations from anywhere in the world?
No, some constellations are only visible from certain latitudes due to Earth’s curvature. Circumpolar constellations are visible year-round from certain locations.
9. How do I use celestial coordinates to find constellations?
Use a star chart or astronomy app that displays right ascension and declination coordinates. Match the coordinates of the constellation you are looking for with the coordinates displayed on the chart or app.
10. What are some resources for learning about the mythology of constellations?
Books on mythology, websites dedicated to astronomy and mythology, and courses on cultural astronomy can provide information about the mythology of constellations.
Conclusion
Learning how to learn constellations can be an enriching and rewarding experience. By following a structured approach, utilizing the right tools and resources, and practicing regularly, you can unlock the secrets of the night sky. Remember, LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to support you every step of the way with our comprehensive resources and expert guidance.
Don’t let the vastness of the cosmos intimidate you; instead, embrace the journey of discovery and connect with the stars. For more in-depth learning, resources, and personalized guidance, visit learns.edu.vn. Expand your knowledge, enhance your skills, and join a community of passionate learners. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. Happy stargazing!